No one is safe from a brain contusion or concussion, even in peacetime. An unfortunate fall, household injuries, routine repairs, or active recreation on a picnic can result in brain dysfunction. Traumatic brain injuries are common injuries to tissue in the head and brain. Modern diagnostics using MRI or CT will not show precise changes in the structure of nervous tissue at the cellular level. It will only reveal swelling, hemorrhage, fractures and other visible changes that pose the main danger - intracranial bleeding, hypoxia and coma. Injuries are dangerous to any part of the brain. But most of the fatal cases occur when the trunk of the central nervous system (the junction of the neck and head) is damaged. After all, this is where the control centers for breathing, heart rate, thermoregulation and other vital functions are located.
Causes of head injuries
The most common culprits of TBI are:
- Road accident. Abroad, more than 80% of all TBIs, regardless of the patient’s age and gender, occur due to transport accidents. In the CIS this percentage is much lower. Difficulties in treating such patients are caused by polytraumas of the chest and throat due to the impact of a car collision. Regardless of the quality of surgical intervention, mortality in this category of patients reaches 30%;
- criminal-domestic origin. In a state of passion, alcohol or drug intoxication, it is easy to start a fight with consequences: head injuries;
- extreme sports. Alpine skiing, snowboarding, and roofing are all potential hazards of brain injury. It’s not for nothing that the average patient in the neurology department diagnosed with TBI is a 25-year-old guy with an athletic build. Most athletes and amateurs neglect protective equipment or safety precautions, and then become clients of neurologists and traumatologists.
Recognizing the symptoms of TBI
The most typical symptoms of a brain injury are:
- loss of consciousness lasting from a couple of minutes to hours;
- disorientation and short-term amnesia. The victim does not understand where he is, what happened and how he got here;
- nausea and vomiting. Due to disruption of the central nervous system, the vestibular apparatus suffers. Therefore, symptoms appear similar to seasickness: dizziness and severe vomiting;
- loss of sensation in a body part or tremors. This is also a manifestation of disruption of the cerebral hemispheres and the relationships between the central and peripheral nervous systems;
- vision problems. In a comatose state, the victim may have no reaction of the pupils to light at all. If a person is conscious, it is difficult for him to focus his eyes. Objects float, lose their outline, and flies dance before your eyes;
- ringing in the ears and local headache.
All these symptoms give rise to suspicion of TBI. If, in addition to the indicated signs, there is noticeable violation of the integrity of the skin and bones, bleeding, then immediately call an ambulance.
( Video : "Traumatic Brain Injury")
Head wound: open
An open head wound is accompanied by a dissection of the skin with the characteristic development of bleeding. The amount of blood discharge depends on the location of the wound, its depth and the cause of its occurrence. The danger of this group of wounds is that there are large vessels on the head, the violation of the integrity of which entails the development of full-scale bleeding. Lack of qualified help can cost a person his life.
Open wound on the head
Open wounds are accompanied by loss of consciousness, nausea, numbness of the extremities, which indicates a concussion and contusion of the meninges. Along with stopping the bleeding, the victim is resuscitated, restoring all vital processes in the body.
Classification of traumatic brain injuries
There are many methods and typologies of head injuries, which differ in foreign and domestic medicine. Without going into complex medical terms, head injuries are divided into open (when the contents of the skull are in contact with the external environment) and closed. The latter are divided into:
- Brain concussion. The mildest TBI. In preschool children, it may even be asymptomatic. In adults, it is accompanied by retrograde amnesia, vomiting and dizziness.
- Brain contusion (or contusion). More serious damage to the tissues of the central nervous system has the character of a focal lesion. Occurs during a strong impact, explosion or fall.
- Compression of the brain occurs due to mechanical trauma. Accompanied by epidural and subdural hematomas, increased intracranial pressure. Often, when the brain is compressed, victims experience a superficial coma, when a person opens his eyes, swallows food, drinks water, but is not in a clear consciousness, periodically falling into a state of stupor;
- A fracture of the base or crack of the skull occurs without lacerations or external damage to the skin. The danger in the condition is the possibility of hematoma, internal bleeding or loss of cerebrospinal fluid;
Open traumatic brain injury is dangerous due to contact of brain tissue with the external environment. With such an injury, there is a high probability of infection, pieces of skin, hair, particles of earth, bullet fragments or other foreign objects entering the skull. Additionally, in general therapy, neurologists combat the threat of sepsis, meningitis and brain abscess.
