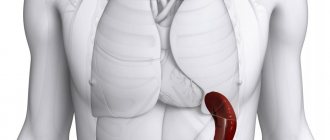
Spleen can be called a filter and storage of blood - nature assigned such tasks to it. This small organ weighing 150-200 grams is located on the left in the peritoneum, above the stomach.
By passing two hundred milliliters of blood through itself every minute, the spleen neutralizes the effect of microbes, waste and toxins in it. A supply of enzyme-enriched blood is accumulated and stored in the spleen until needed by the body.
The spleen is involved in the creation of white blood cells.
Scientists have recently discovered that it produces blood cells (monocytes) needed to repair damaged heart tissue.
How does damage to this organ threaten the body, and how can it be helped in this case?
Splenic rupture: first aid
Among injuries to the abdominal organs, this injury occurs in approximately thirty percent of cases. It is accompanied by pain, which is first localized in the left side of the abdomen, and then spreads to its entire area.
The rupture will be accompanied by bleeding, and only a specialist knows how to stop it, so the first thing to do is call a doctor!
If internal bleeding is not stopped in time, death will occur. Death from splenic rupture is possible with a loss of two to five liters of blood. The rate of flow depends on the size of the wound and the intensity of the process.
Sometimes a loss of three hundred milliliters of blood is enough for anoxia (oxygen deficiency) to occur and death to occur.
While waiting for professional help, urgent measures need to be taken:
- Place the victim carefully, without sudden movements, on his back and ask him not to move so that the bleeding does not increase.
- Apply an ice pack to the area where the pain is felt.
- You can press and hold the solar plexus area firmly until emergency services arrive, this will compress the abdominal aorta and reduce blood loss.
Treatment of splenic rupture
Most often, surgeons remove the organ. But the absence of a spleen provokes a sharp deterioration in the patient’s health. In particular, patients become more susceptible to infections. Researchers say most minor organ injuries can be treated without surgery. To treat patients, blood transfusions are performed. To prevent the patient from dying, it is necessary to hospitalize. In most cases, the entire spleen is removed during surgery, but sometimes doctors can repair minor damage.
Doctors resort to an alternative method of treatment when the disease is less dangerous. We are talking about removing an organ using a laparoscope. A special tube is inserted into the abdominal wall through a small incision. Other medical instruments are inserted through additional incisions. It depends on the patient’s condition which methods will be used to treat the consequences, and, accordingly, how long he can live.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured spleen?
Sharp pain is not always an immediate sign of damage. A rupture can occur in two stages: first, the glandular tissue is torn, at which point the person feels a slight push in the abdomen on the left.
The flow of blood first occurs into the capsular sac of the spleen, but, accumulating there, it breaks into the abdominal cavity, and the affected area becomes larger. Then the victim feels increasing pain in the abdomen.
In the first hours after a rupture of the spleen, a person suffers from pain in the left hypochondrium, in the upper part of the peritoneum, in a third of cases it is also felt under the left shoulder blade or in the shoulder.
Further symptoms of splenic rupture will be dizziness, darkening of the eyes, nausea and vomiting, severe weakness, hemorrhoidal shock with loss of consciousness. Symptoms appear that resemble those of peritonitis.
Causes leading to splenic rupture and classification of such injuries
As already noted, splenic injuries are most often observed with blunt abdominal trauma. While a penetrating wound, for example, a bullet or knife, most often occurs in the small and large intestines. In third place are conditions that combine aspects of compression and penetrating trauma to the abdominal organs in the event of an explosion. This phenomenon is often observed in military environments, as well as among specialists conducting field blasting operations or controlled demolition of buildings.
Although the spleen is relatively protected by the rib cage, injuries due to this deceleration occur in motor vehicle accidents, direct blows to the abdomen as a result of domestic violence or gaming activities, and while riding a bicycle.
Iatrogenic causes of spleen injury include accidental damage to the organ in the case of colonoscopy. Moreover, more than half (56.1%) of the injured patients underwent laparotomy and splenectomy with the most common pathologies such as splenic hematoma (47%), laceration (47%), and rupture (33.3%).
It all depends on the types and quality of spleen damage
- Contusion - the parenchyma of the organ is damaged, but the integrity of the capsule is preserved.
