When opisthorchiasis is diagnosed, treatment and medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Tablets for opisthorchiasis of synthetic origin. They include many side effects and contraindications. However, they have an important advantage - they help get rid of the infection in a short time.
The treatment is complex, which involves the use of anthelmintic and choleretic drugs, enzyme preparations, as well as medications that affect the motility of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
How dangerous is opisthorchiasis and why treat it?
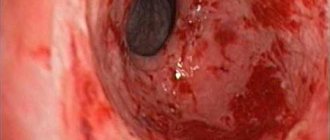
Opisthorchids are distinguished from many other helminths by their inability to reproduce in the host’s body. Instead, the worms lay eggs, which are released naturally in the feces. The main danger of parasites and their eggs is that they clog the bile ducts and can cause cholelithiasis. Patients with opisthorchiasis also develop:
- Anemia. Worms feed on blood and mucous secretions of the bile ducts. Because of this, digestion is disrupted, and nutrients do not reach the organs and systems in the required volumes.
- Ulcers. With their suckers, helminths injure the mucous membrane of the organs in which they parasitize. The bile and contents of the digestive tract eat away at these injuries, resulting in painful ulcers.
- Narrowing of the bile ducts and impaired intestinal motility. These complications of opisthorchiasis are caused by thickening of the mucous membranes due to the constant irritating effects of worms.
- Anaphylactic shock. A consequence of an excessive immune response to exposure to toxins and the parasites themselves. In the absence of help, it leads to death.
The likelihood of complications directly depends on the duration of opisthorchiasis. Therefore, at the first signs, it is recommended to carry out the necessary examinations in a hospital setting and select drugs to combat opisthorchiasis.
Causes of opisthorchiasis
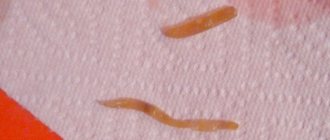
The culprits of this dangerous disease include two types of trematodes. Their structure consists of a flat body with a sucker in front and a similar organ on the abdominal cavity. The larvae of the parasite are pale yellow in color. Sexually mature trematodes are mainly found in the bile ducts and all organs in one way or directly connected with them in humans, cats, dogs, foxes, and arctic foxes. Their intermediate link is mollusks.
Opisthorchiasis is a natural disease. The danger comes from infected people and carnivorous animals. Trematode eggs, which are excreted in the feces of these infected living creatures, end up in fresh water bodies. There they are swallowed by Bithinia mollusks. It is in them that larval opisthorchists develop and reproduce without sexes; they ultimately, having a tail consisting of cercariae larvae, swim out into the water spaces. After the penetration of cercariae into cyprinid fish, their gradual transformation into metacercariae begins.
Rating of drugs for opisthorchiasis
Medicines to get rid of helminths are prescribed by a doctor. Most often, the drug is in the form of tablets, but in some cases emulsions are used. Tablets for opisthorchiasis are selected according to contraindications and possible side effects. You also need to take into account the patient’s age and the complexity of dosage calculation.
Wormil
A popular drug for opisthorchiasis based on albendazole. Causes disruption of metabolic processes in adult parasites, larvae, and eggs. Adults are prescribed tablets, children - syrup. The dosage depends on the patient’s weight; the medicine is taken under the supervision of a doctor according to a developed regimen. When compiling it, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account.
Contraindications to taking this medicine for opisthorchiasis are age under one year, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and individual sensitivity to substances in the composition of the drug.
Praziquantel
A broad-spectrum drug that paralyzes the muscle activity of worms. It is used both as a medicine for opisthorchiasis and to destroy other types of helminths. The dosage is calculated once; 25 mg of medication should be given per 1 kg of patient weight. Take 3 times a day for three days.
Contraindications include pregnancy and lactation, the presence of any parasites in the eyeballs, as well as cysticercosis and liver failure.
Biltricide
An effective remedy for opisthorchiasis and other helminthiasis. The active substance is praziquantel, which makes the drug an analogue of the drug of the same name.
Treats opisthorchiasis by improving the conductivity of calcium into the cells of the parasite. This causes lactic acid poisoning of the worms.
