Why does the appendix become inflamed?
The children's horror story about eating sunflower seeds with skin and inflammation of the appendix is nothing more than a horror story. There is no connection with seed skins and appendicitis. According to surgeons, the most common causes of inflammation are blockage of the appendix by a tumor, a parasite, infectious pathogens, problems with blood vessels, and inflammation of the lymphoid tissue, which was mentioned above.
To summarize the above, I note that there is no need to remove the appendix for prevention, and no one will simply remove it for you. The operation is indicated only in case of inflammation - appendicitis. But I will tell you in the near future how to recognize it in time, as well as what assistance should be provided to the patient upon the arrival of an ambulance.
Symptoms of appendicitis
Here we will describe in detail the main and secondary signs of this disease. Please, if you find at least one of them in yourself, call an ambulance immediately!
- Key symptoms. Abdominal pain occurs in the navel area and gradually moves to the lower right part of the abdominal region. When you press on your stomach, especially in these areas, you experience a persistent painful sensation. Don't wait to call an ambulance if your stomach feels hard or swollen. Under normal conditions, the tissues of this area are soft and pliable to pressure. It hurts to stand and walk. You cannot move without feeling constant pain, it is easier for you if you lie crouched. A characteristic sign of appendicitis is pain when pressure on the abdomen is suddenly released.
- Additional signs of illness. These signs are not necessarily inherent in appendicitis, but their presence indicates any other serious disease that immediately requires medical intervention:
- fever, body temperature above 38 °C;
- constipation combined with periodic vomiting;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- painful urge to have a bowel movement, often false;
- pain in the back area.
What is appendicitis
Appendicitis, or inflammation of the appendix - the vermiform appendix of the cecum, is a rather serious problem and threatens to rupture if the operation is delayed. A rupture will lead to peritonitis - infection of the abdominal cavity, followed by the death of the patient, so appendicitis is not something to joke about.
For reference, I will say that until the beginning of the last century, operations to remove the inflamed appendix were not carried out, therefore, if a person had appendicitis, this meant inevitable death from peritonitis. This is how people lived all the years; if you are destined to die from a ruptured appendix, then no one will help.
But then it became even more interesting, after the physiology and anatomy of the digestive system was studied in full, proposals began to arise in the medical community about the advisability of preventive removal of the appendix, so to speak, for prevention, so that it would not become inflamed in the future.
Appendix
One of the elements of the cecum is the vermiform appendix, an important organ in the immune system of the gastrointestinal tract. It has individual features of the location of the right side of the abdominal cavity.
Previously, doctors removed the appendage as unnecessary, but after this it was discovered that children’s mental abilities and immunity were deteriorating and such manipulations were stopped. The appendix regulates the intestinal microflora and helps destroy pathogenic organisms.
When the appendix becomes inflamed, appendicitis is diagnosed, which is accompanied by severe pain and requires immediate excision. Self-medication and ignoring the disease are unacceptable.
The appendix is an intestinal atavism that does not play a special role in digestion, but is very dangerous when inflamed.
What is the appendix?
The vermiform appendage of the cecum in the intestine is the appendix. The process of the cecum is oblong in shape and is located on the posterolateral wall of the cecum. The size of the human appendix is about 7-10 cm in length and 1 cm in diameter. It extends from the intestines to the pelvis.
Appendicitis is located on the right side in the side, but the location options according to other organs in the body are individual. Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis. Over the period of human evolution, the anatomy of the appendix has changed.
Previously, it was a functional organ of the digestive system.
Possible atypical location of the appendix. In this case, the symptoms of inflammation may differ from the main indicators. The area bordering the intestine consists of folds (mucosal cells).
For many years, medicine considered the appendix an unnecessary and useless organ. Its meaning and role were not established, so it was removed.
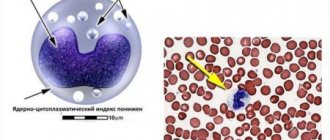
Inside the appendix there are many islands of lymphoid tissue, which is a component of the body's immune system.
