Suspension for the stomach: advantages and contraindications
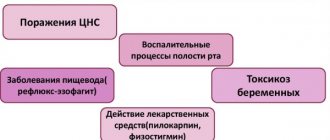
The stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which helps break down proteins. This acid is the reason why the stomach contents are acidic in nature with a pH level of 2 or 3 when acid secretion is active.
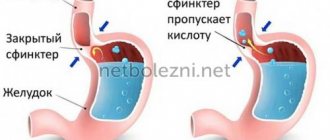
The pH level is a measure of the acidity in the stomach: the lower the number, the more acidic. The stomach, duodenum, and esophagus are protected from acid by several defense mechanisms.
The mucous membrane protects the delicate tissues of the inner surface of these organs from the corrosive effects of acid and the occurrence of erosion.
However, this barrier can be damaged by injury, disease, or poor nutrition. The acid begins to corrode the walls of the stomach and intestines, which can ultimately lead to ulcers.
In some cases, weakening of the annular sphincter, which serves as a barrier between the esophagus and the stomach, can lead to the reflux of its contents back into the esophagus, injuring its inner surface.
In such situations, gastric suspensions help - antacid medications that neutralize stomach acid. The contents of the stomach become less aggressive, the person suffers less from pain and heartburn.
Advantages
With the advent of new treatments for gastrointestinal diseases, such as proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor blockers, antacid drugs have lost some ground. However, gastric suspension is still very popular in the pharmaceutical market.
Its main advantage is its speed of action, which is invaluable when you need to quickly relieve pain. And, it is worth adding, lower cost.
- Aluminum carbonate antacids may be used to treat and manage hyperphosphatemia (abnormally elevated levels of phosphate in the blood). They bind phosphate in the intestines and prevent its absorption into the body. Because of this ability, these drugs can be used on a low-phosphate diet to prevent the formation of kidney stones. After all, kidney stones are composed of various elements, including phosphates.
- Calcium carbonate antacids are used in conditions of calcium deficiency, such as postmenopausal osteoporosis, because some of the calcium is absorbed into the body.
- Magnesium oxide antacids are used to treat magnesium deficiency caused by diet or medications that deplete magnesium in the body.
Classification
Antacid drugs are classified by type of action (absorbable and non-absorbable), by type of action (local and systemic), by the number of active substances (combined, multicomponent), as well as anionic and cationic. Anionic are preparations with calcium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate. The cationic ones include gels of aluminum and magnesium hydroxides.
Gastric suspension is supplied to the pharmaceutical market in two forms - a large bottle and small bags containing a dose for one dose. In terms of price and volume ratio, bottles are, of course, more profitable, but sachets are extremely convenient when traveling to work, out of town or when traveling.
There are also options for antacid-containing drugs in the form of lozenges (for example, Gastal), chewable tablets (Rutacid), and effervescent tablets (Alka-Seltzer).
Effect
When antacids are taken on an empty stomach, they provide acid protection for 20-40 minutes because they quickly pass into the duodenum. After eating (and about 1 hour after that), antacids reduce acidity for at least three hours because food slows the removal of the antacid from the stomach.
Antacids such as sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate have the greatest neutralizing power. But are not used for long periods of time due to the increased risk of adverse effects.
Indications for use
As a rule, a suspension for the stomach is taken when gastrointestinal symptoms of gastritis and peptic ulcers (stomach pain, nausea, heartburn) have already occurred. Or to prevent their occurrence (for example, the need to attend a family celebration).
Before use, it is recommended to carefully study the instructions, and best of all, consult a doctor.
But if the patient experiences the following symptoms: he is vomiting blood, there is blood in the stool, difficulty swallowing, a feeling of a foreign body stuck in the esophagus, or his stomach hurts for several hours in a row, it is better to consult a doctor. Perhaps you won’t be able to get by with just a stomach suspension.
Mechanism of action
Thanks to our school chemistry course, we all remember that an acid can be neutralized with an alkali; This is approximately what happens in the stomach when taking an antacid. The acid is neutralized and no longer affects the walls of the stomach and intestines and does not corrode them, causing pain and nausea.
Antacids also work by inhibiting the activity of pepsin, a digestive enzyme produced in the stomach. It is active only in an acidic environment and, like acid, is considered harmful to the mucous membrane of the stomach, duodenum and esophagus.
