The qualitative level of blood composition constantly changes over the course of life. A special table of hemoglobin norms for women by age will help prevent the appearance of pathological indicators in the analysis results.
Monitoring changes in the blood formula is one of the simplest and most accessible opportunities to prevent the development of many diseases of the female body.
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing blood pigment found in red blood cells that transports oxygen to tissues. According to its structure, hemoglobin is classified as a complex protein, the core of which contains iron, which binds oxygen molecules. It is hemoglobin that colors blood red.
After delivering oxygen to the tissues, hemoglobin attaches carbon dioxide and carries it to the lungs. Thus, this blood particle should be regarded as an element that provides the main transport functions of blood - nutrition and respiration.
Changes in hemoglobin levels indicate a violation of the oxygen-transporting function, which leads to the development of various diseases - anemia, renal failure, hypoxemia and ischemia.
Under the influence of chemicals, carbon monoxide and an increase in blood sugar levels, hemoglobin acquires pathological forms, which can only be detected through analysis.
How to determine hemoglobin level
To find out the level of hemoglobin, laboratory tests are used on blood samples taken from a finger. During the procedure, the number of red blood cells and the presence of abnormal cells are determined.
Blood is drawn on an empty stomach and no earlier than 8 hours after the last meal.
Norm of hemoglobin in the blood of women by age: table
Due to the specifics of the body, standard levels of iron in the blood of women are lower than those of men, but higher than those of children, and amount to 112-150 g/l.
During special periods of life - during pregnancy or menstruation, the composition of the blood changes, but this is not considered a sign of abnormalities if the test results correspond to the accepted norm.
Normal hemoglobin level after 30 years
Blood composition indicators change with age. In women under the age of 30, the hemoglobin level in the blood reaches the maximum possible level. Whereas after overcoming the 30-year mark, a gradual decline in indicators begins.
Normal after 40 years
The process of decreasing hemoglobin is observed throughout a woman’s life. Therefore, after 40 years, the hemoglobin norm in women is already 5 g/l lower than in thirty-year-olds. Changes in the composition of the blood become especially noticeable closer to the age of 50, when women enter the stage of menopausal restructuring of the body.
Hemoglobin after 50 years
In women over 50 years of age, hemoglobin levels usually fall below the established norm. This is due to the instability of the hormonal balance characteristic of menopause. The woman becomes more emotional, and her resistance to stress noticeably decreases, which is reflected in the composition of the blood.
During menopause, in order to raise hemoglobin levels to normal, doctors recommend taking medications that normalize hormonal levels and adjusting your diet with an emphasis on healthy vitamin- and iron-containing foods.
The exception is foods that suppress iron absorption:
- milk;
- chicken protein;
- bread, pasta, cereals;
- strong drinks, including coffee and tea.
In addition, you should increase your water intake.
Normal hemoglobin level after 60 years
The female body after 60 years is characterized by the completion of hormonal changes and a slowdown in metabolic processes. Since the need for nutrients is no longer as high as before, the level of iron in the body gradually decreases.
To normalize blood composition, older people need to follow a special diet aimed at increasing iron-containing foods in the daily diet.
Characteristic signs
An increase in hemoglobin in the blood can be assumed if a man has the following symptoms:
- weight loss without changing diet;
- bleeding gums;
- elevated temperature;
- dizziness;
- blurred vision;
- bluish tint of the skin of the hands and feet caused by cyanosis;
- decrease in vital energy;
- dysfunction of the genitourinary system;
- bowel dysfunction;
- muscle and joint pain;
- increased skin sensitivity, itching, rashes;
- purple spots on the skin.
A high level of hemoglobin in the blood explains why there is a lack of appetite, insomnia, hearing impairment, and an increased heart rate in men.
High hemoglobin in men is often discovered completely by accident, during a general clinical blood test for preventive purposes. If its level has increased to 180 g/l or higher, measures should be taken as soon as possible to eliminate the source and normalize the values.
In almost all situations, this disorder is associated with the course of one or another illness. However, there are a number of physiological factors that do not have a pathological basis.
Symptoms most often remain invisible to a person. However, it should be borne in mind that when the concentration of the main component of the blood - red blood cells - increases, headaches and dizziness appear, problems with concentration and emptying the bladder, as well as decreased performance. The basis of diagnosis is a general blood test, but it is not enough to determine the causative factor. The diagnostic program is selected individually for each person.
Treatment is limited to the use of conservative methods - men need to eat certain foods and also take medications. The possibility of correction using traditional medicine is also not excluded.
Signs of low hemoglobin levels
A decrease in the amount of hemoglobin in plasma indicates a metabolic disorder and the development of anemia. Such conditions are considered pathological and require correction.
A decrease in the number of blood cells is accompanied by a deterioration in health.
Most often, pathological changes are indicated by:
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- pale skin;
- dry mouth;
- dizziness;
- arrhythmia;
- migraine;
- peeling nails;
- excessively falling out, brittle and dry hair;
- increased fatigue;
- caries;
- dyspnea;
- dry lips and cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Anemic processes are often manifested by loss of smell and taste, especially in pregnant women.
If deviations from the norm are insignificant, special drug treatment is not required, it is enough to follow a work and rest schedule, ensure proper sleep and reconsider your attitude to nutrition and bad habits.
Causes of low hemoglobin
Despite the fact that anemia is an independent disease, doctors tend to regard its occurrence as a signal of the presence of other health problems.
