Home / Cancer Treatment / Treatment of Anal Cancer
- Doctors
- Tomotherapy
- Reviews
- Cost of treatment
- Risk factors
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis and treatment
The anal canal is the end section of the digestive tract that connects the rectum with the external environment. Anal cancer arises from cells in the perianal skin or anal canal.
Tomotherapy
Radiation therapy is a method of treating cancer using x-rays that destroy tumor cells. There is a gradual exposure of the affected area to a certain dose of radiation, as a result of which the cancer cells die.
In the case of anal cancer, the tumor itself and regional lymph nodes are irradiated.
To achieve maximum effect, chemoradiotherapy (a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy) is used, which is the main ORGAN-SAVING method of treating patients with anal canal cancer.
The advantage of irradiation is the possibility of preserving the organ and the function of independent defecation.
Tomotherapy is the most effective method of radiation therapy, which preserves the functions of all organs located in the irradiation zone (bladder, intestines, femoral heads, genitals). The absence of radiation damage leads to better tolerability of treatment, rapid recovery of the body and preservation of quality of life. (see link)
Definition.
Anal cancer is a tumor that occurs in the area of the anus between the upper edge of the anal canal and its transition to the perianal skin, which is covered with hair.
Among the wide variety of histological forms of malignant neoplasms in this area, the leading place (50-75%) is occupied by squamous cell (epidermoid) cancer. This tumor is more often detected among people over 50 years of age. Among patients with anal cancer, women predominate. The male:female ratio varies according to various sources from 1:2 to 1:7. The risk of anal cancer increases in women who have previously been treated for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix or vagina.
Reviews
I would like to express my deep gratitude to the entire team of the radiation therapy center - attending physician Maria Viktorovna Aglullina, nurse Gulfiya Khafizova, medical registrar Venera Diyarova - for their kind, sensitive attitude towards me. During this difficult period of struggle and treatment, the attitude of the people around you and the medical staff is very important. I wish all employees good health, happiness and love! Thank you so much for everything!
Patient from Kazan
July 30, 2020
All reviews
Rushana's story, lung cancer
“Hello, my name is Rushana, I live in the city of Kazan and I ended up in this center, like many people, probably unexpectedly. Because for most of our lives we do not imagine that we might encounter anything else, that there might be some serious difficulties in our lives that we have not yet overcome.
All stories
Cost of treatment for anal cancer
| Name of service | price, rub. | Unit measurements |
| Consultation with an oncologist and radiotherapist | 0 | PC. |
| Consultation with a pediatric oncologist | 0 | PC. |
| Repeated consultation with specialists | 500 | PC. |
| Primary topometry on a specialized computed tomograph | 15 000 | procedure |
| Repeated topometry on a specialized computed tomograph | 7 000 | procedure |
| Primary dosimetric planning of radiation therapy (tomotherapy) | 20 000 | PC. |
| Repeated dosimetric planning of radiation therapy (tomotherapy) | 7 000 | PC. |
| Radiation therapy (tomotherapy), including IMGRT (*) | 223 000 | well |
| Radiation therapy (tomotherapy) stereotactic radiosurgery(*) | 250 000 | well |
| Accompanying drug therapy: intravenous administration in the treatment room (excluding the cost of medications) | 1 000 | procedure |
| Accompanying drug therapy: intramuscular administration in the treatment room (excluding the cost of medications) | 200 | procedure |
| Topometric marking | 750 | procedure |
The type of radiation therapy and the number of sessions of the course are determined by the medical commission individually for each patient based on the location, nosology of the tumor and taking into account the medical history.
Free online consultation
Sign up
Prevention:
- Moderate physical activity
- To give up smoking
- Proper nutrition
- Using condoms
- A timely visit to a doctor (proctologist, surgeon, oncologist) if you complain of discomfort, pain, or the presence of a formation in the anal area. Some changes in the lining of the anal canal seem harmless, but in the future they can transform into cancer.
Diagnostics
Anal cancer can be diagnosed using the following measures:
- taking an anamnesis, during which the doctor finds out whether there have been cases of cancer in the anal area in the family,
- initial examination of the skin around the anus, as well as the rectum using rectal mirrors,
- palpation examination of the rectum,
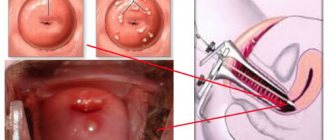
- performing sigmoidoscopy (examination of the walls of the rectum using a sigmoidoscope),
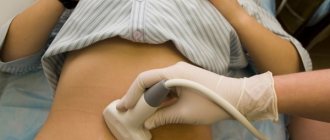
- ultrasound examination of the rectum and organs located in the abdominal cavity,
- conducting magnetic resonance or computed tomography,
- biopsy of the tumor for histological examination.
