Reasons for appearance
The birth of the disease is associated with an unacceptably large accumulation of bilirubin, associated with improper metabolic processes, when the balance between its formation and excretion from the body is disturbed. This substance is brown crystals, which are, among others, part of the main components of bile.
There is indirect (unbound) and bound bilirubin. The first is a consequence of the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is released when red blood cells are destroyed. It is a toxic formation, does not dissolve in water and is not excreted from the body.
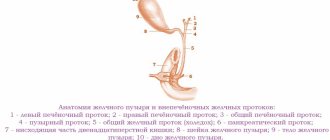
The “birthplace” of this specific formation is the spleen and other important systems (bone marrow, lymph nodes), where it binds to blood proteins albuminamines, passes to the liver and there turns into a straight line.
Bilirubin is considered a poison. If the body's systems function without failure, it is excreted through the rectum during the acts of defecation and urination. If insufficient functioning of the bile excretion pathways is detected, then the overwhelming amount of this substance accumulates in the blood, and the remainder is excreted through the skin, as a result of which they change color. When the concentration of this substance in a sick person exceeds 2.5–3 mg/dl, yellowness of the mucous membranes and skin occurs.
Jaundice can occur as a result of:
- a) the appearance of neoplasms of different origins in the liver;
- b) pathologies in the work and structure of the bile ducts;
- c) damage by harmful microbes;
- d) undesirable postoperative consequences;
- d) the use of certain medications.
Attention! Not to be confused with false or carotene jaundice, caused by an oversaturation of carotene formed in the body due to excessive use of beets, pumpkin, carrots, citrus fruits, as well as when taking medications such as quinacrine, picric acid, etc. With false jaundice, yellowness does not affect the mucous membranes, Only the skin changes color.
The disease is quite difficult to detect in a timely manner, since the incubation period (latent course of the disease) of jaundice can last several weeks, and sometimes several months, depending on the time during which the disease lasts. The disease can occur in the following forms: acute, protracted, or progress to the chronic stage.
Signs of illness
The manifestations, symptoms of jaundice, and the nature of the course are different. It depends on the provoking disease and the general condition of the patient.
The main and first sign of jaundice is a violation of skin pigmentation. It turns bright yellow. In protracted forms of the syndrome, it may turn dark brown.
Associated symptoms include:
- Hepatomegaly (pathological enlargement, hardening of the liver)
- Heaviness, pain arising in the right hypochondrium
- Nausea, vomiting bile
- General malaise, weakness, drowsiness
- Muscle and joint pain
- Darkening of urine
- Stool discoloration
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
This is interesting: Subhepatic jaundice: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Clinical manifestations and signs of jaundice directly depend on what disease it is caused by. Some types of liver damage are characterized by an asymptomatic course. Infectious diseases remain latent for a long time. During this period, a person infected with hepatitis becomes a carrier of the virus. On average, the incubation period for jaundice lasts 2-4 weeks. For hepatitis B and C, it can reach 8-12 weeks or longer.
Symptoms of jaundice (photo)
The disease can be detected by the following signs:
- yellowness of the skin, eyeballs, sclera;
- increased dimensions of the liver and spleen;
- increased content of red blood cells in the blood;
- the presence of a venous network in the abdominal area.
In adults, these manifestations are usually accompanied by headache, belching, aversion to food, weight loss, muscle pain, fever, body temperature rises, spasmolytic pain attacks in the right half of the chest, discoloration of stool (excess bilirubin gives it a gray color). color), and the urine becomes dark in color.
Second jaundice. Hepatic
The culprit of this jaundice is liver pathology . If its cells, hepatocytes, are destroyed, bilirubin (both free and bound) is released into the blood. This type of jaundice is characterized by a saffron-yellow, reddish color. Initially, the icteric color appears on the sclera of the eyes and the soft palate, then the skin becomes colored. Urine becomes dark in color, but feces, on the contrary, become discolored (due to liver pathology, the enzyme stercobilin, which causes coloring, is not synthesized from bilirubin).
