Drug poisoning, everything about it, what its first signs are, is described in the article. Find out how to provide first aid correctly and in a timely manner from the text. Alarming findings from forensic overdose deaths indicate a rise in the number of overdose deaths so high it may be considered an epidemic.
Over the past couple of decades, poisoning from smoking mixtures has been added to drug overdose, and the contingent of people who have received such a diagnosis is often not easy to persuade to begin addiction treatment in order to avoid trouble.
It was drug poisoning that came in second place in Russia. The first is alcohol intoxication, but intoxicating drugs, unlike alcohol, inhibit the excitability of the cough and respiratory centers and reduce the performance of the brain. Drug poisoning stimulates the vagal nerve, which is responsible for both motor functions and sensitivity of the skin surface.
Types of drugs
An important point in determining the cause of drug poisoning is a thorough examination. Each substance has its own antidote, the timely use of which will facilitate the fight for the life of the victim. Poisoning with narcotic analgesics, for example, can lead to cardiac arrest; other drugs affect the nervous system. Among narcotic drugs, separate groups are distinguished.
► Opiates, these include:
- Heroin.
- Poppy straw.
- Opium acetylated.
- Raw opium.
- Methadone.
► Cannabinoids:
- marijuana;
- hashish;
- oil.
► Cocaine:
- Cocaine leaves.
- Cocaine paste.
- Crack.
► Hallucinogens (psychoactive substances):
- LSD;
- psilocin;
- psilocybin;
- ecstasy;
- hallucinogenic mushrooms.
► Amphetamines:
- Ephedron.
- Pervitin.
- Ephedrine.
► Sleeping pills:
- barbiturates;
- benzodiazepines.
► Inhalants:
- Acetone.
- Petrol.
- Glue "Moment".
- Hair fixation spray.
- Insect repellents.
► Smoking mixtures:
- spices.
► Signs of opiate poisoning:
- Severe constriction of the pupils.
- The face burns and itches.
- Slow, incoherent speech.
- Decrease in temperature.
- Dry skin, pallor.
- Respiratory depression and irregularity.
- Impaired sensitivity of the body surface.
► Symptoms of cocaine poisoning:
- persistent pupil dilation;
- shortness of breath even at rest, increasing tachycardia;
- dizziness, poor orientation in space and time;
- severe weakness throughout the body;
- hallucinations of various types;
- temperature and blood pressure may be elevated.
► Signs of cannabinoid overdose:
- Frequent unpredictable mood swings.
- Dry mouth.
- Reasonless laughter.
- Dilated pupils.
- Attack of hypertension and tachycardia.
- Unstable emotions.
► Symptoms of hallucinogen poisoning:
- intense hand tremors;
- causeless euphoria;
- increase in blood pressure and heart rate;
- dilated pupils;
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- poor spatial orientation.
► Signs of intoxication with psychostimulants:
- Strong headache.
- Diarrhea.
- Vomiting, nausea.
► Criteria for overdose of sleeping pills:
- breathing is suppressed;
- kidneys refuse to work;
- the pupils, initially constricted, subsequently dilate;
- the nervous system can be paralyzed to the point of coma.
► Symptoms of poisoning due to substance abuse
- Trembling in limbs.
- Excitement, aggression.
- Strong headache.
- Vomiting, attacks of nausea.
- Intense insomnia.
What are the symptoms of drug poisoning?
Different substances have different effects on the human psyche, the main symptoms of drug use are as follows:
- pallor, swelling and bruises under the eyes;
- atypical condition of the pupils of the eyes;
- speech impairment (speech that is too slow, meaningless, delirium);
- lack of coordination;
- anxiety, secrecy, panic attacks;
- injection marks.
Drug poisoning is manifested by increased dry mouth, surges in blood pressure, spasms and convulsions. In most cases, vomiting occurs. How to relieve drug intoxication before the ambulance arrives - read on.
Factors and reasons
Forensic medical examination reveals that an overdose can be obtained either through negligence or intentionally. Symptoms of drug poisoning may not be obvious if:
- administering the wrong drug by mistake;
- use an unknown substance;
- too large a dose of medication;
- allow intoxicants to be mixed, add them to an alcoholic cocktail;
- taking a drug for the first time after a long break.
