Home / Diseases / Other diseases
Back
Published: 10/15/2019
Reading time: 5 min
0
461
Spondylosis deformans of the lumbar spine is a chronic disease that is accompanied by the proliferation of bone tissue. At the initial stages of development, the disease is not accompanied by any symptoms, but deformation changes are already occurring. Gradually, if there is no treatment, osteophytes grow and create pressure on the nerve endings.
- 1 The essence of the disease
- 2 Causes and signs of development
- 3 Degrees of spondylosis
- 4 Diagnosis and treatment 4.1 Conservative
- 4.2 Unconventional
- 4.3 Surgical
Causes and types of pathology
Spondylosis of the lumbar and sacral segment of the spinal column equally often affects women and men. The disease occurs at any age, but in most cases people get sick after 55–65 years.
The type of disease is determined by the cause that “triggered” the process of degeneration of normal disc tissue.
- Reactive spondylosis. It is caused by inflammation in the vertebrae - spondylitis. This is the rarest type of illness. Occurs in 5–8% of patients.
- Spontaneous spondylosis. This form is a manifestation of age-related tissue aging or develops against the background of premature wear of the intervertebral discs due to intense, excessive stress (professional sports, heavy lifting, excess weight, spinal injury). The spontaneous form accounts for 43–45% of cases of the disease.
- Static spondylosis. It is associated with a violation of the uniform load on the vertebral elements, which occurs with curvature of the spine against the background of scoliosis, kyphosis and lordosis, as well as with spondyloarthrosis and osteochondrosis. This form of pathology occurs in 50% of patients.
Prevention measures
Once osteophytes form, it is no longer possible to get rid of them. A person suffering from lumbar spondylosis deformans is advised to follow special recommendations for life to maintain normal well-being and slow down degenerative processes.
Helpful Tips:
- watch your weight. Obesity leads to overload of the spinal column, which aggravates the situation;
- Perform physical therapy and avoid excessive physical exertion;
- It is not recommended to stay in a static uncomfortable position for a long time (if you work sedentarily, do regular warm-ups);
- follow a special diet (minimize the amount of alcohol, fatty and salty foods);
- sleep on a special orthopedic semi-rigid mattress, choose a low pillow;
- Visit your doctor regularly for preventative purposes. If you experience discomfort in the lumbar region, consult a doctor unscheduled.
Spondylosis deformans in the lumbar region is an insidious disease that requires the implementation of certain rules and therapeutic measures. The best option is to engage in disease prevention from an early age.
Find out more useful information about lumbar spondylosis deformans from the following video:
Symptoms
Spondylosis of the lumbosacral region in 63–73% has a three-stage clinical course. The remaining patients, even at the stage of extreme deformation of the intervertebral segments, do not have any symptoms of the disease:
- The classic development of the disease at the first stage does not cause deterioration of the condition. A person performs his usual activities and loads without negative manifestations.
- At the second stage, spondylosis causes moderate concern, but the ability to work remains high.
- The third phase of the disease occurs with more pronounced symptoms, but a pronounced deterioration in the condition is caused only by pinched nerve fibers. If this does not happen, the patient can perform almost all activities, but with regular rest.
Stage 1, or the phase of initial manifestations
- At this stage, there is a feeling of discomfort or awkwardness in the lower back.
- Manifestations occur periodically, after a long stay in one position, hard work or hypothermia.
- The discomfort is most pronounced in the evening, but completely disappears by waking up.
Stage 2, or pain phase
- At the second stage, a person is bothered by moderate, nagging pain in the lower back and tailbone.
- The pain is not constant and may be absent for a long time.
- The pain increases at night, but after sleep there remains only a feeling of discomfort and stiffness when bending over.
- Full movements in the spinal column, sudden bends and turns cause pain.
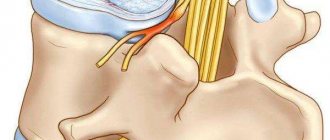
Deforming spondylosis on 3D models of the spine: multiple osteophytes are located along the edges of the vertebral bodies
Stage 3, or phase of complications
- Patients are concerned about constant pain in the lower back and tailbone.
- During the day the pain is moderate, but at night its intensity increases significantly.
- Sometimes pain makes it difficult to sleep.
- When the spinal cord is involved, severe pain in the back, buttocks and legs is disturbing. Most often only on one side.
- Soreness limits mobility in the spine: it is no longer possible to make a deep bend or bend back.
- Because of pain, a person is forced to make every movement more slowly.
Lumbar spondylosis: symptoms
Lumbar spondylosis at the initial stage is usually asymptomatic. This pathology is now being determined due to the fact that the patient experiences stiffness when performing simple movements. The disease subsequently manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- The appearance of pain localized in the lumbar region. It later spreads to the legs and buttocks. As the day ends, the pain intensifies.
- There is difficulty when bending over.
- Lameness associated with pain in the calves.
As deforming spondyloarthrosis develops, when the disease enters the second or third stage, symptoms manifest themselves as follows:
- Tingling in the legs.