Where is it located and its location options in the body?
The most common is the pelvic location of the appendix.
The vermiform appendix has a pelvic location. The location is the iliac region of the fossa on the right side.
It happens that it is located in a different place: above or below the specified area. Rarely located in the abdominal cavity. Depending on the individual structural features of the body, the placement of the appendix in the patient is different.
The topography of the appendix is shown in the table below.
PositionDescription and localization
| Pelvic (descending) | The process is closely adjacent to the peritoneum, being inside and heading to the pelvic area |
| Medial | Located in parallel with the ileum, close to the midline of the abdomen |
| Lateral | Located in the right lateral paracolic canal |
| Front | On the front of the intestine |
| Ascending (subhepatic) | Pointed upward with the tip of the apex |
| Retrocecal | Located behind the cecum |
The pelvic position is the most common, found in almost every second person. With pathology of the appendix in this position in women, the symptoms of the disease are confused with gynecological problems. Being in the retroperitoneal cavity, the appendix is difficult to examine.
Functions performed
The appendage of the rectum is a useful organ of the abdominal cavity. The main function is to help the immune system protect against negative microorganisms. Its functions are related to the digestive system and affect the mental abilities of children.
If for some reason beneficial bacteria are washed out in the gastrointestinal tract, the function of restoring microflora is performed by the appendix together with the cecum. As a result, dysbacteriosis is prevented.
Medicine differs in the concept of how much weight the intestinal appendix occupies and why it is needed, but it is precisely established that when the intestinal appendage is removed, the child’s rate of memorization of information and perception decreases and problems with the digestive system appear.
This is due to the lack of necessary microorganisms produced by the appendix.
Diseases and their treatment
When the appendix becomes inflamed, nausea occurs and body temperature rises.
When the mesentery of the appendix becomes clogged with feces, a pathological increase in the number of parasites and negative microelements begins in the appendix.
During this process, an inflammatory reaction begins in the mucosa. In this case, difficulties arise in the movement of blood through the vessels, which nourishes cells and tissues, as a result of which tissue dies.
Signs of inflammation in the patient have strong symptoms: sharp cutting pain in the abdominal cavity, fever, nausea. Only a doctor can determine the cause of the disease after palpation and diagnosis. Self-medication and delaying going to the hospital can lead to a number of serious disorders and problems.
Pain syndrome may also indicate the presence of a malignant formation on the appendix and the chronicity of development. For any pathology, the process is cut out - the main method of treatment.
What is appendicitis?
Stagnant processes in the appendix provoke the development of pathogenic organisms and inflammation of the organ. As a result, a disease called appendicitis develops. When there is a sharp pain in the lower abdomen, a person immediately fears the development of the disease and immediate surgery.
Not many people know the location of appendicitis; they often wonder: is appendicitis located on the left or right? The area of its location corresponds to the location of the appendix, respectively, appendicitis is on the right. The disease has 2 forms - catarrhal and chronic. In the first stages, the worm-shaped element of the cecum swells and blood circulation is impaired.
In the future, the situation worsens, affecting the walls of the mesentery of the process. It is worse if the abdominal cavity becomes inflamed. Symptoms of appendicitis:
- acute abdominal pain;
- lack of appetite;
- temperature increase;
- stool retention;
- urination increases:
- weakness and irritability;
- nausea, vomiting.
The manifestation of symptoms depends on the age and health of the patient. The patient looks pale and tired. In such a situation, it is necessary to urgently hospitalize the person for surgery so as not to provoke a rupture.
Tumors of the appendix
Pain and other symptoms can be caused not only by appendicitis, but also by the presence of a tumor in the appendix. It is very difficult to determine at stages 1–2; it is often detected during the process of metastasis. It is characterized by slow growth up to a diameter of 2 cm. This disease does not affect the serous membrane of the organ.
The causes and nature of the disease cannot be clearly determined, and the problem can only be eliminated by excision of the formation. In the case of the development of a malignant tumor and the spread of cancer cells, chemotherapy and laser therapy are used.