Among the main reasons causing a deficiency of blood cells:
- lack of B vitamins and iron-containing foods in the diet;
- bleeding, including ulcerative, menstrual, postpartum, postoperative, and donation;
- dysbacteriosis;
- infectious, autoimmune and hereditary diseases;
- release of insulin during tumor processes in the pancreas;
- hypothyroidism;
- hepatitis;
- stress;
- drug abuse.
In addition, a decrease in the number of red blood particles is typical for women on weight loss diets.
Treatment of low hemoglobin
It is possible to improve the blood count with low hemoglobin thanks to an integrated approach to treatment. Along with drug treatment, it is necessary to change your diet and lifestyle.
Drug treatment involves taking iron-containing drugs - Aktiferrin capsules, Ferry syrup, as well as the combined products Ferrofolgamma and Irovit. The choice and prescription of medications can only be made by the attending physician. The average course of medication is two weeks.
A therapeutic diet involves introducing into the diet foods that increase iron levels in the body or improve its absorption. All types of vegetables deserve special attention, as well as apples, apricots, pumpkin, seaweed, pomegranates, herbs, nuts and citrus fruits.
The list of the most useful products of animal origin includes all types of meat and seafood, liver, kidneys and chicken yolks.
In addition, you should increase the amount of spices such as cinnamon, mint, thyme and anise in your daily menu.
Changing your lifestyle involves regular physical activity, a good night's rest, and giving up bad habits.
High hemoglobin in women
An increase in hemoglobin levels is fraught with no less serious health consequences than its decrease. Excess iron in the body manifests itself in drowsiness, increased fatigue, difficulty urinating, the appearance of bright spots against the background of pale skin, enlarged liver, decreased vision, weak or absent appetite, and the appearance of age spots.
Such violations may indicate the development of:
- erythrocytosis;
- bone marrow pathologies;
- hypertension;
- diabetes mellitus;
- intestinal obstruction;
- oncological diseases;
- heart pathologies;
- diseases of the respiratory system.
A temporary increase in red blood cell counts is possible after a blood transfusion. Also, a high level of red blood cells is characteristic of people living in high mountains or working at heights - pilots, crane operators, climbers.
Other nonspecific causes of increased hemoglobin include smoking, dehydration due to taking diuretics, burns, and old age.
Signs of changes in hemoglobin in plasma in one direction or another often coincide. To determine the exact cause of the disorders, a complete medical examination is necessary.
How to reduce hemoglobin in the blood?
To normalize elevated levels of red blood cells in plasma, doctors recommend taking blood thinning medications. The list of the most effective drugs includes Curantil, Acecardol, Cardiomagnyl, Vazonit. Additionally, hepatoprotective drugs are used, as well as products containing zinc, calcium, phosphorus and manganese.
In particularly difficult situations, doctors may use erythrophoresis or gastrotomy to remove excess red blood cells.
Dietary nutrition involves the consumption of foods that suppress the absorption of iron - all types of dairy products, pasta and bakery products, cereals.
What should hemoglobin be in men: when health is ironclad
Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. A significant part of the iron in our body is “stored” in hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells - erythrocytes. Its task is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Hemoglobin is responsible for cellular respiration. In addition, hemoglobin regulates the acidity of the blood and maintains its healthy pH.
The normal hemoglobin level for men is 130–170 g/l. This is slightly higher than for women - for the fair sex, 120–150 g/l is considered the norm. The reason for this difference is the effect of male sex hormones on the process of hematopoiesis. Men's blood contains more red blood cells (it is this factor that makes men somewhat more resilient and allows them to endure more significant physical activity).
The hemoglobin level may deviate slightly in one direction or another. Small fluctuations are usually caused by completely physiological reasons. For example, athletes and residents of high mountains have slightly higher hemoglobin levels - serious training and a lack of oxygen in the air force the body to produce more red blood cells so that the process of cellular respiration is not disrupted.
The hemoglobin level in men gradually decreases over time. After the 50th birthday, this figure can be 118–139 g/l. In most cases, these changes are not a cause for concern. By the age of 80, the normal hemoglobin level is within the range of 110–130 g/l.
Small changes in hemoglobin levels can be observed throughout the day - in the morning its level is usually slightly lower, and in the evening - slightly higher [1]. All these fluctuations are insignificant and, as a rule, do not exceed 17%.
However, sometimes tests reveal too low or high hemoglobin in men. What caused these changes?
If the level is high: higher is not better!
It would seem: if hemoglobin is so important for health, then increased hemoglobin in men should be a good sign. However, it is not. Too high hemoglobin in men signals health problems and can itself cause trouble.
An increase in hemoglobin levels in men by 20 g/l or more is considered a significant deviation from the norm. High hemoglobin in men can be a consequence of heart or pulmonary failure, intestinal obstruction, cancer, or diabetes. Low hemoglobin in men is also observed with dehydration, which can be caused by both insufficient fluid intake and too rapid loss of fluid due to vomiting or diarrhea.
Normal hemoglobin level in blood during pregnancy
The changes that occur in the body of the expectant mother are also reflected in the level of hemoglobin. First of all, pregnancy is characterized by the accumulation of fluid, resulting in physiological dilution of the blood and a decrease in the concentration of red blood cells.
The normal hemoglobin level in pregnant women is 110-155 g/l.
A pathological decrease in indicators in pregnant women is possible against the background of iron and folic acid deficiency. As the fetus grows, these substances are consumed first, and their gradually increasing deficiency leads to anemia.
A low level of hemoglobin during pregnancy can negatively affect the development of the fetus or provoke premature birth.
