The human salivary glands are designed to play a dominant role in the initial stages of the digestive process. There are three pairs of salivary glands:
- sublingual,
- parotid,
- submandibular.
They all produce about 2 liters of saliva per day. Saliva moisturizes the oral cavity, prevents the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the mucous membrane, and helps proper articulation. With its help, food enters the throat without any obstacles.
As you already understand, saliva plays an important role in human life. For normal health, not only the quality, but also the quantity of saliva is important.
Is excessive saliva a reason to panic or not?
There are several known variants of excess salivation:
- Increased salivation at night . At night, saliva should be produced much less than during wakefulness. It also happens that the salivary glands begin their work much earlier than the whole body wakes up. Then you can observe how excess liquid drains from the sleeper’s mouth. Another reason for increased saliva production at night is nasal congestion, missing teeth or malocclusion.
- Nausea and excessive salivation. This state of the body occurs during pregnancy, gastritis, and peptic ulcers. Only a specialist can determine the true cause.
- Increased salivation after eating. The following is considered the norm: when a person eats, saliva should be released, and when the meal is finished, this process should stop immediately. If you have stopped eating and your mouth is full of saliva, this may be due to the presence of worms in any of the organs.
- Excessive salivation and belching. These symptoms occur with diseases of the stomach or digestive system.
- Saliva production above normal can be observed with lacunar angina.
Video about the causes and treatments of drooling in adults
Therapy depends on the cause of increased salivation.
If underlying diseases are identified, it is necessary to undergo a course of therapy. Patients with poor dental health require oral sanitation. Depending on the severity of the case, your doctor may recommend special treatments for hypersalivation. Some techniques provoke side effects. The doctor is obliged to take into account the benefits of the procedures and assess the possible risks.
Specific methods:
- cryotherapy. Exposure of the salivary gland area to liquid nitrogen causes saliva to be swallowed more frequently. The course is long, there are contraindications;
- prescribing drugs that suppress the secretion of salivary glands. Scopolamine and Platiphylline are effective. Side effects: tachycardia, vision problems, excessive dryness of the oral mucosa;
- massage of the facial area, physical therapy for nervous disorders, consequences of stroke, neurological diseases;
- Botox injections. Drugs injected into certain areas of the glands partially block fluid production. The effect is noticeable for six months;
- selective removal of the salivary glands by surgical method. A complication is a violation of the sensitivity of the facial nerves.
The use of home remedies should be discussed with your doctor. If excess saliva is caused by dental diseases or inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, traditional medicine recipes will perfectly complement drug therapy. Sometimes rinsing alone can get rid of the problem.
Drooling in adults (the reasons are determined by a therapist or a specialist doctor to whom the patient was referred on the recommendation of a therapist) is diagnosed by a number of signs, which can be noticed during a visual examination of the patient or during the analysis of the patient’s own feelings:
- volume released in 10 min. saliva increases to 5 ml (normally this figure should not exceed 2 ml);
- frequent urge to swallow accumulated fluid in the mouth;
- cough caused by irritation of the mucous membrane by an excessive amount of saliva entering the person’s throat;
- change in taste perception (products with a pronounced taste, for example, chocolate or citrus fruits, begin to seem tasteless or bitter, salty to the patient);
- irritation of the skin around the mouth or in its corners (usually the skin becomes dry, a small rash appears, causing itching);
- wet spots on the pillow after sleep;
- nausea or vomiting (caused by excess saliva entering the throat).
The diagram lists the causes of drooling in adults.
Despite the fact that hypersalivation in mild forms does not cause much discomfort to a person, ignoring its manifestations is extremely dangerous. If excessive salivation is caused by internal diseases, then, without starting timely treatment, you can not only encounter complications of existing pathologies in the future, but also undermine your overall health.
Possible reasons
The motives for excessive salivation are not entirely clear. There may be several reasons for increased salivation. And only a doctor can accurately determine the source of the occurrence.
- Disease of the oral cavity (sore throat, stomatitis, gingivitis, etc.) Pathogenic bacteria enter the body through the oral cavity, settle on the mucous membrane and enter the salivary canals. As a result, the glands swell and inflammatory processes begin in them. In this case, hypersalivation is a kind of protective reaction to irritation of the mucous membrane.