Contraindications
Contraindications depend on the specific drug and are indicated in the instructions contained in the package.
For example, some antacids should not be taken if you have impaired kidney function or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
An allergic reaction to aluminum hydroxide is a contraindication to taking an aqueous gastric suspension that contains aluminum carbonate (for example, Maalox, Almagel, etc.).
Antacids containing aluminum hydroxide should be used with caution in patients who have recently experienced major upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
For patients with conditions such as high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, and those on sodium- or salt-restricted diets, it is important to pay attention to the sodium levels in sodium antacids such as sodium bicarbonate.
Antacids should not be given to children under six years of age.
Side effects
The side effects of antacids depend on the substances they contain. For example, antacids containing aluminum compounds slow down peristalsis, which can lead to constipation.
On the contrary, antacids with magnesium have a laxative effect, which, if taken frequently, can cause diarrhea. Therefore, it is recommended to alternate these two groups of antacids with each other.
In reviews of the aluminum-containing stomach slurry, people reported experiencing loss of appetite and muscle weakness.
A complete list of side effects can be found in the instructions for the specific drug.
If you use other antacids or antimicrobials at the same time, the effects of the gastric suspension may change. The risk of side effects may increase or the drug may not work properly. Therefore, before choosing a suitable suspension, it is important to tell your doctor about the medications you are taking.
Gastric suspension may interact with the following drugs and products:
- Ascorbic acid.
- Bisphosphonates.
- Cephalosporins.
- Citrates.
- Corticosteroids.
- Cyclosporine.
Suspension for gastritis: features of various types of drug and folk recipes
Modern antacid preparations, in addition to the main active component, contain additional substances. They help reduce the likelihood of side effects, relieve pain, and help treat certain diseases. For example, a gastritis suspension with simethicone reduces flatulence. And alginates help protect the esophagus during recurrent reflux esophagitis.
Non-absorbable
One of the most popular groups of antacids is non-absorbable. Although they act more slowly than adsorbent ones, they differ in comparison with their longer therapeutic effect. If the drug contains aluminum compounds, this means that this medication has an additional protective effect.
It envelops the damaged mucous surface of the stomach with a protective film. This gastritis suspension acts more slowly than absorbable ones, but its effect is longer lasting. They do not affect the acid-base balance and also cannot cause the so-called. "acid rebound" After a sharp decrease in acidity, after some time it reaches the previous level and even exceeds it.
Adsorbent
Adsorbent suspensions for gastritis, as the name suggests, adsorb (or, simply put, absorb) the contents of the stomach or intestines. This includes the well-known activated carbon and preparations based on it, as well as medications containing polyvinyl pyrrolidone, lignin, organic compounds such as pectin, and so on.
Drugs for the treatment of intestines
Do not think that gastritis suspension is only good for treating stomach diseases. Adsorbents are also good for the intestines - they absorb toxins, pathogenic microelements, harmful substances that have entered the body, and in case of bloating, even gases. Adsorbents are good during intestinal infections, poisoning, excessive alcohol consumption and overeating.
Natural antacids
If you have mild symptoms, you don’t have to run to the pharmacy—you can use natural remedies. If you have discomfort in the stomach, it helps to eat something with a soft texture and enveloping effect. For example, bananas, boiled starchy vegetables (the well-known potatoes or carrots) or liquid oatmeal or wheat cereal.
Mineral water is also good for stomach diseases. Eating figs and raisins helps - these are some of the most alkali-forming dried fruits.
Traditional recipes:
- Freshly squeezed potato juice helps a lot - the starch it contains envelops the walls of the stomach, protecting them. Before meals, take 2 tbsp. l.
- Flax seed is another natural antacid. 1 tsp. crushed seeds, pour a glass of water on the floor and slowly heat in a water bath. Consume half an hour before meals.
- White clay is one of the safest adsorbents. It is almost completely harmless and can be used even by small children.
- Aloe juice . Fresh fleshy leaves are squeezed out, the resulting fresh juice in the amount of 1 tsp. dilute in half a glass of water and drink after meals. It is worth noting that aloe juice can have a laxative effect, so you should carefully monitor the body's reaction to it.