The dosage is selected according to weight, the administration lasts from one to three days. Contraindications are age under 4 years, pregnancy and cysticercosis, as well as individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Chloxyl
Anthelmintic medicine in tablet form. The active ingredient is hexachloroparaxylene. The dosage is calculated based on the patient’s weight. The action of the drug against opisthorchiasis is based on the suppression of the muscle and nervous activity of adult parasites. Contraindications to the use of the drug are pathologies of the cardiovascular system and liver.
Populin
A herbal remedy based on aspen bark and hill solyanka. The mechanism of action is similar to praziquantel, so the drug is used as an analogue for allergies to the original medication.
Populin is intended for the treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults and children over 4 years of age. Contraindications are disturbances in the functioning of the hepatobiliary system. For adults, use lasts a month; a dose of syrup is diluted in half a glass of water. For adults, a teaspoon of the substance is required, for children under 6 years of age, 1 g of the drug is needed, at the age of 7-12 years, 2 g are prescribed 3 times a day. Children take medicine for opisthorchiasis for a week.
Nemozol
Suspension and tablets based on albendazole. Gently cleanses the bile ducts and digestive tract from adult parasites, eggs, and larvae. Children are prescribed a suspension of 20 ml three times a day for 3 days. Adults take tablets, calculating the dosage by weight.
Contraindications to taking the medicine are cardiovascular pathologies, elevated levels of liver enzymes in the blood, and retinal diseases.
Albendazole
The mechanism of action of this drug against opisthorchiasis is to block glucose metabolism in the tissues of the parasite. Adult opisthorchids, as well as their eggs and larvae, are exposed. When taking it, be sure to use choleretic medications, since the remaining drug is excreted through bile.
The dosage form is a suspension, which makes dosage easier for children. For adults, the drug is supplied in the form of chewable tablets. Contraindications include liver failure and cirrhosis of the organ, as well as periods of pregnancy and lactation, children under 2 years of age.
Ecorsol
The product is similar to Populin - also made from aspen bark and hill solyanka. Belongs to the category of dietary supplements, often prescribed in addition to the main treatment of opisthorchiasis. Admission is allowed from 3 years of age; it is prohibited to take the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
The dosage is calculated according to age. Adults take 3 teaspoons three times a day; children from 6 to 12 years old need 2 teaspoons. Children under 6 and over 3 years old drink 1 teaspoon of the drug. The course of treatment lasts 7-30 days depending on the severity of the disease.
Biosinol
The Chinese dietary supplement is available in capsules. Contains an extract from aspen bark, as well as the patented biomodule “Dienay S”. Take 1-2 capsules 2 times a day for 2-3 weeks. This supplement is prohibited for children, pregnant and lactating women, and people with purine metabolism disorders.
Opisthorchiasis: herbal treatment
There are many fishing enthusiasts in our country, but not all of them know the dangers of not following the rules for preparing the catch. Freshwater fish are often infected with a trematode known as the liver fluke or cat fluke, which causes a natural focal disease, opisthorchiasis, with extreme prevalence in river basins where fish from the carp family live.
- Epidemiology
- How and by what signs to determine the disease?
- Diagnostics
- How is opisthorchiasis treated?
- Diet
- Drug therapy
- Herbal treatment
- Kvass from celandine
- Garlic with milk + herbs
Epidemiology
Humans, dogs, cats are the main sources of infection. Infestation occurs when eating poorly salted or insufficiently cooked or fried fish. In the human body, parasites cause traumatic damage to the gallbladder and ducts, duodenum, pancreas and liver with the formation of cysts, stenoses, ulcers and erosions; helminth eggs are laid in them, which are subsequently excreted along with feces and, ending up in fresh water, mature to the larval stage.
Mollusks and snails (the first intermediate hosts) swallow them, providing an opportunity for the transformation of the larvae into the next stage, which, in turn, awaits the second intermediate host - freshwater cyprinids, here the parasite matures to an invasive state. Cats, dogs, other fish-eating animals and humans receive the causative agent of opisthorchiasis from raw fish, becoming the definitive hosts.
How and by what signs to determine the disease?