The cause of hepatic jaundice can be viral hepatitis and some other infectious diseases that affect the liver. Hepatocyte death can also be caused by liver cirrhosis and toxic damage.
Types of jaundice
Jaundice affects not only adults, but also children. Therefore, let's start with the types of jaundice in children - physiological and neonatal.
Physiological jaundice
Physiological jaundice occurs in newborn babies (about 60–70% of children are affected by it); signs are detected on the third or fourth day of life and are caused by adaptation to the new environment that has arisen. It is detected in children born before the required nine-month period has expired, and therefore weakened. The skin, mucous membranes and sclera become yellowish. The child constantly wants to sleep and sucks poorly.
Neonatal jaundice
It can be observed in newborns (see photo above). It is detected in the first two to four days after the birth of the child. It is faced by prematurely born babies, twins and those children whose mothers suffer from diabetes.
Jaundice in newborn babies cannot be treated with medications, because... it is not, strictly speaking, a disease, the general condition of the body does not cause concern, but is associated with the immaturity of life support organs, enzymatic immaturity, and not well-functioning metabolic processes. After a short period of time it disappears.
If the child's symptoms do not disappear in the future, it is necessary to resort to treatment. Since indirect bilirubin is a neurotoxic poison, its maximum amount causes severe intoxication of the body, which negatively affects the child’s nervous system, which can subsequently lead to irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex, subcortical nuclei and delayed mental development of the baby.
In adults, other manifestations of this disease are observed.
Conjugation jaundice
It is inherited, is not an independent disease (sometimes it can be confused with physiological jaundice), and is detected when disruptions occur in the metabolic processes in the liver, which leads to an increase in the presence of bilirubin in the blood. Appears from the use of certain medications, as a consequence of congenital pathologies.
Hemolytic (suprahepatic) jaundice
It is not caused by pathology in the process of breakdown of red blood cells, a high concentration of unnecessary substances and problems in removing it outside the internal organs. It can be caused by anemia suffered from tropical fever, as a result of the toxic effects of drugs and when harmful substances such as arsenic, lead, hydrogen sulfide, and snake venom enter the body.
Hepatic (parenchymal) jaundice
A very common type of disease. Associated with changes in the structure and function of hepatocytes. This type is provoked if the patient has cirrhosis of the liver, viral hepatitis, malignant tumors are detected, with drug-induced liver damage, or excessive alcohol consumption. The color of the skin changes from yellow to red. Accompanied by the usual symptoms.
Subhepatic (mechanical) jaundice
Its appearance is caused by a violation of the excretion of bile due to narrowing of the lumens of the biliary tract due to the presence of malignant tumors, the existence of helminths, stones in the bile duct, scars and other reasons. Characterized by a yellow-green complexion.
Mostly women suffer. In young people it is benign and is a consequence of cholelithiasis . In this case, they resort to endoscopic papillosphincterotomy (up to 90% of stones in the bile duct are removed). In older women - due to the appearance of a malignant tumor, then radical treatment is necessary.
Causes of jaundice
The syndrome is characteristic of a wide range of diseases. Occurs with pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, and biliary tract. Hyperbilirubinemia is possible in other pathologies.
Provoking factors:
- Infectious lesions (Botkin's disease, hepatitis B, C, D)
- Autoimmune, toxic hepatitis
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Oncological lesions
- Parasitic infestation
- Acute, chronic intoxication
- Severe metabolic disorders
- Blood poisoning (sepsis)
- Liver failure
- Cholelithiasis
- Pancreatitis
- Cholecystitis
- Congenital deformities, developmental anomalies
Causes of jaundice include improper use of medications, obesity, and poor diet. Pathologies accompanied by such manifestations often appear in people suffering from alcoholism, drug addiction, and violating hygiene standards. The risk group includes employees of potentially hazardous enterprises and hazardous industries.
