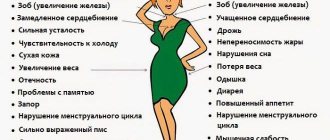
Main symptoms:
- White spots on the oral mucosa
- White curdled vaginal discharge
- White plaque on the genitals
- Pain during intercourse
- Burning in the vagina
- Seizures in the corners of the mouth
- Itching in the vagina
- Skin erosions
- Itchy skin
- Crusts on lips
- Getting wet
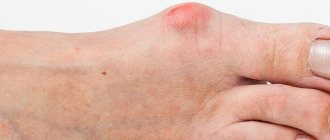
- Swelling of the nail folds
- Redness of the skin at the site of the lesion
- Redness of the nail folds
- Redness of the penis
- Redness of the oral mucosa
- Bubbles on the head of the penis
- Scales on the skin
- Scales on the oral mucosa
- Peeling skin
Skin candidiasis is an infectious disease that develops as a result of damage to certain areas of the skin by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Many people face a pathology such as skin candidiasis. The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida, which actively develop on the skin or mucous membranes, causing one or another symptom.
Online consultation on the disease “Skin Candidiasis”.
Ask a question to the experts for free: Dermatologist.
- Causes
- Forms and symptoms
- Establishing diagnosis
- Features of treatment
Hundreds of varieties of fungus live both on the human body and on surrounding objects - in the soil, on animal hair, on food, etc. Therefore, infection can occur in a variety of ways, and the fungus affects both adults and children, regardless of floor.
There are several main forms of development of candidiasis, which depend on the location of the fungus, these are:
- skin candidiasis;
- mucous membranes;
- genitals;
- intestinal candidiasis.
In addition, there is a generalized form, in which the fungus spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body, affecting various organs. Often generalized candidiasis has a chronic course.
Causes and risk factors
The causative agent of skin candidiasis is yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. They belong to opportunistic microflora and normally live on the mucous membrane of the vagina, mouth, intestines, and also on the skin. Activation of a fungal infection and the development of the disease occurs in the event of a decrease in the general defenses of the body and disruption of normal microbiocenosis.
Risk factors for the development of cutaneous candidiasis are:
- metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity, dysproteinemia);
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- chronic somatic diseases;
- hypovitaminosis conditions;
- hyperhidrosis;
- therapy with antibiotics, corticosteroids or cytostatics;
- vaginitis;
- taking oral contraceptives.
There are also a number of environmental factors, the influence of which increases the risk of developing cutaneous candidiasis. These, first of all, include high humidity and elevated ambient temperatures, which create optimal conditions for the life of fungi of the genus Candida and help the infection to become active. That is why skin candidiasis is often diagnosed in dishwashers, housewives, bathhouse and swimming pool workers. Similar conditions conducive to the development of fungus on the skin are created when wearing clothes made from artificial fabrics that do not allow air to pass through.
Skin candidiasis is often detected in confectionery workers. Fungi are present in considerable quantities in the raw materials used in confectionery production. In conditions of high ambient temperature, skin sweating increases, which creates favorable conditions for the development of mycotic lesions. The prerequisite for their occurrence is the systematic maceration of the skin of workers’ hands with organic acids (malic citric, lactic) and sugary substances.
Complex therapy for skin candidiasis includes a diet low in carbohydrates, especially easily digestible ones (sugar, confectionery, honey).
Peculiarities
Cutaneous candidiasis is an infectious fungal disease with superficial lesions of the skin. Most often, cutaneous candidiasis is caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans. In rare cases, other varieties of Candida fungus are found - stellatoidea, tropicalis, parapsilosis, guillermondi, kursei and pseudotropicalis.
This pathogen belongs to an endogenous infection of an opportunistic nature, i.e. it can remain in the human body for a long time, without showing itself in any way, but becoming more active when favorable conditions are created. Thus, the presence of the fungus Candida albicans in the gastrointestinal or oropharyngeal microflora is considered common, but this microorganism does not live long on the skin of a healthy person. The situation changes in the presence of provoking factors that turn the fungus into a pathogenic pathogen.
An environment with a pH of 6.1-6.6 is considered optimal for Candida. At the same time, they are able to tolerate very acidic environments with a pH of 2.4-3.1 for a long time, while only their activity slows down slightly. The fungus prefers a temperature of 26-29 °C, which is optimal for its development, but exists quietly at 4-42 °C. When boiled, the parasite dies within 1-2 minutes.