Source: https://med88.ru/lechenie-gastrita/suspenzija-dlja-zheludka/
Choosing the right pain remedy
All gels and suspensions used in the treatment of abdominal pain can be divided into groups:
- Antacids are drugs aimed at neutralizing gastric juice. Some also contain painkillers and coating substances.
- Alginates are compounds related to polysaccharides, when interacting with hydrochloric acid, under the catalytic action of enzymes they form colloidal alginic acid, which has an enveloping effect. Due to its large molecular weight, this acid is not absorbed into the walls of the stomach, but is excreted entirely. To the general advantage of this group, it must be added that while the drug is in the stomach, the secretion of acid slows down.
- Enterosorbents are substances that bind toxins through adsorption and absorption. The difference between adsorbents and absorbents is in the process of absorbing toxins. Adsorbents absorb only the surface layer, absorbents - the entire volume. Therefore, a characteristic that must be taken into account when purchasing an enteric sorbent is the active surface, which shows the maximum absorbent surface area. The higher this indicator, the more effective and faster the drug works. A high index (>50 m 2 /g) of the active surface indicates that absorption occurs in volume, i.e. it is an absorbent. Low ( 2 /g) indicates absorption by the surface, i.e. this is an adsorbent.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of gastritis
Gastritis is a stomach disease characterized by an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ. The presence of accompanying symptomatic signs requires immediate medical intervention. Therapy involves the use of medications to treat gastritis.
You should take medications only as prescribed by a doctor, depending on the degree and type of disease identified by the diagnostic results.
Drug therapy
After laboratory tests and a comprehensive examination (radiography, endoscopy, ultrasound), the gastroenterologist prescribes a treatment regimen, which necessarily involves taking medications.
Prescribed medications for gastritis are aimed at eliminating the cause of the inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa, relieving unpleasant symptomatic signs of the disease, which include:
- vomiting, nausea;
- pain in the abdomen and stomach of various types;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- unstable stool;
- bloating, gas formation;
- weakness;
- Possible increased body temperature.
Depending on the nature of the disease, the doctor prescribes drug treatment. Choosing a medication for gastritis on your own can lead to serious complications.
Typology of medications
Drugs for the treatment of gastritis vary depending on the form of the disease. There is a list of modern medications designed to relieve symptoms and effectively treat the disease in adults:
- medications for moderate and hyperacidity;
- medications for low levels of hydrochloric acid;
- antacids;
- adsorbents;
- electrolytic agents;
- antihistamines;
- blockers;
- gastroprotectors;
- antispasmodics, painkillers;
- antimicrobial, antibacterial drugs.
Medicines for gastritis differ in purpose and contraindications for use. Before use, it is necessary to know the exact cause of the inflammatory process in the stomach in order to avoid causing irreparable harm to health.
Medications for moderate and hyperacidity
Increased secretion is associated with a high level of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which contributes to the erosion of the walls of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ. Acidity higher than normal disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and does not allow the body to absorb the vitamins and minerals it receives.
Symptomatic signs of the disease are:
- pain in the stomach, rib area;
- the appearance of heartburn, belching;
- vomiting, nausea;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- diarrhea.
Medicines for gastritis with a high level of acidity are aimed at normalizing the excess secreted substance and protecting the damaged mucous membrane from the appearance of ulcers. The composition of the medicines includes aluminum phosphate, magnesium hydroxide and carbonate, and hydrolcides.
The most effective drugs for normalizing acidity are:
- Omeprazole;
- Almagel;
- Maalox;
- Gaviscon;
- Gaviscon Forte;
- Pancreatin;
- Phosphalugel;
- Rutacid;
- Famotodin;
- Roxatidine.
These components should reduce stomach acidity and eliminate symptomatic signs. There are proton pump inhibitors that stop the production of hydrochloric acid. Medicines with this effect are:
- Rabeprozole;
- Nolpaza;
- Ezocar;
- Pantoprazole;
- Esomeprazole.
Medicines, tablets and gel for gastritis with high acidity help maintain a moderate level throughout the day, stopping the formation of substances at the cellular level and reducing the production of enzymes.