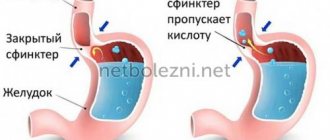
- Deviation from the norm in the state of the digestive system . If disturbances occur in the functioning of the pancreas or liver, salivation begins to be released at a reflex level. One of the common causes of hypersalivation, which is associated with the gastrointestinal tract, is increased acidity.
- There are cases when the cause of increased salivation is certain nervous diseases . With cerebral palsy, the secretion of saliva also increases, and this occurs due to impaired coordination of the oral muscles.
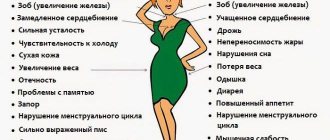
- Thyroid gland dysfunction . Hormonal imbalance usually leads to excessive salivary secretion.
- Pregnancy . In women in this position, the cause of excessive salivation may be heartburn.
- Side effects of drugs . Some medications may have the side effect of hypersalivation. The solution to the problem is to reduce the dose of the drug or completely stop it. There is no way to do this without consulting a doctor.
- Helminths (worms) . This cause most often occurs in children.
- Problems with the nasal septum or allergic runny nose.
- Special jaw structure. Improper bite or jaw closure can lead to increased salivation. Sleep disturbance.
Classification of the disease
Doctors distinguish two types of hypersalivation:
- true. Increased salivation is associated with problems within the body and the influence of negative factors. The volume of fluid in the oral cavity really exceeds the norm;
- imaginary. There are no pathological changes; the patient has convinced himself of the existence of a problem. The salivary glands work normally; there is no need for frequent fluid removal. With imaginary hypersalivation, the help of a psychologist is required.
Classification depending on the reasons causing an increased volume of saliva in the oral cavity:
- hypersalivation during pregnancy. The problem most often occurs in the first trimester with the development of toxicosis. Sometimes a false form appears, aggravated by heartburn. Excess saliva is an attempt to “fill” the acid with alkali. Due to the high concentration of calcium bicarbonate, doctors classify saliva as an alkaline medium;
- an abundance of secretion in the mouth with pseudobulbar or bulbar syndrome. Patients suffering from cerebral palsy have poor control of the oral muscles. In some cases, the volume of fluid secreted by the salivary glands per day is 10 or more times higher than normal;
- nocturnal hypersalivation. During sleep, the body weakens control over reflexes, and fluid leaks out of the mouth involuntarily. Rare cases should not cause alarm. If the problem occurs 3-4 times a week, be sure to be examined by a therapist, dentist, or neurologist;
- drug-induced hypersalivation. One of the drugs that often provokes excess saliva is Nitrazepam. The problem often arises when using antihistamines, diuretics (diuretics);
- psychogenic type of disease. The exact factors causing this unpleasant symptom have not yet been established. The problem causes significant discomfort. Patients suffering from this type of hypersalivation have to carry several handkerchiefs with them;
- a side effect for colds and viral diseases, during which nasal congestion is noted. After influenza or ARVI is cured, the volume of saliva returns to normal.
Treatment of increased salivation
If you are concerned about this problem, first of all, you need to go to a therapist.
If necessary, he will arrange a consultation with specialists of a narrower profile. The doctor will determine the predisposing factor and find out the root cause of the disease. Treatment will depend on this.
Methods used in therapy:
- suppress the secretion of salivary fluid anticholinergic drugs : riabal, platifilin, scopolamine,
- selective surgical removal of the salivary glands ,
- radiation therapy as a way to scar the salivary ducts,
- facial massage and exercise therapy are used for neuralgic disorders,
- Botox injections directly into the salivary glands will block excessive saliva production for 5 - 7 months,
- cryotherapy. A long-term treatment method that allows, at a reflex level, to increase the frequency of swallowing saliva,
- homeopathic treatment. For example, Mercurius Heel.