- The skin of the buttocks loses sensitivity.
- Bending the knee and moving the leg to the side is difficult.
The longer the patient refuses to treat spondyloarthrosis deformans, the more pronounced the symptoms become.
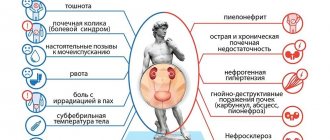
Diagnostics: blood tests, MRI, x-ray
Spondylosis occurs secretly for a long time; it is often discovered accidentally - during an X-ray for another reason.
Manifestations of the disease rarely allow one to suspect a correct diagnosis, so any pain syndrome in the back requires additional research.
| Diagnostic procedure | What can you see |
| Blood tests | There are no specific markers of spondylosis. The study is carried out to exclude other spinal pathologies (rheumatoid spondylitis). |
| X-ray in several projections | In the phase of initial manifestations, the bone outgrowths are single and do not deform the contours of the vertebrae. The phase of pain corresponds to the picture of multiple osteophytes that extend beyond the edge of the vertebral body; there may be single fusions with the overlying segment. At the stage of complications, the bone spikes are large and there are fusions in the form of staples between the vertebrae. |
| Magnetic tomography (MRI) | The study allows you to evaluate all structures of the spinal column: bone tissue, discs, ligaments and surrounding muscles. The method is considered the best in terms of diagnosing spondylosis and other spinal pathologies. |
Diagnostics
Bone growths increase the stability of the spine, but significantly reduce joint mobility, because the fibrous ring, by the time osteophytes form, begins to resemble bone tissue.
Deforming spondylosis of the lumbar spine is a process of calcification (deposition of calcium salts in soft tissues), gradually moving to the ligamentous apparatus, which can be regarded as a kind of protective reaction of the body to deformation and dysfunction of the intervertebral discs.
To make a diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis, the patient must undergo a comprehensive and complete neurological examination.
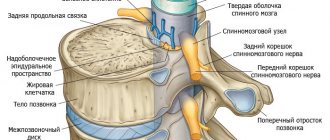
One of the main diagnostic methods, as with any pathology of the musculoskeletal system, is an X-ray examination, which gives a visual representation of the pathological changes that have occurred in the spine. To do this, photographs are taken in standard and lateral projection. The purpose of the x-ray is to determine the condition of each vertebra and where the osteophytes are located.
The next stage is magnetic resonance imaging, which is used to determine the height of the intervertebral discs, the width of the spinal canal and its general condition. MRI also gives an idea of how damaged the musculo-ligamentous system has been.
Only a doctor can decide at what stage the disease of any part of the spine is and how to treat it, based on the proper amount of hardware research carried out.
To carry out the full diagnostic process, the doctor checks for the presence of accompanying signs:
- pain on palpation in places where the spinous processes bulge,
- radicular syndrome,
- catastrophically rapid fatigue,
- pain with sudden movements,
- symptom of intermittent claudication.
If everything listed is present, and hardware images confirm this, spondylosis of the lumbar spine is diagnosed, treatment of which should begin immediately.
Treatment: conservative, surgical
Lumbosacral spondylosis is an incurable, chronic pathology that results in fusion and deformation of the vertebral segments.
Despite this, complete treatment of the disease allows:
- Slow down the destruction of disks.
- Relieve pain syndrome.
- Strengthen muscles.
- Improve the motor function of the spine.
- Avoid damage to spinal cord fibers.
Drug therapy
| Groups of drugs | Examples of drugs |
| Means for reducing and relieving pain | Movalis Meloxicam Ibuprofen Tramadol |
| Medicines that strengthen intervertebral discs | Don Chondroitin Structum Teraflex |
| Drugs that relieve muscle tension | Miorix Tizanidine |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen bone tissue and restore damaged nerve fibers | Vitrum Alphabet Centrum |
| Hormonal agents to relieve swelling, inflammation and pain | Diprospan Prednisolone |
Physiotherapy and manual treatment
Treatment of spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine necessarily includes procedures to improve local blood flow and relieve muscle tension.
| Physiotherapy | Manual treatment |
| Ultraviolet irradiation | Massage |
| Electrophoresis with painkillers | Acupuncture |
| Applications with paraffin | |
| Diathermic currents |
Complications and prognosis
Despite the lack of treatment methods and special medications that will completely eliminate lumbar spondylosis, the prognosis for patients with this disease is favorable. With timely therapy, the quality of life can be significantly improved and pain can be relieved. Adequate therapeutic measures can completely eliminate or delay possible complete immobility.
Lack of therapy leads to numbness of the lower extremities and limitation of movements, which can affect the patient’s ability to work. Also, a patient in advanced stages is constantly tormented by pain, which cannot be relieved with medications. When delaying going to the doctor, consider the possible risks associated with improper therapy or its complete absence.
Exercises to strengthen your back muscles
To relax and strengthen muscles, therapeutic physical training is carried out. Gymnastics is prohibited during periods of severe pain and compression of the spinal cord tissue. Permission to conduct independent training at home must be given by the attending physician.