The role of hemoglobin in the lives of men and the importance of maintaining the norm
Experts warn: if the level deviates greatly from the norm, this can lead to dysfunction of internal organs and systems. Also, such a violation often leads to a weakening of the immune system and the occurrence of dermatological problems. This is primarily due to the fact that protein is responsible for the supply of oxygen to cells.
Also, this iron-containing component helps control the pH level in the blood serum. To minimize the risk of developing health problems, you need to maintain normal hemoglobin levels.
Hemoglobin levels are monitored using a complete blood count
Hemoglobin is a means of transporting oxygen molecules from the lungs to all tissues and organs. Iron protein helps control blood pH. It contains iron, which, when oxidized, can accept or release carbon dioxide and oxygen.
Hemoglobin levels in men are slightly higher than in women. This is explained by the fact that for the active growth of muscle mass, testosterone is required, which requires a larger volume of oxygen; accordingly, the number of blood cells must be significantly higher.
If the hemoglobin level increases or decreases significantly, many organs and systems of the body suffer. Their functionality is impaired, immunity decreases, and skin quality deteriorates. This is why it is important to maintain normal levels.
Hemoglobin level in women during menstruation
Even the smallest bleeding affects the level of iron in the body, reducing it and causing a feeling of drowsiness and weakness. This process is natural, since during menstruation the body loses a certain amount of blood, and its replacement occurs slowly.
Moreover, a delay in menstruation can cause a slowdown in the maturation of red blood cells and, as a consequence, a drop in blood viscosity. As a result, with the onset of the menstrual period, blood loss increases, further reducing hemoglobin levels.
If the discharge is too small, this may be a sign of increased iron levels in the blood and an increase in its viscosity. Similar symptoms are characteristic of a number of diseases of the cardiovascular system and diabetes.
If, after taking tests, the doctor reports low hemoglobin, he diagnoses the patient with anemia. All women should know what this disease threatens, how it appears, and how to replenish iron levels.
Reduced hemoglobin
Some of the most common causes of anemia are:
- blood loss (traumatic injury, surgery, bleeding, colon cancer or stomach ulcer);
- nutritional deficiencies (iron, vitamin B12, folic acid);
- bone marrow problems (bone marrow replacement for cancer);
- suppression of red blood cell synthesis by chemicals;
- renal failure;
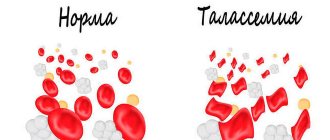
- abnormal hemoglobin structure (sickle cell anemia or thalassemia).
Lack of iron in the blood is an important sign of pathology. Often, low levels of iron-containing protein occur due to depletion of the body.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin levels
The main reasons for the development of iron deficiency anemia include the following:
- formation of tumor neoplasms;
- diseases caused by parasites;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- pathologies of the digestive tract;
- heavy blood loss (bleeding, donation);
- systemic blood diseases;
- strict diets, drying, vegetarianism;
- excessive consumption of chocolate and caffeinated drinks;
- alcohol intoxication.
Low hemoglobin in men is less common than in women. A lack of iron-containing protein in the body, which is responsible for transporting oxygen, is accompanied by general malaise. The patient is worried about weakness, headaches, and increased heart rate. A man's skin turns pale and his performance decreases.
How to increase hemoglobin?
If the amount of iron in the blood is low, you should also undergo an examination to help determine the cause of anemia. Most often, this condition can be managed with a diet that includes more foods that contain a lot of iron and other essential minerals. Usually it is advised to eat more meat, cereals, legumes, and nuts.
If the iron deficiency is too great, it will be extremely difficult to cope with it with diet alone. In this case, you need to take special anti-anemia medications that contain iron. In addition, vitamins B and C are usually prescribed. Vitamin C is necessary for these drugs to be absorbed better; it improves blood quality. At the same time, during treatment it is advised to avoid dairy products, since they, on the contrary, contribute to insufficient absorption of necessary substances.
What are the dangers of anemia?
The less hemoglobin in the blood, the lower the amount of oxygen in the cells. They are not working at full capacity. Failures occur in all organs. This affects the performance of the body. Can lead to depression, headaches, drowsiness, fatigue, and lethargy.
The immune system weakens and the body stops resisting infections. Frequent colds appear, which are difficult to treat. Due to muscle relaxation, there is aching in some tissues, which is why urinary incontinence occurs. You should pay attention to signs of decreased hemoglobin:
- the skin becomes dry;
- pale skin and lips;
- nails are brittle, hair falls out;
- lips are cracking;
- dizziness and headache (to the point of loss of consciousness);
- prostration.
If you notice similar manifestations in yourself or your loved ones, urgently hurry to donate blood. If the analysis shows hemoglobin 70 in a woman, the doctor prescribes drug therapy. It is important not to delay treatment! Low levels of the element in the blood are very dangerous. If you do not raise it in a timely manner, hemoglobin will drop even lower, and various organ pathologies may develop.
To find out why this condition is dangerous, you need to learn about the existing stages of anemia. It occurs in three stages:
- Light – indicator from 90 to 110.
- Average – from 70 to 90.
- Heavy – less than 70.
So, if the iron level drops below 70, the patient is in a severe stage of anemia. Only a doctor can help here.
Hemoglobin 70 in pregnant women
This low rate should be taken seriously, especially by expectant mothers. If you do not take measures, in addition to the above dangers, the following will appear:
- many existing pathologies become chronic;
- hair falls out profusely, teeth deteriorate, nails crumble and break;
- heart failure appears;
- the liver enlarges.