Thus, skin candidiasis is generated, as a rule, by its own pathogens, which have been in a latent state for a long time inside the body. Their penetration occurs almost immediately after birth or in the mother’s womb, which explains the possibility of the disease at any age under the influence of a number of factors. Naturally, infection can also occur through direct contact with an infected person, most often through sexual contact. Skin candidiasis itself is a reflexive reaction of the body to the active activity of the pathogen, which leads to an inflammatory process and damage to the skin tissue.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the location of the lesion, cutaneous candidiasis is divided into the following forms:
- candidiasis of the skin of the genital organs (usually occurs in combination with damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs);
- candidiasis of large (inguinal, axillary) skin folds (candidal intertrigo);
- candidiasis of the skin of the feet, hands and interdigital spaces;
- candidiasis folliculitis – mycotic infection of the hair follicles of the scalp, armpit, mustache and beard (candidiasis of the facial skin);
- diaper dermatitis - affects the skin of the perineum in infants and bedridden patients when using diapers (the most common form of skin candidiasis in children);
- bandage cutaneous candidiasis - occurs on the back of bedridden patients, as well as under plaster casts when the skin is wet (especially in patients with diabetes).
Treatment of the disease with medications
Candidiasis in children (so-called diaper dermatitis). Accompanied by weeping skin, swelling, and tumors.
For superficial skin candidiasis and its mild course, local remedies that can be applied to the skin are sufficient. These can be various ointments and creams, lotions and solutions. Good results are obtained by such products as Pimafucin, Lamisil, Econazole, Miconazole, and nystatin ointment. A solution of Clotrimazole, aniline dyes, borax, etc. helps very well. Ointments for candidiasis are applied to the lesions in the morning and evening until all symptoms of the disease completely disappear. Once there are no signs of the disease left, you cannot immediately stop treatment, because in this case there is a high probability that the fungus will return again. It is necessary to gradually switch to using medications up to once every 2-3 days. This is necessary to consolidate the effect. In this mode, treatment continues for another 15-20 days.
Important. In addition to using external agents, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that caused skin candidiasis. Otherwise, success may not be achieved, since the disease will constantly return.
Cream "Candide". Used on the recommendation of a doctor. Any self-medication is not allowed.
In addition, it is advisable to enrich the diet with vitamins and minerals, take a course of B vitamins, and strengthen the immune system with ascorbic and nicotinic acids. You should review your menu. It is advisable to exclude sweets from it, reduce carbohydrate intake and increase protein intake.
Cream "Pimafucin". An effective remedy for skin candidiasis. Use according to instructions as prescribed by a doctor.
In severe cases of skin candidiasis, systemic treatment is prescribed. In this case, the impact on the fungus should be both from the inside and from the outside. Therefore, ointments and tablets (or capsules) are combined. Lotions with various solutions can also enhance the effect of drugs. However, you should not self-medicate; you must first consult a doctor to find out which fungus caused skin candidiasis.
In addition to drugs that attack fungal bacteria, antibiotics can also be used.
Important! You should not stop treatment at the first signs of improvement or when the clinical manifestations of the disease disappear. Treatment of cutaneous candidiasis should continue for some time.
Symptoms
Lesions in skin candidiasis are usually initially located in large natural folds (in the groin, armpits, between the buttocks and under the mammary glands). In the future, they can spread to other parts of the body, leading to the development of candidiasis of the skin of the face and genitals.
In the affected area, hyperemic, edematous areas appear on the skin, the surface of which is covered with papules, pustules and blisters. After the bubbles open, erosions with clearly defined scalloped edges form in their place. The erosive surface is smooth and shiny, covered with a characteristic whitish coating. Along the periphery of the lesion there are separately located pustules, vesicles, edematous-erythematous spots, and papules.
With candidiasis of the facial skin, fine blistering rashes are mostly localized around the perioral area. In addition, patients complain of the appearance of cracks and cracks in the corners of the mouth, and increased dryness of the skin.
Conditions favorable for the development of fungus on the skin are created by wearing clothes made from artificial fabrics that do not allow air to pass through.
Diaper dermatitis is the most commonly observed form of skin candidiasis in children. The cause of its occurrence is usually a violation of the rules of hygienic child care. The main symptom of diaper dermatitis is the appearance of vesiculopustular rashes or scaly rashes on the inflamed skin of the perineum, which are accompanied by severe itching.
