Often women face a problem called cervical cyst. What it is? The photo will demonstrate it in full, and in the article we will understand the features, causes and methods of treating this pathology. About 10-15% of women who have entered the reproductive stage experience formations on the cervix.
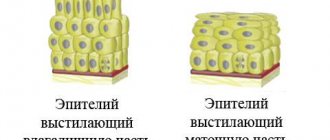
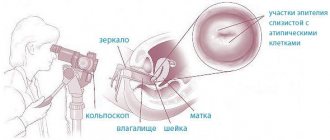
Brushes on the cervix are dilated, blocked glands located on the side of the vagina and in the uterine canal. It all starts with an inflammatory process, due to which the excretory ducts become clogged with secretions and become wider. Normally, mucus should be removed, but it remains in the duct. The doctor can see the pathological process both through ultrasound and during colposcopy.
We will tell you how to treat cysts on the cervix later. First, let's look at the symptoms.
Symptoms
Often, a woman learns about her problem at an appointment with a gynecologist, when she comes for her next preventive examination. The disease has no pronounced symptoms - no pain or discomfort. The menstrual cycle is not disrupted.
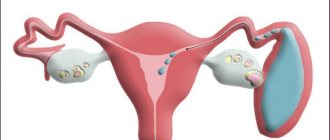
Mucous neoplasms are located in the transformation zone. In appearance they are white and quite dense. The size can reach up to 3 centimeters. Only an endometrioid cyst (develops against the background of endometriosis) can cause weak bleeding observed before menstruation.
Whether cysts in the cervix are dangerous depends on their size. If a patient rarely visits a doctor, the following unpleasant symptoms may begin to bother her:
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- copious unusual discharge from the genital tract.
Source: zdravlab.com
Causes
A woman, having seen a photo of a cyst on the cervix, will definitely want to know the reasons. Unfortunately, it is impossible to define them unambiguously. There are only predisposing factors, which are listed below:
Delivery. Quite often the cervix is injured during childbirth. The recovery process is not long in coming, but sometimes, due to scars, the functioning of the glands is disrupted and the duct is blocked. As a result, a cyst forms.
Termination of pregnancy - abortion. If the procedure is performed incorrectly, a cervical canal cyst, as well as any other neoplasms, may appear.
Climax. The onset of menopause is accompanied by thinning of the uterine membranes, so the glands become vulnerable. Any irritants lead to the secretion of more mucus than necessary, so the ducts can become clogged, forming multiple endocervical cysts.
Infection. Any infectious processes in the genital area can cause the appearance of neoplasms, since the uterine tissues are swollen due to bacterial attack and the outflow of mucus is disrupted.
Brushes on the cervix may also have less probable causes. Here they are:
- installation of a spiral inside the uterus;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- inflammatory diseases (endometritis, adnexitis, cervicitis and colpitis);
- other diseases of the genital area, for example, endometriosis.
Nabotovs
A very dense yellowish-white formation called a cervical follicular cyst or Nabothian cyst may appear in the vaginal part of the uterus. Why these cysts occur is unknown to medicine. There are only assumptions:
- chronic inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- hormonal imbalance;
- erosion and ectopia of the cervix.
Usually formations are found in young women under the age of 45. Like other cysts, Nabothian cysts are formed according to the same principle - the ducts of the Nabothian glands become clogged with desquamated epithelium and become larger, and as a result, a neoplasm is formed in these areas.
Small-sized brushes on the cervix do not require treatment, only observation. When they begin to grow, the gynecologist may suggest surgical intervention.
Like other neoplasms, a woman does not feel Nabothian cysts at all - the pathology is asymptomatic. They can only be detected by a gynecologist. To confirm the diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed, namely:
- identification of infections, if any;
- ultrasonography;
- colposcopy;
- smear for oncocytology.
Nabothian cyst in the cervical canal, according to many experts, does not require any treatment. It will not resolve on its own, but it also does not interfere with the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
In each specific case, the doctor decides whether to remove it or not. If removal is recommended for you, then there is no need to worry. Currently, quite gentle techniques have been developed with the help of which multiple endocervix cysts of the cervix will become a thing of the past - quickly and practically painlessly.
How does it arise?
