Symptoms of apoplexy
How can you tell if an ovarian cyst has burst? First of all, it must be said that the signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst are clearly visible and it is very difficult not to notice them. The most important symptom of a ruptured ovarian cyst is acute pain in the lower abdomen. If the cyst of the right ovary ruptures, the pain is localized on the right side, if on the left, then, accordingly, on the left. The second constant symptom is internal bleeding.
There are a number of specific signs that characterize apoplexy:
- high body temperature,
- general weakness,
- dizziness,
- cardiopalmus,
- low pressure,
- nausea, vomiting,
- loss of consciousness,
- unusual vaginal discharge.
As you can see, if an ovarian cyst bursts, the symptoms are quite eloquent, but the problem is that similar painful sensations may also correspond to other diseases. Therefore, in order to understand what is really happening in the body and what threat exists, you should immediately seek medical help.
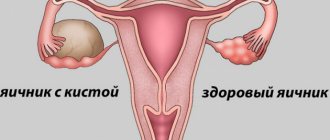
Enlargement of the right side with cystic ovarian formation
Why does an ovary burst?
style=»display:inline-block;width:300px;height:250px» data-ad-client=»ca-pub-1988978294092243″ data-ad-slot=»9486525726″>
Factors predisposing to the occurrence of apoplexy include:
- Oophoritis or (salpingoophoritis in chronic form).
- Inflammatory and adhesive processes in the pelvis.
- Imbalance of sex hormones.
- Pathological changes in the vessels supplying blood to the ovary.
- Some blood diseases and taking anticoagulants.
These factors create a favorable background for the development of apoplexy.
The following reasons can directly lead to ovarian rupture:
- Abdominal injuries (impacts, falls on hard objects).
- Excessive physical activity.
- Active sexual intercourse.
- Fast horse riding.
- Vaginal examinations and douching if carried out ineptly.
However, it is worth noting that in some cases, ovarian rupture occurs in complete rest, even when the woman is sleeping. Therefore, this disease cannot be excluded in such situations.
Course of the disease
Depending on the dominant symptoms of ovarian apoplexy, 3 forms are distinguished:
Anemic With it, signs of internal bleeding predominate - weakness, severe dizziness, chills, fever, dry mouth. When examining patients, doctors detect low blood pressure and a rapid pulse. Painful This form occurs with severe pain. The pain is usually localized in the lower abdomen and lower back. Mixed In which the patient exhibits all signs of apoplexy at the same time.
It follows that sudden ovarian rupture can be suspected by the appearance of sharp abdominal pain, accompanied by severe weakness, in the middle or end of the menstrual cycle, or after a slight delay in the next menstruation. However, injury or physical activity does not always precede the development of the disease.
Types of cysts and classification of pain during rupture
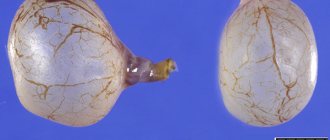
All formations are divided into two groups, functional and non-functional types. Functional ones include:
- follicular cyst, a formation that arose at the site of an unopened follicle. If the egg is not released, the follicle begins to grow. This type of pathology is not dangerous to health and does not require treatment. If such a cyst bursts, then the woman experiences vomiting, acute cramps in the lower abdomen that do not go away after taking painkillers,
- luteal (corpus luteum cyst) - formed after the release of the egg from the follicle. The corpus luteum plays an important role during pregnancy - in the first trimester it replaces the placenta. After 14 weeks, the corpus luteum resolves on its own; if this does not happen, it begins to increase in size and develops into a cyst. If this type of formation bursts, the woman experiences pale skin, rapid heartbeat and decreased blood pressure.
Rupture of a non-functional ovarian cyst is quite dangerous, as it is fraught with the most dire consequences. Nonfunctional neoplasms include:
- Dermoid cyst. It is formed in girls in the womb. It increases in size as the girl herself grows.
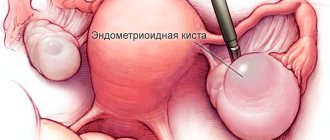
- Endometrioma. It is a consequence of hormonal imbalance, contains blood and blood clots inside,
- Cystadenoma. It is similar in structure and content to dermoid. There are cases when doctors, during examination, confuse it with a malignant formation,
- Carcinoma. Contains cancer cells and is the most dangerous type of formation. The only treatment option is surgery.
How to understand that a non-functional type of ovarian cyst has burst? Symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst of this type are characterized by their severity - acute pain and severe internal bleeding, spillage of the contents of the ruptured cyst. Extensive bleeding can cause anemia, loss of consciousness and death.
Causes of cyst rupture
Many women are interested in the question: can an ovarian cyst burst in a completely healthy person. Doctors most often answer this question in the affirmative, because this trouble can be caused not only by poor health, but also by a number of other factors:
- pathological condition of the walls of ovarian vessels. For example, vascular sclerosis or varicose veins make the walls of the neoplasm fragile and increase the risk of apoplexy,
- hormonal disorders. In the absence of ovulation, the follicle accumulates fluid, increases in size and bursts,
- long-term use of medications that affect blood clotting,
- frequent and prolonged inflammatory processes of the ovaries. The walls of the ovary become loose, the vessels lose their elasticity and become more vulnerable.
The causes of ovarian cysts can also be mechanical, for example:
- abdominal injuries due to an accident, bad fall or surgery,
- excessive training in the gym, horse riding, active sex life.
Can a woman's ovarian cyst burst?
