About the disease
Amblyopia is an ophthalmological disease that is characterized by persistent unilateral or bilateral vision loss.
The main cause of visual impairment is organic pathology of the visual sensory system of the eye , which cannot be treated with optical means.
The disease can be asymptomatic, but sometimes the following signs appear: unstable fixation of vision, impaired color sensitivity, coordination, orientation in space, decreased visual acuity of varying degrees.
The disease must be treated at an early stage. The main goal of therapy is to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology. Treatment is carried out with medication or surgery.
Symptoms
A child with amblyopia usually does not notice the alarming symptoms of the disease or simply does not attach importance to them. Therefore, only the baby’s parents can identify the disease. To do this, you need to carefully observe the behavior and habits of their child.
Symptoms of amblyopia in a child:
- lack of clear fixation of gaze on objects;
- difficulties with orientation in unfamiliar places;
- deviation or closing of one eye while reading or performing other activities;
- poor vision in the affected eye, which can be detected by closing the other eye.
In adults with hysterical amblyopia, symptoms appear suddenly, after suffering stress or emotional shock. The patient suddenly notices a deterioration in central and peripheral vision. Unpleasant symptoms may persist for several hours, days or even months.
Refractive amblyopia grade 1–2 often affects people with high degrees of myopia and farsightedness who have refused to wear glasses for a long time. The disease develops gradually and affects both myopic eyes. Having decided to put on glasses or contact lenses, the patient discovers that the correction no longer helps him achieve one hundred percent vision.
Causes of lazy eye syndrome
Amblyopia can occur for various reasons:
- Strabismus;
- Nystagmus (rhythmic twitching of the eyeballs associated with a neurological disorder);
- Severe myopia and hypermetropia, when the difference in optical power between the eyes is greater than 3 diopters;
- Astigmatism;
- Ptosis is a disease of drooping eyelid;
- Conditions in which there is an obstacle to light reaching the retina (cataracts, clouding of the cornea and lens, scar tissue changes);
- Impaired color perception (you can read about color blindness here).
Types of amblyopia
Answering the question of what amblyopia is, it should be said that this disease can be confused with other pathologies that also lead to decreased visual acuity. Therefore, to avoid such a mistake, let’s consider the types of amblyopia.
There are primary and secondary forms. The primary ones include:
- Refractive amblyopia, which appears in children with untimely correction of ametropia. There are one-sided, two-sided, symmetrical and asymmetrical.
- Dysbinocular amblyopia. As you might already guess, the basis of this pathology is a disorder of binocular vision, which is provoked by strabismus and the lack of timely treatment. As practice shows, this pathology is more clearly manifested in the eye that is squinting.
- Mixed amblyopia, which is expressed in both refractive and dysbinocular forms.
- Hysterical amblyopia. Decreased vision in this case occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system. Most often, the cause may be psychological trauma.
About secondary amblyopia, you should know that the cause of this disease can be a pathology of the visual organ, which has been successfully eliminated. But because of this, a decrease in vision could occur.
This includes:
- Obscuration amblyopia, which appears as a result of a pathology of the visual organ that prevents the appearance of a picture on the retina. The most common manifestations include congenital or acquired cataracts. The obscuration form can appear in one or both eyes.
- Neurogenic amblyopia. The cause may be diseases of the optic nerve. To date, cases of complete recovery have been recorded. It should be noted that treatment of this pathology begins after surgery.
- Maculopathic. It develops after suffering diseases of the central and paracentral zones of the retina.
- Nystagmic amblyopia. It is called when the time period for which the image remains in the central zone of the retina decreases.
- Combined amblyopia. Manifests itself as a combination of the above forms.
Amblyopia classification
There are several types of amblyopia:
- Primary, or congenital. It is formed during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus and is associated with abnormal development of eye tissue. Risk factors for congenital amblyopia are cerebral palsy, intrauterine growth retardation syndrome, low birth weight, and preterm pregnancy.
- Secondary, or acquired. Caused by the presence of eye diseases, treatment can only be achieved by treating the underlying disease.
In addition, depending on the causative factor, there are the following forms of amblyopia:
- Strabismatic (dysbinocular). This disorder occurs with strabismus, when the brain perceives information coming from only one eye. Dysbinocular amblyopia can be with correct (central) fixation, when the image is focused in the central areas of the retina, and with incorrect fixation, in which the image falls on the peripheral part of the retina. Strabismatic type of amblyopia is diagnosed in 70% of cases.
- Deprivation (obscuration).
Caused by acquired or congenital clouding of the refractive media of the eye (cornea or lens). Strabismatic type of amblyopia is diagnosed in 70% of cases. - Refractive amblyopia . It is caused by persistent refractive error that cannot be corrected for a long time.