Diagnostics
If characteristic symptoms occur, you should immediately contact a hospital dermatologist, gastroenterologist, hepatologist or infectious disease specialist. After an external examination, during which subcutaneous cholesterol deposits are detected, an increase in the volume and hardness of the liver, spider veins, a decrease in body weight, and conversations about the patient’s previous illnesses, the doctor prescribes:
- analysis of the general and biochemical composition of blood;
- tests to detect harmful components (including bilirubin) in blood plasma and urine;
- ultrasound and tomographic examination of the diseased organ;
- sometimes a liver biopsy to determine the nature of the disease and the degree of its development;
- Ultrasound and computed tomography of the pancreas and kidneys;
- carrying out tests for the presence of particularly dangerous hepatitis viruses.
Can you get jaundice?
This thought usually appears when someone close to you already has jaundice (symptoms). In adults, how is this disease transmitted and is it dangerous for other family members? Jaundice itself is a consequence of other diseases, so every effort must be made to prevent infection of other family members. The only exception may be a disease caused by a hereditary predisposition; this also includes jaundice in newborns and pregnant women, which is the norm and is associated with hormonal changes. And also those types of jaundice that were not caused by a third-party pathogen. Most viral infections are transmitted through close contact, as well as through food and drink, so precautions should be strictly observed. A common cause may be viral hepatitis. This disease is transmitted not only from person to person, but also from animals with hepatitis - dogs or cats. In this case, the virus is transmitted from an animal to a person only through direct contact; food and water are not contaminated in such cases.
Treatment
Types of treatment are divided into medications, surgery, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures, and diet. For removable symptoms, conservative treatment is indicated; if the disease is advanced, surgical intervention (liver transplantation) is used. The goal of treatment is to destroy the remaining bilirubin in the blood plasma, get rid of the virus, prevent the occurrence of liver cirrhosis and reduce the risk of the disease for others.
Conservative therapy
- medicinal : administration of antihistamines, corticosteroids. The range of drugs used for treatment is quite wide. Of these, we can mention: Liv 52, Karsil, Ovesol, Essentiale Forte . Each has its own specific application.
Important! You cannot choose medications on your own, without consulting a doctor.
- physiotherapeutic procedures:
- a) the use of plasmapheresis (purification of blood plasma from toxins by filtering it using special devices). This procedure is expensive, especially since several sessions are required. They are usually carried out in medical institutions, sometimes at home. Indicated in case of liver problems, autoimmune hepatitis, and intoxication of the body;
- b) the use of phototherapy;
- c) ultrasound in the area of the affected organ;
- compliance with the required diet.
If treatment is not started promptly, the disease will progress and it may not be possible to achieve remission. Dangerous complications arise that can only be eliminated by liver transplantation.
In case of viral hepatitis, antiviral drugs are not used; the drugs used help to minimize the concentration of existing toxins and remove them from the internal organs.
Patients are administered detoxification drugs, glucose, vitamins, hepatoprotectors, which have a stimulating effect at the cellular level, helping to restore cell structures. After treatment procedures, liver function is usually completely restored.
Treatment methods vary for different types of disease.
In the case of subhepatic jaundice, surgery is indicated to eliminate the causes that interfere with the excretion of bile masses: malignant formations are removed, stones are crushed, and in some cases the gallbladder is removed.
Suprahepatic jaundice - in this case, existing anemia is treated. In severe situations, blood transfusion is necessary.
Treatment of infectious jaundice is carried out in a hospital. Antiviral therapy is carried out to help maintain the liver.
Attention! There are no complications with jaundice, since it is a combination of symptoms, but insufficient treatment of the diseases that cause jaundice leads to serious damage to body functions.
Diet
To speed up the return to normal life and restore normal metabolism, you must follow the established diet. You should focus on using edible foods enriched with a complex of vitamins and microelements.
In acute cases of the disease, a carbohydrate diet is prescribed, including a large amount of liquid in the form of compotes, jelly, and vegetable decoctions. Steamed or boiled fish and meat dishes are introduced into the diet. Oil (vegetable or natural butter) is consumed in limited quantities. During the recovery period, diet No. 5 is used - low-fat dairy products, low-fat meat and fish products, grain bread. This diet can last for a whole year.