Medicines for low acidity
A low level of hydrochloric acid can lead to inability to digest food, and as a result, the body does not absorb the necessary vitamins, substances for growth and development, as well as disruption of the metabolic process. Untimely treatment of the hypacid form of the disease can lead to gastroduodenitis and tumor formation.
Symptomatic signs of low acidity are:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- gagging after eating;
- frequent dizziness, malaise;
- Body temperature may be increased.
Enzymatic, acid-containing medications containing pepsin and betaine are prescribed as remedies for low acid levels. Such medications include:
- Festal;
- Panzinorm;
- Acidin Pepsin;
- Betaine Pepsin;
- Limontar;
- Histaglobulin;
- Pentagastrin;
- Prozerin;
- Etimizole;
- Plantaglucid.
For gastritis with low acidity, medications are prescribed that should increase acid production and restore secretion.
Antacids
Antacids are prescribed for gastritis with high acidity and heartburn. These types of medications normalize the concentration of secreted gastric juice. Antacids that reduce hydrochloric acid levels contain useful chemicals:
- aluminum hydroxide, magnesium;
- aluminum phosphate;
- hydrotalcite;
- magnesium carbonate, calcium.
Preference should be given to proven medications for heartburn and gastritis. The use of traditional methods can provoke a greater increase in the level of acidity in the stomach. Antacids include:
- Almagel;
- Phosphalugel;
- Rutacid;
- Rennie;
- Maalox;
- Talcid;
- Gaviscon.
Antacids are intended for gastritis of any form, severity of the disease. For heartburn, you need to use drugs that have a calming, anesthetic effect. Drugs with an enveloping effect are not absorbed into the blood, so the duration of exposure to medications increases.
Adsorbents
Drug treatment of chronic gastritis and acute forms of the disease using adsorbents does not make sense. These drugs, which are inexpensive, are intended to remove toxins and infections at the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process. Adsorbents include:
- Activated carbon;
- Enterosgel;
- Polyphepan.
Electrolytic agents
Electrolytes are used to relieve symptomatic signs of stomach disease. Gastritis is accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea, which inevitably leads to dehydration.
Electrolytic preparations are intended to normalize water-salt balance.
The atrophic type of the disease is characterized by a violation of the process of absorption and assimilation of consumed food, so taking electrolytic drugs is mandatory.
These drugs include:
- Dextrose solution;
- Regidron.
Antihistamines
Autoimmune, atrophic, erosive forms of the disease require the use of antihistamines designed to reduce the amount of biogenic compounds. Histamine destroys the gastric mucosa due to its high content in the body. Elevated levels may be due to an allergic reaction to the drugs used. The best antihistamines are:
- Famotidine;
- Cimetidine;
- Twegil;
- Suprastin;
- Loratadine.
Blockers
These drugs prevent the production of substances that negatively affect the condition of the gastric mucosa. It is necessary to treat atrophic, erosive, autoimmune, anacid gastritis with the help of drugs that block:
- histamine production:
- Cimetidine;
- Ranitidine;
- Famotidine;
- Telfast;
- Erius.
- substances that provoke vomiting - prokinetic agents:
- Cerucal;
- Eglonyl;
- Raglan.
- increased levels of hydrochloric acid - antisecretory drugs:
- Pantoprazole;
- Rabeprozole;
- Omez;
- Esomeprazole;
- Sanpraz;
- Kvamatel;
- Gistak.
Gastroprotectors
Chronic gastritis must be treated with gastroprotectors. Protective drugs are:
- Venter;
- De-Nol;
- Biogastron;
- Hilak-Forte.
Medicines that restore the gastric mucosa have an enveloping effect, therefore they are prescribed for the treatment of acute gastritis.
Gastroprotectors protect the digestive organs from bacteria, infections, toxins, and help normalize the intestinal microflora due to their effect on pathogenic substances.
For acute and chronic gastritis, you can use gels or suspensions (Almagel, Phosphalugel) to prevent damage to the mucous membrane and relieve symptoms (heartburn, pain syndromes).
Antispasmodics
For gastritis, accompanied by the appearance of spasms of various types, it is necessary to use painkillers. Medicines safe for children and pregnant women include:
- No-shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Spasmalgon;
- Metacin;
- Drotaverine.
Analgesics containing metamizole sodium, for example, Baralgin, help relieve severe pain. Such medications are contraindicated for categories of the population at risk (children, pregnant women, people with cardiovascular diseases).