( Video : “Brain contusion: severity, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment”)
Diagnosis of head injuries
When the victim is admitted to the hospital, he will undergo a series of procedures and consultations:
- examination by a neurologist. He ascertains a concussion or other TBI injury, determines the degree of its severity and the general condition of the central and peripheral nervous systems;
- X-ray of the skull. Most public clinics do not have MRI or CT scans, but they do have an X-ray room. The study determines the presence of skull fractures and other injuries;
- Ultrasound of the brain. The study detects the presence of hematomas or other damage inside the brain structures;
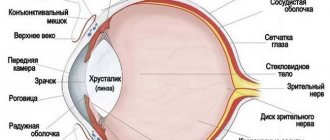
- consultation with an ophthalmologist. The doctor examines the fundus of the eye, determines increased intraocular pressure, retinal detachment or congestive discs;
- MRI and CT. The most informative methods for diagnosing the degree of damage to brain tissue due to head injuries. A detailed image in several projections is displayed on the screen. It is enlarged to better examine all changes in tissues, vessels or parts of the brain. The only disadvantage of this diagnosis is the high cost of the procedure and its inaccessibility in most domestic clinics.
Head wound: classification
Considering the nature of the damage, there are several types of wounds:
- 1. Puncture wound of the head - occurs as a result of penetration of a sharp thin object (nail, awl, needle) into the head, which is extremely life-threatening. The deeper the object enters the head, the higher the risk of death.
- 2. Chopped wound of the head - develops due to mechanical impact on the head area of a sharp heavy object: a saber, an ax, parts of a machine in production.
- 3. Incised head wound - formed as a result of penetration of a sharp flat object: a knife, a sharpener, a scalpel. Accompanied by large blood losses.
- 4. Bruised head wound - occurs when exposed to a blunt object: a stone, a bottle, a stick. Accompanied by the appearance of a hematoma.
- 5. Lacerated head wound – the wound has no clear boundaries; its formation is provoked by the impact of a blunt object that damages the outer skin, muscle layer and nerves.
- 6. Gunshot wound to the head - characterized by penetration of a firearm bullet into the head, which can fly out (through wound), or can get stuck in the meninges.
- 7. Bite head wound – develops from animal bites. Requires complex treatment with the appointment of antimicrobial therapy and the administration of anti-rabies serum.
Based on the depth of damage to the head area, wounds are classified into:
- soft tissue damage;
- damage to nerve fibers;
- damage to large blood vessels;
- damage to bone tissue;
- damage to parts of the brain.
Each wound has its own causes and characteristics. In the event of accidents or disasters, injuries can be complex and include several types of wounds that have their own characteristics.
Treatment of patients with TBI
Treatment of victims occurs only in a hospital setting in the neurosurgical department. In the presence of internal hematomas, surgical intervention is performed to normalize intracranial pressure and restore blood circulation.
The main principle of treatment is complete rest for a week or 10 days. The patient is protected from strong external irritants (bright light, strong odors, loud sounds). Reading books or watching TV is also prohibited. After all, this is an additional load on the eyes, and they are tightly connected to the brain.
Drug therapy includes taking medications for:
- restoration of metabolism in the nervous tissue of the head (picamilon);
- vascular drugs (Cavinton);
- painkillers (analgin, No-Shpa);
- sedatives based on valerian, motherwort, hop cones.
Additionally, after the end of bed rest, active rehabilitation begins using physical therapy, yoga, massage and alternative methods of treatment.
Features of treatment
Treatment of a wound localized on the head depends on the nature of the damage. For closed injuries and hematomas, ointments containing heparin are used. During therapy, the patient's condition is monitored dynamically.
Large, lacerated open injuries require immediate treatment with further suturing.
The course of treatment involves taking medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Analgesics.
- Nootropics that improve blood circulation in the vessels of the head.
- Antibiotics.
- Hemostatic drugs.
The medications are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the severity and nature of the wound in the head area. Timely provision of first aid can save a person's life.
First aid for traumatic brain injury
There is a clear algorithm for what the victim should do before the doctors arrive. His environment should:
- The very first thing: call the doctors.
- Provide air access and normal breathing. Not only open the windows, loosen a tight belt or unfasten the collar, but also remove vomit from the mouth. If the person is unconscious, then position him by turning him on his side, fixing his head.