- Anisometropic . Occurs when the optical power of the two eyes differs from each other by more than 3 diopters. This feature is a serious obstacle to the formation of a complete visual sensation.
- Hysterical. This variant of amblyopia is rare. It may be accompanied by impaired color perception and the appearance of scotomas (this is the loss of areas from the field of vision).
Why does hysterical amblyopia occur?
Hysterical amblyopia can occur in both adults and children. It occurs due to severe stress, emotional shock, prolonged negative experiences, prolonged depression, that is, psychogenic factors.
With hysterical amblyopia, the cerebral cortex inhibits the process of visual perception, so the clarity of vision decreases. Also, a patient with this diagnosis has deteriorated color perception, intolerance to bright light, and sometimes “blind spots” appear in the field of vision.
Compared to other types of amblyopia, the hysterical form is considered the most favorable because it is more treatable than others. With proper therapy, a person with a similar disorder completely restores visual functions.
Degrees of the disease
Depending on the level of vision loss, amblyopia is divided into degrees.
Weak degree (from 0.4 to 0.8 diopters)
Low degree amblyopia is asymptomatic; visual impairment can only be detected after visiting an ophthalmologist. The danger of this degree of disease is that if treatment is not started on time, it can drag on for a long time.
This is why it is so important to visit your doctor regularly. Early diagnosis of amblyopia guarantees a quick and complete recovery.
Medium degree (from 0.2 to 0.3 diopters)
Moderate amblyopia has mild symptoms that can easily be confused with ordinary fatigue and age-related changes in the eyes. That is why this degree of disease is easier to identify in children.
The patient's eyes turn red, a slight pain appears, and concentration deteriorates . A person cannot look at one point for a long time; the image of objects when moving the eye is blurry. The eyes get tired quickly, the patient often squints, trying to look at an object, and sometimes gets a headache.
High degree (0.05 to 0.1 diopter)
High degree amblyopia in children is characterized by more pronounced symptoms. The eyes quickly get tired, pain and intense headache appear. The patient is poorly oriented in his surroundings, his movements are clumsy , which indicates a lack of coordination.
When a person with amblyopia watches TV or reads a book, he covers the affected eye with his hand. A typical symptom of this degree of illness in patients of a younger age category is tilting the head towards the object that they want to look at. In addition, patients' visual acuity decreases. The disease can only be cured surgically.
Very high degree (from 0.04 and below)
This degree of the disease is often accompanied by strabismus and visual fixation disorder. Also, this stage of amblyopia is manifested by all high-grade symptoms.
Severe amblyopia is more often diagnosed in patients of a younger age category . To restore vision, the patient must strictly follow the instructions of the attending physician. Therapy is complex and time consuming.
Amblyopia can be either unilateral (affecting one eye) or bilateral (affecting both eyes).
Degrees of amblyopia
Based on indicators of such a parameter as visual acuity in patients suffering from this pathology, several degrees of amblyopia are distinguished:
- I degree - is considered the smallest, virtually invisible and does not cause the patient any obvious discomfort. Visual acuity at this degree is 0.8−0.9.
- Grade II is still considered an indicator of mild amblyopia, but a person may experience some of the symptoms listed below. Visual acuity, accordingly, decreases and is equal to 0.5−0.7.
- III degree - called moderate amblyopia. The clinical picture manifests itself in full, visual acuity drops to 0.3−0.4.
- IV degree - severe amblyopia. Despite the scary name, it is still possible to treat this grade without surgery. Visual acuity is 0.05−0.2.
- V degree - the maximum possible and severe amblyopia. When checking the patient, the level of his visual acuity is below 0.05.
Symptoms of the disease
Anisometropic amblyopia in children occurs against the background of severe myopia (more than 8 diopters), hypermetropia (more than 5 diopters) and astigmatism. It is rarely accompanied by strabismus and is detected before the age of 7 years.
The main difference between refractive amblyopia is that it is asymptomatic. In this regard, it is detected during preventive examinations in children.
Refractive disease has an asymptomatic course. Obscurational is accompanied by symptoms.
Obscurational amblyopia accompanies cataracts, clouding of the cornea and lens, and hemorrhage into the vitreous cavity. Decreased visual acuity is accompanied by a feeling as if a person is looking through a thick curtain.
Each type of amblyopia is accompanied by a progressive decrease in vision.
Causes of the disease
According to statistics in Russia, about 2% of the population is susceptible to the disease, most of them children. The disease, in 90% of cases, occurs in 2 variants of the course of amblyopia:
- Refractive amblyopia;
- Dysbinocular form.
Most often it can occur for the following reasons:
- Impaired blood circulation in the retinal vessels of the eyeball in premature infants;
- Bad heredity;
- For reasons of impaired brain capacity and activity;
- Affected by cerebral palsy;
- Eye cataract disease;
- Diseases expressed in deviation of the normal refraction of the eyes.