- Damage to the capsule with preservation of parenchyma at the site of rupture.
- Single-stage rupture - simultaneous organic damage to both the capsule and parenchyma;
- Two-stage rupture - first of all, the parenchyma is damaged, and a little later the capsule is torn.
- Injuries with spontaneous bleeding. This type of injury is characterized by simultaneous injury, in which a blood clot temporarily seals the boundaries of the rupture, and the bleeding slows down or stops completely. No clinical picture is observed. After some time, the blood clot is squeezed out under pressure, bleeding opens and the first symptoms appear.
There are some risk factors that increase the likelihood of spleen damage and slow healing. These conditions include pre-existing medical conditions, which can markedly increase the risk and severity of splenic injury. Infectious mononucleosis, malaria and hematological disorders can lead to acute or chronic enlargement of the spleen. This is often accompanied by thinning of the capsule as the spleen becomes more fragile. In addition, this creates a more widespread impact on slowing down recovery processes.
Splenomegaly in the vast majority of cases leads to severe injuries and the need for splenectomy.
Why does the spleen rupture?
- The main, but not the only cause of organ damage is a concussion or bruise due to a blow to the peritoneum or ribs, as a result of a fall from a height, a transport accident and other traumatic factors.
- Infections and inflammations in the body are a common cause of splenic rupture because they increase the size of the organ, which is extremely unfavorable for its tissues. Tuberculosis, hepatitis, pyelonephritis, and liver diseases pose great dangers.
- Excessive tension of the peritoneum during heavy lifting or during intense labor is dangerous for the spleen.
- During pregnancy, the volume of blood in a woman’s body increases, and this is also a threatening factor for organ tissue.
Diagnostics and prevention
The spleen is examined using ultrasound.
Modern equipment for ultrasound and x-rays makes it possible to detect an enlarged spleen in the early stages. It is important to undergo regular abdominal examinations to guard against unwanted consequences. For prevention, you should follow the following rules:
- If you have a cold, you should never break bed rest.
- During pregnancy, women are required to wear a special bandage that will reduce pressure and traction on the organs
- During training, you should not overexert yourself; physical activity should increase gradually
- It is important to follow the rules on the road - accidents often cause damage to internal organs
- Do not lift heavy objects, especially without training
- For sports, especially extreme sports, you need to purchase special protective clothing.
An important prevention can be maintaining a healthy lifestyle: avoiding drinking alcohol (preventing the occurrence of liver cirrhosis), smoking, and junk food. You should reduce your intake of salty and spicy foods and drink more clean water. You should take a disease such as malaria seriously: undergo examinations and carefully select vacation spots.
Splenic rupture occurs not only in people at risk; it can happen even in the healthiest person. Safety precautions should be followed to maximize the chances of preserving this organ. Thus, a splenic rupture is a fairly dangerous event that requires special knowledge to deal with this situation correctly. A person can live without it, however, the performance of some functions is noticeably reduced.
Read along with this article:
- Spleen: why is the organ needed, normal size of the spleen and...
- What organs is the spleen located next to, what is it for...
- Why is spleen cancer dangerous?
- Spleen diseases - symptoms and causes
- Spleen diseases: symptoms of the most common diseases
- Which side is the human spleen on and its main functions?
- Health Encyclopedia: Symptoms of an Enlarged Spleen
- Spleen: normal organ size
- 20 reasons why there is a stabbing pain in the left side under the ribs
How is a splenic rupture recognized?
- Diagnosis is carried out through ultrasound. It helps not only to detect injury, but also to establish pathological enlargement of the organ even before it ruptures.
- A blood test with a study for a decrease in hemoglobin and leukocytosis will give an idea of the changes in the spleen area.
- X-ray of the abdomen and chest allows you to see under the diaphragm a homogeneous (homogeneous) shadow created by fluids in the organ. This is how hemorrhage is determined. In addition, an x-ray will help you see that the diaphragm is raised, the stomach is dilated, and the colon is displaced to the right and down. These are signs of damage to the spleen.
- A more accurate method of studying the condition of the splenic vessels is angiography, but this procedure takes a lot of time.
- Laparoscopy: examination of the abdominal cavity using an optical system. The device is inserted into a puncture on the abdominal wall, and a magnified image is displayed on the monitor screen. The study allows us to identify the source of the lesion, the amount of blood accumulated in the peritoneum due to rupture of the spleen.