Previously, the patient undergoes diagnostics: ultrasound examination, x-ray and blood test.
Source: https://PishcheVarenie.ru/appendiks/cherveobraznyj-otrostok.html
Appendix and its functions
The appendix is an appendage of the cecum, extending from its posterolateral wall, having a cylindrical shape and a length of 2 to 13 cm with a diameter of 5-8 mm.
The functions of the appendix, or ventricular appendix, are:
- participation in many processes of the immune system, which is possible due to the presence of many lymphatic vessels in it. It is in these vessels that cells are present that provide the body with protection from the effects of viruses and bacteria;
- preservation of beneficial microflora necessary for the normal function of the digestive system. The appendix stores a large number of bacteria that are able to restore lost beneficial microflora during intestinal dysbiosis (for example, after long-term use of antibiotics).
Main functions of the appendix
Why does a person have an appendix? This question has been asked by doctors for a long time.
At the beginning of the 20th century, a “list of useless organs” was even compiled from 180 “rudiments”, which included the appendix, tonsil, spleen... The appendix was classified as a dangerous rudiment that causes appendicitis.
Famous biologist I.I. Mechnikov believed that it was necessary to remove not only the cecum, but also all the large intestines of a person, because It is there that putrefactive processes occur that poison the human body. And the British surgeon William Lane even began performing similar operations on his patients until he was criticized. Now doctors are proposing, instead of a “list of useless organs,” to create a list of little-studied organs.
Many years of research have shown that the appendix plays an important role in the human body. Today, the appendix has three main functions:
- protective;
- secretory;
- hormonal.
The appendix is of great importance in protecting the body from foreign bacteria. In the submucosal layer of the walls, formations of lymphoid tissue accumulate, which are called Peyer's patches. It has been proven that the process contains about 6000 lymphatic follicles. This amount is reached in humans by the age of 11-16, when the immune system is strengthened.
If a person has lost beneficial bacteria due to illness or stress, microflora is supplied from the appendix, which prevents the development of dysbacteriosis. The intestines are repopulated with beneficial bacteria. After surgery for appendicitis, digestive disorders are observed, and human immunity is significantly reduced. The appendix acts as a kind of “incubator” in which beneficial bacteria are stored.
The shoot secretes a secretion containing juice and mucus. The secretion contains biologically active substances amylase and lipase. It has been proven that this secretion enhances intestinal perilstatics and is capable of decomposing starch.
The appendix produces hormones that are involved in bowel function, which helps the digestion process.
Scientists have put forward hypotheses about the valvular, endocrine, contractile activity of the appendix. There is a version that the organ is important in transplantation: it produces antibodies, which leads to an incompatibility reaction during organ transplantation.
Classification
The classification involves division not only according to the localization of retrocecal appendicitis, but also according to the stage of development of the pathological process:
- Catarrhal. Duration - 10-12 hours, symptoms are varied, often disguised as other existing diseases. The pain begins near the navel, gradually going down to the right side of the peritoneum, and is constant.
- Phlegmonous. Inflammation spreads throughout the appendix, the organ swells, increases in size, and pus literally melts the membranes of the appendix. The patient's condition worsens, but the pain may subside. The main danger is the breakthrough of purulent exudate and the development of peritonitis.
- Gangrenous. The stage of tissue death of the appendix develops already on the third day of the pathological process. The disease progresses due to lack of treatment, and the rate of development of the gangrenous stage may be determined by the age of the patient. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, weakness, tachycardia and lack of fever.
- Appendicular infiltrate. A complicated form, characterized by the accumulation of inflammatory exudate around the appendix. The disease is more often diagnosed in adolescents; acute pain gradually subsides, but intoxication persists.
Any form of the disease requires surgical intervention, but sometimes, with a stable course of the inflammatory process and positive dynamics in its treatment, it is possible to prescribe antibacterial therapy.
Appendix diseases
All diseases are included in ICD-10 and are noted under the numbers K35-K38 . The number range includes dysplasia, fistulas, intussusceptions, stones, cysts, neoplasms, foreign bodies, trauma, diverticulitis, endometriosis, strangulated hernia (the cecum gets into the hernial sac).