If no serious pathology is identified, you can try treatment with folk remedies:
- with water pepper extract after each meal;
- Lagochilus intoxicating . Rinse your mouth with a solution prepared in a water bath 2 times a day after meals;
- crushed viburnum berries are used to rinse the mouth. You can also drink viburnum several times a day, adding it to tea;
- rinsing with shepherd's purse extract ;
- drinking lemon water or unsweetened tea .
What is sialadenitis? Causes, symptoms and proper treatment.
What are the causes of dry mouth? We look for the “culprit” and get rid of the symptom.
Folk remedies
If there are no serious factors that could lead to too active salivation, then folk remedies that help normalize salivation may be useful.
There are many of them. For example, you can rinse your mouth after eating with tincture or water pepper extract, which can be purchased at the pharmacy.
You can also use a tincture of a plant such as Lagochilus intoxicating. For the same mouth rinse, you can use an infusion of viburnum in water or a tincture based on shepherd's purse herb.
For rinsing, you can use all vegetable oils , decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, and so on. You should not forget to brush your teeth, try to eat starchy foods to a minimum, and take additional vitamins. Additionally, you can drink water with lemon juice.
Traditional recipes do not always help. If there is no effect, then there is no need to waste your time. It is worth going to the doctor, as the cause may be much deeper and more serious than you think.
Increased salivation in a child
Infants
In children 3–6 months old, hypersalivation is considered common. Babies of this age drool reflexively. If teeth begin to erupt at 9–12 months, increased salivation should not frighten parents. Cutting teeth at any age is the basis for excessive secretion of fluid from saliva. Other reasons are already pathology. Excessive saliva in children can be a symptom of a concussion or head injury.
Hypersalivation in infants can be caused by gastrointestinal problems and viral infections.
Older children
The reasons for increased salivation may be the same as in infants (except for teething), plus psychological problems.
Helminthiasis is also one of the reasons for excessive salivation in children.
Salivation norms
Average salivation rate: 2 ml of fluid per 10 minutes.
Hypersalivation causes a lot of inconvenience to a person, reduces the quality of life, and provokes various complications. But how can you tell if fluid is being released in excessive amounts? To do this, it is enough to familiarize yourself with the standard indicators.
In healthy people, the salivary glands secrete about 2 ml of liquid in 10 minutes, but it does not flow out of the mouth. Any pathologies and irritants provoke the reproduction of saliva, which is noticed by increased swallowing and the desire to spit out the contents of the oral cavity.
You should contact a specialist immediately if, in addition to intense salivation, other symptoms are noted: nausea, sore throat, heartburn. Changes in the color and smell of saliva should also alert you. In a healthy person, the liquid is clear and without a characteristic odor. In some diseases, saliva becomes cloudy and foul-smelling.
Natural processes include the following cases of excessive saliva production:
- teething in babies;
- changes in hormonal levels in adolescents and women after 40 years of age;
- while carrying a child;
- when wearing dentures and decor;
- while eating.
The oral cavity is moistened around the clock to preserve normal microflora. A larger volume of saliva is secreted reflexively under the influence of certain stimuli: beautifully decorated dishes, aromatic smells coming from the kitchen.
The norm is that 2 ml of saliva should accumulate in the oral cavity within 10 minutes. In patients diagnosed with hypersalivation, the volume of fluid during the same period reaches 5 ml or more.
Etiology
Excessive salivation can be formed against the background of a wide range of various predisposing factors, which are usually divided into two large groups - physiological and pathological.
The first category of reasons includes:
- the process of food consumption - in such cases, increased salivation is necessary to facilitate the passage of the food bolus through the esophagus, and this also ensures normal digestion;
- feeling the smell of appetizing food - salivation occurs when a person feels hungry. This is also explained by the appearance of some ingredients, for example, when people see a lemon, they secrete a lot of saliva at a reflex level;
- addiction to such a bad habit as smoking cigarettes - nicotine acts as an irritant that affects the receptor apparatus;
- period of puberty – in this case, such a sign is a physiological norm;
- menopause - in addition to increased salivation, women experience increased sweating;
- unsuitable dentures that irritate the oral mucosa and receptor apparatus;
- period of intrauterine development of the fetus. Increased salivation during pregnancy is normal due to hormonal changes in the female body. It is noteworthy that such a sign disappears as imperceptibly as it appears. However, its appearance can be provoked by pathological conditions.