A person who has persistent suicidal tendencies may take a large dose of the drug intentionally, with the goal of committing suicide. Poisoning occurs due to the huge amount of drug accumulated in the body as a result of constant use. In this case, the usual dose for a drug addict will become fatal, which will exceed the concentration compatible with the normal functioning of the body.
A person's age is one of the factors influencing the possibility of poisoning. The results of a forensic medical examination confirm that the body is most often susceptible to overdose in children and the elderly.
Another risk factor may be a chronic disease and the method of drug use. Intravenous injections expose the body to the drug more quickly, while oral administration provides a slower absorption of the drug into the blood.
Danger of overdose
Intoxication of the body with narcotic drugs threatens, first of all, cardiac arrest and interruption of breathing. This effect on the body is caused by poisoning with narcotic analgesics, since they depress the nervous system, disrupting blood flow in the body. Cheerful dope can cause swelling of the brain and lungs, which will cause death.
Lethal, according to forensic medical examinations, is the death of tissue and the development of necrosis, resulting from strong compression of body parts due to a banal awkward position. Internal hemorrhages and injuries resulting from loss of spatial orientation become the cause of human death.
It must be remembered that fatal intoxication is possible not only in a drug addict, but also in a patient who takes an unfamiliar potent drug for the first time!
Cannabis-based substances cause irreversible changes in the heart muscle, lung tissue and liver. Taking psychostimulant drugs, you can get paralysis of the arms and legs, dementia, and a paranoid state. Cardiac arrest is often caused by the depressant properties of these substances.
Opiates are responsible for damage to bones, lungs and liver. Poisoning with a sleeping pill can lead to convulsions and psychosis. Attacks of schizophrenia, split personality, panic - the reasons for this are overdoses of hallucinogens.
Classification of narcotic substances
The speed with which drug poisoning can develop depends on many factors, primarily on the type of drug itself and the method of administration. Today, all narcotic substances are conventionally divided into the following groups:
- opium derivatives. There are natural (from poppy seeds), synthetic and semi-synthetic. These include heroin, morphine, codeine, promedol, etc.;
- cocaine group: leaves, coc paste, crack, etc.;
- hemp derivatives: hashish and oil, tetrahydrocannabinol, weed, etc.;
- amphetamines and non-amphetamines (also called stimulants): ephedrine, pervitin, methamphetamine, etc.;
- hallucinogens and psychedelics. There are plant origin (mushrooms) and synthetic ones. These include: LSD, DOB, ayahuasca, mescaline, psilocybin, etc.;
- hypnotic and sedative drugs (including sleeping pills): barbiturates, benzodiazepine, phenobarbital, nozepam, senuxen, etc.;
- toxic volatiles: gasoline, chloroform, nitrous oxide, glue, dichloromethane, etc.;
- salts, spices, new synthetic substances not yet classified as narcotic drugs.
Diagnosis of drug intoxication
Signs of drug poisoning that are administered by injection include injection marks that should be looked for on the crooks of the arms, ankles, and groin. Drugs taken orally are more difficult to recognize. The first signs of drug poisoning vary in nature. Please pay attention to:
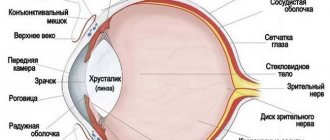
- Too narrowed or dilated, unnatural pupil.
- Inappropriate mood, lethargy, or, conversely, an excited state.
- Frequent and intermittent breathing.
- Vomiting, nausea, diarrhea.
- Confusion or lack thereof.
- Visions, hallucinations.
- Heart and headache.
- In case of poisoning with psychotropics, there may be an increase in temperature and fever.
- Sustained tremor of the limbs indicates cerebral edema.
First aid techniques
The timeliness of a set of measures to provide pre-hospital support services determines how high the chances of survival are for a person who has been poisoned. The first aid for drug poisoning after diagnosis should be to provide the person with fresh air.
In a stuffy room, you need to open the window, check if the victim’s tongue is stuck if he is unconscious. If fears are confirmed, you need to open access to breathing.