Inflammatory process
Appendicitis is a common surgical situation that makes up the bulk of emergency interventions . The disease is characterized by the onset of an inflammatory process in the appendix and the rapid development of complications. Appendicitis has specific symptoms that are differentiated by the doctor almost immediately.
There are two main forms:
- spicy;
- chronic.
Chronicity of appendicitis develops if the inflammatory process does not progress to the necrotic or gangrenous stage and resolves itself with antibiotic therapy. If in the acute process the symptoms are bright, then in the chronic form the signs are blurred and appear sluggishly.
Note! Typical manifestations of appendicitis during exacerbation, in addition to pain, are hyperthermia, malaise due to intoxication, spasms in the area where the inflamed appendix is located.
Mucocele
Mucocele is understood as a cystic neoplasm of the appendix , which increases the secretion of mucus and reduces its volume. Initially, it is a benign neoplasm, but has a high risk of malignancy.
The true reasons for the development of mucocele are not fully understood , but in most cases the trigger factor is considered to be a chronic inflammatory process.
The clinical picture of the disease is blurred , discomfort comes to the fore, mainly in the right part of the lower abdomen, abnormal bowel movements, and chronic dysbacteriosis in children. If the cyst reaches an impressive size, it can be detected by palpation.
Cancer tumor
Appendiceal cancer is characterized by the formation of carcinoid, a particularly malignant tumor . This is the common form of all malignant neoplasms of the appendix. The tumor is limited and rarely metastasizes.
Contributing factors are considered to be inflammation, autoimmune diseases, chronic constipation, and excess serotonin production.
Typically, diagnosing appendicitis is not difficult ; surgical intervention is prescribed almost immediately. Before the manipulation, an ultrasound is prescribed, which excludes other pathologies of the cecum with similar symptoms and complications.
Doctors' opinion
Doctors do not recommend early removal of the appendix without signs of inflammation. The following reasons contribute to this:
- Inflammation does not occur in all people; it is impossible to determine the risk of appendicitis in advance, and such an operation can leave an unaesthetic scar in the area of the iliac fossa.
- Removal of a non-inflamed appendix can lead to negative consequences for the intestines, including adhesions and intestinal obstruction.
- Removal may be too traumatic for the patient; postoperative complications may not correspond to the risk from a possible inflammatory process.
Doctors believe that any operation should be performed as necessary and for special indications. The planned and urgent nature of appendectomy involves a serious burden on the body (anesthesia, rehabilitation, the need for antibacterial therapy).
Acute with hyperthermia
When a person develops acute appendicitis, the temperature most often rises to 38°C. Later it will be higher. This means that complications have arisen:
- perforation in the process;
- periappendicular abscess;
- Peritonitis is common.
There are times when the temperature is immediately below 40°C or higher and a person has chills. Sometimes purulent intoxication occurs. Its signs:
- tachycardia;
- leukocytosis is high;
- tongue dry and coated.
Structure of the appendix
The appendix is an elongated vermiform appendix extending from the posterolateral wall of the cecum and connected by a small opening. This opening is surrounded by mucous tissue called the valve.
The walls are similar in structure to the wall of the large intestine and consist of an internal epithelial layer, a submucosal layer, muscular and serous, which covers the outside. The serous outer layer supplies the appendix with blood.
The human appendix ranges from 7 to 10 cm. After the operations, the smallest length was recorded - 2 cm and the longest - 26 cm.
According to the structure, the process has three parts: the base, which is attached to the cecum, the body and the apex. There are three forms of the organ:
- stem-shaped - equal thickness along the entire length;
- germinal - thickness as a continuation of the cecum;
- cone-shaped - the base is narrower than the top.
The diameter of the entrance to the hole is 1-2 mm. This prevents the intestinal contents from entering the appendix. Many people know that the appendix is located on the right side. In fact, the localization can be different, although the process always extends from the cecum. In 45% of patients after surgery, an organ descending to the pelvic cavity was discovered. Anatomy classifies such an appendix as descending.
