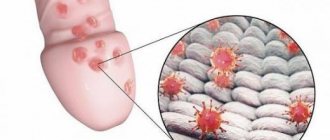
What it is
Hidradenitis is a pathology of the sweat glands caused by an inflammatory process. The most common causative agent of infection is Staphylococcus aureus. The disease can be chronic. According to the location they are distinguished:
- inguinal;
- in the armpit area;
- and hidradenitis pilaris (in men).
The neck, face and mucous membranes are affected in rare cases.
Women who have reached puberty are most susceptible to the disease. The etiology of hidradenitis is quite simple: a bacterial infection enters the mouth of the hair follicle through a wound on the skin. At this stage, you can see a small pimple or abscess, a little painful, possibly with a pus cap. As the infection grows, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the sweat glands and provoke an increase in foci of infection.
There are several stages in the development of a bitch udder:
- Redness and pain on palpation.
- The appearance of red boils.
- Spontaneous opening of abscesses, appearance of purulent discharge.
- Scarring stage.
Often, patients take only local treatment methods - all sorts of lotions and creams, which allows them to forget about the problem for a while. But soon after a slight remission and the scarring stage, the wolf's udder appears again and all stages of the disease are repeated.
With proper treatment, the pathology can be eliminated within 5-7 days.
But, oddly enough, people who have been tormented by a bitch’s udder for several years turn to doctors. This statistics is due to the fact that in our country the system of self-diagnosis and self-medication is very “developed”. In the early stages, a knotted udder can be confused with furunculosis, folliculitis and a number of other skin pathologies. Due to improper treatment, the disease begins to progress and scars appear.
Hidradenitis in an uncomplicated form does not bring much discomfort to the patient, except for an obvious cosmetic defect. But as inflammation increases, crusting, tissue damage, and sepsis may occur.
general information
Popularly, this disease is called “bitch udder.” This disease can affect representatives of any nationality. Moreover, it most often develops in people of the Negroid race.
This disease occurs somewhat more often in women. This is not due to anatomical features, but to the fact that representatives of the fair half of humanity more often shave hair from the skin, in particular in the armpit area. As a result, the apocrine sweat glands are injured, which leads to the development of the disease. In men, this pathology most often develops in the groin area. In other places where apocrine sweat glands are located, this disease appears much less frequently.
Note. Hidradenitis never affects children, since their apocrine glands are inactive before puberty.
Typically, hidradenitis develops when the apocrine sweat glands are affected by Staphylococcus aureus
Signs of hidradenitis or how to distinguish knot udder from other skin diseases
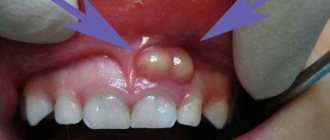
photo of the formation of hidradenitis
Hidradenitis of the armpit is localized mainly in the area of only one armpit. In some cases (complicated by concomitant chronic diseases), lesions appear on two armpits and in the folds of the mammary glands.
At the infection stage, the nodules have the red shape of inflamed pimples. They itch when sweating and are painful on palpation. Unlike furunculosis, hidradenitis extremely rarely appears on the face and in the shoulder girdle. In places where there are no sweat glands or hair, hidradenitis appears as a concomitant dermatological phenomenon.
The udder is pea-shaped and has a blue-red hue for a long time (with furunculosis, pimples with a purulent cap, small). Unlike folliculitis, hidradenitis does not affect the scalp. At the second stage, the knotted udder has a pronounced round shape and is very painful. Several lesions can merge into one.
At the maturation stage, the patient experiences general weakness, pain at the site of inflammation, fever and other signs of infection. At the third stage, the nodules begin to soften, become less painful and open.
Opened lesions can fester for several days, and serous fluid with blood fragments may be released. Thick purulent masses have an unpleasant, pungent putrefactive odor. As soon as the discharge from the wound ends, it heals. In patients with the chronic form, new lesions and ulcers appear next to the scars, which later heal.
Traditional treatment for bitch udders
Additionally, you can use traditional methods of treatment: apply baked onions to the inflammatory focus, and also make an ichthyol cake. Please note that alternative treatment is allowed to be used when the pathological process is just beginning. It is forbidden to use traditional methods at an advanced stage.
Recipe 1. Flour with yolks
Take a small amount of flour, add three egg yolks, then honey and lard. You should have a dough. The lozenge is applied to the affected area and changed every 12 hours.
Recipe 2. Tibetan patch
Take laundry soap, rye flour, add a tablespoon of sugar, vegetable oil, warm water - 200 ml. Boil everything and add church candle wax at the end. Then you need to wait for the mixture to cool. The cake is applied to the sore spot before going to bed.
Recipe 3. Rye flour with full-fat sour cream
Take full-fat sour cream - 3 tablespoons, the same amount of rye flour. We make a thick cake and apply it to the affected area. Apply the compress at night.