During pregnancy, the child also suffers from severe anemia. He, like his mother, lacks red blood cells - erythrocytes. And this leads to improper nutrition of the fetus, to a lack of important elements for it. The child may be born with severe pathologies or with congenital anemia.
When the hemoglobin level reaches less than 70, critical anemia occurs. Here you need urgent help with medications.
Ways to increase hemoglobin
The doctor prescribes an urgent administration of the drug with iron in liquid form, intramuscularly. After emergency treatment, a diet and iron-containing medications are prescribed. They should be treated with caution by patients prone to allergies. You should warn your doctor about this.
From this article you will learn: how and why anemia occurs, what ways to treat it, and what level of hemoglobin is considered critical.
Anemia or anemia occurs when the number of red blood cells decreases. In a blood test, this indicator is expressed as the concentration of hemoglobin, an iron-containing pigment that gives red blood cells their red color.
The main function of these blood cells is to supply oxygen to the organs and tissues of the body. Anemia causes hypoxia, which affects the entire body. The course of the disease in the early stages may be accompanied by almost no symptoms. This is precisely why anemia is dangerous. Oxygen starvation affects the activity of the brain and heart muscle, reduces immunity and provokes the development of other pathologies.
In some cases, anemia can be a symptom of other diseases: cancer, internal bleeding, pathologies of the hematopoietic system and gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, a decrease in hemoglobin cannot be ignored. Determining the cause and treatment is necessary if the indicator deviates by more than 5 g/l.
Why is high level dangerous?
Even if we do not take into account the original cause of the increase in the amount of hemoglobin, hyperhemoglobinemia itself poses a risk of deterioration of blood circulation in all organs and tissues, as well as the risk of venous thrombosis, shortness of breath, increased fatigue, decreased immunity and increased blood pressure. For pregnant women, there is a threat of malnutrition of the fetus - fetoplacental insufficiency. In children, if it lasts for a long time, mental and physical development may be delayed. This is due to the fact that against the background of an absolute or relative increase in the number of red blood cells, blood thickening occurs, which in turn leads to a deterioration in hemodynamics (blood circulation).
If we take into account that hyperhemoglobinemia is only a consequence of the influence of some cause, then it becomes clear that the main cause may carry more threatening consequences than just a high level of hemoglobin. Tumor changes in the above organs and tissues that are not identified or left untreated are especially dangerous, because they pose an immediate threat to life.
Hemoglobin norms in the blood of a healthy person
Hemoglobin is a variable quantity, its concentration varies according to the age and gender of a person.
Hemoglobin norms for healthy people are presented in the table.
| Age | Norm (g/l) |
| From birth to 2 weeks of life | 135-200 |
| 1 month | 115-180 |
| 2 months | 90-130 |
| At the age of 2-6 months | 95-140 |
| From six months to 1 year | 105-140 |
| From 1 year to 5 years | 100-140 |
| From 5 to 12 years | 115-145 |
| During puberty (12-15 years) | M - 120-160, F - 112-152 |
| From 15 to 18 years old | M – 117-160, F – 115-153 |
| Adults | M – 130-170, F – 120-155 |
| Pregnant women | 1st trimester – 112-160, 2nd trimester – 108-144, 3rd trimester – 100-140 |
| Aged people | M – 125-165, F – 120-157 |
Normal hemoglobin levels vary from person to person, so it is important to determine whether hemoglobin 114 is bad or normal for the body before raising it. During the period of active growth, puberty and bearing a child, a slight decrease in the indicator is a natural process, but it is necessary to ensure that it does not deviate significantly from the norm. A specialist should decipher the results of a blood test and determine the causes of anemia.
Prevention and prognosis
To ensure that the hemoglobin content in males does not deviate upward from the norm, you just need to follow the following simple preventive recommendations:
- maintaining a healthy and moderately active lifestyle;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- taking medications only as prescribed by the attending physician;
- preventing chemicals and toxic substances from entering the body;
- consumption of at least two liters of fluid per day;
- Regularly undergoing a complete preventive examination at a medical institution.
High hemoglobin levels can be easily corrected. However, if you refuse qualified help, both the above complications and frequent relapses of characteristic symptoms, as well as a worsening of the problem associated with the underlying illness, may occur.
source
Causes of anemia
Hemoglobin synthesis is a complex hematopoietic process that involves the digestive system, bone marrow, adrenal glands and circulatory system. A person’s diet and lifestyle are of considerable importance. To maintain normal hemoglobin, the following conditions must be met:
- The body received a sufficient amount of iron;
- The gastrointestinal tract must ensure normal absorption of iron;
- Vitamin C, which improves iron absorption, and vitamins B9 and B12, which are involved in the synthesis of hemoglobin, should be supplied with food;
- There were no disorders of the kidneys, hematopoietic system or cardiovascular system.
Based on these conditions, it is possible to determine the range of causes of anemia. In 80% of cases, anemia is caused by iron deficiency, this is due to insufficient intake of iron into the body from food or an increased need for a microelement.
Among other problems that can provoke deficiency anemia, the most common are:
- Lack of B vitamins;
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which iron is not absorbed;
- Donation.
There are other forms of anemia that are caused by serious pathologies:
- Blood loss (open and closed bleeding) is the cause of posthemorrhagic anemia;
- The presence of cancer is the cause of posthemorrhagic and hemolytic anemia;
- Pathologies of the hematopoietic system are the cause of hypoplastic and aplastic anemia.