The structure of the human appendix can have different locations:
- ascending – attached to the peritoneum from behind (13% of operated patients);
- medial – located closer to the white line of the abdomen (20% of operated patients);
- lateral – located at the lateral abdominal wall (20% of patients).
The vermiform appendix is sometimes located in the left sidewall. In medicine, this phenomenon is called “mirror” anatomy. It is very rare that an organ is missing - the “rudiment” disappears. Doctors have also recorded cases of the presence of two processes.
An inflamed human appendix usually duplicates the symptoms of inflammation of the organ next to which it is located. If, for example, it descends to the pelvic cavity, pain due to inflammation affects the bladder or uterus with appendages. This is why it can be difficult for doctors to diagnose appendicitis.
It is interesting to note that some mammals have an appendix: rabbits, sheep, horses. In horses it is very large, because its purpose is to process rough parts of plants. Cows, cats, and dogs do not have this organ.
Location and structure
The appendix extends from the medial-posterior surface of the cecum below 3 cm from the point where the small intestine enters it and is covered by peritoneum on all sides. Its length, on average, is 9 cm, in diameter it reaches up to 2 cm. The lumen of the appendix in some people, in particular in the elderly, can become overgrown, causing inflammation - appendicitis. This condition requires urgent hospitalization as it can be fatal.
We recommend reading:
Diseases of the sigmoid colon: symptoms and signs of disease, their treatment
Depending on how the cecum is located, there are several options for the normal location of the appendix:
- Descending. It occurs most often (50% of cases). When the appendix is inflamed, it is worth keeping in mind that it is in close contact with the bladder and rectum.
- Lateral (25%).
- Medial (15%).
- Rising (10%).
The appendix opens into the cecum through the opening of the appendix and has a mesentery that extends from its beginning to its end. Its mucous membrane has a large amount of lymphoid tissue, and the general structure is the same as that of the cecum - serous, subserous, muscular, submucosal and mucous layers.
To remove or not to remove the appendix
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OTOkizCTzAE
For modern doctors, this question no longer arises. Sometimes the appendix takes the entire blow from the infection, and an inflammatory process develops - acute appendicitis. If surgical intervention is not undertaken, there is a risk of complications: peritonitis and abscess may develop. In this case, there is a threat to the life and health of the patient; there is only one solution: remove.
In recent years, acute appendicitis has been diagnosed by doctors more and more often, which is associated with poor diet, weakened human immune system, and poor environment.
Intestinal diseases accompanied by diarrhea contribute to dysbiosis. In such cases, patients who have undergone surgery for appendicitis receive effective conservative treatment, including prebiotics and probiotics that normalize the intestinal microflora.
Nature does everything intelligently. The human body does not contain anything unnecessary or random. Modern medicine continues to study the features of the appendix; the question of “is it needed” is no longer raised. Today there is only one conclusion: the appendix should be removed only in case of acute appendicitis. It is important to remember that this organ is an important defender of human immunity.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of appendix diseases comes down to laboratory and instrumental studies:
- blood tests (shift of the leukocyte formula to the left), urine and feces;
- anal smear for pathological discharge.
The gold standard for diagnosing pathologies of the appendix is ultrasound of the abdominal and pelvic organs , colonoscopy for long-term inflammation, magnetic resonance imaging.
If appendicitis is detected, surgical intervention is prescribed using the abdominal or laparoscopic method. In most cases, a cavity incision is made, which leaves a wide diagonal scar.
Functions and significance
What is the appendix for? The debate about the significance of the rudimentary process still continues, but after its removal no significant changes occur.
It is generally accepted that the body performs the following functions:
- protective – the content of lymphoid tissue ensures a normal immune response;
- preservation of beneficial microorganisms and the formation of intestinal microflora;
- content of original colonic microflora.
Over the years, the function of the appendix of the cecum is inhibited, and its size decreases. After removal, the immune system continues to work to the same extent, the body adapts to the effects of environmental and internal factors.