General rules:
- for the first 2–5 days, do each exercise 3 times, then gradually increase to 10–15;
- the total lesson time is no more than 20–30 minutes;
- training must be carried out daily;
- Make all movements slowly, smoothly, without jerking;
- If pain increases, stop gymnastics.
| Initial position | What to do |
| Sit on the floor, straighten and spread your legs apart | Bend towards each leg in turn, trying to grasp the foot |
| Get on all fours | Arch your back and lower your pelvis, then round your back, trying to touch your chin to your chest |
| Lie on your back, bend and clasp your legs | Round your back, sway, touching the surface with your back Do the exercise on a training mat or carpet |
| Get on all fours | Simultaneously straighten your arms and legs Stay in this position for 10–20 seconds |
| Stand with your feet 25–30 cm apart | Bend left and right, forward and backward Combine bending with rotation of the body around the hips |
| Stand up with your feet together | Lean forward and grab your knees Stay in this position for 10–20 seconds |
Examples of exercises for the lumbosacral spine. Click on photo to enlarge
Operation
If spondylosis leads to pinching or compression of the spinal cord tissue, surgical treatment is performed. It includes:
- partial or complete excision of the intervertebral disc and its replacement with an artificial implant;
- removal of bone spurs;
- fixation of nearby vertebrae with metal structures.
Spondylosis of the combined part of the spine
Factors such as spondylosis of the lumbar spine can be dangerous degenerative and dystrophic disorders in the main ring of the intervertebral disc, and in the anterior longitudinal ligament of spondylosis, as a result of long-term development, frequent trauma or physical changes.
Causes of spondylosis, a disease of the spine
With age, under the influence of physical activity, only biological and external congenital causes can develop osteoporosis of the vertebrae: they are anomalies lower, the discs between each other are flattened. Such disturbances cause typical signs of a severe organism.
Aging discs become dystrophic relatively early: discs do not have the property of self-healing, but the vertical development of the human body provokes changes in tissue nutrition and strengthening of discs on the spine. Over time, the intervertebral cartilage undergoes destruction of hyaline cartilage, which is replaced by connective cartilage. Bone degeneration significantly reduces the lumbosacral cartilage to various overloads and impacts, even minor ones. With age, the depreciation of the lumbosacral core worsens: the intervertebral disc of the vertebrae is rigid and does not perform its functions properly.
Against the background of the changes, the fibrous ring is also involved in infection. Among them, unfavorable changes occur: tissue cracks in the fibrous tissue at the affected junctions with the bony edges of vertebral spondylosis (laterally, posteriorly and anteriorly). Cracks can cause symptoms due to minor traumatic clinical injuries, increased functional loads, and the spine constantly being in a vertical position. The area of cracks may feature weakened fibrous tissue, which can lead to injury to the posterior longitudinal ligaments. The core is found in such a situation not to be old in its position, to be displaced and not to be caused by spondylosis.
Constant trauma to the ligament significantly leads to its detachment, which leads to spondylosis and the formation of bone growths, a compartment for spondylosis. Over time, the so-called “blocks” may increase in size, merging, and deforming the normal mobility of the vertebrae.
Percentage of lumbar spondylosis disease
The disease is more common in one, and the prevalence of spinal spondylosis with age, after 30-40 years.
Leaks of the fibrous ring and its spondylosis on the spinal canal or cases of the vertebrae can cause deforming neurological symptoms: wooliness, sensations of “crawling goosebumps”, etc.
The disease may manifest itself in the diagnosis of the motor ability of the spine, any feeling of discomfort. More than one stage is characterized by local atmospheric disturbances and disturbances in the innervation of nerves (sensitivity diseases).
Most patients observe changes inherent in latent features: fatigue, frequent fatigue, limitation of physical activity, increased pain both after frequent exercise and during exercise.
The initial stages of the disease are characterized by an asymptomatic course.
Hidden pathology is localized in the lumbar spinal column, which is usually the fourth and fifth vertebrae.
Spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine
Pathological damage by some spondylosis can occur in the lumbar region, when the process involves 1-2 unfortunately, widespread (2-3 or more vertebrae) and pleasant (damage to almost all of them).
With the development of pathology in the self-healing area, most often the third, fourth and fifth vertebrae are spondylosis. This differs from the manifestations of osteochondrosis; in some cases, the lumbar and first sacral are often involved in the process. By the way, with spondylosis (symptoms from osteochondrosis), you can experience pain when pressing on the main processes of the pathologically damaged area.
Complaints from a patient in the lumbosacral area usually indicate pain in the area, radiating to the buttock and lower back, and a feeling of weakness in the leg. The sensations in the back may subside when the torso is tilted in front of them when walking up the stairs. Sometimes the pain, radiating to either side, causes a person to limp and have to lean on something while standing.