- If the victim is thirsty, wet his lips or let him rinse his mouth. But don't let him drink too much, otherwise the vomiting will worsen.
- Secure the patient's body. Often with TBI there is a violation of the integrity of the bones of the skull or spine. In order not to cause even more harm, try not to move the victim, do not allow him to walk or sit down on his own.
What is forbidden to do during TBI
If a head or brain injury is suspected, the person should not be moved unnecessarily. After all, there may be a fracture of the skull bones and the fragments are displaced during movement, causing even greater harm. Doctors also do not advise taking any medications on your own. Banal aspirin will not only ease the headache, but will also increase bleeding. This is especially dangerous if blood collects inside a hematoma. The main thing when you suspect a TBI is not to panic, but to call doctors. After all, the speed of recovery after a brain injury or other troubles depends on the start of therapy. Ideally, it should start within the first hour after the injury.
First aid algorithm
First aid, regardless of the type of wound, is carried out according to the following scheme:
- 1. Stop bleeding - apply a clean bandage, cloth or gauze to the wound site and press firmly to the wound site. Apply cold, which will constrict the blood vessels and reduce bleeding.
- 2. Disinfect the area around the wound, but not the wound itself - the surface of the skin is treated with brilliant green, iodine or any disinfectant.
- 3. Monitor the general condition of the victim - control breathing and heartbeat, and in their absence, indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration are performed.
- 4. Take the patient to the hospital, fixing the head in a motionless position.
It is recommended to slightly raise the victim’s head, which will impede the flow of blood and reduce the appearance of bleeding.
Absolutely forbidden:
- press into the wound and set bone fragments on your own,
- wash deep wounds with water,
- independently remove foreign objects from the head,
- Give the victim medication.
A bruised wound to the scalp is almost always accompanied by a concussion and vomiting. Therefore, the patient is placed on his side, with a cushion placed under his head.
In case of a laceration, it is necessary to transport the patient to the hospital as quickly as possible, as stitches will be required. You can treat a head wound with brilliant green or iodine if it is minor.
Causes of a non-healing wound
The healing time of the pathological cavity without complications is 3 weeks. A non-healing wound can occur as a result of a tick bite or non-compliance with treatment rules.
Deviations can be caused by external and internal reasons:
- oncology;
- blood clotting disorder;
- presence of pus;
- changes in the walls of blood vessels in the head;
- disruption of cell nutrition;
- the presence of additional infections in the body;
- violation of epithelial proliferation;
- avitaminosis.
The healing process of head wounds is affected by medications and care.
If hygiene rules are followed, inflammation does not develop, and damaged scalp is restored in a short time. If foreign bodies enter the cavity, resumption is delayed.
Specifics of urgent actions
Help is provided to the victim after a brief examination. If you have symptoms of a fracture, you should immediately call a team of medical professionals. Pay attention to these signs:
- Severe pain in the area of the injured part of the back;
- Complete or partial loss of sensation in the limbs;
- Unnatural body position;
- Possible lack of consciousness;
- Possible cessation of cardiac and respiratory activity;
- Involuntary acts of urination and defecation.
Damage to the vertebrae is a dangerous injury, so first aid should be provided with extreme caution. The actions of a rescuer are simple, but they require constant presence next to the victim, patience and psychological support.
Let's consider the basic emergency care algorithm, which consists of the following actions:
- Examine the patient and check the functioning of his vital systems: breathing, heart, pulse;
- If there are no signs of life, begin resuscitation;
- In the absence of consciousness, the victim should be in a position on his side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract;
- If the patient is conscious, help him take an analgesic;
- If there is severe bleeding, take measures to eliminate it: use a tourniquet, a pressure bandage, or compression.
It is necessary to observe at all times that the victim is at rest and does not make any movements.
We list the most important of them:
- Do not try to change the position of the patient’s body or move him yourself;
- Do not place it on soft surfaces;
- Do not try to adjust the vertebrae yourself;
- If there is no sensitivity, do not rub, pinch or jerk your limbs;
- Do not use medications other than analgesics.
If it is not possible to call medical workers, take the patient to a health care facility yourself. Remember that without special medical equipment and devices, this must be done very carefully. It is important to do these steps correctly:
- Find a hard, flat object, such as a door;
- Secure the patient's head and neck;
- Carefully transfer the victim onto a makeshift stretcher in the position in which he was before;
- Watch the position of your head at the time of shifting.