Candidiasis of the skin of the interdigital spaces is usually observed in people who frequently come into contact with the ground (residents of rural areas, greenhouse workers, owners of summer cottages) and preschool children. It is characterized by redness of the skin between the fingers and the appearance of small blisters on it.
Candidiasis of the skin of the genital organs in most cases is combined with fungal balanitis, balanoposthitis in men or colpitis, vulvovaginitis in women.
In rare cases, skin candidiasis takes a chronic course. Most often, this is facilitated by defects in T-lymphocytes, i.e., insufficiency of the immune system. Exacerbations of the disease occur several times a year, with each exacerbation the affected area increases slightly. In the most severe cases, infiltrates appear on the skin, having vaguely defined contours, the surface of which, at the time of exacerbation, is covered with serous-sanguineous crusts, penetrated by mycelial threads.
Candidiasis
696 27 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Candidiasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Candidiasis is an infectious disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It is caused by the active proliferation of fungus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genital and internal organs and on the skin.
All representatives of the genus Candida belong to opportunistic microorganisms, that is, they are constantly present in the normal microflora. But with a decrease in immunity, changes in hormonal levels and for a number of other reasons, these fungi can begin to actively colonize the mucous membranes and skin.
The most common members of the genus are Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. In 90-95% of cases of urogenital candidiasis, C. albicans is the dominant pathogen.
The first contact with fungi of the genus Candida occurs during the passage of the child through the birth canal. However, the medical literature describes cases of detection of these microorganisms in amniotic fluid, which indicates the possibility of a vertical (transplacental) transmission route. Transmission of the fungus of the genus Candida also occurs through breastfeeding, skin contact between the child and the mother, and through household and food routes.
These microorganisms produce endotoxins and enzymes that cause cell death and tissue necrosis, which enhances the adhesive (attachment to cells of the mucous membranes or skin) ability of the fungus and ensures penetration into tissue.
Overproduction of these and a number of other substances determines the pathogenicity of representatives of the Candida family.
Causes of candidiasis
- Exogenous (external) factors facilitating the penetration of fungi into the body:
- occupational hazards leading to frequent skin damage;
- prolonged exposure to a warm and humid environment;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes.
- Factors leading to a decrease in the body's resistance:
- presence of chronic diseases;
- long-term use of drugs that disrupt the natural microflora;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress, disturbances in sleep and rest patterns.
Risk factors for developing candidiasis
- Metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis), diseases of the immune system (HIV infection), endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, etc.).
- Long-term use of certain drugs: hormonal contraceptives, systemic glucocorticosteroids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, cytostatics.
- Long stay or living in an area with high humidity and temperature, comfortable for the circulation of fungal spores in the environment.
Classification of the disease
Based on the localization of the process, the following are distinguished:
- Urogenital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa.
- Superficial candidiasis.
- Interdigital candidiasis.
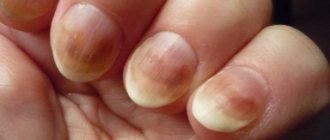
- Candidiasis of periungual ridges and nails.
- Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Urogenital candidiasis (UGC)
– a widespread disease: according to medical statistics, about 75% of women of reproductive age have registered symptoms of UGC at least once.
There are acute and chronic forms of urogenital candidiasis, candidiasis of the vulva, vagina and other urogenital localizations.
In some cases, when diagnosing, a clarification is used: complicated or uncomplicated UGC, which reflects the number of exacerbations per year and the severity of the disease. Symptoms of female urogenital candidiasis
- The appearance of white-yellow cheesy or creamy discharge from the genital tract. The intensity of discharge may increase before menstruation, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels.
- Unpleasant sensations, itching in the genital area, often aggravated by sexual intercourse or urination.
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, the presence of damage to the skin of the genital organs (cracks, microtraumas).
- In the chronic course of UGC, dryness of the mucous membranes of the genital tract develops.
Symptoms of male urogenital candidiasis
- Redness, swelling, discomfort in the genital area.
- Whitish discharge of a cheesy structure from the genital tract.
- Pain and burning during sexual intercourse and urination.
Superficial candidiasis
can be erythematous (the main symptom is reddened areas of the skin with a weeping surface) and vesicular (the formation of papules, vesicles and pustules in the affected area - inflammatory elements located in the superficial layers of the skin). The lesion begins with large folds of skin, gradually spreading to other areas of the body. In the depths of the folds, weeping occurs (separation of serous exudate through the smallest defects of the epidermis), a violation of the integrity of the skin contributes to the addition of a secondary infection.