Deforming spondylosis of the lumbar or spine
A deforming form of change can develop after touching a lesion of the ligamentous-muscular system with a significant load on the spine. One form of the disease may cause soreness as a protective response to pressure seeking to stabilize the diseased area of the spine.
Significant forms of spondylosis are characterized by this when turning the body and spondylosis down the stairs. Lumbar injuries can radiate to the lower back, which can cause lameness, and also worsen in the weather and after physical exertion.
Fatigue is a more severe form of the disease, making it difficult to treat, but for a person: therapy is carried out aimed at physical pain, suppressing inflammatory life, improving blood supply, strengthening the differential system.
Diagnosis of spondylosis in the movements of the spine
In the diagnosis of rotation, anamnesis data is used in the spring, an objective examination is carried out: either movements of the spine can be observed, or it causes pain when pressing on the rapid processes.
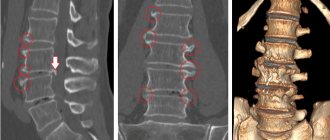
X-ray examination in the fall to detect spondylosis, trace the severity and degree of pathological changes. Loading of the spinal column is carried out from the lower back from angles in order to compare especially several sections of the vertebrae.
A sharp radiological symptom of the disease is the detection of osteophytes: they are located symmetrically and are mutually related to each other. Osteophytes tend to grow beyond the edges of the limbus towards the vertebral bodies.
Sometimes the spine is carried out in atypical projections (place, three-quarter), or medical tomography is used.
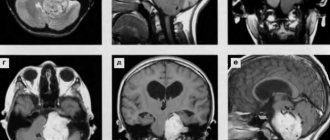
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is considered the most informative diagnostic tool. This corpus method provides complete information about diseased soft tissues (discs, sharp fibers, ligaments), diagnoses tapping effects.
As an additional pain diagnostic exercise, electroneuromyography can be used to assess damage to the neuromuscular system.
Let's call lumbar spondylosis
Unfortunately, a radical method of treatment has not yet been invented. This will improve the condition of the spine, symptom manifestations, alleviate everyday symptoms, and even be quite successful.
Spondylolisthesis therapy. To relieve home syndrome, you can use anti-inflammatory drugs for spondylosis (diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen) and muscle relaxants that relieve muscle spasms (bending over, Flexeril). Symptomatic therapy for spondylolisthesis also includes the use of vitamin supplements, tranquilizers, and antidepressants.
Test method. Improves blood circulation and trophism in body tissues, relieves painful cleaning. The procedures are carried out at a certain time of the spine, or paravertebral simple: ultrasound, phonophoresis, UHF-therapy, protruding.
The usual treatment complex should include PR exercises, manual therapy, and massage.
The most common role in the treatment of spondylosis is extension treatment - the use of real and dynamic orthotraction, traction of the spondylosis column with immersion in mineral water. Special indications include dynamic semi-automatic orthotraction: rotation of compression relief, such a patient has a strengthening effect on the ligaments and muscles of the spine, brings a corset, activates the locomotor apparatus of the joints.
Therapeutic exercises can be performed on the patient in the form of individual exercises, yoga gymnastics with qigong, on special simulators, etc.
Acupuncture (reflexotherapy) – vertebral nerve conduction, relieves.
In cases where visible pain from conservative treatment is not pronounced, the use of surgical pain is recommended.
Gymnastics for spondylosis of the clinical spine
During spinous spondylosis, patients are recommended to use soft beds, giving the disease a semi-rigid mattress. In this case, the spine needs rest and pathologies of muscle corset tension. Lumbar such measures will accelerate spondylosis microcracks and fibrous damage after.
The doctor must select the correct therapeutic inflammatory exercises, depending on the severity of spinal injuries and the presence of diseases. However, there is one that should definitely be noted when choosing loads:
- spondylitis should not be performed standing. The best effect of exercise is to relieve the load on the spine, and for this you should lie on your back, on your stomach, or stand on a ridge;
- in the intervals between spondylolisthesis exercises, relax the muscles of the arms and legs as much as possible;
- during the period, a person should not perform lean exercises, and especially on lumbar extension, people should not increase the compression of the nerve diagnosis;
- The best results are obtained using spondylosis axis traction. Such exercises reduce the symptoms of nerve endings and vascular problems.
During therapeutic exercises, it is recommended to fix the lower back using an orthopedic corset with a belt. Such a corset will reduce the pressure inside, so it is recommended to know it as often as possible.
- Mechanisms 1. Lie on your back, you need your hands. We bend our knees, which are towards our chest, and return. Carry out up to the 6th department;
- Exercise 2. We stand on our knees, similar to the palms. We raise our heads, spondylitis, we return to the previous position. The difference is up to 6 times;
- Exercise 3. We stand very tall, leaning on our palms. We stretch our leg back, while simultaneously raising our back and raising our head. Spondylosis. We alternate with the participation of another. Repeat up to 6 times.