The cervical canal, which connects the uterus and vagina, is lined with a special mucous layer - the endocervix. On its surface there are a large number of glands that produce thick and viscous mucus, cork. Its task is to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the uterine cavity. But in different phases of the menstrual cycle, the properties of the secretion change.
During ovulation, it becomes more liquid with an increased level of acidity, and this allows sperm to penetrate the uterine cavity and move towards the egg.
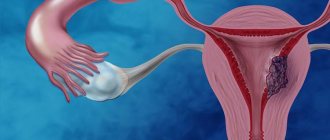
Blockage of the excretory ducts of the endocervical glands, which continue to produce secretions, can lead to the growth and development of cavities. This pathology is called retention or nabothian cysts, benign neoplasms of the endocervix. They may be visible only under a microscope or grow up to several centimeters. It looks like a durable capsule with liquid contents.
Classification
Formations can be divided into several groups depending on the reason for which they arose.
- Traumatic. They appear if there was an injury that caused tissue displacement when damaged.
- Tumor. Here we are talking about cysts that arise against the background of cancer.
- Infectious. A cyst in the cervical canal of the cervix can occur due to the active activity of harmful microorganisms.
- Dysontogenetic. Such neoplasms are usually congenital and have individual characteristics.
- Retention. If the gland produces a lot of fluid, then the duct may not be able to withstand such an excessive load.
Let's talk about the latest formations in more detail.
Retention neoplasms are often a congenital pathology due to disorders of the endocrine system and exocrine glands. Such a cyst of the cervical canal of the cervix is a duct clogged either with thickened secretions or particles of epithelium in which fluid has accumulated.
A cyst can occur due to inflammation, infectious diseases, traumatic ruptures during childbirth or abortion. And in this case, the formation is detected only by a gynecologist during an examination. The examination tactics are the same as for detecting nabothian cysts.
When asking a doctor, cysts on the cervix - is it dangerous? Most likely, the answer will reassure you, since there is no threat to life. Individually selected treatment will relieve the woman of the problem, preserving the functions of the cervix, so that in the future there will be no problems when planning a child and subsequent pregnancy.
Doctors' opinions regarding the removal of cysts are divided. Some people believe that the formations are dangerous due to the possibility of suppuration, so you need to get rid of them as soon as possible. An alternative opinion is that you can try suppositories for cervical cysts or other medications first.
Nabothian cysts of the cervix: symptoms of the disease
Naturally, many women are interested in questions about whether there are any specific signs that are worth paying attention to. In fact, such neoplasms are rarely accompanied by external manifestations. Single Nabothian cysts of the cervix, as a rule, develop asymptomatically and are discovered quite accidentally during routine gynecological examinations.
But large neoplasms or multiple cysts can lead to some problems. In particular, as these structures grow, they can close the lumen of the cervical canal. In such cases, women complain of abdominal pain before and during menstruation, as cysts complicate the release of menstrual flow. In some cases, such a cervical retention cyst leads to difficulties with conception or infertility.
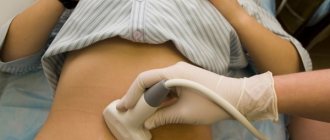
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is of particular diagnostic value in cases of suspected neoplasms. The gynecologist will prescribe this procedure without fail after examination on the chair, taking smears and colposcopy. Thanks to the capabilities of ultrasound, the specialist assesses how much the tissue structure has changed, whether blood circulation is impaired, and also determines both the size of the internal genital organs and the size of tumors.
A woman will want to know about cervical canal cysts, what they are and how to treat them, immediately after the examination, which is carried out using a transvaginal sensor inserted into the vagina, always with a protective agent - a condom. Usually, two research methods are used at once - from the inside and through the abdomen, in order to get the most complete picture of the condition of the female genital area.
Consequences
Any woman, after discovering the disease, wants to know: why is a cyst on the cervix dangerous? Can it develop into a malignant tumor?
We hasten to reassure you - this kind of formation never turns into cancer. The only problem is that the cyst begins to grow, and this is an obstacle to normal sexual life. Rarely, a tumor causes infertility. Most likely, we are talking about a physical barrier that prevents sperm from penetrating the egg.