It is important. A pregnant woman is obliged to take care of the health of her child even before his birth.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, ophthalmologists conduct a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- Visometry (visual acuity testing using Sivtsev or Orlova tables);
- Perimetry (determination of visual fields);
- Checking color perception using Rabkin tables;
- Tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- Biomicroscopy of the eyes;
- Skiascopy (examination of the refractive ability of the eyes);
- In case of strabismus, the angle of strabismus is determined on the synoptophore ;
- Fundus examination;
- Ultrasound examination of the eyes , and, if necessary, magnetic resonance imaging is additionally performed.
These studies are recommended to be carried out after cycloplegia - dilation of the pupil by instilling special drops (for example, atropine or cyclodol).
In controversial clinical cases, consultation with related specialists (for example, a neurologist) may be necessary.
Diagnosis of amblyopia
A list of the following studies is intended to help the doctor determine or refute the diagnosis of amblyopia:
- determining the level of visual acuity using various tables: from letters for adults, to pictures and geometric shapes for preschool children and primary school students;
- if this is possible, then it is highly advisable to conduct perimetry;
- determination of color perception using a special polychromatic Rabkin table;
- determination of dark adaptation using an adaptometer;
- application of tonometry and determination of the angle of strabismus on the synoptophore.
In addition, they examine the transparency of the eyes in transmitted light, examine the fundus of the eye, do electroretinography, ultrasound, computed tomography and MRI. Patients are recommended to consult a neurologist to rule out diseases of the nervous system.
Treatment of amblyopia in children
As for congenital cases of amblyopia of the eye, the success of its treatment largely depends on how early it is detected. In most cases, successful correction of amblyopia can be performed before the age of 7 years.
The older the child, the less chance of vision restoration.
Occlusion is the most effective treatment method
Occlusion of the eye can be:
- Direct (when the eye that sees better is closed);
- Reverse (close the eye that sees worse);
- Alternating (both eyes are closed alternately).
The eye is covered with a bandage or an opaque sticker (occluder) placed on glasses.
One of the types of occluder: with the help of a suction cup it is fixed to the glass of glasses, and thanks to its anatomical shape, it tightly covers the eye.
It should be noted that occlusion requires a lot of patience from both children and parents. For many reasons, children refuse occlusion: inconvenience, ridicule of peers, cosmetic defect, etc.
The task of the ophthalmologist and parents is to clearly explain to the child why treatment is needed. In addition, the child needs constant support and encouragement.
Optical correction
This method of combating amblyopia involves wearing contact lenses or glasses . Glasses are a more budget-friendly product that is accessible to absolutely every person. In turn, contact lenses have several advantages:
- Not noticeable;
- Do not narrow the field of view;
- Do not distort visible objects;
- Convenient to use.
Active visual treatment
It includes several techniques that improve or restore fixation and eye movement, their accommodative ability, as well as spatial perception.
For this purpose, specially developed computer programs for the treatment of amblyopia, prismatic glasses, laser stimulation, stimulation with light and electromagnetic waves, and the use of various devices (for example, synoptophore, amblyocor) are used.
Physiotherapy methods can be used in complex treatment: medicinal electrophoresis, reflexology, as well as vibration massage.
Penalization
Eye exercises for preschoolers Correctly putting on and removing contact lenses
This is
a method of correcting amblyopia, which involves deliberately deteriorating the vision of the dominant eye (that is, the eye that sees better).
This is done by instilling atropine. A decrease in visual acuity in the healthy eye leads to activation of the amblyopic eye. Penalization is used when a child is under 4 years of age.
Exercises
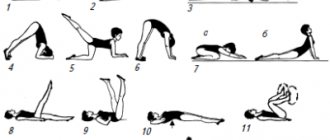
Treatment of amblyopia in children at home includes eye exercises. As part of complex therapy, you can perform special eye exercises for amblyopia in children:
- Stand by the window, cover your healthy eye with your hand, and slowly bring the paper with the text to the sore eye. It is necessary to bring it until the text is difficult to distinguish. Then, at the same pace, move the paper away from your eye until the letters become visible again.
- Before using exercises, consult your doctor about their use.
Cover an electric lamp with a power of 70 W with a black paper circle, the diameter of which is 8 mm. Cover your healthy eye with your hand and look at the light bulb for 40 seconds. Then look at the white paper, which must first be hung on the wall. An image of a black circle from the lamp should appear on the paper.
- Place a black paper cap on a 100 W lamp and cut a hole with a diameter of 5 mm. Take the red film and cover the hole in the cap with it. Sit in front of the lamp at a distance of 400 mm and do not take your eyes (sore eye) off the red dot for 3 minutes. The room should be dark, and the assistant turns the lamp on and off every 3 seconds. Repeat daily for 90 days.