Interdigital candidiasis
localized in the space between the fingers. In this case, redness of the skin is noted, followed by the appearance of bubbles in transparent contents. The disease spreads quickly in close groups (in kindergartens, schools, etc.).
Oral mucosal candidiasis (OCOR)
Oral candidiasis causes discomfort, especially when eating - burning, pain, dryness. Depending on the location of the process, several forms of oral candidiasis are distinguished.
Often, CSOPR and the gastrointestinal tract accompanies immunodeficiency conditions: HIV infection, acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or congenital immunodeficiency (for example, with T-lymphocyte pathology). In the presence of these diseases, candidiasis occurs with the most severe symptoms, is difficult to treat, and is aggressive in nature.
The most common manifestation of CSOPR is candidal stomatitis, which mainly affects infants and adults with weakened immune systems.
With this pathology, the oral mucosa turns red, swells, and whitish films with a cheesy consistency appear on it. In the initial stages of the disease, plaque is easily removed. As the disease progresses, the films become denser, are difficult to separate, and when removed, the bleeding mucous membrane is exposed.
With candidal stomatitis, the tongue may be affected, which is manifested by redness of the back of the tongue, the appearance of plaque and desquamation of the epithelium. These symptoms are accompanied by severe pain in the affected area when talking, eating, and palpating the tongue.
Smokers, more often than other types of CSOPR, develop chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, accompanied by the formation of white, merging plaques that rise above the surface of the hyperemic mucosa.
With this pathology, the consistency of saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foaming; there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, a gray or white coating on the mucous membrane. In 10-40% of cases, this clinical form of candidiasis becomes malignant (i.e., becomes malignant).
Older people most often develop a chronic atrophic form of oral candidiasis. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. The lesion is often localized under dentures, which causes pain.
Candidal cheilitis and candidiasis of the corners of the mouth mainly occur in children and the elderly. The lesion is usually bilateral, with the formation of red, painful cracks in the corners of the mouth, covered with an easily removable white coating or scales. With a long course of the disease, a bacterial infection may occur.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
The diagnostic search algorithm for candidiasis of any localization includes taking material from the affected area, followed by microscopy and culture to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
In order to diagnose conditions that lead to a decrease in immunity, a general blood test is used;
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the lesion for subsequent direct microscopy (the detection of oval-shaped cells with fungal pseudomycelium is a diagnostic sign of candidiasis).
Source: likar.info
Also, in order to determine the pathogen, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) and PCR diagnostics can be used.
Skin candidiasis is often diagnosed in dishwashers, housewives, bathhouse and swimming pool workers.
The quantitative determination of Candida fungi is of greater diagnostic importance, since they are present on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and are normal. For this purpose, a bacteriological examination of the scraping material is carried out (inoculation on Sabouraud's medium). In addition, this analysis allows you to accurately identify the pathogen, and most importantly, determine its sensitivity to antifungal agents.
To identify concomitant diseases that could provoke the development of skin candidiasis, the following laboratory tests are additionally prescribed:
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- immunogram;
- determination of glucose concentration in blood serum;
- clinical blood test.
Skin candidiasis requires differential diagnosis with the following diseases:
- erythematous lupus;
- recurrent genital herpes;
- favus (wolf lichen, scab);
- psoriasis of skin folds;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- eczema.
Diagnosis of cutaneous candidiasis
During the initial examination, the doctor pays attention to the presence of affected areas on the skin. Next, a scraping is taken from the pathological area to detect infectious fungi. When analyzing scrapings, the presence of oval-shaped cells is identified, which includes elements of mycelium. To identify the type of pathogen and determine its response to an antimycotic drug, bacterial culture is performed. It is also possible to carry out tests such as PCR, RIF, ELISA. In this case, it is necessary to establish the number of pathogenic fungi in the body to make an accurate diagnosis. To determine the causes of the disease, blood and urine diagnostics, an immunogram, and an HIV test are required.
Treatment of skin candidiasis
Treatment for skin candidiasis consists of taking antifungal agents:
- drugs from the azole group (Fluconazole, Econazole, Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Isoconazole, Ketoconazole);
- antifungal antibiotics (Levorin, Natamycin, Amphotericin B, Nystatin);
- other antimycotic drugs (undecylenic acid preparations, Naftifine, Terbinafine, Ciclopirox, Dequalinium chloride, Flucytosine).