A paracervical cervical cyst discovered during pregnancy does not pose any danger to the health of the woman or the fetus. She is treated after delivery.
Features of a retention cyst
Hearing the word “cyst,” many women immediately get scared, imagining a tumor. But there is no need to sound the alarm. Having learned what Nabothian cysts are and how they affect the functioning of the cervix and other organs of the reproductive system, you will breathe a sigh of relief. Below are some facts about this phenomenon:
- Education is not passed on through unprotected sex;
- It does not affect the state of hormonal levels, and therefore does not lead to menstrual irregularities;
- Not inherited;
- Does not in any way affect the usual way of life. There are no contraindications to sports, sunbathing, bathing, or sexual activity;
- It never develops into cancer.
Treatment
When drug therapy is unsuccessful, the doctor suggests surgery. Many women are surprised by this decision, because a cyst of the cervical canal does not even give any symptoms, why then use such a radical method? As we have already said, education itself does not cause any harm, but in the case of bacterial infection, an inflammatory process can begin, which poses a rather serious threat to women’s health.
Note that even if your cervical canal cyst requires surgical treatment, there is no need to worry too much. The procedure takes little time and does not require hospitalization - you will be relieved of the problem on an outpatient basis. The procedure is prescribed only after the end of menstruation. And just by the beginning of the next cycle, the wounds formed during removal will have time to heal.
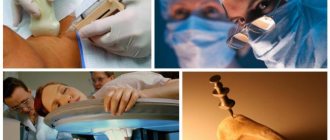
The operation goes quickly. The gynecologist punctures the cysts with sterile instruments and disinfects the affected areas with special antiseptics. As you can see, the process is very simple, it can hardly even be called operational.
What a cyst on the cervix looks like, a photo, or rather a diagram, will show you in detail all the features so that you can imagine what and how is happening to your reproductive organ. And in place of these bags there will be only a slight redness after the doctor finishes the punctures.
The woman will be able to go home after the operation in a few hours. For two days you may experience painful aching sensations and slight discharge from the genital tract. At first they are bloody, and after a few days they turn yellow and completely disappear within a week. If a cyst bursts on the cervix, the symptoms will be the same.
In both cases, to speed up the regeneration process, vaginal suppositories are needed, which will be prescribed by the gynecologist. The duration of their use does not exceed 10 days. After puncturing the formations, the woman is recommended to have sexual rest until complete recovery. After your menstrual cycle, you should visit a doctor to evaluate the condition of your cervix.
If the medicine against cervical cysts is not effective, and punctures are prohibited for some reason, then the doctor may suggest cauterization, either with a device that has some kind of physical effect, or with chemicals. Or a combined option.
A modern and widespread technique is radio wave therapy. It is usually prescribed to women who are planning a pregnancy. The high-frequency wave will quickly get rid of the tumor. A laser device will also help remove cysts in a non-contact manner, but it is used quite rarely.
Cryodestruction has become increasingly popular recently. The procedure involves the use of low temperatures and liquid nitrogen. The patient does not experience pain. The methods described above have their pros and cons, which your doctor will tell you in more detail.
Nabothian cysts of the cervix: treatment, removal
Specific drug treatment is required only if inflammation, hormonal disorders or other causes of the disease were identified during diagnosis. In such cases, antibacterial (in the presence of sexually transmitted infections), anti-inflammatory or hormonal therapy is carried out. Only after this can the issue of eliminating the tumor be resolved.
Removal of nabothian cysts of the cervix can be carried out in different ways. First you need to puncture the tumor, removing all its liquid contents. After this, you need to remove the cyst capsule itself, since otherwise there is a high risk of relapse. Various methods are used for removal:
- surgical excision of the cyst and parts of surrounding tissue using an endoscope;
- cauterization of the cyst capsule using electric currents (electrocoagulation);
- laser therapy - allows you to remove capsule tissue using a laser beam without causing serious complications, including infection or bleeding (the fastest and safest method, which, however, is quite expensive);
- destruction of the capsule shell using ultrasound;
- cryodestruction - freezing capsule tissue using liquid nitrogen;
- removal of the cyst using a radio wave “knife”.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed medications that reduce the likelihood of infection and also promote rapid healing and regeneration of cervical tissue.