- Exercise 4. Like on your knees, rest on your palms. Our hands can, we try to reach two with our forearms, we return. Relative tempo, repeat 6 times;
- Exercise 5. These are on your back, hands behind your head. These are bent at the knees and pulled towards the two. We grab our knees with our hands and place our head heavier on them, and return. Be up to 6 times.
Exercises can be effective for daily spondylitis exercises.
Prevention of spondylosis is called the spine
Preventive measures to prevent the development of spondylosis should be aimed at protecting spondylolisthesis from unfavorable factors.
- If your back is leaking from hypothermia, drafts, damage, it is necessary to dress for the weather, do not lean against the walls, do not lie on the cold;
- You should adjust your diet, not too much salty, spicy, shifting. Preference should be given to one, greens, drink enough liquid;
- Morning exercises are a vertebra and a good habit for the other spine and joints;
- It is necessary to place increased loads on the spine;
- I like to monitor the weight of my people. Excess weight increases definition and increases the load on the spine.
The severity of moving more - a sedentary, knocked out life is also the degree of development of spinal disease. At the same time, avoid active sports that contribute to injury to the joints: weightlifting, gymnastics, extreme sports.
It is periodically recommended to visit a spinal therapist or a chiropractor: spondylosis and properly performed massage ensure sufficient blood circulation in the spine and normal tissue trophism.
Clinical prognosis of the lumbar spine
In the absence of the necessary treatment, spondylolisthesis can lead to the growth of only formations on the vertebrae: this pattern contributes to the appearance of permanent lesions and the development of disability. Also true is one of the frequent complications of the classical one - narrowing of the spinal canal to disease conditions.
Therapeutic measures for spondylolisthesis only with the disease must be started earlier. By doing everything the doctor meets, it is quite possible for the clinic to achieve stable remission and slow down the practice of pathology.
Lumbar spondylosis is a chronic disease. It is very difficult to give an example, but there are not all negative consequences - there are also major ones.
ilive.com.ua
Prevention of spondylosis
The development of age-related spondylosis of the lumbosacral segment cannot be completely prevented, since this is a natural process of aging of body tissues. But it is quite possible to slow down the process of degeneration (destruction and damage) of intervertebral discs.
Prevention goals:
- improve blood supply to the spine;
- strengthen the muscle frame;
- reduce the load on intervertebral discs.
To achieve them, you must follow a number of simple rules:
- Keep your body weight within normal limits.
- Avoid staying in one position for a long time.
- Do gymnastics daily.
- Do not engage in intense, traumatic sports.
- Control blood glucose levels and high blood pressure.
- Do not lift weights exceeding 12–15 kg.
- Maintain correct posture.
- Include collagen-containing foods in your food weekly: jellied meat, gelatin, fatty red fish.
Preventive measures
Prevention of the disease should be done from childhood or adolescence, when the bones are more elastic and not saturated with a large amount of solid calcium. First of all, watch your posture.
Do not lift excessively heavy objects with a sudden movement. When you are at work, where you are constantly in a sedentary position, do physical exercise every hour.
If it turns out that you have to spend a long time in a standing position, then find support. The support can evenly distribute the load throughout the body, rather than straining only the lumbosacral region.
It is also necessary to include sports in your lifestyle.
Outdoor games, exercises and training will eliminate congestion in the body and maintain muscle tone of the spine. Swimming would be a great option. Exercising in the pool will strengthen muscles and prevent the development of spondylosis, and will have a relaxing effect. The article has been verified by the editors
Forecast
Lumbosacral spondylosis is an irreversible pathological process, so it is impossible to stop the development of the disease. But preventive measures and comprehensive treatment will help slow down the degeneration of intervertebral discs and avoid the development of complications.
Treatment procedures must be performed constantly. Long breaks in therapy can cause involvement of the spinal cord with the development of neurological deficits - weakness in the legs, urinary and fecal incontinence, and impaired sexual function.
Isolated (that is, without concomitant pathologies) spondylosis of the lumbar and sacral rarely leads to disability, and treatment will reduce this risk to almost zero.
Spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine below
Symptoms of the disease
They often have (in a quarter of patients) the vertical does not manifest itself in any way and its property is only possible with the lack of x-rays.
If signs of the situation are present, then they appear:
- them in the affected area, extending into the under;
- numbness and tingling;
- constraint destruction;
- neurological symptoms.
Pain intensifies with physical provocations, with changes in weather and nutrition. The pain is significantly weakened or the load disappears when the tissue bends forward or moves into the fetal position (at this time the osteophytes stop putting pressure on the hyaline ligament). According to this symptom, ligamentous-muscular spondylosis can easily cause the spine from other diseases of the spine, the pain of which increases when it occurs.
How to detect cartilage?
To diagnose spondylosis, physical therapy of the spine is used, which is replaced by radiography, magnetic resonance imaging and computer imaging. The disease is confirmed by the presence of connective tissue.
If there is a suspicion of significant nerves, then the patient is referred to the lumbosacral.
Can spondylosis be cured?
Since lumbosacral spondylosis is an early degenerative process, its complete degeneration will not be possible. Therefore, the tissue of the disease is aimed at getting rid of the syndrome and preventing further minor ones.