Identifying the true cause of low hemoglobin is the key to the effectiveness of getting rid of anemia. Along with the treatment of the underlying disease, an iron supplement is always prescribed; it is necessary to replenish the resulting deficiency. And for iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements are the main treatment.
Important! The drug Hemobin will help replenish the lack of iron in the body. Thanks to its natural composition, it can be used to treat anemia even in children and pregnant women.
Increased level
When hemoglobin is higher than normal, this is also bad.
Exceeding the protein norm is not very noticeable outwardly, but destructive processes occur inside the body, which as a result can lead to pathologies of almost all systems and organs. To avoid negative consequences, you need to deal with the problem medically.
Hemoglobin in men may increase due to the following reasons:
- Oncological diseases;
- Pulmonary insufficiency (usually associated with a long history of smoking);
- Disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal obstruction;
- Diabetes.
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin in men
A decrease in hemoglobin is more noticeable by external signs.
But an increased rate of hemoglobin in the male body can be determined by some symptoms:
- Decreased performance. With an increase in protein, lethargy and fatigue are observed, in which there is absolutely no strength or desire to do anything. I want to sleep all the time, but neither coffee nor energy cocktails help.
- Loss of appetite. As with low hemoglobin, there is a decrease or loss of appetite, which as a result of fasting can cause dizziness and stomach pain.
- Decreased vision. Sharpness is lost and vision begins to deteriorate. But this process is long-term, so it is not immediately possible to determine the increase in red blood cells.
- Malfunction of the urinary system. Increased hemoglobin can cause urinary tract infections. When going to the toilet for minor needs, pain is observed.
- Instability in sex. The reproductive system fails. There may be a constant erection, or, conversely, partial impotence.
- Pale skin. If you do not seek help in time and remain with elevated hemoglobin for a long time, blood circulation is disrupted and subcutaneous capillaries collapse. As a result, the skin turns pale.
Degrees of anemia
There are three degrees of anemia: mild, moderate and severe. A blood test can determine it. The degree of anemia will be indicated by a reduced hemoglobin level and a decrease in the amount of serum iron (normally its content is 10.6-21.4 µmol/l). Its unit of measurement is grams per liter or milligrams per milliliter.
Mild degree
The diagnosis of the first degree of anemia is made when the hemoglobin level is below 110 g/l and above 90 g/l. In this case, serum iron reaches a value below 10 µmol/l. It is important to note that in early childhood and during pregnancy this may be a normal option.
The course is practically asymptomatic. Sometimes weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and pale skin are possible.
If the test result showed hemoglobin 90, how to raise it to normal? Mild anemia is most often associated with a deficiency of iron, folic acid or vitamin B12. Treatment consists of taking iron supplements and vitamin complexes or individual vitamins. The course of treatment is about a month.
Average degree
With the second degree of anemia, oxygen starvation begins to manifest itself more clearly. Headaches, noticeable pallor of the skin and visible mucous membranes, dry skin, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (constipation, bloating, diarrhea), rapid heartbeat appear. Children may experience developmental delays. This diagnosis is made if hemoglobin drops to 70-90 g/l and serum iron to 7.7 µmol/l.
If hemoglobin is 80 or lower, how to increase the level? Treatment of moderate anemia is determined by its cause:
- Iron deficiency - long-term use of iron supplements, treatment continues for some time after hemoglobin reaches normal;
- B12-deficiency anemia – with cobalamin injections, treatment continues for 2 months;
- Folate deficiency anemia - taking folic acid;
- If anemia is a symptom of another disease, treatment combines eliminating the underlying cause and replenishing the deficiency of vitamins and microelements using the above methods.
Hemoglobin level is 70, how to increase it? This value is conditionally considered critical. In this case, urgent medical attention and further correction of the resulting deficiency of iron and vitamins are necessary.
Severe degree
A decrease in hemoglobin below 70 g/l is characteristic of severe anemia; the doctor must decide how to increase the level. It is almost impossible to bring your body to this state with improper nutrition; the cause of third degree anemia is a serious illness or significant blood loss. A life-threatening decrease in hemoglobin is below 40 grams per liter.
If a blood test shows hemoglobin 70, how to raise it must be decided urgently. The first thing the attending physician should do is to identify the cause and eliminate it. Then long-term use of iron supplements is prescribed to replenish the lack of iron reserves in the body.
Symptoms of severe anemia:
- Brittle hair and nails, deterioration of their condition;
- Chills;
- Feeling of numbness in the limbs;
- Change in taste habits;
- Increased size of the liver and spleen.
For any degree of anemia, iron supplements are used as the main or additional treatment. Most of them cause a lot of side effects and have numerous contraindications. This is due to the fact that they contain inorganic compounds of ferric iron, which are poorly absorbed and form free radicals.
These drugs can be replaced with Hemobin. Its composition is unique - it contains only natural ingredients. Namely, similar in structure and structure to human hemoglobin, purified hemoglobin from farm animals and vitamin C, which improves the absorption of iron. Heme iron is divalent. It is in this form that iron is absorbed in the human body. It has high bioavailability (almost 100% of iron is absorbed).
Numerous studies have shown that Hemobin is safe for children and pregnant women, does not cause side effects or allergies, and provides an effective increase in hemoglobin. Hemobin is indicated in the treatment of any degree and form of anemia as a source of large amounts of iron, as well as for the prevention of anemia in people at risk.