The incubation period lasts about three weeks. The clinical picture of opisthorchiasis in immigrants differs from the disease of indigenous residents of endemic areas in its severity and severity of clinical manifestations. In the latter, primary-chronic forms are more often observed, expressed in the form of biliary dyskinesia, chronic cholecystopancreatitis.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular...
Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach...
Acute opisthorchiasis can occur easily with low fever and weakness; after a couple of weeks the condition improves and the disease enters the chronic stage. But there are also severe forms:
- typhus-like;
- gastroenterocolitic;
- hepatocholangic.
With the typhus-like variant of opisthorchiasis, a person develops:
- severe fever;
- chills;
- skin rashes;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- severe headache;
- weakness;
- myalgia;
- arthralgia;
- cough.
The hepatocholangic variant is distinguished by such symptoms as:
- liver damage;
- pancreas;
- biliary tract – jaundice;
- hepatomegaly;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- girdle pain or in the right hypochondrium.
The gastroenterocolitic variant is manifestations of:
- colitis;
- enteritis;
- gastritis and duodenal ulcers, that is, pain, nausea, stool disorders.
After 2-3 weeks, the symptoms subside; if no treatment is given, then opisthorchiasis becomes chronic, which can last for years, manifesting itself as chronic gastroduodenitis, colitis, chronic cholecystitis and pancreatitis; a secondary infection may occur with the development of hepatitis, intestinal infections, and so on. .
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis based on the detection of eggs in feces is possible only no earlier than 1 - 1.5 months from the moment of infection; before this, when making a diagnosis, they rely on the history and clinical manifestations of the disease; preliminary confirmation of infection is possible through blood tests (biochemistry, serological tests).
How is opisthorchiasis treated?
Diet
They start with a diet. Treatment table No. 5 according to Pevzner (hepatic) is suitable, which involves split meals in small portions with the exception of:
- fried;
- fat;
- salty;
- smoked products:
- sweets.
And the inclusion of steamed, boiled, vegetable and fermented milk products in the diet.
Drug therapy
Anthelmintic drugs are prescribed by a doctor taking into account the patient’s age, the severity and duration of opisthorchiasis, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The treatment is carried out in a hospital, is staged, requires preparation (the first stage), then taking praziquantel (Biltricid), then a long rehabilitation period to restore the impaired functions of the stomach, intestines and liver, since the drug "Biltricid" is quite toxic, its use does not work without a trace for the human body.
Alternative medicine
Herbal treatment
Treatment of opisthorchiasis with folk remedies (herbs) is carried out in a common tandem of medical measures. Medicinal plants help restore the function of affected organs after the main course of medication.
Herbal preparations with enveloping, anti-inflammatory and choleretic effects are used. For example, in equal parts (one teaspoon each):
- St. John's wort;
- tansy;
- red clover;
- agrimony;
- thyme;
- wormwood;
- peeled green pumpkin seeds.
All raw materials are mixed, poured with a liter of boiling water, infused for at least three hours, after straining, take half a glass a day before meals for a year.
Kvass from celandine
Opisthorchiasis is also treated with kvass from celandine; this unpretentious plant is found anywhere. Kvass is prepared like this:
- one glass of washed and chopped plant is wrapped in gauze with a piece of flint stone;
- place at the bottom of a three-liter glass container;
- pour a glass of sugar;
- add a tablespoon of sour cream;
- top up with whey and leave in a warm, dark place for two weeks.
The course is half a glass three times a day before meals, until the kvass runs out.
Garlic with milk + herbs
Another recipe is widely known: treatment of opisthorchiasis with a decoction of garlic in milk (3 cloves per glass). For three days, drink in the morning 2 hours before meals. After this, they continue the course with herbs:
- mix one teaspoon each of yarrow herb, wormwood and 3 cloves;
- pour a liter of water;
- boil in an enamel container for 10 minutes, then cool, strain through cheesecloth.
Drink 1 glass in the morning before meals for three days. After 14 days, repeat the course. The next step is to eat a tablespoon of raw pumpkin seeds, ground in a coffee grinder, in the morning on an empty stomach for 6 months.