- Laparocentesis is piercing the abdominal wall with a special hollow instrument (trocar) and inserting a catheter through it, through which the contents of the peritoneum are sucked. This way you can determine whether there is blood in it. The source of the hemorrhage cannot be found using this procedure.
- If the tissue surrounding the spleen cannot be separated, the abdominal cavity is opened.
- Ultrasonography allows you to see a wound on the body of the spleen if its size is at least one centimeter.
- One way to accurately diagnose is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The protocols obtained as a result of the examination will help to distinguish even minor deformations on the organ.
Diagnostic methods
The main method for diagnosing splenic rupture is x-ray. On photographs of the chest and abdomen, there should be a characteristic black spot on the left side - traces of internal bleeding. Other signs of this injury are impaired position of the diaphragm (the muscle that is involved in breathing), an increase in the size of the stomach, and a change in its position. Endoscopic examination methods (laparocentesis) are also used in diagnosis. A camera or simply a hollow instrument is inserted into the cavity and the extent of bleeding and its presence are determined.
When is it necessary to remove the spleen?
The bleeding that accompanies a ruptured spleen is life-threatening, so the goal of surgery is to stop the bleeding.
A safe and effective way to stop this is to remove the organ. After all, during the work, the spleen is constantly filled with blood, and such pressure can tear the sutures placed during the operation.
Lacerated, through wounds, multiple ruptures and cracks in the spleen, which are not compatible with the normal functioning of the organ in the future, serve as an indication for splenectomy (the so-called operation to remove the spleen). The organ will also be removed if it is torn from the vascular pedicle on which the splenic vein and artery are located.
Serious soft tissue hematomas of the spleen pose the risk of sudden rupture, so this is also a reason for resection.
Getting rid of an organ is a reliable method, but not the only one.
Who is most at risk of rupture?
People with cancer are most susceptible to splenic rupture.
Prevention of chronic diseases is especially important. If they are not detected in time and the progress of their development is not monitored, then the capsule covering the spleen will quickly become tense and thin. A rupture of this capsule is critically dangerous for humans and requires immediate medical and surgical intervention.
A special risk group is people with cancer. Their immune system undergoes a sharp weakening, the general condition of the body deteriorates significantly, which leads to increased tension on the work of the spleen.
Recent observations have shown that a procedure such as a colonoscopy can significantly increase the risk of splenic rupture. It is an examination of the mucous membrane of the small intestine. Pregnant women have a high chance of splenic rupture. Enlargement of the fetus increases the level of pressure in the abdominal cavity, and in addition, blood flow to the organs increases. Rupture often occurs during even successful childbirth - in about 3% of women.
Read: Black stool: causes of pathology and when to panic
To identify and establish a rupture, the victim undergoes a thorough and careful examination and history taking. It is important to correctly interpret the data that the doctor received from the patient himself and during laboratory tests.
Moreover, even a highly qualified doctor is not always able to 100% confirm the diagnosis. Among all recorded cases, only 10-15% were diagnosed with splenic rupture before surgery. In other cases, the diagnosis was confirmed during the operation.
People who do not complain about their health, and especially those who are at risk, need to undergo regular examinations for preventive purposes. Detecting an enlarged spleen in the early stages increases the chance of a positive outcome.
How to live with a sewn-up spleen?
If the organ has been preserved, further therapy involves taking good care of your health. It will be necessary to exclude or minimize traumatic situations fraught with contusion of the spleen. Heavy loads on the abdominal area are contraindicated. The slightest suspicion of relapse should prompt a medical examination.
A healthy diet and a moderately active lifestyle will help avoid diseases that will cause a pathogenic environment to attack the blood and, consequently, the spleen.
If the spleen was removed?
It is possible to live without this organ, since its activity is compensated by the work of the liver and bone marrow.
And yet, having lost the main filter, the body becomes more vulnerable to infection. That is why after splenectomy the patient is vaccinated against the most dangerous infectious diseases.
One of the unique functions of the spleen - neutralization of obsolete platelets - remains unreplaced, therefore there is a risk of thrombosis. This is why, after removal of the spleen, it is necessary to take blood thinners (anticoagulants) and be monitored by a hematologist.