Free the person's neck and chest from constricting clothing, a tight collar or scarf, and unfasten the tight clasp on the throat and chest. Lay the victim on his side, allowing him to breathe freely, secure the position with his lower leg or arm extended. Be sure to call a team of doctors. Do not leave a person alone in case of poisoning, since resuscitation measures may be needed at any time.
For a conscious victim, in case of poisoning, it is necessary to do mandatory, repeated gastric lavage with cool boiled water every 30-40 minutes. The solution can be made more useful by adding a pinch of salt to restore metabolic processes.
The repetition of the procedure is explained by the fact that the walls of the stomach secrete traces of the narcotic substance for a very long time, and if they are not removed, the remains are reabsorbed into the blood.
What to do if there is no gag reflex - press on the root of the tongue. Lethargy and confusion make it difficult to perform auxiliary procedures, so use ammonia, which you need to bring to the person’s nose, moistening a cotton swab in it.
If there is no ammonia, you can intensively rub your earlobes, tickle your nose with a handkerchief or a blade of grass. Such actions will help stimulate breathing and the vascular system, preventing loss of consciousness due to drug poisoning.
If you are sure that drugs were taken orally, after cleansing the stomach, give the victim sorbents so that they bind the remaining toxins. When taking psychostimulants, an enema will help promptly remove waste products from the intestines. in the absence of breathing and blood circulation, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration (mouth-to-mouth method), then indirect cardiac massage.
Wrap the person in a blanket while monitoring his condition while waiting for an ambulance. Try to make sure that he lies on his side and has free access to air. You can give the victim a diuretic if he is in satisfactory condition, this will help the body cleanse itself faster. Do not forget about slightly salted water for drinking in large volumes.
Causes of drug poisoning
Before the medical team arrives, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with saline solution; it reduces the absorption of toxic substances and neutralizes some compounds. To prepare a solution, stir 3 teaspoons of salt, 1.5 teaspoons of soda, and 3 tablespoons of sugar in 3 liters of water. After washing, you must take polyphepan, activated carbon or other sorbents. If you feel drowsy or lethargic, rub your earlobes and bring ammonia to your nose.
The victim, who is in an unconscious position, is placed on his side, making sure that his tongue does not sink in. If there is no heartbeat, perform cardiac massage and artificial respiration. A person with psychogenic arousal is calmed down and restrained.
Opiate drugs include codeine, methadone, morphine, meperidine, heroin, acetylated opium solution. Each of these substances is highly toxic, and overdose is often fatal.
The acute phase is characterized by:
- confusion;
- cyanosis;
- constriction of the pupils;
- slurred speech;
- shallow breathing;
- slow heartbeat;
- drooping upper eyelid;
- nausea and vomiting;
- affective states;
- loss of the ability to move limbs.
If you do not provide help, blood pressure drops, breathing slows down, the brain swells, and death can occur. If you find someone who has been poisoned, immediately call specialists, provide conditions for normal respiratory function, and if cardiac activity stops, perform a cardiac massage. If intoxication is caused by oral ingestion of opiates, rinse the stomach.
Important! It is forbidden to give coffee or drugs that act on the central nervous system. Help must be provided quickly so that drug poisoning does not lead to depression of the respiratory center.
Poisoning with drugs from the opiate group is considered one of the most common types of intoxication.
After the harmful substance is eliminated at least partially, the patient will experience withdrawal symptoms. In this state, a person experiences various mental disorders that arise after using drugs. It can last approximately three weeks. At this time, the addict will suffer:
- muscle pain,
- irritability and aggressiveness,
- convulsions,
- problems with the digestive system.
To become addicted to opiates, you simply need to use them on a regular basis for about a month. The first signs of drug poisoning by this subcategory of harmful substances are:
- constriction of the pupils;
- pallor of the skin and its dryness;
- temperature drop to 36 degrees and below;
- itching of the tip of the nose and in the frontal region;
- speech problems;
- losing oneself in space;
- lowering the sensitivity threshold;
- irregular breathing rhythm;
- decrease in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle.