Conclusion
Opisthorchiasis mainly affects the liver and bile ducts, so it is advisable to include the use of tubes in treatment to improve the outflow of bile. There are special anti-parasitic programs using natural raw materials (pumpkin, cloves, black walnuts), which have proven themselves well in adults and children over 7 years old.
There are many folk recipes, however, it should be remembered that opisthorchiasis is a serious helminthiasis; treatment requires complex medications and herbs with a long rehabilitation period and always under the supervision of doctors.
source
How to increase the effectiveness of treatment: auxiliary therapy
Along with anthelmintic therapy, drugs are prescribed that minimize the side effects of the main drugs. The doctor must prescribe:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Nimesulide. They stop fever and relieve inflammation caused by opisthorchiasis.
- Hepatoprotectors. These drugs protect the liver from toxic effects, and also accelerate the recovery of its cells - hepatocytes. It is recommended to take them at least three times a day throughout the entire course of treatment for opisthorchiasis. Examples: Essentiale forte, Essliver, Karsil, Tykveol, L-Carnitine, Antral, Heptral.
- Antihistamines - Suprastin, Loratadine, Erius, Claritin, Zyrtec. Taking these drugs clears up an allergic rash due to hospithorchiasis, relieves nasal congestion and stops lacrimation. They should be taken until all allergy symptoms disappear.
- Additionally, choleretic agents are prescribed - cholekinetics (Xylitol, Sorbitol, magnesia, as well as vegetable oils, for example, olive). They accelerate the leaching of parasites and their eggs from the bile ducts.
- In case of exhaustion as a result of opisthorchiasis, multivitamin complexes (Duovit, Multitabs) and enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin) are prescribed, which accelerate the absorption of nutrients from the digestive tract.
Trying to get rid of opisthorchiasis on your own is undesirable. It is better to get tested and undergo a full course of treatment on the recommendation of a doctor.
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease that is caused by a trematode worm, which has another name - cat fluke. Worms pose a danger to the liver and gall bladder, in which they parasitize. Moreover, the disease is really serious and dangerous, because the final host of these worms can be any carnivorous animal, including humans. But opisthorchiasis will have to be treated using a whole range of drugs.
Treatment
The doctor prescribes therapy and selects a treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis. Self-medication is unacceptable.
It is possible to get rid of the disease, but if it is re-infected, treatment and recovery will take longer.
Drug treatment of opisthorchiasis
Photo from parazitsos.ru
The basis of treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults is antiparasitic drugs. Chloxil, Praziquantel and Biltricide are effective. By adhering to the treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis, the parasites can be eliminated in 2-3 days. If necessary, re-therapy is allowed no earlier than after 4-6 months.
Before starting antiparasitic treatment of opisthorchiasis, preparation is necessary, which includes medications from other groups:
- hepatoprotectors – Karsil, Hepatrin;
- choleretic - Odeston, Kholagol, Allochol;
- antihistamines – Suprastin, Tavegil;
- digestive enzymes – Pancreatin, Creon;
- anti-inflammatory drugs - Ascorutin, Butadione.
Opisthorchiasis takes a long time to be treated, usually in a hospital. After recovery, the patient faces a long period of rehabilitation, about 2-3 months. The same anti-inflammatory, choleretic drugs, and agents that support liver function are prescribed.
Based on the high risk of re-infection over the next 3 years, the patient should be observed by a parasitologist.
Traditional methods of treating opisthorchiasis
Folk remedies do not get rid of parasites, but enhance the effectiveness of the main treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults. The following recipes can be used:
- tincture of aspen measles - 50 g of raw material, pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave for 2 weeks, drink 1 tbsp. l. 3 weeks;
- St. John's wort decoction – 1 tbsp. l. Brew in 500 ml of boiling water;
- chanterelle mushroom tincture – 1 tsp. raw materials pour 150 ml of vodka, leave for 3 weeks, and then drink 1 tsp. for the night.
It is worth coordinating traditional medicine with your doctor in advance.
Diet for opisthorchiasis
Dietary nutrition for opisthorchiasis is not much different from the usual. It is necessary to eat vegetables, herbs, fruits, berries, cereals, dairy products, and include butter and sunflower oil in the menu.