Since folic acid is needed to restore the way blood is formed, you need to include beef and chicken liver, green vegetables, yeast, and cabbage in your diet. To provide the body with fiber, it is suggested to consume oatmeal.
You should limit your consumption of carrots, citrus fruits, and pumpkin. For all types of jaundice, carbonated drinks, strong tea or coffee, chocolate, alcohol, fatty and spicy foods that unnecessarily burden the liver are contraindicated. Meals are fractional, food is taken in small portions.
Treatment of jaundice
The measures by which jaundice is treated are prescribed individually based on the clinical picture. There are many therapies aimed at eliminating the processes that lead to an increase in bilirubin levels.
The main treatment method is the use of anti-jaundice medications. Patients are prescribed drug therapy that helps normalize the level of bile pigment, restore liver function, and improve the functioning of the digestive system.
The following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiviral (for hepatitis)
- Hepatoprotectors
- Choleretic
- Enzymatic
- Detoxification solutions
- Diuretics
- Vitamin complexes
- General strengthening
- Sorbents
For some diseases (cirrhosis, cancer, mechanical obstruction of the bile ducts), surgical treatment is prescribed. Liver surgeries have a wide range of contraindications and often lead to complications. However, in severe diseases, surgical intervention is the only way to restore the functioning of the organ and eliminate the risk to the patient’s life.
This is interesting: Glucose 5 percent for newborns with jaundice: indications and method of use
During the treatment period, a diet is prescribed. It is aimed at relieving the liver and other organs of the digestive system. All types of fatty foods are excluded from the diet. A dietary regimen with an increased amount of proteins, complex carbohydrates, and plenty of drinking is observed.
When considering how to treat jaundice, you need to remember the categorical prohibition of self-medication. Therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a physician, in full accordance with the recommendations.
Preventive actions
To prevent undesirable consequences, the following conditions must be met:
There is no anti-jaundice vaccine, because we are not dealing with a disease, but a symptom, a pathological manifestation of a hidden disease. Today, vaccinations are given only against the hepatitis virus.
In conclusion, it is worth saying that compliance with preventive measures and timely consultation with a doctor if warning signs appear will significantly reduce the risk of jaundice.
Prevention of jaundice
The main task of preventing jaundice is to eliminate provoking factors. This is a multifaceted process, including changing the way of life, giving up bad habits, and adjusting the diet.
A specific method of preventing the disease is vaccination against jaundice. Vaccination is carried out against viral hepatitis, as this is the most common cause of icteric syndrome. Vaccinations are given to newborns on the first day of life. Adults are vaccinated if indicated or if they are in a high-risk group. After vaccination, which includes 3 injections, the patient develops stable immunity to viral infection.
Related events:
- Quitting alcohol
- Healthy eating
- Full drinking regime
- Moderate physical activity
- Maintaining hygiene
- Preventive medical examinations
- Removal of parasites
What does jaundice look like in newborns? Photos
Even in the maternity hospital, jaundice may appear in newborns (photo 3). Everyone has bilirubin in their blood, but in a newborn it is formed faster, in larger quantities, and excreted more slowly. Physiological jaundice of newborns manifests itself for many reasons:
- Intrauterine development requires an increased content of red blood cells. Their rapid destruction after childbirth leads to excess bilirubin;
- Hypothermia, starvation;
- Bilirubin increases rapidly if meconium passes late;
- The child’s liver is not yet mature and has a deficiency of bilirubin-carrying protein.
Symptoms of jaundice in newborns begin to appear in maternity hospitals. They appear by the 3-4th day of life, are observed for only a couple of weeks and disappear. Premature babies may have similar symptoms for up to a month. This type of jaundice is not contagious and does not pose a danger to the child.