Causes of hidradenitis
Hidradenitis is classified as one of the forms of pyoderma (bacterial infections that cause pustular lesions of the skin). Pathogenic microorganisms can be introduced after shaving, combing, or squeezing pimples. Hidradenitis in the armpits in women is common, since this area of skin is subject to frequent destruction during hair removal, and sweating increases the number of bacteria.
The occurrence and development of infection can be influenced by a number of factors; triggers for the disease can be:
- high degree of sweating;
- previous dermatological diseases;
- working conditions that do not meet sanitary standards;
- wearing dirty underwear;
- frequent use of products that mask the smell of sweat;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear;
- pregnancy;
- microtraumas.
In people with normal immune functions, hidradenitis resolves within a week or two with the use of oral antibacterial drugs and local external ointments.
The complicated form is accompanied by the constant appearance of weeping ulcers, scarring, and an unpleasant odor. The long course of hidradenitis, which cannot be treated with drugs of choice, indicates concomitant pathologies.
Diseases that make it difficult to get rid of a bitch's udder:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- HIV;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- systemic disorders of lymph outflow;
- obesity.
A common cause of complications can be neglect of personal hygiene rules or incorrectly selected care products for this area of skin.
Hidradenitis in the groin and labia area develops in most cases in girls during puberty. The first symptoms of the disease are itching, redness and soreness. Lesions affect the groin area and can spread to the inner thighs and labia majora. The inguinal form of the disease is painful and with a large number of complications. The process is aggravated by the inaccessibility of lesions to fresh air and constant contact with items of clothing.
Unlike the axillary form, the knotted udder in the groin has a wide focal localization and can manifest itself in dozens of abscesses at the same time. This type of pathology often becomes chronic, which is difficult to get rid of. A complication of hidradenitis inguinalis can be deep inflammatory processes of adjacent tissues, the formation of scars and fistulas in the urethra, weeping ulcers, purulent arthritis, the appearance of purulent inflammation on the rectal mucosa.
In its advanced form, the disease involves a complex of skin inflammatory processes such as folliculitis of the scalp, acne, cutaneous tuberculosis, and granulomatulosis. In men, hidradenitis of the groin area often spreads to the buttocks and anus.
Method of surgical treatment of hidradenitis
Radical intervention for purulent lesions of the sweat glands includes the following steps:
- Local anesthesia. Anesthesia of the superficial layers of the skin is carried out using injections of novocaine or lidocaine.
- Surgical opening of ulcers. The doctor uses a scalpel to dissect the area of protrusion of the infiltrate. The length of the incision is usually 2-4 cm.
- Removal of purulent masses and nearby subcutaneous tissue. Radical excision of inflamed and modified skin tissue helps prevent the development of relapse.
- Rinsing the surgical field with antiseptic solutions, which should be at room temperature.
- Installation of drainage, which is a sterile rubber strip or tube. Drainage ensures unimpeded drainage of pus for several days.
Wound care after radical intervention is carried out according to the following rules:
- At home, the patient should wash the surgical incision area daily with weak antiseptic solutions.
- The patient must come to the surgeon every day for examination and washing of the wound surface.
- The surgeon removes the drainage mainly 3-4 days after surgery, after which the incision area is covered with a sterile bandage.
Bitch udders in pregnant women
Hidradenitis is a common disease during pregnancy. There are several reasons why sweat glands become inflamed in pregnant women:
- decreased immune function;
- decreased skin elasticity;
- gaining extra pounds;
- hypovitaminosis;
- pregnancy diabetes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- excessive sweating.
Hidradenitis during pregnancy can be localized in the armpits, in the folds of the mammary glands and in the groin. During pregnancy, they try to use only local drugs for treatment. The use of antibiotics and surgical excision of ulcers is not indicated until the end of the second trimester.
Consequences and complications of hidradenitis
Purulent-inflammatory damage to the sweat glands can be complicated by the following diseases:
- Cellulitis is a diffuse purulent process of soft tissues, which is a consequence of the spread of staphylococcal infection from the primary focus. This complication is accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature and a significant deterioration in the patient’s general well-being.
- Abscess . Limited suppuration of the skin is characterized by the formation of an inflammatory capsule, which prevents further spread of infection.
Attention! Treatment of phlegmons and abscesses is exclusively surgical and requires immediate hospitalization in a surgical hospital.
- Sepsis , which is the most severe consequence of hidradenitis. This complication is a purulent lesion of the circulatory system. Penetration of staphylococcal infection into the blood often ends in death.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis for knotted udders includes:
- external examination by a dermatologist;
- visiting an infectious disease specialist;
- taking a blood test for bacteriological culture;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- urine collection;
- histological analysis (for complicated purulent form).
in the photo, hidradenitis (bitch udder) under the armpit.