What can cause injury
Knowing the mechanisms of damage will help you quickly navigate when providing timely assistance. The most common causes of spinal injuries leading to severe consequences include:
- Falls from a height, as well as as a result of loss of consciousness;
- Injury due to careless diving in bodies of water;
- Accidents (traffic, domestic, industrial, etc.);
- Disproportional loads on the spine;
- Excessive sports activities;
- Injuries during childbirth;
- Gunshot, knife wounds and injuries as a result of explosions;
- Aging of the body, leading to wear of the discs between the vertebrae and drying out of cartilage tissue;
- Massive blow to the back;
- Chronic diseases leading to a fracture of the spinal column (osteoporosis, tumor processes).
Various situations leading to damage to the musculoskeletal system are characterized by their own statistics of damage to one or another part of the spinal column. In transport accidents, in most cases the cervical spine is affected; in industrial accidents, the lumbosacral spine is affected. Childbirth complications lead to stretching of the spine.
Prevention methods
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. This is especially true for serious injuries, which could have been avoided in most cases by following safety rules.
- During team sports, cycling and other active activities, it is necessary to use protective equipment. A helmet and other sports accessories will help protect your head during collisions, falls and impacts.
- Use seat belts and monitor the condition of the vehicle's braking system when traveling.
- Obey traffic rules both as a driver and as a pedestrian.
- Ensure the safety of children in the apartment. Do not leave unattended. Limit access to traumatic objects. Eliminate the possibility of unstable heavy pieces of furniture falling. If necessary, use soft bolsters and pillows to cover sharp corners of cribs and sofas.
- During icy conditions, follow safety rules. Anti-slip pads on your shoes will help you avoid falling.
- Do not walk along buildings when the snow is melting and there is a risk of icicles and ice falling from the roofs of tall buildings.
Following safety precautions will reduce the chance of getting a traumatic brain injury.
Types of injuries
In order not to harm the patient when providing first aid, you need to be well aware of the types of spinal injuries. They are classified depending on the location, degree and depth of the lesion, as well as the method of deformation of the musculoskeletal system. Based on the nature of the damage, spinal injuries are divided into the following types:
- A fracture is a violation of the anatomical integrity of the vertebrae, as well as muscles, blood vessels, and nerve tissues, accompanied by a lack of motor activity and threatening life. It is most often diagnosed in the cervical spine.
- Dislocation - damage to the joints as a result of displacement of the vertebra above in relation to the lower one. It is typical for the cervical part of the spine, less often it occurs in the lumbar region.
- A bruise is a disorder of the spinal column that preserves the general structure of the spinal cord and in particular the vertebrae. Often accompanied by the formation of bruises, tissue necrosis and difficulty in the movement of cerebrospinal fluid along the spinal canal, and damage to the nerve roots. Mainly the lower thoracic and first lumbar vertebrae are injured, less often the cervical ones.
- A ruptured disc is a bulging of the inner layer or tearing of the outer layer, irritating and damaging a nerve root.
- Long-term compression syndrome is a pathological disorder of organs and systems due to blood poisoning with toxins after prolonged massive crushing of soft tissues or compression of the vessels of the extremities.
- Paraplegia is paralysis of the upper and lower extremities as a result of spinal cord injury.
At the site of injury, injuries to the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine, as well as simultaneous damage to several parts, are diagnosed. According to statistics, the most common disorders are those associated with the lumbosacral region, while in 25% of cases injuries to the cervical and thoracic region are diagnosed.
Main symptoms
A bruised wound to the forehead, back of the head, or parietal area is accompanied by various symptoms. If the injury is mild, then over time all unpleasant conditions will disappear, but with serious damage, loss of consciousness and other serious problems may occur.
Among the main symptoms are:
- severe pain in the head. This occurs due to vascular spasms;
- nose bleed;
- dizziness;
- feeling of weakness;
- the appearance of trembling in the arms and legs;
- a bump, bruise, hematoma, or wound may appear in the area of impact;
- movement coordination disorder;
- gagging;
- nausea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- disturbance of consciousness, clouding of reason;
- a sharp increase in temperature.
It is worth noting! Bruising of the soft tissues of the forehead, back of the head, and parietal area is considered a dangerous injury. If it gets worse, the person may lose consciousness, and if the damage is severe, the person may fall into a coma. For this reason, no symptom should be ignored.