An ovarian cyst can rupture at any time. The likelihood of pathology in certain conditions:
- pregnancy - the risk of apoplexy remains, it can occur when there is excessive pressure from the growing fetus on the uterus or due to impaired hormone levels, therefore, if the size of the formation is more than 8 cm, surgery is required,
- period of menstruation - at this time the cyst tends to decrease or completely disappear, so the likelihood of its rupture is minimal in the absence of physical activity and sexual intercourse,
- sexual contact - with intimate intimacy, the risk of apoplexy increases significantly due to intense mechanical stress and a rush of blood to the genitals,
- trauma to the abdomen and pelvis – if the ovary and nearby organs are injured, the likelihood of pathology occurring is high, especially if the formation is large,
- lifting weights and excessive sports activities – contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which, if this condition persists for a long time, leads to the cyst bursting,
- hormonal imbalance – provokes disruption of the menstrual cycle and lack of ovulation, which is fraught with the rapid growth of a large number of formations that can burst under external influences,
- bleeding disorder - this pathology poses a danger if it ruptures in the form of heavy blood loss.
Most often, several factors simultaneously lead to apoplexy of an ovarian cyst, so if one of them is present, you should be careful during physical activity and regularly visit a gynecologist to monitor your health.
Diagnosis of apoplexy of education
A primary gynecological examination cannot accurately detect a ruptured ovarian cyst, since the symptoms of this pathology may indicate other ailments. A more accurate diagnosis can only be made after a complete examination, which includes:
- blood and urine tests,
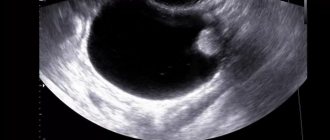
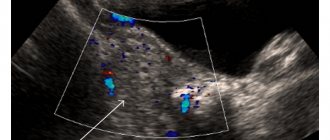
- performing ultrasound,
- CT scan of the ovaries,
- detection of hormonal disorders,
- detection or exclusion of infection,
- performing a puncture,
- laparoscopic diagnosis.
A puncture examination allows you to find out whether fluid or blood is accumulating in the abdominal cavity. Blood tests will determine at what stage the inflammatory process is, and a CT scan will accurately indicate whether the cyst on the ovary has burst or the cause lies elsewhere. In some cases, an accurate diagnosis is made after an ultrasound examination.
Possible complications and consequences of pathology
The occurrence of consequences if the ovarian cyst bursts is not necessary. With timely medical intervention, the following conditions can be avoided:
- severe painful shock
- severe anemia,
- oophorectomy,
- infertility,
- development of oncological processes,
- adhesions in the pelvis,
- purulent peritonitis - extensive inflammation in the abdominal area.
In the most severe cases, death is possible.
Treatment of cyst rupture
What to do if apoplexy of an ovarian cyst occurs in women? In this case, there are two treatment options, conservative and surgical (surgery). Drug therapy is prescribed only for rupture of the follicular cyst. Hormonal agents, a complex of vitamins, and anti-inflammatory drugs are used. In case of weakened immunity, immunostimulating complexes are additionally prescribed.
The patient is prescribed bed rest and the use of cold compresses on the left side if the left ovarian cyst has ruptured, and if the right ovarian cyst has ruptured, on the right side. The use of painkillers is prohibited, as they can blur the picture of the disease when new symptoms appear. If an ovarian cyst ruptures, treatment is carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor. If the condition does not worsen, the patient is discharged home after a few days. At home, she must strictly adhere to all doctor’s recommendations.
There are two types of surgical treatment – laparoscopy and laparotomy.
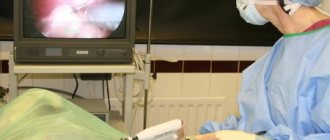
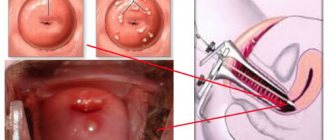
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a non-cavitary operation that is performed under general anesthesia. To carry it out, you need special equipment, which is also used to diagnose pathology. Laparoscopy for ovarian apoplexy lasts approximately 30-40 minutes and usually has a favorable outcome. Small incisions are made in the patient's abdominal cavity through which instruments are inserted. Using a miniature camera, an image is transmitted to the screen, thanks to which the surgeon controls all his actions. The operation is aimed at:
- eliminating sources of bleeding. Damaged vessels are ligated or cauterized,
- carrying out resection. Tissues that cannot be restored are removed, and the ovary itself is stitched together,
- removal of spilled blood and tumor contents. When an ovarian cyst ruptures, internal bleeding begins. If you do not cleanse the organs of blood and the contents of the burst formation in time, inflammation, infection, and adhesions may develop.
After laparoscopy, the patient is discharged home on the 7th day.
Laparoscopy
Laparotomy
Laparatomy is an abdominal operation that is performed in emergency cases. The patient is given general anesthesia, and the abdominal wall is opened horizontally with a scalpel. The advantage of this type of treatment is a complete overview of the disease picture. The surgeon examines the internal organs and performs resection of the ovary. The issue of complete organ removal can only be decided after an examination. At the end of the operation, the organs are cleared of blood and cyst contents, and the abdominal wall is sutured. After laparotomy, the patient must be under medical supervision for at least 14 days.
Nowadays, traditional methods of treatment have become popular, which help relieve pain in the lower abdomen and promote spontaneous resorption of the cyst. However, it should be remembered that such methods can only be used after consulting a doctor. You can find out the TOP 10 effective remedies for treating cysts at home HERE.