Increased secretion of saliva in women, men and children can be caused by the following gastroenterological pathologies:
- stenosis of the esophagus or narrowing of the lumen of this organ - this may be a consequence of the inflammatory process, the influence of chemical and thermal burns;
- inflammatory process localized in the mucous layer of the stomach - salivation is observed both with gastritis with high acidity and with low hydrochloric acid content;
- ulcerative lesions of the duodenum or stomach;
- acute or chronic pancreatitis.
Excessive salivation in a person can also be caused by a number of dental problems, including:
- stomatitis or susceptibility to inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- gingivitis or the development of inflammation in the gums;
- inflammatory damage to the tissues of the salivary glands of an infectious nature, which is also called sialadenitis.
Often this manifestation occurs due to diseases of the nervous system. This category of reasons is presented;
- stroke and vagotonia;
- Parkinson's disease;
- bulbar palsy;
- some forms of schizophrenia;
- inflammation of the trigeminal or facial nerve;
- neuroses and psychoses;
- malignant or benign brain tumors;
- oligophrenia, idiocy and cretinism.
It should be noted that increased salivation in adults and children can also be caused by:
- rabies and uremia;
- parasitic or helminthic infestations;
- vitamin PP deficiency;
- poisoning by certain chemicals that can enter the body through inhaled air, with food or liquid, or through the skin. This includes mercury and iodine, bromine and chlorine, copper and tin;
- irrational use of medications, in particular anticonvulsants, M-cholinomimetics and lithium preparations;
- diseases of the nose and kidneys, less often of other internal organs.
It is worth highlighting the reasons for the development of the main symptom in infants:
- a banal inability to swallow saliva - this condition is typical for children under two years of age. This disorder goes away on its own when the child reaches four years of age. If this does not happen for some reason, then the child should be shown to a pediatrician or ENT doctor. This need is due to the fact that excessive salivation can negatively affect speech activity;
- eruption of baby teeth is the most common factor that leads to increased production of saliva and children. It is noteworthy that in such cases, salivation will be observed during sleep.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of the disease, start with an appointment with a therapist.
If there is excessive salivation, it is worth making an appointment with a therapist. After the examination, the doctor, if necessary, will refer you for tests and to a specialist. You may also need to consult a neurologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, or parasitologist.
During the diagnostic process, a number of studies are carried out:
- examination of the patient;
- identifying associated symptoms;
- familiarization with hereditary factors;
- functional analysis, which makes it possible to determine the amount of saliva secreted.
Not all patients seek help on time. Many do not consider the problem serious or are embarrassed to bother specialists “on such trifles.” Untimely diagnosis and late initiation of therapy drive some diseases deeper and transform them into a chronic form.
To clarify the diagnosis, the therapist refers to specialized specialists:
- neurologist;
- dentist;
- gastroenterologist;
- endocrinologist;
- parasitologist
A special analysis is required to determine the volume of secretions of the salivary glands. In most patients, only a complete examination can determine the cause of the problem.
Preventive measures
Often excessive salivation is a sign of chronic pathologies or acute processes in various parts of the body. Monitoring background diseases and timely visits to the doctor for existing pathologies will help prevent this unpleasant phenomenon.
Other useful activities:
- regular oral hygiene;
- quitting smoking, or, as a last resort, reducing the number of cigarettes smoked per day to a minimum;
- visits to the dentist every six months for timely detection of diseases of the teeth and gums;
- medical examinations to monitor the condition of the body;
- food with sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals. Refusal of foods that worsen the condition of the digestive system. Reducing the consumption of food that provokes an abundance of plaque on the teeth, tongue, and gums;
- prevention of helminthic infestations, personal hygiene.
Increased salivation (hypersalivation) in people has various causes. If a problem is identified, do not treat yourself: without eliminating the provoking factors, it is impossible to get rid of the pathology. During therapy, follow your doctor's recommendations. Remember: only an integrated approach to the treatment of hypersalivation will give results.