Common signs that help to visually recognize a drug addict who prefers drugs from the opiate group include a person’s indifference to the environment. The patient experiences apathy and appears indecisive. In addition, patients appear older than their real age.
Since the respiratory center most often suffers during intoxication after taking opiates, people around the addict are required to provide him with qualified pre-medical assistance in a timely manner. This will save the victim’s life and control breathing. The main principles of assistance include:
- calling an ambulance;
- laying the victim on one side with the knee bent;
- providing fresh air, even to the point of unbuttoning tight clothing;
- gastric lavage, which is carried out only if the patient remains conscious;
- taking enterosorbents (even simple activated carbon will do);
- bringing consciousness, if the victim faints, using cotton wool and ammonia.
If the drug addict’s breathing and pulse cannot be traced, then he will need to be provided with urgent resuscitation assistance: artificial respiration and chest compressions.
Opiates are the most dangerous drugs in terms of the number of poisonings, especially during the first doses. One of the reasons for the high mortality rate is that in 90% of cases, opiates are administered intravenously.
Common opiates: Heroin, Methadone, Morphine, Krokodil (Desomorphine), poppy straw.
Characteristic signs of overdose:
- Severe weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
- The pupils are constricted and do not respond to light.
- Severe skin itching.
- The red face gradually turns pale and acquires a bluish tint.
- Coordination of movements and clarity of speech are impaired.
- Body temperature drops sharply below 36 degrees.
- Painful sensations are dulled.
- Breathing is weak, pulse can be felt with difficulty.
Important! Opiates cause paralysis of the respiratory center. Without immediate resuscitation, the likelihood of death from suffocation is very high.
03/21/2018
- Cannabis derivatives – oil, marijuana and hashish.
- Opiates: they can be synthetic (Promedol and Medintil), semi-synthetic (Heroin), and also natural (Morphine, Omnopon, Codeine).
- Cocaine – crack, leaves and cocaine paste.
- Amphetamines – Amphetamine itself, as well as Ephedrine, Pervitin, Ecstasy, etc.
- Sedative, hypnotic drugs: benzodiazepines (Nozepam and Seduxen), barbiturates (Phenobarbital).
- Hallucinogens: natural – poisonous mushrooms, synthetic – LSD.
- Other drugs – Clonidine, Pipolfen, Diphenhydramine, etc.
After using drugs of this group, you feel warm in your head. During drug intoxication, a person feels peace and drowsiness quickly appears. When the drug is removed from the body, withdrawal begins to develop, manifested by mental disorders. The following manifestations are typical for this period:
- miosis - too narrow pupils;
- pale and dry skin;
- speech disturbance (dysarthria);
- body temperature decreases;
- itching, burning of the tip of the nose and forehead;
- decreased tactile sensitivity;
- ataxia develops (impaired coordination);
- breathing becomes slow, shallow and irregular;
- the heart rate decreases (bradycardia).
It is very easy to recognize an opium addict, as he is characterized by apathy, indifference to everything, and lack of communication. Quite often such people look much older than their actual years. It is important to know that drugs belonging to the opiate group strongly depress breathing, so in case of an overdose, paralysis of the respiratory center may occur. In this situation, medical care is extremely important.
- first you need to call an ambulance, noting the symptoms of drug poisoning;
- lay the patient on his side, bend one knee;
- ventilate the room, free the chest from clothing;
- rinse the stomach with saline solution, but only if the victim is conscious;
- give enterosorbent (activated carbon, Smecta);
- in case of fainting or lethargy, use ammonia;
- if there is no breathing, it is important to begin resuscitation by performing artificial respiration and chest compressions.
First aid in such a situation is extremely important, since the future life of the drug addict depends on it.
Psychostimulants are drugs that stimulate a person’s mental and physical activity. These include Amphetamine, Caffeine, etc. If taken in large dosages, poisoning may develop. The first stage is characterized by emotional stress, aggression and excessive talkativeness.
- vomiting and nausea;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- headache.
If the degree of poisoning is too severe, consciousness fades, body temperature drops, blood pressure drops, and sometimes convulsions occur. In this situation, it is impossible to do without urgent resuscitation of the victim. As for first aid, it is necessary to call an ambulance, stop taking the drug, and also, if conscious, rinse the stomach with a weak saline solution.