Treatment of anemia with hemobin:
The duration of treatment with Hemobin is on average 20-30 days. Taking the drug must be accompanied by monitoring the level of hemoglobin and continue treatment until the indicator returns to normal and for some time after reaching a normal level for the accumulation of iron reserves.
Today you learned: why anemia occurs, how it manifests itself and what to do if hemoglobin drops below normal.
A blood test showed hemoglobin 70 - what to do? A reduced level of hemoglobin in the blood carries a certain danger to the human body, therefore, with such indicators, everyone should be careful about their health. However, many people are not aware of the low value of one of the blood elements, so they do not pay attention to minor problems occurring in the body. But if at the initial stage iron deficiency has practically no symptoms, then as the situation worsens, negative signs of pathology may develop, leading to serious complications. To avoid unpleasant symptoms and take the necessary measures in time, it is necessary to control the amount of hemoglobin in the bloodstream.
Increased hemoglobin
Content
Those suffering from anemia will say: “Lucky guys, your hemoglobin is elevated. This means your head is not spinning, you have enough strength to turn the earth over even without a support point.” Is it so? Is it possible to be jealous? If hemoglobin in the blood is increased, what does this mean?
The level of red blood cells in the blood cannot be constant even in a healthy person. If you get injured or your monthly cycle begins, your hemoglobin drops. Everything has healed and ended - he can return to normal again. We dealt with this in the previous article. But something else is surprising: every third person has increased hemoglobin. What is the danger or is it not worth worrying about?
As a result of an increase in hemoglobin over a long period, deterioration in many parameters is observed:
- disorder in the functioning of the kidneys and genitourinary system: colic, pain, cystitis, etc.;
- visual acuity decreases;
- the skin becomes pale, in some even yellowish;
- a person gets tired quickly and wants to sleep all the time. This has already been discussed somewhere, hasn’t it;
- complete or partial lack of appetite.
But all these consequences are superficial. But the real danger is much more serious. High hemoglobin - why is it dangerous? Increased red blood cells make the blood thicker. In case of wounds, it stops quickly, and this is a definite plus.
If you look at it from a different angle, the circulation of viscous blood is slowed down, which means that the heart and internal organs are not receiving enough oxygen. And low speed means plaque settles on the walls of blood vessels, causing blood clots to form.
The result is a heart attack, heart attack, stroke, thrombosis.
Finding out the reasons
Not only low but also high hemoglobin is dangerous; the reasons for men and women are largely similar. And yet there are differences.
If men have high hemoglobin, the reasons may lie in the characteristics of their professions.
- Pilots operate at high altitudes. They don’t notice it, but their body senses a lack of oxygen in the blood. The blood reacts to such messages by increasing hemoglobin.
- To quickly achieve results (read, a beautiful body), bodybuilders take steroids and anabolic steroids.
- Men smoke a lot: cigarettes, cigars, hookahs, etc. (grandmothers would say - don’t put this nasty thing in your mouth, and psychologists would explain this unhealthy desire to shove oblong cylindrical objects into your mouth in their own way).
If a woman has high hemoglobin, the reasons may be the same (female pilots, bodybuilders and smokers also occur). But there is one reason unique to them.
- During pregnancy, a woman's body is unpredictable. And who knows how he will react to conceiving and bearing a child.
- Let's add here the work of a flight attendant - she also flies at high altitudes.
The remaining reasons for men and women are common:
- Athletes involved in cross-country sports (skiing, skating, running) spend a lot of time outdoors. Oxygen must enter the blood more actively and be distributed throughout the body (frequent inhalations and exhalations), which is why hemoglobin can increase.
- Residents of high altitude areas (like pilots and flight attendants) also need high hemoglobin so that oxygen can be released from the thin air and circulated through the circulatory system.
These are external factors. If you notice that there is increased hemoglobin, the reasons may be due to a health condition.
- Diabetes mellitus, if glucose levels increase. Hemoglobin protein attaches to glucose atoms and drags them through the blood instead of oxygen.
- In diseases of the heart and kidneys, there is also a lack of oxygen - blood does not circulate at the required speed throughout the organs. From this appears erythrocytosis - an increase in red blood cells in the blood serum.
- Dehydration.
- Gaisbeck syndrome.
- Stress.
- Burns.
- Hereditary hemoglobinemia.
- Hemolytic anemia caused by problems with the gallbladder.
- Pernicious anemia, as a consequence of problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Oncology.
- Increased content of B vitamins: B12 and B9.
- Pulmonary or congenital heart failure.
- Poisoning.
If there are any of the above reasons, then your hemoglobin may be high - get checked. And if hemoglobin is elevated, what does this mean? It needs to be reduced. But first, let's look at the symptoms themselves.
How to recognize high hemoglobin in women? The symptoms are the same as in men, if the former are not pregnant, and the latter do not fly or swing constantly.
- The tips of the fingers and toes turn pale due to insufficient blood supply.
- As a result, your fingers feel cold.
- It’s hard to concentrate and come up with a smart thought - the brain is depleted of oxygen. Do not confuse increased hemoglobin with a prolonged rush at work.
- Pre-infarction or pre-stroke condition.
- Difficulty or, conversely, too frequent urination.
- Decrease in visual acuity.
- Loss of appetite.
- I want to lie down and do nothing (do not confuse it with laziness).
- Blood pressure rises for no apparent reason.
- Aches bones and joints.
- We haven’t walked much, but the veins are swollen, which means the blood is thick and clots are settling on the walls.