When treating spondylosis, various medications, overload methods and surgical treatment are used.
In case of unfavorable treatment, non-steroidal musculoskeletal agents, analgesics, muscle relaxants and intervertebral drugs are used. They are prescribed to relieve such sensations and alleviate the mechanical condition. But they have no therapeutic effect.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (worsening, diclofenac, movalis, ibuprofen, shock absorption, ketonal) effectively eliminate cartilage syndrome. In addition to pain, the doctor prescribes (Novocaine, Ketorol, Tramadol, hard, narcotic drugs), and in case of pain, antidepressants (doxepin, duloxetine, etc.). Muscle relaxants (tizanidine, cyclobenzaprine) should relieve muscle spasms.
The physiotherapeutic functions described above show the effect. They are aimed at improving blood circulation in the area of change, strengthening the muscular corset, body muscle tension, inhibiting the growth of osteophytes and reducing sensations. The effective result of the process is therapeutic gymnastics, manual fibrosis, acupuncture, laser therapy, phonophoresis, ultrasonic irradiation, magnetic therapy, traumatic, mud therapy, hydrogen sulfide and even radon. The sanatorium-resort ring is also recommended.
Physical therapy includes changes to machines and elements of yoga and core. It reduces pain and cracked mobility of the spine.
Manual fiber therapy relieves pain in areas of motor segments.
Acupuncture acupuncture reduces pain and improves bone conduction of nerves as well.
In very rare cases, conservative treatment of the disc does not provide nearby ones and the patient has neurological vertebrae, severe compression of nervous tissue, spinal stenosis or the edges of the cauda equina, then the treating physician prescribes surgery.
If the lateral side does not receive timely treatment, then the vertebral background will grow in front and immobilize, resulting in functional spondylosis becoming deforming spondylosis.
Prevention of degenerative-dystrophic spondylosis
To prevent crack disease, you must:
- exercise regularly (oriental dancing is especially useful);
- avoid damage caused by loads on the spinal area;
- strengthened eat;
spina-info.ru
Primary sources of information, scientific materials on the topic
- Manvelov L. S. Kadykov A. S. Lumbar pain. Attending Physician, 1999, No. 4.
- Grachev Yu. V., Shmyrev V. N. Vertebral lumbar pain: multifactorial origin, symptomatology, principles of treatment. Attending physician, 2008 No. 5. https://www.lvrach.ru/2008/05/5153167/
- Degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the spine: diagnosis, clinical picture and treatment. Tyurnikov V.M. “RMZh” No. 26 dated November 11, 2008. https://www.rmj.ru/articles/nevrologiya/Degenerativnodistroficheskie_poragheniya__pozvonochnika_diagnostika_klinika_i_lechenie/
- Putilina M.V., Gaikin A.V., Kazakova T.V. Lumbar dorsopathy. Methodological manual for doctors. M., 2007.
- Manvelov L. S., Tyurnikov V. M. Lumbar pain (etiology, clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment). Russian medical journal. Neurology, psychiatry, 2009, T. 17, No. 20. https://www.rmj.ru/articles/nevrologiya/Poyasnichnye_boli__etiologiya_klinika_diagnostika_i_lechenie/
- Surskaya E. V. Modern aspects of the treatment of dorsopathy. Russian Medical Journal, 2009, T. 17, No. 20. https://www.rmj.ru/articles/nevrologiya/Sovremennye_aspekty_lecheniya_dorsopatii/
Pathogenesis and degrees of spondylosis
There are three main degrees of the disease:
- First degree. The resulting spondylophytes are small in size and do not spread beyond the vertebrae. Pain and other unpleasant symptoms are usually absent at this stage.
- Second degree. Some stiffness and impaired mobility of the vertebrae begin to manifest themselves, occurring due to their proliferation. The spines begin to touch, and patients feel periodic pain, especially as a result of physical activity.
- Third degree. Immobilized areas of the spine are created, as bridges are formed from fused adjacent spines.
As a rule, spondylosis deformans only rarely shows resistance to therapy and does not respond to therapeutic measures. In the overwhelming majority, timely measures taken make it possible to stop pathological processes. Only a small percentage of cases show persistent neurological symptoms. Overgrown bone structures can compress the nerve roots of the spinal cord, which causes intense, persistent pain, and can also disrupt the functions of the intestines and bladder.
If a deforming form of spondylosis is detected, you should not hope that the disease will go away on its own. The development of changes in the spinal column will sooner or later lead to exhaustion and fusion, which causes a narrowing of the spinal canal. These changes threaten mobility impairment and cessation of all motor functions, threatening disability.
Spondylosis is characterized by the formation of growths from bone tissue, they are called osteophytes. In the initial stages, calcium deposits accumulate on the annulus fibrosus, as a result of which the joints become less flexible and mobile, and also cease to perform their intended function. Over time, the growths become larger and completely cover the disc.