In a chronic course, diagnosis includes a series of tests to identify the causes of weakened immunity.
This series of diagnostic procedures is aimed at excluding pathologies with similar symptoms. Wolf udders are often confused with mycoses, manifestations of sexually transmitted diseases, carbuncles, boils, tularemia and pathologies of the lymphatic system.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact if I develop hidradenitis?
In the early stages of the disease, a dermatologist treats hidradenitis. If conservative treatment turns out to be ineffective, and pus has formed inside the abscess, then contact a surgeon. He will open the cavity and place a drain to remove its contents.
At the doctor's appointment
Survey.
The doctor collects complaints to distinguish hidradenitis from a boil, sebaceous cyst, phlegmon, skin tuberculosis:
- how long ago did the lump appear?
- whether its appearance was accompanied by pain and itching;
- how quickly the knot grew;
- whether the temperature is elevated;
- what is the general condition;
- Have you ever had cases of hidradenitis before?
The doctor also asks about concomitant diseases that can cause a decrease in immunity. To determine hereditary predisposition, the specialist will find out whether there have been cases of furunculosis and hidradenitis in the family.
Inspection of the lesion.
A doctor examines the affected area of skin
At the same time, he draws attention to the following symptoms of hidradenitis:
- an abscess in the shape of a pear or nipple;
- reddish-bluish tint of the skin over the abscess,
- the skin is swollen, hot, tense;
- thickening of the skin around the abscess - infiltration;
- the presence of seals in the surrounding area, lumpy skin. This may indicate that the infection has spread to other glands;
- fluctuation that accompanies the softening of the node - fluctuations of pus inside the cavity;
- absence of necrotic core;
- an ulcer that formed at the site of opening of the cavity;
- swelling of the limb as a result of compression of the lymph nodes and impaired lymph outflow.
When is a bacteriological examination prescribed?
The diagnosis is made based on the characteristic clinical picture. Differentiate with boils and colliquative tuberculosis.
Considering the specificity of clinical manifestations and the unique location of the purulent-inflammatory process, establishing a diagnosis is not difficult. It is placed after a physical examination and receipt of laboratory test results confirming the disease.
Required:
- Clinical blood test revealing indicators of inflammation: leukocytosis, accelerated ESR.
- Bacteriological culture of purulent discharge to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Analysis is necessary in treatment to select an antibacterial agent that has a detrimental effect on the infectious agent.
- Immunogram. Helps assess the general state of the immune system and identify which specific components need to be brought back to normal. The analysis is indicated for a chronic course with multiple relapses.
Differential diagnosis consists of excluding furunculosis, felinosis, tuberculosis of the armpit lymph nodes, lymphogranulomatosis or lymphadenitis. Each disease has its own characteristics.
The right decision would be to go to the doctor if you suspect hidradenitis on your own. 2 criteria that the doctor uses to make a diagnosis:
- Basic
From a patient interview, it was found that periodic painful and suppurating rashes appear more than 2 times in 6 months.
What does the lesion look like: nodules, fistulous tracts, scars. Where is the lesion: all those places where the apocrine sweat glands are.
- Additional
From a patient interview, there are people with hidradenitis in the family.
No bacteria were found in the discharge from the nodule, or the beneficial bacteria we talked about earlier were found.
It is rare, but sometimes necessary, to take a tissue biopsy (removing a small piece of tissue to be examined carefully). A biopsy may be needed to make a correct differential diagnosis.
Diagnosis of hidradenitis comes down to examining the patient’s blood (increased ESR, leukocytosis is observed), as well as an external examination of the patient.
Diagnosis of hidradenitis is not difficult, since the diagnosis can be established during a visual examination of the patient. In order to accurately confirm it, clinical tests are prescribed. As a rule, they show an increase in the level of leukocytes, a decrease in red blood cells, and an increase in ESR. All this suggests that an inflammatory process is developing in the human body.
If the disease occurs in a chronic form, then in this case the contents are collected from the formation in order to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to certain antibiotics.
Therapy methods
Hidradenitis is treated with a wide range of therapeutic measures. This complex includes: antibacterial therapy depending on the causative agent of the infection, local therapy (painkillers, drugs that accelerate wound healing), surgical excision of ulcers. In the chronic form, treatment of concomitant diseases and triggers is prescribed.
The treatment method is developed individually depending on the stage of the disease. At an early stage, it is necessary to get rid of hair in the focal area, but without damaging the skin. It is best to use nail scissors. Wipe the infiltration area with a disinfectant (calendula tincture, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green). Do not use drugs that can cause burns (concentrated alcohol, pepper and iodine tinctures).
Afterwards, you need to apply a bandage or patch soaked in chlorophyllipt or dioxylin. This procedure must be repeated every 4-6 hours. If after 5 days the infiltrate does not resolve on its own, increases in size and becomes purulent, it is necessary to apply antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed only when the udder reaches the stage of abscess formation.