Excluded from the diet:
- alcohol;
- coffee, cocoa, chocolate;
- fatty meats, poultry, fish;
- margarine;
- baked goods, flour products;
- hot spices;
- smoked meats
It is important to adhere to the diet even after completing the course of treatment for opisthorchiasis.
Treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis
Only a specialist can determine helminthic infestation and its type, so if the following symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- malaise, as during a cold;
- allergic skin reactions;
- disturbances in the digestive tract;
- increased body temperature;
- the liver enlarges and this is felt upon palpation.
These signs indicate that the disease is in an acute stage, from which this disease is determined. If treatment is not started when such symptoms appear, the disease will become chronic. Its main feature is that the symptoms of the acute stage subside during it and it seems that the disease has passed on its own, but it still continues to progress. The almost complete absence of symptoms is the main danger of the chronic stage. However, opisthorchiasis is also treated during it.
Before starting treatment, tests are prescribed to determine the type of invasion and its stage. There are only two main diagnostic methods:
- A general blood test, during which the very presence of helminthic infestation is determined.
- Analysis of stool for helminth eggs or traces of their vital activity.
The complex of drugs and dosages will be selected individually for each patient, taking into account his age, weight, individual characteristics and contraindications. Therefore, it is very important not to engage in treatment on your own, but to do everything strictly as prescribed by the doctor and be under his supervision. The entire therapy in this case usually takes no more than two weeks, but depending on the severity of the disease, it can take several months.
Special symptoms of opisthorchiasis in women
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
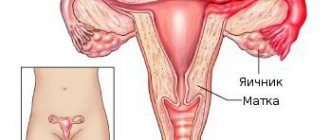
Opisthorchiasis is a complex systemic disease, during which flatworms enter the human body, conduct their life activities there and disrupt the integrity and functions of internal organs and systems. The liver, pancreas, gallbladder and choleretic ducts are at risk.
Speaking about women, the course of the disease and possible complications may differ slightly, but one fact remains unchanged - the disease requires immediate medical treatment.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in women: features of symptoms
The first characteristic symptoms of opisthorchiasis in women may appear 2-3 weeks after infection:
- mild symptoms: increased body temperature (up to 38 degrees), which lasts 1-2 weeks;
- severe parasite damage: fever up to 39 degrees, pain in joints and muscles, skin rash, loose stools and vomiting;
- acute form: intense headaches, sleep disturbance, agitation or inhibition;
- with liver damage: enlarged lymph nodes, bloating, pain in the right hypochondrium;
- chronic form: nausea, refusal to eat fatty foods, bitterness and dryness in the mouth, abdominal pain, refusal to eat.
For women with this diagnosis, depressive states are typical, which negatively affects the condition of the whole organism. A peculiarity of the signs of opisthorchiasis in women is the fact that the disease provokes an exacerbation of pain during menstruation. In addition, the menstrual cycle will be constantly disrupted, which also negatively affects the female organs.
Why is opisthorchiasis dangerous for women's health?
For women, opisthorchiasis is dangerous because with increased intensity of infestations, parasites can provoke the development of serious diseases, for example, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, stomach ulcers, gastritis, and heart problems.
If opisthorchiasis becomes chronic, it can provoke disorders of the nervous system, which leads to sudden changes in mood, depression, sleep disturbances, increased irritability and confusion.
In general, doctors say that opisthorchiasis increases the risk of miscarriage or early labor. Also, during lactation, a parasitic infection will negatively affect milk production, so in this case the woman needs hospitalization and immediate treatment.
Treatment methods
Opisthorchiasis is a systemic disease, so it is treated using a complex method. The infectious disease specialist will divide the entire course of treatment into three stages:
- Preparation. At this stage of time, with the help of various medications, a woman is helped to cope with the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, namely inflammatory processes, allergies, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. The woman is prescribed a special diet that reduces the consumption of fatty foods.
- Deworming. At this stage of treatment, the infectious disease specialist prescribes antiparasitic medications, taking into account the toxic effects and stage of development of the disease. Usually this treatment is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
- Restoration of the body. The doctor prescribes additional medications that will help improve the functioning of the damaged internal organs after the life of the parasites. These can be various enzymes, probiotics and prebiotics. They also prescribe a course of immunomodulators and vitamins that will restore the body’s protective functions.