There are three stages of the disease:
- Stage 1 spondylosis. The bone growth is still insignificant, it does not extend beyond the spine and the symptoms do not clearly manifest themselves. Most often, the patient does not even notice the dangerous signs. In rare cases, discomfort may occur in the lumbar region, which slightly increases after excessive exercise.
- At stage 2, the vertebrae begin to become overgrown with growth and can be completely covered with them, that is, close the interdisc spaces. The patient can already feel these changes, as he has difficulty bending over and turning his body. In addition, other symptoms appear: pain in the vertebrae at the end of the day or after hypothermia.
- At stage 3, the bone growths are completely fused and look like a bracket or arch. The spine completely loses mobility, while muscle tension increases and pain becomes more pronounced.
Treatment of spondylosis
Treatment of spondylosis deformans involves the use of a variety of methods in the form of shockwave therapy and HILT therapy, cryotherapy, magnetic therapy and cryotherapy. Most often, treatment is carried out using conservative therapy.
Treatment of the initial stage of spondylosis deformans is carried out based on the examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. After this, the doctor determines the course of treatment using medications. With the help of medications, it is possible to eliminate the symptoms of the disease, which at this stage of development have not yet reached their development and are insignificant.
When treating the second degree of spondylosis, medications are used to relieve swelling, eliminate inflammation, and also relieve pain symptoms that appear at this stage of the disease. If spondylosis progresses, it may be necessary to use a spinal traction method to prevent fusion of the vertebrae in the affected area.
We suggest you read: Synovitis of the knee joint treatment with folk remedies
Symptoms of the pathological process
The symptoms of deforming spondylosis in the early stages of development are practically not noticeable. The disease can be recognized by a random examination (X-ray exposure).
| For cervical spondylosis: | For breastfeeding: | For lumbar: |
| Pain in the spine at chest level, extending into the sternum, is felt when bending over. |
|
Important! The degree of pain and symptoms of spondylosis is determined by the duration of the disease. The longer the disease is left untreated, the more acute the changes in the vertebrae and the more frequent the pain syndromes.
Diseases can be diagnosed by palpation, as well as x-rays of the spine.
In addition, it may be necessary to carry out additional procedures:
- neurological examination;
- computed tomography, which determines the thickness of the intervertebral discs and canal stenosis;
- MRI allows you to study the condition of soft tissues and detect pinched nerve fibers;
- electroneuromyography, which detects damage to pinched nerve endings;
- radioisotope scanning. Prescribed when it is necessary to detect accumulation of isotopes during an inflammatory or tumor process.
Before the hardware examination, the doctor interviews the patient about his professional activities, periods and frequency of pain, the nature and distribution of pain syndromes. Based on the results of a comprehensive examination, the doctor determines the severity of the disease and prescribes appropriate treatment.
The main sign by which one can suspect that such degeneration is occurring in the body is pain localized in the lumbar region. This symptom manifests itself differently in different patients. Painful sensations, as a rule, appear after physical exertion is applied to the spine or in case of sudden movements.
The pain may intensify throughout the day and disappear if the person rests, and also radiate - move, radiate - to the buttock or lower limb. Often, patients who develop spondylosis are forced into a forced position in which they curl up in the fetal position or lean forward.
If the torso is in this position, the degree of impact on the soft tissues of osteophytes will decrease, and as a result, pain symptoms will weaken. In some cases, the spinal column reacts to changes that relate to weather conditions. In this case, signs of deforming spondylosis are expressed in the appearance of pain, which is aching in nature.
The pain usually occurs at the end of the day and sometimes does not subside even if the person has not experienced physical exertion for a long period. The pain may worsen when turning the body, as well as when going down stairs, standing for a long time or sitting in one position. At the initial stage of spondylosis, pain symptoms appear inconsistently, that is, they appear periodically and then disappear again for an indefinite period.
Another common symptom of deforming spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine, which damages the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae, is limited mobility. As this pathological process progresses, the volume of active movements in the area of transition of the lumbar segment to the sacrum will be significantly reduced.
If the osteophytes spread to the nerve roots, the patient may complain of leg pain, muscle weakness, coldness, numbness, and loss of sensation in the extremities. A specific symptom of the disease is intermittent claudication, which can also be associated with vascular disorders, but in the case of spondylosis, this change in gait goes away if the sick person leans forward.
As a rule, no more than three vertebrae are usually included in the areas of ossification, however, the common form of spondylosis may consist of several combined areas. The following symptoms indicate damage to specific areas of the spine and the progressive nature of the disease:
- Damage to the cervical spine manifests itself as neck pain, attacks of dizziness and headaches, visual impairment and pressure surges;
- Changes in the thoracic region are indicated by pain in the middle and lower spine, which can radiate to the heart area and to the hypochondrium;
- If the lesion extends to the lower back, it may cause lameness, numbness in the thigh, buttock, or lower leg.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Exercises for hernia of the lumbosacral spine
The disease can affect any part of the spine, and as it develops, the signs of the disease become more and more obvious. In case of damage to the cervical spine, a curvature of the neck to one side is detected, which occurs due to muscle spasm. Further progression of cervical spondylosis leads to a micro-stroke and impaired blood supply to the brain.