- initially there is a constriction of the pupils, after which they become too dilated;
- the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired;
- respiratory depression occurs;
- as a result of central nervous system depression, coma develops.
- first of all, it is necessary to call an ambulance team, otherwise the person may die;
- by rinsing, cleanse the stomach of poisons and toxic substances;
- Using activated carbon or other sorbent, bind toxins and evacuate them from the body.
The rest of the therapy is carried out by medical professionals.
The value of first aid is so great that it allows you to save the life of the victim and alleviate the condition even before the doctors arrive. That is why it is important to know how and when to help a person, since he really needs it. To summarize, we can say that over the past twenty years, cases of drug poisoning, overdoses, and deaths have become more frequent.
Addict
Healing procedures
In no case should you refuse hospital treatment for poisoning, even if the injured person felt great relief after first aid. A feature of drug intoxication is that the effect of the drugs lasts much longer than the effect of the antidote. This can cause further severe deterioration of the condition, and the person risks falling into a coma or dying.
You cannot treat a patient yourself. Do not give him alcohol or medications, this can aggravate the person’s condition or blur the overall picture of poisoning. Forensic medical examinations have repeatedly indicated death as a result of refusal to hospitalize such patients. The clinic carries out the following measures to restore the body:
- treatment with an antidote - it is selected individually;
- the lungs are ventilated artificially, cleansing;
- blood pressure and temperature decrease;
- the stomach is washed and diuresis increases;
- the consequences of dehydration of the body are relieved by introducing the necessary drugs;
- the metabolic process is activated;
- the circulatory system becomes alkalized;
- Antibiotics are used to avoid complications.
Be sure to tell doctors the information that the person was poisoned intentionally. In this case, help may be needed not only for the body, but also for the psyche. In the complex treatment of intoxication, you can also use folk remedies, making infusions of herbal preparations that effectively help remove toxins from the body.
Here are some recipes:
- Melissa, Ivan-tea, chestnut blossom, mint - everything is taken equally and poured with boiling water. You need to consume the infusion by adding a compote of diuretic berries: Cranberries, lingonberries, cherries.
- Dry walnut leaves are crushed and brewed at the rate of two tablespoons per two cups of boiling water. Leave for 24 hours, drink a quarter glass a day.
- Dried raspberries, spoonful of cinquefoil, add a small spoonful of milk thistle and pour half a liter of hot water. Drink 100 grams daily.
- An infusion of St. John's wort helps well, along with rose hips, nettles, horsetail and clover. All ingredients are poured into a spoon with 0.5 liters of boiling water and left for 6 hours. Drink 50 grams several times a day.
Video: drug poisoning.
Treatment in hospital
In a hospital setting, the poisoned person will be prescribed rehabilitation therapy, which includes:
- carrying out long-term and intensive ventilation of the lungs;
- the use of antidotes that are selected individually, since they have the ability to neutralize specific types of drugs;
- restoration of blood pressure through the administration (intravenously) of adrenergic agonists;
- cleansing the body of toxic products by thoroughly washing the gastric cavity or artificially increasing diuresis;
- the use of a 3% solution of sodium bicarbonate to alkalize the circulatory system;
- carrying out dehydration of the body using drugs such as Lasix and Mannitol;
- improvement of metabolic processes in the tissues of the central nervous system with the help of Piracetam and Actovegin;
- prevention of possible complications with the use of antibiotics.
This is interesting: Letter to the victim of an accident 2020
Prevention
To avoid accidental poisoning from potent drugs, do not leave medications within a child's reach. Use stickers with the name written in large letters if there are visually impaired people in the house. Throw away medications that do not have a label, the name has been erased, or there are no instructions with indications. Don't let your child play with them!
Pharmacological medications should be taken strictly under the supervision of a doctor. It is best for people with drug addiction to undergo a course of treatment, cleansing them from the effects of the drugs. You cannot carry out therapy on your own; medical supervision will ensure successful recovery. Only in a specialized clinic will the victim be able to provide the full range of procedures that will lead to good results.