A more detailed list of medications and correctly prescribed regimens for taking them are indicated in the previous article.
Protecting yourself from opisthorchiasis
And all preventive measures are based on the fact that the source of opisthorchiasis is fish.
- When cooking fish, you should adhere to the processing rules: heat treatment for at least 25 minutes, salting - 300 grams of salt per 1 kg of fish for 3 weeks, drying - at least 3 weeks.
- In the process of cleaning and cutting fish, you need to use separate tools, after which they are thoroughly washed with detergents.
- You should avoid buying fish from unknown sources. In stores, the fish undergoes checks and receives a certificate for permission to be sold.
- You should avoid eating raw fish.
- For prevention purposes, you should regularly take prophylactic antiparasitic drugs.
Doctors strongly recommend that the whole family take antiparasitic drugs at least once every six months for prevention purposes.
Diet
Treatment of opisthorchiasis does not begin immediately with taking medications, but with a diet that will help prepare the body for a course of medications. The diet is not strict and consists of the following measures:
- sweets are temporarily excluded;
- Food that is too fatty and heavy is also not suitable;
- high carbohydrate content is excluded (that is, it is not recommended to eat bread, potatoes, cereals);
- consumption of vegetables and fruits is encouraged;
- more dairy products;
- more acidic foods, for example, berries;
- Foods containing a lot of fiber are great for your diet (for example, beans, rice, greens, nuts).
First stage
Depending on the severity of the disease, the following groups of drugs are initially prescribed:
- Antihistamines. It is best to use the latest generation of drugs that act faster, without containing substances that cause side effects. These medications are needed to get rid of allergic reactions.
- Choleretic drugs are used in the severe stage. Among them are choleretics and cholekinetics.
- Antibiotics. Often parasitic infestations cause inflammatory processes due to bacterial infection.
In this case, additional saline solutions and gemodeses can be prescribed to protect against severe intoxication of the body. Mezim, Penzital and other medications that normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract will also be useful. Smecta and other enterosorbents will be needed if absorption in the small intestine is impaired. The preparatory part, depending on the severity of the disease, the patient’s condition and concomitant diseases, which may include cholecystitis, pancreatitis and even hepatitis, can last from 10 days to 3 weeks.
Basic treatment
Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease, so it requires potent medications.
And the more advanced the disease, the more drugs are needed to combat it. At the same time, the acute and chronic stages are usually treated with the same medications, however, auxiliary ones may differ in the amount and strength of the effect.
As a positive point, it can be noted that the list of drugs used in most cases is small. Moreover, a repeat cycle is usually not required and the helminths die in one go. This happens due to the fact that all of the medications presented below are quite toxic not only to humans, but also to parasites. Therefore, one application is more than enough.
Praziquantel
This is one of the most effective medicines used to treat opisthorchiasis. The active substance affects the metabolism and nervous system of parasites, causing paralysis. Because of this, the parasites die.
The dosage is calculated individually depending on the age and weight of the patient, and due to the fact that the drug is potent, it is usually taken for only 1 day. For the same reason, it is recommended that they undergo treatment in a hospital in order to carefully monitor the occurrence of side effects and provide timely assistance to the patient. You can also take the drug for prevention.
Praziquantel is not used:
- Children under 4 years old.
- People with liver disorders.
- Pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Side effects that Praziquantel may cause are:
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- headache and dizziness;
- disorientation, loss of attention;
- sweating;
- attacks of fever;
- skin allergic reactions;
- drowsiness.
The drug is potent, so it is important to follow all dosages and doctor’s instructions exactly. Treatment regimens will always be very different between adults and children. You will have to change your diet, which will need to be continued during the entire course of treatment, so that the substances in the products do not react with the components of the medicine.