During self-diagnosis and self-medication, antibiotic therapy is often useless due to the resistance of pathogens to the active component of the drug.
For successful antibacterial therapy, the discharge is collected for bacteriological culture to establish the exact type of bacteria and determine the most effective means to eliminate it. Taking the medication lasts no more than 10 days. For hidradenitis, tetracycline antibiotics are prescribed (if Staphylococcus aureus is detected). Tetracyclines also prevent the spread of the disease and its transition to other skin infections (furunculosis, sycosis and others). Tetracyclines are prescribed to adult patients with unimpaired renal and hepatic function.
Macrolides are new generation antibiotics, allowed from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Cephalosporin antibiotics are prescribed in case of severe infection. Act on pathogenic streptococcal microorganisms. They are used primarily for the groin form of the disease to prevent infection of the urinary tract. Cephalosporins are nephrotoxic and are not recommended for chronic kidney pathologies.
Lincomesin preparations are ointments with an antibacterial effect and have no side effects. They can cause allergies only in case of individual intolerance.
The complex takes vitamins, corticosteroids and antihistamine ointments. In the chronic stage, the formation of fistulas and scars, surgical excision of foci of infection is used for effective treatment. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than 45 minutes for large affected areas.
Treatment at home
There are many “folk” recommendations on how to get rid of a bitch’s udder, but some of them may contradict common sense and aggravate the pathology.
If you decide to get rid of a bitch udder without the help of a doctor, you need to know a few basic rules of therapy, and only then resort to folk recipes.
- If a growth with purulent discharge appears, warm bandages should not be applied under any circumstances.
- You cannot open boils and try to sanitize them yourself.
- You cannot apply ointments and masks directly to open ulcers.
An effective and absolutely safe method of treating hidradenitis without drugs is sunbathing. Just clean your armpit of hair and lie in the sun. Unfortunately, this method only helps at the early stage of the disease.
You can wipe the inflammation with decoctions and tinctures of herbs that have antiseptic properties (calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, celandine).
In some sources you can read that you can cure a bitch udder with the help of an onion or curd compress. However, there is no confirmed data on the effectiveness of such methods.
Signs of the disease
Even a person who has nothing to do with medicine can independently identify this disease.
To do this, you need to know what the udder looks like externally, what symptoms and course the disease manifests itself.
The first manifestation of hidradenitis is the appearance of a node resembling a capsule. As a rule, it hurts, and over time it can begin to secrete pus.
Due to intoxication of the body, the disease can also manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Fever (it can reach 38 degrees or higher);
- Disease of the udder is usually accompanied by a deterioration in general health and weakness;
- Headache.
If all these signs appear, you should urgently seek medical help. You need to visit a dermatologist or surgeon. In the absence of proper treatment, the course of the disease will worsen, and serious complications cannot be ruled out.
Some people, having noticed a formation on the body that looks like a bitch's udder, accompanied by the listed symptoms, apply warm compresses, which should not be done.
Such compresses contribute to the dilation of blood vessels, thereby provoking the spread of infection. In this case, fistulas with the subsequent appearance of scars may be added to the listed symptoms.
If the disease is not treated promptly, other serious consequences are possible. Considering that the infection affects the layers of the skin quite deeply, it is possible that it penetrates the body through blood vessels and lymph nodes.
This is fraught with the development of various diseases of internal organs and blood poisoning.
Nutrition for hidradenitis
Adjusting the diet for hidradenitis is indicated for patients with a chronic form of the disease who have endocrine disorders.
For overweight people, calorie restriction and a low-carbohydrate diet are recommended. In addition, it is advised to avoid fatty and spicy foods. A diet rich in vitamins and fiber helps speed up recovery.
In case of hidradenitis suppurativa, you need to give up sweets and baked goods, since such products provoke the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. It is undesirable to eat hot and spicy foods, which provoke increased sweating.
Prevention
The basis of preventive measures is compliance with all norms and rules of personal hygiene and careful care of the groin area and armpits. To avoid illness, women need to use high-quality razors that do not injure the skin, and products that moisturize the skin before and after shaving. Pharmaceutical skin care products, foams and gels with an antibacterial effect, plant-based products from the Lierac company, have a good preventive effect. If you cut yourself while shaving, you should immediately treat the wound with an antiseptic.
The intensity of sweating plays an important role in the development of the disease. Dermatologists advise washing your armpits more often, using soap or foam with antibacterial agents. It is also recommended to use deodorants in the form of a spray or wet roll-on deodorants. Dry and cream products, although effective, clog the follicles, disrupting the sweating process, and causing inflammation. Underwear should be made from natural, breathable materials and loose-fitting. In summer, clothing should not create friction in areas of increased sweating.