Physiological jaundice in newborns does not require treatment, and with proper care of the baby it quickly goes away. One of the best preventative measures for the disease is frequent breastfeeding. Colostrum for a newborn is also a laxative, helping to quickly pass meconium.
Sometimes infants experience hyperbilirubinemia, in which unconjugated bilirubin affects the brain - this is kernicterus in newborns. Premature babies are the most common cases among those affected. The first symptoms of a dangerous disease are:
- Poor sucking;
- Constantly relaxed posture;
- Rare breathing;
- Brief convulsions;
- Sharp reaction to stimuli.
This jaundice looks like in newborns in the first phase: the baby turns blue, the long muscles of the neck and head are in constant tension, wheezing is observed in the lungs, and the eyes are wide open. Next comes a more dangerous phase - the spastic phase, in which the nuclei of the brain are affected. The newborn constantly screams, all muscles tense, breathing is upset.
Nowadays, elevated bilirubin, like dermatitis in infants, is treated with phototherapy. This common method is very effective. Typically, jaundice in infants is treated for no more than 96 hours.
Often the disease jaundice (photo below) develops as a consequence of certain factors:
- Congenital infections;
- Premature delivery;
- Maternal diabetes;
- Minor hemorrhages of the baby;
- Administration of antibiotics to a newborn;
- Swallowed blood.
Main types of syndrome
Jaundice of newborns is classified into the following types according to different criteria:
- Physiological
- Pathological.
Also, depending on the type of bilirubin predominant in the blood, newborn jaundice is distinguished with a predominant increase in direct or indirect bilirubin.
Pathological neonatal jaundice can be congenital or acquired.
Depending on the reasons that led to the formation of jaundice, the following types are distinguished:
Suprahepatic. Jaundice, formed due to excess bilirubin synthesis. With congenital anomalies, this is revealed in the pathological structure of erythrocyte membranes, defects in the structure of hemoglobin, and erythrocyte enzymes. Acquired pathologies include hemolytic disease of newborns, postpartum hematomas, and other pathologies leading to an excess of hemoglobin.
- Hepatic. Jaundice, formed when the uptake and excretion of bilirubin is impaired. Congenital jaundices include Gilbert's, Crigler-Najjar's, and jaundice due to congenital thyroid deficiency. Acquired – pregnative, infectious.
Subhepatic. Mechanical jaundice. Congenital jaundice is caused by abnormally formed bile ducts and cystic fibrosis. Acquired mechanical jaundice occurs when the patency of the biliary tract is impaired due to hepatitis suffered in the perinatal period, with bile thickening syndrome, as well as other pathologies leading to a narrowing of the lumen of the ducts.
Physiological jaundice of newborns develops a couple of days after birth, occasionally on the 5th day. The level of free bilirubin in the blood reaches 120 µmol/l. With yellowish skin, the baby’s liver remains at a normal size, and his overall health practically does not deteriorate. Transient jaundice, as a rule, rarely extends below the navel and is obvious in bright light.
Sometimes a protracted form of the syndrome is observed, which intensifies with a lack of fluid, that is, milk, which happens in the first days after childbirth with exclusive breastfeeding.
Only when it persists for a long time does jaundice of a newborn affect his well-being. Then the baby becomes lethargic, capricious, drowsy, and does not breastfeed well. Newborns with prolonged jaundice may develop problems with the functioning of the hepatobiliary system later in life.
With proper nutrition, careful attention to the child’s condition, and care, within a couple of weeks there will be no trace of jaundice left in the newborn.
In premature babies, the skin turns yellow a little earlier (1–2 days), increases within a week and subsides after three. The level of indirect bilirubin is determined within the range (137-171 µmol/l).
The digestive system of premature babies is more underdeveloped, so it is more difficult for it to cope with high bilirubin and takes longer.
In addition, the lifespan of red blood cells in premature babies is shorter, which leads to a greater number of destroyed red blood cells and the bilirubin released from them. In premature infants, jaundice often worsens to the point of bilirubin intoxication.