We described all these symptoms above. If you notice them, get tested. The following hemoglobin indicators should alert you:
- for men – above 170-180 grams per liter;
- for women - more than 150 grams per liter.
Why is high hemoglobin dangerous in women and men? In addition to the unpleasant state of a somnambulist, high hemoglobin can provoke a heart attack and even lead to death - a blood clot breaks off from the walls of blood vessels and instantly clogs the arteries. So we are urgently looking for ways to reduce hemoglobin.
Reducing hemoglobin
How to reduce hemoglobin in women and men? This can be done using dietetics and folk remedies, as well as medications.
Dietetics
It would be logical to assume that increased hemoglobin in women and men can be reduced by those foods that cannot be eaten if you are anemic.
It is forbidden:
- meat, offal (tongue, liver), game, smoked meats;
- beets, red vegetables and fruits, radishes;
- caviar;
- fast foods;
- full-fat milk, butter;
- cereals: buckwheat, rolled oats;
- soda;
- sweets;
- drink and drink;
- smoke.
Conclusion: you should not eat any foods that contain large amounts of iron and vitamin B12.
Can:
- seafood;
- lean fish;
- legumes;
- salads and vegetables with green fruits;
- cottage cheese;
- sour cream, kefir and other fermented milk products;
- chicken;
- drink more clean water (you remember about the water diet).
Dishes should not be fried, only boiled, raw, stewed or baked.
The table will help you navigate through foods containing iron. We choose those that contain less of this mineral.
Folk remedies
Hemoglobin concentration is an important indicator of blood composition. A deviation of its level from the norm, up or down, indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body, which need to be identified as quickly as possible.
- lethargy and increased fatigue appear;
- blood pressure jumps up;
- drowsiness is observed during the daytime, and in the evening it is difficult to fall asleep, insomnia;
- bruising from minor injuries;
- causeless nosebleeds;
- skin redness;
- noticeable blurred vision;
- complications of the functioning of the genitourinary system;
- headaches and lightheadedness;
- dry and itchy skin, especially noticeable after water procedures;
- painful sensations in the joints and abdomen;
- partial or complete lack of appetite.
There may be no symptoms for some time, and the person will not experience any discomfort. However, the disease that caused the increase in hemoglobin will not go away on its own and will appear sooner or later.
Due to their physiology, men are stronger and are able to withstand significant physical activity. They require additional oxygen, which is provided by a higher hemoglobin content.
In the female body, decreased hemoglobin is more often observed, rather than increased. But both are undesirable phenomena.
The growth of iron-containing protein during pregnancy is especially dangerous, since it signals complications in the development of the fetus or the presence of kidney and liver diseases in the expectant mother.
A pregnant woman needs to take vitamins very carefully. They can lead to enzyme disorders, which lead to excessive iron absorption.
Menstruation can affect hemoglobin levels. If they are heavy and last longer than usual, then dehydration is possible. First, this causes a so-called false increase in hemoglobin, and only then – its decrease and anemia.
Gradually the level of the substance decreases. By the first birthday, hemoglobin should be between 105 and 135 g/l. Exceeding the norm may indicate blood diseases, congenital heart disease, and lung problems.
Increased hemoglobin in children manifests itself with the same symptoms as in adults. The baby gets tired quickly, weak and drowsy. This condition is not typical for a baby, since a healthy child is always active and cheerful.
Parents will certainly contact their pediatrician, who will first order a blood test.
Increased hemoglobin is a pathological condition, indicating the presence of ailments. They need to be diagnosed as quickly as possible and treatment should not be delayed.
Sometimes this effect is a result of lifestyle or a consequence of taking medications. In each individual case, the decision is made by the doctor based on tests.
- Excessive smoking is associated with increased levels of carbon monoxide in the blood and can also lead to increased levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
- Life at high altitude or a consequence of the profession. High levels of red blood cells accumulate in response to low oxygen concentrations in the air. Because there is less oxygen in the blood, the body tries to make up for the deficiency by creating more red blood cells and continues to produce them until there are too many. The phenomenon occurs among pilots and flight attendants, as well as frequent flyers, skiers, rock climbers, etc.
- Large industrial cities with polluted air, in which the amount of harmful microparticles is much higher than normal and, as a result, oxygen is less than normal, are no less a threat. Less oxygen, more red blood cells and more hemoglobin.
- Bone marrow can also be overstimulated by testosterone replacement therapy.
- Taking certain medications: anabolic steroids (such as synthetic testosterone) or erythropoietin. Therefore, it is better to pump up muscles slowly and naturally; rapid increase with steroids is fraught with many problems.
- Some drugs used by athletes for doping.
- Overdose or misuse of the drug Epoetin Alpha (Epogen, Procrit)
- Burns.
- Dehydration (dehydration due to diarrhea or lack of fluids).
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Excessive exercise.
- Problem with the right side of the heart.
- Scarring or thickening of the lungs (pulmonary fibrosis), emphysema, and other severe lung diseases.
- Rare bone marrow diseases that cause an abnormal increase in the number of blood cells (polycythemia vera).
- Heart disease, especially congenital heart defects.
- Kidney tumors.
- Dehydration (from diarrhea or lack of fluids).
- Hypoxia (low oxygen levels in the blood).
- Exposure to carbon monoxide (usually associated with smoking).
