Causes of inflammation of the ovary on the right side
Oophoritis or inflammation of the right ovary most often develops as a consequence of a previous infection, as well as in the absence of adequate therapy. Spreads to nearby tissues, resulting in complications. The main factors that can cause the development of the disease in a woman of reproductive age:
- Frequent abortions, unsuccessful gynecological operations.
- Chronic inflammatory processes of the reproductive system.
- Fungal infections that last a long time, leading to the development of complications.
- Systematic hypothermia, which creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Doctors most often diagnose inflammation of the ovary on the right side in the following patients:
- women without a regular sexual partner, who come into contact with different men,
- representatives of the fairer sex taking uncontrolled contraceptives or hormonal drugs,
- women who have undergone several gynecological operations performed surgically.
Often, girls, wanting to look attractive, despite the weather conditions and time of year, ignore advice that can preserve reproductive function (do not sit on a cold surface, wear warm clothes, etc.). Such neglect of one’s own health is the cause of severe consequences and the development of pathology of the reproductive system.
Much depends on the bacteria that caused right-sided inflammation of the ovary. The main infectious agents are the following:
- Often the disease develops against the background of staphylococcus infection. This bacterium is resistant to many drugs and is extremely toxic.
- The inflammatory process on the right can provoke infection with streptococcus.
- Often the causative agents of the disease are nonspecific, we are talking about chlamydia, mycoplasma, and E. coli.
In a fungal infection, the causative agent is considered to be a fungus of the Candida class, which is constantly present in the body, but under certain circumstances begins to behave aggressively (multiply at double the speed).
Formation process and reasons for appearance
A healthy woman has two ovaries that produce eggs. The size of each can be compared to a walnut. The ovaries are located on either side of the uterus. Every month, the right or left ovary produces a cell. Completing this process starts the monthly menstrual cycle. Each egg is enclosed in a special sac. It is called a follicle. It is located inside the ovary. Here the egg matures until it is ready for fertilization. The process is carried out under the influence of the hormone estrogen. On the 14-15th day from the start of menstruation, the polyps burst. As a result, the egg is released and enters the fallopian tube. Here she can subsequently be fertilized by sperm.
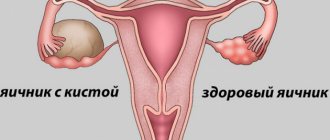
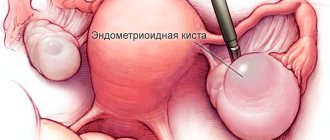
However, the above process does not always go smoothly. Sometimes the dominant follicle does not rupture. Instead of bursting, it continues to grow. At the same time, more and more liquid accumulates in it. As a result, it turns into a follicular cyst. Sometimes the corpus luteum can also turn into it. However, such phenomena occur extremely rarely in practice.
Most ovarian cysts are benign. They disappear on their own within a few weeks. In this case, specialized treatment is not required. Pathology can occur in women of all ages.
The exact causes of the development of ovarian cysts have not been established to date. However, experts identify a number of situations that increase the risk of pathology. The list includes:
- the woman has already encountered ovarian cysts in the past;
- the patient has irregular menstruation;
- the first menstruation occurred very early;
- there are hormonal disorders;
- the patient suffers from infertility;
- the woman previously had abortions;
- treatment of malignant neoplasms in the breast was performed with tamoxifen;
- there is general obesity, or a large amount of fatty tissue is observed in the upper part of the woman’s body.
Symptoms of right-sided pathology
When the right ovary is inflamed, a woman is concerned about certain signs. Much depends on the severity of the pathological processes, as well as on the severity of the manifestations. Main symptoms of the disease:
- the right lower abdomen hurts, the sensation intensifies during movement, performing standard actions,
- there is a significant increase in body temperature, up to the development of fever, the indicator rises above 39 degrees,
- severe intoxication of the body is observed, which directly indicates the course of the pathological process,
- characteristic symptoms of inflammation of the right ovary in a woman are accompanied by general weakness, apathy, and drowsiness.
The inflammatory process can have both acute and chronic forms:
| Form type | Description |
| Acute form of inflammation of the right ovary | The signs of the disease are pronounced, they cause serious concern and disrupt the way of life. It is impossible not to notice the presence of problems; hospitalization, inpatient treatment, and medical procedures are required |
| Chronic form of inflammation of the right ovary | The symptoms are mild, the patient feels unwell, but does not associate it with inflammation of the ovaries. Pain may be experienced during sexual intercourse, before or during menstruation, but the sensations gradually subside. There is no increase in temperature, but the general condition is cause for concern |
In the chronic type of the disease, it is prone to relapse, that is, the main signs of an acute inflammatory process on the right appear periodically.