The intensity of the disease is not directly dependent on the body weight of premature babies, but is associated with the degree of fetal underdevelopment, diseases of the mother, and the course of her pregnancy.
Brief classification of jaundice
There are several types of symptoms:
- jaundice of full-term newborns;
- premature babies;
- hereditary, arising from endocrine pathology;
- jaundice in children with birth injuries and asphyxia;
- medicinal, which is caused by the administration of large doses of vitamin K, chloramphenicol, quinine and other things.
There is also pregnane jaundice, which occurs in breastfed babies in the first week of life or 7-14 days after birth.
General recommendations for jaundice
Early passage of meconium (delay can be a provoking factor for jaundice) is facilitated by placing the baby on the mother's breast immediately after birth. Even during a caesarean section, doctors try to place the baby on the mother’s chest as early as possible. Physiological jaundice goes away faster when breastfeeding. During light treatment, the number of applications should be increased by approximately 20%.
For physiological jaundice of a newborn, sunbathing for 30 minutes daily is recommended. Frequent walks and breastfeeding (you can express it and give it from a bottle) are also recommended. Regular monitoring by a pediatrician is necessary. These methods will allow the baby’s body to quickly adapt to new conditions and cope with the production of bilirubin.
Prevention of jaundice in newborns
During pregnancy, mommy should eat well, rest and lead a healthy lifestyle. This will increase the chances of giving birth to a strong, full-term baby. The body of such children copes well with adapting to the new environment and their organs quickly remove toxic substances. Their signs of jaundice are mild or completely unnoticeable. Healthy plant foods support the mother's liver, which ensures normal nutrition for the baby. You can take a tincture of alfalfa leaves with dandelion root or leaves. These are sources of minerals and vitamins that stimulate the liver and intestines.
Breast milk is considered the main medicine for the treatment and prevention of physiological jaundice. It is important to put your baby to the breast from the very first minutes after birth. Valuable colostrum contains all the substances that help the tiny body cope with the jaundice problem.
What is the danger of jaundice (consequences)
Complications caused by jaundice depend on the form, type and treatment provided. If pathologies are not detected in a timely manner, serious consequences can occur:
- toxic poisoning;
- High levels of bilirubin can cause a reduction in albumin production. As a result, the baby may suffer from albuminemia;
- with the development of nuclear jaundice, toxic substances that enter the brain cause impaired vision, hearing, retarded mental development, cerebral palsy, paralysis;
- in the future, the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer increases;
- liver pathologies;
- weakened immune system;
- fatal outcome.
Postpartum physiological jaundice does not affect the development of the baby. It is not contagious and passes without a trace.
Breastfeeding jaundice
Safe jaundice, which can last longer than three weeks, can occur due to natural feeding of the baby with mother's breast milk. The fact is that milk contains a substance that blocks the child’s liver enzymes. Doctors have not yet been able to figure out why nature blocks this mechanism.
If a mother wants to make sure that her baby has breastfeeding jaundice, she should switch to formula for a few days. As a rule, the yellow tint of the skin and mucous membranes will noticeably lighten. If this is the case, then you can calm down and calmly return to natural breastfeeding.
Diagnosis of a physiological symptom
The physiological state of the baby is diagnosed during the stay in the maternity hospital by a neonatologist who is the first to examine the baby after birth, or by a pediatrician. When visually assessing the child's condition, the Cramer scale is used. So, the first degree is characterized by yellowness of the face and neck, the second - the spread of a yellow tint to the navel, the third - to the level of the knees. In the fourth degree, jaundice covers the baby’s entire body, but excluding the palms and soles of the feet; in the fifth degree, the newborn is completely painted in “autumn” colors.
The norm of bilirubin is determined as part of the diagnosis of physiological jaundice in newborns. In the first degree, its content does not exceed 80 µmol per liter, in the second - 150 µmol/l, in the third - 200 µmol/l, in the fourth - 300 µmol/l, in the fifth - 400 µmol/l. A blood test of the mother and child, liver tests, and a urine test are also taken. Ultrasound diagnostics of the liver, bile ducts, and X-rays of the abdominal cavity may be performed.