- Polycythemia is a chronic blood cancer in which the bone marrow produces too many red blood cells. The consequence of this is increased hemoglobin. The disease results from problems with the bone marrow, which produces all red blood cells and platelets and most white blood cells. When this process is disrupted, cell production becomes disrupted and can lead to various health problems. Although the exact cause of polycythemia is unknown, research has found that a specific gene mutation is responsible for almost all cases. The disease is more common in men than women and is rare in people under 40 years of age, but there are cases of childhood morbidity.
- Fatigue.
- Itching (especially after a warm shower). This is the result of white blood cells (whose levels may also be high) releasing the chemical histamine.
- Headache.
- Sweating (at night or during the day).
- Blurred vision or dark spots before the eyes.
- Painful burning or numbness in the arms or legs.
- Bleeding from the gums and severe profuse bleeding even from minor cuts. Sometimes nosebleeds and pronounced bruising.
- Bone pain.
- Hesitant breathing.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Early feeling of fullness when eating.
- Pain under left ribs.
- Problems with concentration.
- Dizziness.
- Insomnia.
- Facial redness or burning sensation on the skin.
- Chest pain.
- Tinnitus.
- With dehydration, for example, the condition will return to normal after the body receives the required amount of fluid. In the absence of obvious diseases, it is better for smokers to give up this addiction.
- In some cases, a fairly effective way to normalize elevated hemoglobin is phlebotomy, also known as bloodletting. Because it takes time to treat the underlying disease, doctors sometimes use this therapeutic procedure, and it is still effective in instantly eliminating the symptoms of diseases with high hemoglobin (polycythemia vera, for example). This treatment is also effective for treating conditions such as chronic lung disease and cyanotic heart disease (both of which can cause elevated hemoglobin levels). One of the main goals of this treatment is to reduce the likelihood of blood clots and the risk of associated side effects.
- To relieve symptoms, medications are prescribed, such as antihistamines to relieve itching or aspirin to relieve pain, burning, and blood thinning associated with the disorder.
- Get a chest x-ray. Lung disease is a common cause of high hemoglobin levels because diseased lungs use less oxygen. Like smoking, oxygen deficiency causes more red blood cells to be produced and hemoglobin levels to rise. A chest x-ray can usually diagnose lung problems that may be contributing to elevated hemoglobin levels.
- drowsiness;
- increased fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- pallor or redness of the skin;
- disorders in the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruption of the genitourinary system;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased blood pressure (for no reason);
- aching joints.
What is hemoglobin and its normal values
Hemoglobin is an element that makes up red blood cells - it is what gives these blood cells their bright red hue. This element provides the body’s cells with oxygen, delivering it from the lungs directly to the systems and internal organs.
In order for hemoglobin to quickly form in the human body, the following conditions must be met:
- Availability of the required amount of iron in the diet.
- Complete absorption of this substance in the stomach and intestines.
- The presence of animal proteins in food.
- Absence of pathological processes in the circulatory system.
- The presence in the body of folic acid and some types of vitamins, which are necessary for the synthesis of red blood cells, which takes place in the bone marrow. If there is a sharp decrease in the level of red blood cells, a decrease in hemoglobin also occurs (it has long been proven that these elements are interconnected).
The level of this element in the blood flow in women and men differs slightly, but at the same time, age does not affect the final results:
- women - 110-140 g/l;
- men - 130-160 g/l.
With low hemoglobin levels, a variety of serious diseases occur in humans. Important: approximately 90% of them are due to iron deficiency anemia.
To find out what the danger of this condition is, you should take a closer look at the stages of anemia:
- mild – a person’s iron level is 90-110 g/l;
- average – 70-90%;
- severe – indicators less than 70%.
If hemoglobin decreases to 70-110 g/l and below, it is imperative to take measures to increase iron-containing protein in the blood under the guidance of a doctor. To ensure an effective result, it is necessary to regularly conduct blood tests for hemoglobin.
What leads to a decrease in hemoglobin levels
Iron protein deficiency does not develop just like that. It can be caused by a variety of reasons or be a symptom of any disease.
The most common are:
- Pregnancy, during which severe and persistent toxicosis appears.
- Side effects of certain medications.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Poor nutrition.
- Smoking.
- Frequent stress on the body.
- Frequent stressful situations.
Diseases that are accompanied by iron deficiency include:
- infections;
- hereditary pathologies - lead to the destruction or disruption of the integrity of red blood cells (these diseases also lead to a decrease in the existence of blood cells);
- jaundice;
- severe blood loss resulting from open injuries, operations, etc.;
- hidden pathologies of the digestive system;
- oncology;
- chemotherapy;
- helminthic infestations.
These and other conditions often lead a person to iron loss.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia
Most often, in the first stages of iron deficiency anemia it can be quite difficult to diagnose visually. Only when health deteriorates, signs of hemoglobin deficiency become more noticeable.
The main symptoms include:
- frequent thirst;
- constant weakness and dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- apathy;
- severe fatigue;
- headache;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- feeling of lack of air;
- constant feeling of drowsiness;
- fainting;
- dry, pale or dull hair, as well as hair loss;
- insomnia;
- brittle, brittle and peeling nails;
- chapped lips;
- taste disturbances (the diet contains mainly dairy products and cereals, while there is a complete refusal of vegetables and meat);
- the appearance of white or transparent spots on the nails;
- excessive sweating;
- muscle weakness;
- frequent migraines;
- addiction to unusual smells.
If hemoglobin is allowed to decrease below 70 g/l, there is a risk of developing acidosis - an increase in acidity. As a result of this reason, a life-threatening condition such as depression of the respiratory centers and cardiac activity may develop.