Don't ignore regular dental checkups!
In order to prevent pathologies that provoke increased salivation, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- perform hygiene procedures in a timely manner, including the oral cavity;
- once every six months, undergo a preventive examination at the dentist, have your teeth professionally cleaned;
- review your diet, use more fresh vegetables and fruits to enrich the body with vitamins and microelements (you should give up salty, smoked and fatty foods);
- lead an active lifestyle, relax in nature, visit fitness centers;
- to refuse from bad habits.
If excessive salivation is a symptom of any disease, you need to undergo medication prescribed by your doctor. Eliminating the problem in this case depends on complete recovery.
If salivation increases, you should immediately seek qualified help. It is easier to eliminate any problem if you start treatment at the initial stage.
Associated symptoms and what they mean
Hypersalivation (also called increased salivation) is characterized by the following symptoms:
- frequent characteristic swallowing movements, creating neurosis in the patient;
- streams of saliva flowing from the mouth, often at the corners of the mouth;
- irritated skin of the chin;
- This phenomenon may also be accompanied by a pustular rash on constantly moist skin.
It is worth keeping in mind that there are:
- True hypersalivation, in which saliva production exceeds the norm of one ml in five minutes.
- False, which occurs due to difficulty swallowing liquid due to certain diseases. For example, sore throat, Parkinson's disease, etc.
False hypersalivation is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. By this feature it can be distinguished from the true form.
How do you understand that the glands in the mouth are working more actively than nature intended?
Characteristic features:
- at short intervals there is a desire to spit out the accumulated saliva even in the absence of appetizing dishes nearby;
- after sleep, the patient discovers a spot on the pillow with secretions of the salivary glands;
- In children, it is difficult not to notice profuse drooling: a constantly wet mouth, wet clothes in the chest area.
Nausea is one of the common accompanying symptoms of hypersalivation.
Hypersalivation is often accompanied by additional symptoms:
- feeling of nausea;
- heartburn, belching;
- difficulty and pain when swallowing food;
- temperature increase;
- general physical weakness;
- signs of intoxication;
- changes in the functioning of taste buds.
There is also a decrease in human activity, a deterioration in the psycho-emotional background due to discomfort associated with intense saliva production. With excessive salivation and sore throat, redness is visible, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
Hypersalivation is manifested in particular by drool appearing in the corners of the mouth. At night, salivary fluid leaks onto the pillow.
Increased salivation and thirst can be symptoms of diabetes.
Diagnosis is carried out taking into account associated factors, which, in combination with hypersalivation, indicate a specific problem.
Excessive production of salivary fluid with constant nausea indicates problems in the digestive system or pregnancy. When the cause is eliminated, the functionality of the glands is quickly restored.
In combination with thirst, increased salivation indicates the likelihood of developing diabetes. Problems in the larynx (severe tonsillitis, sore throat) are also possible.
The feeling of a lump in the throat with intense saliva production signals inflammation occurring in the larynx. Sometimes a lump in the throat prevents you from swallowing liquid, causing pain. Most often, the cause lies in the following diseases: sore throat, stomatitis, purulent tonsillitis, abscess. If the symptom of increased salivation is complemented by an increase in body temperature, fever, and swollen lymph nodes, you should not hesitate. Delaying treatment allows complications to develop that threaten the patient’s life.
Also, a lump in the throat with strong salivation is felt with obstruction of the esophagus and volvulus. In this case, nausea and pain in the abdominal cavity are noted.
Causes of excessive salivation
What does it mean? When saliva is secreted very profusely, that is, more than is sufficient, we speak of increased secretion, or so-called hypersalivation.
There are several factors that contribute to the development of this condition:
- the use of certain medications, the side effect of which may be increased salivation;
- metabolic disorder;
- neurological diseases;
- acute poisoning or toxic infection;
- otorhinolaryngological pathologies.
The causes of increased salivation in adults are usually associated with diseases of the digestive system and neurological disorders, and the causes of increased salivation in children are with acute respiratory viral infections and chronic diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, adenoiditis, sinusitis, otitis media). Increased salivation in children under one year of age is most often the norm.