- Sit up straight, head level, move your eyes to the left and then down. Don't blink during the exercise. When tears flow from your eyes, stop the exercise.
There are many more effective exercises: you can look at the nose with both eyes, perform circular movements, etc.
The main thing is to exercise regularly and follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Amblyopia therapy
Treatment of this disease cannot be carried out without an ophthalmologist. It is worth noting that untimely therapy leads to permanent loss of normal vision.
In children, contact or night lenses are often used for therapeutic purposes. Laser correction can be performed. If necessary, various operations are performed: eyelid surgery, surgery for clouding of the cornea, and resorption therapy is also carried out in the presence of hemophthalmos.
In some cases, active or passive pleoptics are used. The essence of passive pleoptics is the occlusion of the dominant eye. With adequate therapy, the dominant eye is closed, and the squinting eye is treated with light, electrical impulses or a laser to stimulate the retina. This treatment is carried out up to 4 times a year to obtain the desired result.
It must be said that for amblyopia, hardware treatment is the main treatment. If the child cannot tolerate occlusion, penalization with atropine is used in the eye that sees better, since a wide pupil reduces visual acuity, and this forces the amblyopic eye to work.
Physiotherapeutic methods such as vibration massage and reflexology are also widely used in treatment. Treatment is stopped when visual acuity in both eyes becomes equal.
In addition, as a maintenance therapy, it is possible for the patient to practice independently using special computer programs for the treatment of amblyopia at home. Their advantages include the following:
- The ability of one program to replace several devices at once.
- Ability to use new visual stimuli, such as three-dimensional ones.
- The interactive process of exercises can quickly captivate the child.
- The program cannot get tired or angry, unlike a medical professional.
- A variety of treatment programs and their settings will allow you to choose an individual course of exercises.
Prognosis and prevention
The medical prognosis depends on many factors, especially the underlying cause and the stage at which treatment is started. Early diagnosis and therapy guarantees a successful outcome and full recovery. The most effective treatment will be for a patient up to 7 years of age, until this time the eye continues to form.
In adult patients, especially with moderate and high degrees of amblyopia, it is not possible to completely restore vision, since visual impairment is irreversible.
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to regularly conduct medical examinations . It is necessary to promptly treat eye diseases: ptosis, clouding of the cornea, lens, nystagmus, strabismus (strabismus).
The patient must undergo a full therapeutic course, strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, wear glasses, eye patches, and be examined regularly. This is the only way to prevent disease and maintain normal vision.
Prevention
You should know that to prevent this disease you simply need to visit an ophthalmologist. An early visit to the doctor, namely within a couple of months after the birth of the child and then every six months, is already half the way to success.
A device called “Professor Pankov’s glasses” has proven itself well, which helps in the prevention and treatment of amblyopia and other eye pathologies. The purpose of the device is to improve visual acuity, relieve tension, strengthen the optic nerve, and form the eye muscles.
Providing the body with the right vitamin-rich nutrition and going outside every day also has a good effect on health.
Treatment of refractive amblyopia
Since this pathology is a consequence of other vision defects, treatment begins with eliminating the causes that caused refractive amblyopia.
Many parents believe that this defect will go away on its own during the development and growth of the child. This is absolutely wrong. Treatment should be started as early as possible.
After a complete diagnosis, the doctor, in some cases, recommends surgery. This could be correction of the position of the eyeball, removal of cataracts, or corneal transplantation. First, simple but effective methods of vision correction are used. Glasses or contact lenses are selected. Pleoptic procedures may then be indicated. This process involves reducing the activity of the healthy eye so that the affected eye operates at maximum activity. This is a kind of training for a defective eye. Next, you need to eliminate ghosting and combine the pictures into one. For this purpose, reflexology, vibration massage and physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Electrophoresis with certain medications helps well.
Manifestation of refractive amblyopia
Any light that hits the retina is converted into nerve impulses that travel to the brain. Based on these signals, a color and three-dimensional image is formed. The main role in this process is played by the center of the retina, which determines the so-called central vision, in addition to which there is also peripheral vision. If central vision is reduced and the defect cannot be corrected with glasses, then ophthalmologists define the pathology as refractive amblyopia. In this case, the diagnosis does not show any changes in the fundus.
With this disease, the area of the brain responsible for vision receives distorted information, and the nervous system begins to develop incorrectly. Children often suffer from this disease and it is dangerous because the visual nervous system may stop developing. But, on the other hand, in childhood, until the visual organs are fully formed, it is easier to perform all corrective and therapeutic procedures. Eliminating refractive amblyopia in an adult is very difficult and the percentage of negative results is high.