Biltricide
Biltricide has the same effect on parasites as Praziquantel. It also affects the metabolism and nervous system of helminths, leading to paralysis and subsequent elimination from the body. This happens due to the fact that Bitricide contains the same active ingredient as Praziquantel. It’s called praziquantel. Biltricide, unlike Praziquantel, is usually used not for one day, but for several. The tablets, each containing 600 mg of the active substance, have special grooves. Thanks to them, these tablets for opisthorchiasis can be divided into equal parts and dosages.
It is taken orally, washed down with water and eaten with a small amount of food, usually a piece of bread. On the second day of taking the medicine, duodenal or blind intubation is prescribed to remove helminths. After this, you can begin the third stage - recovery.
The contraindications of the drug are similar to Praziquantel, and the adverse reactions are as follows:
- Headache and dizziness.
- Weakness, sadness, emotional instability.
- Impaired coordination of movements and problems with orientation in space.
- A feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, vomiting (the doctor will need to tell you the exact time of vomiting).
- Temperature.
- Allergic rashes.
- Bad dream.
If these side effects occur, the doctor may prescribe additional sorbents. Usually this is provided for at the stage of selecting medications, and if the body cannot cope with such serious drugs, the doctor will not prescribe them and will choose something easier.
Useful video about the symptoms and treatment of opisthorchiasis in adults
List of sources:
- Beer S.A. Biological aspects of the problem of opisthorchiasis // Parasitology. 1977. T. 11. No. 4. P. 289-299.
- Beer S. A. Opisthorchiasis // Human helminth infections: Epidemiology and control / F. F. Soprunov, E. S. Shulman, E. S. Leikina, etc.; Ed. F. F. Soprunova (USSR-SRV). - M.: Medicine, 1985. - P. 102-119. — 368 p. — 9000 copies.
- Beer S. A., Belyakova Yu. V., Sidorov E. G. Methods for studying intermediate hosts of the causative agent of opisthorchiasis / Academy of Sciences of the KazSSR, Institute of Zoology. - Alma-Ata: Science of the KazSSR, 1987. - 88 p.
- Beer S. A. Biology of the causative agent of opisthorchiasis. - M.: T-vo scientific publications KMK, 2005. - 336 p. — 500 copies. — ISBN 5-87317-204-8.
- Bocharova T. A. The causative agent of opisthorchiasis and other muscle parasites of carp fish in the Lower Tom basin. - Tomsk: Tomsk State University Publishing House, 2007. - 66 p.
- Pustovalova V. Ya., Stepanova T. F., Shonin A. L. Opisthorchiasis. - Tyumen: Publishing house TGMA, 1999. - 10 p. — ISBN 5-93574-040-0.
- Sidorov E.G. Natural focality of opisthorchiasis / Responsible. ed. E. V. Gvozdev; Academy of Sciences of the KazSSR, Institute of Zoology. - Alma-Ata: Science of the KazSSR, 1983. - 240 p. — 1700 copies. Review
- Zerchaninov L.K., Shpilko V.N. Opisthorchiasis and diphyllobothriasis. — Tyumen: Book. publishing house, 1963. - 24 p.
- Ilinskikh E.N., Novitskiy V.V., Ilinskikh N.N., Lepekhin A.V. [[1] Invasions of opisthorchis felineus (Rivolta, 1884) and metorchis bilis (Braun, 1890) in humans in various regions of the Ob-Irtysh river basin] (Russian) // Parasitology: journal. - St. Petersburg: Nauka, 2007. - T. 41, issue. 1. - pp. 55-64.
Albendazole
Albendazole has a milder effect on the human body than the first two drugs.
The active ingredient of this medicine is called albendazole, and is found in a concentration of 400 g per tablet. Also, due to its mild effect, Albendazole has more approvals for use. So, children can take it not from 4 years old, but from 2. Pregnant women and nursing mothers still remain at risk. Also, the drug should not be taken by patients with cardiovascular diseases and intolerance to certain components of the drug. Side effects include:
- headache and weakness;
- nausea, vomiting, acute abdominal pain;
- skin rash, itching.
Since Albendazole is a mild medicine, it is used only in cases where the disease has not developed into a severe stage and has not spread greatly. Medicines against opisthorchiasis with similar effects are Vormin and Vermox. Of all three drugs presented, Albendazole is the most inexpensive.