In the case of single lesions, antifungal agents are used topically, in the form of ointments.
Source: napalce.ru
In a common process, local treatment is combined with systemic treatment, i.e., the use of antifungal ointments is accompanied by oral administration of drugs of the same effect. The duration of the course, frequency of medications and their dosage are determined in each specific case by a dermatologist.
In rare cases, skin candidiasis takes a chronic course. Most often, this is facilitated by defects in T-lymphocytes, i.e., insufficiency of the immune system.
Self-medication is unacceptable! Exceeding the required dosage can lead to the development of a toxic effect, which is significantly pronounced in antifungal antibiotics, and an insufficient dosage will contribute to the transition of the disease to a chronic form and the development of resistance of the pathogen to traditional therapy.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis, in addition to eliminating the pathogen, is aimed at restoring its functions, strengthening the patient’s body’s defenses, and treating concomitant diseases.
Complex therapy for skin candidiasis includes a diet low in carbohydrates, especially easily digestible ones (sugar, confectionery, honey).
During treatment, the skin in the affected area should be kept clean and dry.
Traditional methods of treating cutaneous candidiasis
Baths with sea salt relieve unpleasant symptoms
In addition to medications, you can use traditional methods to treat candidiasis. The following help a lot:
- The affected areas of the skin are lubricated with calendula oil solution every day. This product is inexpensive and can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Baths with sea salt. It dries the skin, so it relieves many unpleasant symptoms.
- You need to take decoctions of medicinal herbs internally. For candidiasis, use chamomile, sage, birch buds, calendula, and juniper berries.
- Lubricating birch or poplar buds with alcohol tinctures helps a lot. They can also be added to bath water. You can make baths for your hands and feet with the addition of these tinctures. For 0.5 liters of water you will need 2 tbsp. l. facilities.
- An infusion of oak bark is also effective against candidiasis, and it has virtually no contraindications. Pour some water into an enamel pan and add a few tablespoons of oak bark. All this is boiled over low heat. The finished mixture is filtered and taken 3-4 times a day.
Oak bark infusion is effective in the treatment of candidiasis
Possible consequences and complications
Without the necessary treatment, skin candidiasis can become chronic and resistant to standard therapy. With each relapse, the pathological process expands, affecting new areas of the skin.
With a significant weakening of the immune system, skin candidiasis can develop into a widespread severe form with the development of damage to the kidneys, brain, heart, eyes and liver, anemia, osteoporosis, and fungal pneumonia. Life-threatening complications are candidal meningitis and endocarditis.
The entry of fungi of the genus Candida into the systemic bloodstream in combination with an immunodeficiency state threatens the development of mycotic sepsis, which in most cases ends in death.
Erosion formed on the skin is an entry point for secondary bacterial infection, which is why skin candidiasis can be complicated by the development of purulent diseases (furuncle, phlegmon).
Activation of a fungal infection and the development of the disease occurs in the event of a decrease in the general defenses of the body and disruption of normal microbiocenosis.
Therapy methods
Treatment of skin candidiasis should be carried out on the recommendation and under the supervision of a physician. The following medications are used for therapy:
- Antifungal drugs: Nystatin, Natamycin, Levorin, Amphotericin.
- Azoles: Ketoconazole, Flucanazole, Clotrimazole, Isoconazole, Econazole, Miconazole.
- Other drugs: undecylenic acid derivatives, Decamine, Terbinavin, Flucytosine, Polygynax.
If the degree of damage is mild, then local treatment is used; it is carried out with antifungal drugs in the form of ointments, which should be used to treat the affected areas of the skin. Laser treatment may also be prescribed. If the skin lesion is widespread or if the disease has become chronic, then you will need to take antifungal drugs in the form of tablets. The duration of oral administration and dosage of the drug are prescribed individually and depend on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
If the dose was insufficient and the duration of taking the drug was not as long as it should have been, this leads to the fact that thrush becomes chronic. In addition to medications aimed directly at the Candida fungus, concomitant pathologies are treated. Immunomodulating agents are prescribed, which, as the name of the group suggests, help improve immunity. The nutrient medium for fungi is sugar, so you should follow nutritional rules and maintain a diet low in carbohydrates and sweets. It is also important to remember about hygiene: you should carefully ensure that the skin is dry and clean.