Causes
Jaundice is a sign indicating disturbances in the functioning of the body in adults and children. The effect of the prescribed therapy will be noticeable only if the cause is discovered. Most often, jaundice affects the body due to disruption of the following organs and systems:
- The circulatory system, the function of which is to produce bilirubin from waste blood cells.
- The liver, which serves as a place for the accumulation and transition of bilirubin into part of the bile.
- The gallbladder, in which bile heats up and affects the large intestine.
How is jaundice treated in an infant?
The pathological form must be treated depending on the type and severity of the disease. The mother and child are hospitalized, diagnosed, and prescribed a course of treatment. If the reason is a discrepancy between the Rh factor and the presence of antibodies, blood transfusions, antibiotic therapy, and physiotherapy are prescribed. Obstructive jaundice is treated surgically. A consultation is created to study the patient’s condition and treatment measures are determined. There is no need to treat neonatal jaundice.
You can help your child overcome this condition at home:
- The newborn is put to the breast on demand. This stimulates the body's metabolism. The more the baby eats and poops, the more toxic bilirubin leaves the body.
- Mom must follow a strict diet to avoid causing digestive problems that aggravate the liver condition. At the same time, nutrition should be balanced and correct.
- It is necessary to ensure sufficient water intake in the mother's diet.
- Sunbathing.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air. When the weather is warm, the arms, face and legs are opened and the stroller is placed under a tree in the shade. Diffused light is very useful. It removes bilirubin from the body.
Pathological jaundice must be treated, taking into account all factors - the course of pregnancy, the mother's illness, ultrasound results, postpartum injuries, and the results of general tests.
Various therapies are used:
- antiviral treatment;
- antibiotic therapy;
- taking choleretic drugs, hepatoprotectors (Ursosan, Ursofalk, which remove bile);
- strengthening the immune system;
- removal of toxins (Hepel, Enterosgel, activated carbon);
- phototherapy.
It turns out that both combined and individual treatment is available. Diuretics and choleretic drugs can accelerate the elimination of toxic bilirubin and neutralize its destructive effects. Doctors prescribe Hofitol in syrup, Ursofalk, Phenobarbital, Hepel, Galstena, Ursosan.
- Hepel cleanses the body of toxic substances. Prescribed by doctors along with Magnesia and Enterosgel.
- Galstena is a natural preparation. Includes phosphorus and sodium sulfate. Galstena reduces bilirubin, eliminates intoxication, and cleanses the liver. Consists of herbs celandine, milk thistle, dandelion.
- Hofitol - in the form of syrup. Natural, herbal, vitamin-containing preparation. Chophytol stimulates the liver and is often recommended by doctors for prolonged jaundice in newborns.
You can prepare a natural, high-quality diuretic at home. This is a rosehip decoction. When breastfeeding, rose hips are brewed in a thermos, infused and drunk a glass three times a day. An infusion of rose hips will remove toxins, normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and promote liver function. Rosehip contains vitamin C many times more than citrus fruits and vegetables. Consuming it in the spring and autumn will be an excellent prevention of viral infections. Mommy will strengthen the immune system of both herself and her newborn at home.
Doctors often recommend phototherapy. This is irradiation under a special green or blue lamp. Ultraviolet light decomposes bilirubin substances into forms that can dissolve in water and be excreted from the body naturally. A 2-3 day course of phototherapy, which is harmless to the baby, is enough. While he is under the lamp, the newborn's eyes are covered with a thick, light-proof bandage. It happens that there are side effects from the radiation of the lamp - redness on the skin, diarrhea, rashes. It is important that while undergoing phototherapy, the newborn receives a sufficient amount of breast milk.
Glucose, activated carbon or Enterosgel is prescribed for severe jaundice in newborns. Glucose stimulates the liver, and charcoal naturally removes toxins and improves intestinal function.