In order to exclude concomitant diseases of the large intestine, the doctor performs irrigoscopy (x-ray with the introduction of a contrast agent into the intestine). Examination of the abdominal organs allows us to determine the presence of regional metastases.
Symptoms of anal cancer. What should you be wary of?
- Bleeding from the rectum is the most common symptom of anal cancer. Often patients independently and unsuccessfully treat hemorrhoids or anal fissure, wasting precious time.
- Itching in the anal area.
- Pain and/or pressure in the anal area.
- The presence of a formation in the anal canal area.
- Changes in the nature of stool, ribbon-like stools.
- Mucous and/or purulent discharge from the anus.
- Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
Each of the symptoms described above can be a manifestation of benign processes. However, you should not self-medicate and delay a visit to the doctor. The earlier the disease is diagnosed and treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of cure and the more favorable the prognosis.
Flow
Anal canal cancer usually grows locally either in the intestinal lumen, or in the thickness of the wall, or in a mixed type. Practitioners distinguish the following stages of tumor growth of this pathology:
- Stage 0 - malignant degeneration of cells is found only in the anus. During this period, there are no symptoms of cancer; if detected, the disease can be completely cured.
- The first stage – the size of the tumor does not exceed 2 cm.
- The second stage is a neoplasm larger than 2 cm.
- Third stage A - a tumor is detected with metastases to neighboring organs (bladder, vagina) or lymph nodes near the rectum.
- Third stage B - the neoplasm metastasizes to the lymph nodes of one side of the groin and neighboring organs, or to the lymph nodes of both sides of the groin and neighboring organs.
- Stage four – cancer spreads to distant organs (liver, bones, lungs, kidneys, brain).
A doctor can detect a tumor during a digital rectal examination, anoscopy (which can be difficult if the tumor is large), or during an endoscopic ultrasound examination. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, which is why it is so important to know the first signs of anal cancer that you should pay attention to.
Treatment
What influences the choice of the type of treatment that is right for YOU?
- Stage of the tumor process.
- The presence or absence of other diseases. Be honest with your doctor. Some diseases are a contraindication for one or another type of treatment.
- Your age.
- The risk of complications from a particular type of treatment.
Factors for the development of this type of cancer
Several factors have been identified that, to one degree or another, have a direct impact on the occurrence of this cancer. Among them are the following:
- Age over fifty
- Anal fistula
- Papilloma virus
- HIV
- Anal sex
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse
- Advanced stage of hemorrhoids
- Anal fissures, pararectal fistulas, polyps, proctitis
- Radioactive irradiation of the pelvic area
It should be noted that it is not at all necessary that in the presence of these factors, anal cancer will develop. But the listed reasons can, under certain circumstances, aggravate the disease, or even provoke its occurrence.
Surgical method of treatment
It is used in case of massive bleeding associated with the tumor process, with a history of irradiation of the pelvic area, in the absence of a positive effect on the tumor within 1.5-2 months after chemoradiation treatment.
In a surgical approach to the treatment of anal canal cancer, the rectum and anal canal are removed, and the remaining part of the intestine is brought out onto the abdominal wall and a colostomy is formed. Unfortunately, this mutilation operation results in the inability to independently defecate for the rest of your life.
However, most patients with anal cancer DO NOT need surgery. The gold standard for treating non-metastatic cancer in this area is chemoradiotherapy.
What is Anal Cancer?
Author of the article: Kutenko Vladimir Sergeevich
Anal cancer , also known as anal cancer, is a pathological change in tissue characterized by the occurrence of malignant neoplasms localized in the anus. The symptomatic picture of anal cancer may consist of blood discharge from the anus, pain during defecation, various bowel disorders, as well as anal itching. The basis for diagnosing anal cancer is digital examination, as well as sigmoidoscopy and biopsy examination. The vast majority of treatment for anal cancer is complex, and consists of combined chemoradiotherapy, and it is also possible to use radical surgical intervention - rectal extirpation followed by installation of a permanent colostomy.