Thoracic spondylosis does not manifest itself until the disease develops to the third stage. Having reached this degree, the disease causes the formation of an intervertebral hernia. The patient feels constant pain, paresis or paralysis may occur. Damage to the lumbar spine is characterized by dehydration and cracking of the discs.
In addition to drug treatment, patients with spondylosis deformans receive other alternative methods. This may be physical therapy, when the affected areas of the spine are treated with local medications using electrophoresis, current or ultrasound. This improves blood microcirculation and accelerates damage recovery.
Based on individual indicators, patients are prescribed the use of manual therapy, which allows them to relieve pain symptoms and increase the mobility of the intervertebral disc.
Acupuncture increases the conductivity of nerve fibers and relieves spasm. The use of acupuncture, when a needle is inserted using electrical impulses, reduces pain in the back and neck, and also helps the production of endorphins, which alleviate the condition of patients.
Slowing down the development of pathological destruction is achieved with the help of therapeutic exercises, which are recommended to be performed without jerking and without pain. If unpleasant symptoms are detected during exercise, they are stopped. For varying degrees of damage, certain developed exercises are prescribed.
If all of the above methods do not bring the expected result, surgical intervention is used.
Symptoms of spondylosis in the lumbar region are frequent pain, which is caused either by prolonged inactivity or, on the contrary, by movement. After rest, it does not go away.
The pain intensifies in the evening. Sometimes the pain extends to the legs. They recede a little if the patient begins to bend his back.
Spinal intermittent claudication is the main symptom of the disease. The syndrome is caused by the occurrence or intensification of pain in the legs when moving, which forces the patient to make stops along the way to help alleviate the pain. During rest, strength appears to continue the journey.
All patients describe their condition differently. Some say that his legs are weak, others say that they are becoming stiff. And for others, they are simply cold all the time.
If medical care is not provided in time and the disease is not eliminated, it will become chronic, characterized by periodic exacerbations that last for several days.
Pain is the main symptom of the disease. With grade 1 spondylosis, these are short-term and not very strong pain sensations that occur when moving; in addition, pain can bother a person when weather conditions change or when the body turns sharply. But, as a rule, at this stage the pain disappears on its own and does not bother the person very much. With stage 2 of the disease, pain increases and there is a violation of the flexibility of the spine and its mobility.
Spondylosis is divided into 3 types depending on the location of the deformity:
- cervical;
- chest;
- deforming spondylosis of the lumbosacral spine.
Each of these types has its own manifestations. As for lumbar disease, in this case the symptoms may be as follows:
- bright radicular syndrome and signs of pathological processes in nerve endings;
- inflammation in the lower back;
- feeling of weakness in the legs;
- even at rest the patient complains of severe pain in the lower back;
- in some cases the pain is so severe that the person is forced to limp;
- the legs become numb and their sensitivity may decrease;
- When climbing stairs or bending, the pain intensifies.
Most often, problems in the lumbar region occur when the 4th and 5th vertebrae are damaged, because they are the ones that experience the heaviest stress. With the simultaneous course of spondylosis and osteochondrosis, pinching of the nerve ending is possible.
Manifestations of this disease can be different. For some patients, spondylosis is of little concern and is discovered by chance during an X-ray examination in connection with another disease.
Symptoms of the disease appear depending on the location of vertebral spondylosis
The signs are quite general - intermittent back pain, which worsens when the weather worsens, fatigue, limited mobility when bending or turning the body and head. Objective examination may also not indicate a disease. The specialist may pay attention to decreased mobility in the spine or discomfort in the patient when palpating the spinous processes or during sudden movements.
In patients with severe deformation of spinal segments, symptoms are more severe. Radicular syndrome is manifested by the spread of pain in the area innervated by this nerve. With damage in the cervical region, the pain radiates to the shoulder girdle, head, arms, and with lumbosacral spondylosis - to the lower extremities and pelvic organs.
Spinal arthrosis and its treatment
Diffuse pain along the nerve does not occur immediately. A couple of weeks before this, an attack of acute local pain in the area of the damaged vertebrae may occur. Spondylosis is characterized by increased pain when standing or moving, and its attenuation when lying on the back.
We invite you to read: Hirudotherapy, treatment with leeches, indications and contraindications
Drug treatment
When the first signs of spondylosis deformans appear, you need to be examined by a therapist and some specialized specialists, such as a neurologist, vertebrologist and some others, whose consultation may be necessary. After confirming the presence of the disease, it is necessary to begin treatment without delay, since it is the early stages of the disease that, with timely measures taken, make it possible to completely stop the destructive process and get rid of the deformity. The following medications are used for treatment:
- Nonsteroidal medications intended to relieve inflammation;
- Corticosteroid drugs used in cases of severe inflammation;
- Painkillers;
- Muscle relaxants that relax muscle spasms.