Despite the pronounced severity of the symptoms, in the acute form of the course, inflammation of the right ovary is easier to stop, and they lead to complications less often.
If the process becomes chronic, an unfavorable situation is created that is dangerous to the life and health of the woman. Since structural changes occur in the right ovary, it is not possible to eliminate pathogenic agents.
Structure of the ovary
Externally, the ovary is protected by the peritoneum and a dense tunica albuginea.
The cortex is located deeper
, which contains a huge number of follicles, yellow and white bodies.
- A follicle (a structural unit of the ovary) is a fluid-filled “bubble” with an egg ripening inside. The dominant follicle produces estrogens.
- The corpus luteum (follicle after ovulation) is a temporary endocrine structure that synthesizes the hormone progesterone.
- The white body is the remnant of the atrophied corpus luteum.
Diagnosis of right-sided ovarian inflammation
There are several ways to diagnose a disease of the right reproductive organ. To give the patient a correct diagnosis, you will need to take several tests and undergo a series of examinations:
- Take a swab of vaginal secretions to determine the causative agent of the infection.
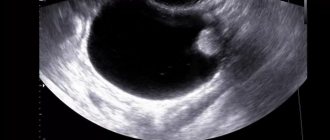
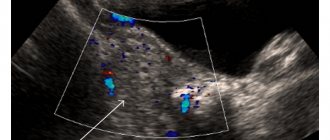
- Perform an ultrasound examination of the organs of the reproductive system.
- Go through a standard gynecological examination using speculum.
- Donate blood samples to determine the number of leukocytes, platelets and other characteristics of the biological fluid.
The above studies will be sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis of the patient. The gynecologist may prescribe other procedures, it depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the woman’s condition.
Treatment of right-sided inflammation of the ovary
Therapy has several directions and involves taking drugs with different spectrum of action. The doctor may prescribe:
- anti-inflammatory drugs,
- antiseptic solutions,
- antibacterial drugs,
- physiotherapeutic procedures to relieve inflammation.
The choice of medications is made by the doctor, it depends on the patient’s condition. Intravenous detoxification solutions are often required.
Prescribed drugs for inflammation of the right ovary
The basis of treatment is antibiotics; other medications complement therapy and help eliminate unpleasant symptoms faster. In addition to anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs, gynecologists use painkillers, as they can eliminate discomfort and reduce the severity of pain.
Doctors use broad-spectrum drugs because the woman needs emergency help that can correct her condition.
Preference is given to combination therapy because it is most effective.
Possible complications of inflammation of the ovary on the right
Any disease, if left untreated, leads to serious consequences. Timely therapy will help avoid this. But if you don’t seek help, the risk of encountering serious complications increases:
- The appearance of adhesions on the organs and tissues of the reproductive system. They significantly impede the movement of the egg and are considered a cause of infertility. Surgery will help restore the elasticity of the tubes and normalize the functioning of the ovary.
- Inflammation of the right ovary that occurs without treatment is fraught with structural changes in the tissue. That is, the inflammation changes its course, becomes chronic, is difficult to stop, and will require long-term use of antibiotics.
- Often pathogenic microorganisms infect the tissues of the digestive system, which increases unpleasant symptoms. Causes digestive disorders.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to start taking antibacterial drugs in a timely manner. The course of therapy is carried out under the supervision of a gynecologist.
How do ovaries work in women?
When the menstrual period begins, the ovaries begin to secrete 3-30 follicles. However, only 1-2 of them mature. Mature follicles are called graafian vesicles. Inside each of them there is a sac with an egg. During ovulation, the follicle ruptures. The egg is released into the abdominal cavity. From there it is sucked into the fimbriae of the fallopian tube. The burst follicle turns into a corpus luteum. A small wound remains in the place of the ovary where the follicle was. If fertilization occurs, pregnancy occurs. Otherwise, the corpus luteum gradually resolves.
In pregnant women, the corpus luteum measures 2 cm. It functions as a secretory gland. After childbirth, the corpus luteum becomes white, after which it is replaced by connective tissue. In this case, roughness remains on the surface of the ovary. This process occurs throughout the entire reproductive period of every woman, that is, until the onset of menopause.
Every year the number of germ cells in the ovaries decreases. So, if in the body of a female embryo there are approximately 1 million eggs in one gonad, then in 45-50-year-old women they are absent. Moreover, in an adult woman, new eggs are not formed, but those that appeared in the embryonic period are consumed.