For a long period of time, anal cancer was considered as a form of rectal cancer, and only in the 50s of the 20th century was the term “anal cancer” introduced and it was identified as a separate nosology. Malignant neoplasms of the anus account for approximately 1-2% of all recorded cases of colon cancer. Anal cancer is most common in people over 50 years of age. Also at risk are men who practice homosexual sex, which increases the risk of anal cancer by 35 times, and the presence of HIV infection by 2 times.
Classification of anal cancer.
Anal cancer
Cancer of the anus and anal canal corresponds to a wide range of different histological forms, which is determined by the complexity of the structure of the anal area, as well as the variety of types of epithelial tissues. The most common form of anal cancer is squamous cell, also known as epidermoid cancer of the anus - about 55% of all cases. It develops somewhat distal to the rectal-anal line, namely from the external tissues of the anus, and subsequently it becomes predisposed to the formation of ulcers. The cloacogenic type of anal canal cancer is less common - 25-30%, and occurs in the transition zone between columnar epithelium and squamous epithelium. Adenocarcinoma is of glandular origin, and melanoma is of skin and mucosal cells.
Anal cancer: concept: causes of occurrence.
The reasons that lead to the development of anal cancer are not reliably known, but nevertheless, it is possible to differentiate some risk factors that, to one degree or another, increase the risk of its occurrence. HIV infection leads to the appearance of genital warts in the perianal area or on the cervix in women, which after a certain period of time leads to corcinogenesis in these areas. Immune deficiency due to HIV, after organ transplantation, and with the use of various immunosuppressants creates favorable conditions for the formation of tumors.
The incidence of anal cancer is influenced by constant irritation of the anus due to the presence of chronic diseases, such as anal fissure, anal polyp, anorectal fistula, and the practice of anal sex.
Anal cancer can also be caused by radiation therapy to treat cervical, prostate, and bladder cancer.
Anal cancer: symptoms.
One of the most common complaints in the presence of anal cancer is the presence of blood in the stool, or the presence of bleeding from the anus. There may also be pain in the anus, which appears slightly at first during defecation, and then more pronounced, radiating to the lower abdomen and genital area.
Many patients complain about pressure and the sensation of a foreign body in the anal area, which is also accompanied by anal itching. Pain and itching are caused by abundant innervation of the anus, muscle hyperspasm, and mucous or purulent discharge from the lesion. Later, anal cancer can lead to bowel problems and enlarged lymph nodes located in the anal and groin areas.
Anal cancer: diagnosis.
Diagnosis is difficult due to the fact that there are a lot of common symptoms and no characteristic signs. For this reason, if anal cancer is suspected, a comprehensive examination is indicated, including a physical examination of the patient, as well as digital, endoscopic, histological and other studies.
It is also mandatory to perform a sigmoidoscopy with a one-time collection of a biopsy sample of suspicious areas for analysis.
Anal cancer should be distinguished from some diseases of the large intestine such as hemorrhoids, polyps, anorectal fistula, etc.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to treat cancer. It is the main treatment method only for patients with distant metastases of anal cancer.
1Jafarov S., Link KH DIFFERENCE IN COLON AND RECTAL CANCER FROM THE POINT OF EPIDEMIOLOGY, CARCINOGENESIS, MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, PRIMARY AND SECONDARY PREVENTION: PRECLINICAL STUDIES. Siberian journal of oncology. 2018;17(4):88-98. https://doi.org/10.21294/1814-4861-2018-17-4-88-98
2https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-podhody-k-diagnostike-i-lecheniyu-raka-pryamoy-kishki
3https://www.oncology.ru/association/clinical-guidelines/2014/01.pdf
Causes of tumors
It is extremely rare to detect a tumor in the anus on your own. A person may notice that even after defecation there remains a feeling of incomplete emptying. Depending on the disease, alarming symptoms such as bleeding, pain or burning may be present.
Benign polyps
Benign polyps in the rectum
Such a tumor at the anus is a fairly common problem in middle-aged and elderly people. Doctors call polyps formations from skin cells. Small neoplasms have a red, inflamed tint, externally resembling a fungus on a thin stalk or a durable round lump.
Polyps intensively appear on the intestinal or anal mucosa during a hormonal surge: childbirth or pregnancy, menopause, diseases of the endocrine system. Therefore, the vast majority of patients with polyps are women. The formations can be multiple, grow strongly and block the lumen in the intestine. In rare cases, with constant injuries from feces, polyps degenerate into malignant areas.
Vascular angioma
Vascular angioma photo
These are formations that grow from soft tissues and tiny capillaries. They are “included” in the general circulatory system of the intestine, feeding from the patient’s body. An angioma can grow quickly, but does not hurt or bother a person. Therefore, rectal bleeding may indicate the disease.