Prevention
Prevention of cutaneous candidiasis includes:
- use of antibiotics only if there are strict indications in the dosage prescribed by the doctor;
- normalization of body weight;
- correction of serum glucose levels;
- refusal to wear tight clothing made from fabrics with poor hygroscopic properties;
- timely detection and treatment of other forms of fungal infection (candidiasis of the oral cavity, mucous membranes, nail plates).
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Differential diagnosis
Candidiasis, or thrush on the body, requires differential diagnosis with diseases such as eczema, seborrhea, favus, lupus, dermatitis and psoriasis. It is necessary to differentiate the pathology from pseudomycosis, which develops due to the microorganisms Corynebacterium minutissimum, as well as other fungal infections, including inguinal epidermophytosis, ringworm. In case of lesions in the groin area and nails, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a bacterial infection rather than a fungal one.
Prevention of pathology
The main preventive measure is to prevent the development of dysbiosis and fungal infections. For this purpose, it is recommended to include fermented milk products in the diet and exclude a large number of flour and sweet dishes from it. It is necessary to monitor personal hygiene, refusing to use antibacterial soap, which disrupts the normal microflora of the skin.
You should not take antibacterial medications for a long time, or discontinue them yourself before the prescribed date.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to regularly diagnose fungal infections in bedridden patients and people who have the following disorders:
- Diseases of the immune and endocrine system;
- Oncology, HIV;
- Blood diseases.
Preventive measures also include:
- Diagnosis and treatment of candidiasis in pregnant women;
- Elimination of candidiasis in infants;
- Treatment of dysbacteriosis;
- Elimination of harmful working conditions;
- Strengthening the immune system.
Diagnosis and treatment of candidiasis in pregnant women
Elimination of candidiasis in infants
Treatment of dysbiosis
Strengthening the immune system
Systemic (disseminated) candidiasis
Systemic candidiasis develops in individuals with severe immunodeficiency and endocrine disorders. The decisive factor is long-term therapy with antibiotics, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. When the barrier protection of the skin and mucous membranes is damaged, fungi penetrate into the blood. Internal organs are affected, most often the endocardium, the central nervous system, less often - bone marrow, striated muscles, bones, joints. In some cases (rarely), with systemic candidiasis, separate metastatic foci are formed.
Candidemia (fungi in the blood) is manifested by fever, chills, shortness of breath, tachycardia and hypotension.
Distinctive features of disseminated candidiasis are:
- Lack of effect from antibiotic therapy.
- The spleen remains within normal limits (increases in bacterial sepsis).
- Development of lactic acidosis, stomatitis, myalgia and hypotension.
Candidal sepsis is rare. It is always difficult and often ends in the death of the patient. The cause of death is multiple microthrombi of fungi of the genus Candida (most often Candida albicans) in the vessels of internal organs.
Signs and symptoms of respiratory candidiasis
The disease develops as a result of long-term treatment with antibiotics.
When the larynx is damaged, the patient's voice changes, coughing attacks appear, and sputum of a mucopurulent nature is released, often mixed with blood.
When the lungs are damaged, the body temperature rises to high levels, weakness and malaise, chest pain appear, and the cough is usually dry, “scratching.” Standard therapy is unsuccessful. The history usually contains indications of previous glossitis and/or stomatitis. Antimycotic therapy has a positive effect.
Rice. 40. The photo shows a disseminated form of pulmonary candidiasis.
Signs and symptoms of urinary candidiasis
Candidiasis of the urinary system indicates a common form of the disease. Elements of fungi (candiduria), protein, casts and red blood cells appear in the urine. Often patients are unsuccessfully treated for a long time with various chemotherapy drugs. Cystoscopy and microscopy facilitate diagnosis.
Candidiasis of the central nervous system
The disease is quite rare, develops against the background of long-term use of antibiotics, sometimes fungi penetrate the brain during abdominal catheterization (with blood) and neurosurgical interventions (through cerebrospinal fluid). In most cases, the cause of mycosis is Candida albicans.
The disease occurs under the guise of a brain tumor, and in some cases candidal meningitis develops. Candida most often affects the brain of children damaged as a result of various intrauterine injuries, during childbirth or in the early postpartum period. Candidiasis of the central nervous system leads to disability in patients, often resulting in death.
Rice. 41. Fungal infection of the brain.