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of hemorrhoidal node photo
With internal hemorrhoids, the bumps grow asymptomatically, gradually filling the space around the anus. Patients feel discomfort when visiting the toilet, notice bloody discharge or itching. The nodes are a sac that is formed from the stretched wall of a vein or other blood vessel. If hemorrhoids are left untreated, blood may stagnate and clots may form in the lumps.
This tumor grows rapidly and begins to put pressure on the endings of the nerve roots. The person experiences severe shooting pains that radiate to the groin. In case of hemorrhoidal thrombosis, the help of a surgeon is required to remove the dangerous clot.
Paraproctitis
Paraproctitis: opening of a purulent lump (fistula)
A rounded neoplasm in the anal canal can be a serious aggravation - paraproctitis. This is a type of purulent formation caused by harmful microorganisms: bacteria, fungi or microbes. A person who suffers from frequent constipation may develop cracks in the lower intestines. When passing feces or improper hygiene, they become infected and suppuration may occur.
Paraproctitis is a purulent tumor or fistula near the anus. It may be accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, pain and other unpleasant symptoms. Acute inflammation often appears in patients who did not even know about hemorrhoids, have weak sphincter muscles or “lazy bowel” syndrome.
Oncological tumors
Rectal cancer photo
In 1–3% of cases, a tumor detected in the anal canal is an oncological disease. Bowel cancer can develop from a polyp and be a consequence of frequent irritation of the anus. Experts still do not know what causes the disease.
Oncology begins asymptomatically, the tumor grows and blocks the lumen in the intestine. Patients note difficulties with defecation, nagging pain in the pelvis, purulent and bloody discharge with feces. They lose weight, feel weak, and notice swollen lymph nodes.
FAQ
How much does a course of treatment cost?
A course of treatment together with pre-radiation preparation costs 258,000 rubles. It is possible to arrange an installment plan for the entire period of treatment.
Is there online consultation?
For residents of other regions, as well as for those who find it difficult to visit a doctor, our center provides the opportunity for free online consultation.
Documents required for online consultation?
To receive advice on the possibility of receiving tomotherapy, you need to send us all your medical records and examinations, including a histological report. A referral for a free consultation is not required.
Is treatment possible for children?
Tomotherapy is most favorable for the treatment of children, since radiation therapy is carried out using a gentle method, without affecting the healthy organs and tissues of the developing child.
At what stage can radiation therapy be used?
In modern oncology, the possibilities of radiation therapy are used very widely at any stage. However, each patient requires an individual approach, since the choice of tactics and treatment plan depends on many factors: location of the tumor, concomitant diseases, age and general condition of the patient. Therefore, to obtain information about the possibility of treatment, it is necessary to consult a radiotherapist.
Date of writing: 09/07/18 Date of update: 08/18/20 Author: Marat Albertovich Sagidov Checked by: Oleg Vitalievich Morov
Symptoms
The main reason why anal cancer is diagnosed late is that there are no symptoms of anal cancer at an early stage of development. In the initial stages, cancer progresses without causing any discomfort or other signs to the patient. Due to the fact that people in most cases do not resort to annual preventive examinations, a tumor in the anus is often discovered by chance during an examination for some other reason.
The first signs of cancer that force a patient to see a proctologist are a small number of bloody streaks in the stool. People often confuse this symptom of anal cancer with a sign of hemorrhoids. Patients who are faced with anal neoplasia suffer from iron deficiency anemia, the tissues of their body are poorly saturated with oxygen, so even without physical activity the patient may experience shortness of breath, the person has pale skin, he is often dizzy and darkened in the eyes. Pain may occur in the pelvic area; also, after going to the toilet, the patient feels that the intestines are not completely emptied. The clinical picture in the later stages of the oncological process consists of:
- severe weakness and chronic decrease in performance,
- rapid loss of body weight,
- loss of appetite,
- pale skin,
- dry mucous membranes,
- gray coloration of the skin on the face.
There are also specific signs of cancer of the anus:
- pain in the rectum,
- alternating constipation and diarrhea,
- false frequent urge to defecate,
- mucus and blood in stool,
- itching sensation in the anus area,
- decreased sphincter tone,
- increasing symptoms of intestinal obstruction.
If metastases spread to other organs, for example, nodes appear in the pelvis or abdominal cavity, then symptoms are added, depending on the organs affected by metastases. Symptoms also depend on the size of the primary tumor.