Antimicrobials
The cause of irritation of the gastric mucosa is the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the body. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs helps suppress the spread of harmful microorganisms, microbes that destroy the microflora and mucous membrane of the digestive organ. Proven drugs for stomach inflammation are penicillin antibiotics:
- Amoxicillin;
- Omeprazole;
- Amoxicar;
- Doxycycline;
- Clarithromycin;
- Flemoxin;
- Amoxiclav.
Untimely use of a group of drugs to eradicate bacteria and harmful microorganisms can lead to internal bleeding and ulcerative formations, areas of scar deformation.
Antacids
An increase in the acidity level of the gastric environment is one of the reasons for the development of gastritis and stomach ulcers. Hydrochloric acid aggressively affects the walls of the organ, corroding them and causing inflammation. Preparations based on compounds of magnesium and aluminum or sodium and calcium help neutralize acidic digestive juice.
Antacids do not dissolve in water, reduce the secretion of pepsin, and can bind some toxins.
The effect of antacids absorbed into the blood occurs faster, but their effect is short-lived, after its end the production of hydrochloric acid may increase. These drugs include: baking soda; Rennie. The drugs are indicated in case of urgent need to reduce the secretion of gastric juice.
Non-absorbable antacids have a longer-lasting effect, but it does not occur immediately:
- Phosphalugel based on aluminum phosphate normalizes the pH balance and protects the walls of the stomach;
- Almagel, Maalox (based on aluminum and magnesium compounds) reduce the amount of digestive juice secreted and gently envelop the mucous membrane; the composition of Almagel A is supplemented with benzocaine, which allows the medicine to be used, including for pain;
- Talcid, Gastal, obtained by combining aluminum, magnesium and calcium, create a protective layer that prevents damage to the mucous membrane;
- Rutacid removes excess hydrochloric acid from the body and stimulates the functioning of the gallbladder;
- Gelusil varnish, in addition to neutralizing acid, has a restorative effect on damaged stomach walls.
Medicines used for inflammation of the gastric mucosa
Therapy for gastritis is carried out with the aim of normalizing the secretion of perchloric acid in the stomach. Depending on whether there is a decrease or increase in stomach acid secretion, the doctor’s prescription of medications also depends. There is no universal remedy for the treatment of gastritis, and it is not possible to invent it.
If the acidity of the stomach is low, then doctors prescribe gastric juice (either natural or artificial). It is necessary to drink it during meals, the dosage is measured very strictly. This juice contains hydrochloric acid, which is necessary for the stomach, as well as a number of enzymes that help digestion.
If the acidity is normal or increased, then antacid drugs are prescribed. Some of the most common are “Vicair”, “Rennie”, “Maalox”, “Almagel”. Medicines that block the release of hydrochloric acid are also often used. The most common representative in this category of drugs is Ranitidine.
Prokinetics
Peristalsis disorders are usually associated with poor diet, prolonged stress, and insufficient physical activity. In the treatment of constipation, drugs that restore the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract help.
Prokinetics can also be prescribed in the complex treatment of ulcers or gastritis.
The most effective medications are:
- Lactiol (Exportal) is a safe laxative that softens stool, increasing its volume and facilitating movement through the digestive system;
- Linaclotide is effective for chronic constipation. The drug is also prescribed in case of irritable bowel syndrome;
- Mucofalk is of plant origin, so it is prescribed even during pregnancy. Doctors recommend this medicine for children too. Plantain seeds, which are part of the drug, stimulate the intestines, cleansing it;
- Castor oil stimulates mucosal receptors and enhances intestinal motility;
- Almond oil and glycerin are considered mild laxatives;
- Resolor affects colon motility, helping to have bowel movements more regularly;
- Prelax is suitable for adults and children, provides first aid for stool retention. Helps restore beneficial microflora;
- Itomed will help with pain in the stomach and intestines. In addition to improving the motor function of internal organs, the medicine relieves heartburn and discomfort in the abdomen;
- Motilium is the most popular remedy for enhancing gastrointestinal motility. Having few contraindications, the drug fights symptoms such as heaviness, bloating, nausea;
- Loperamide and Diamidine, on the contrary, slow down the movement of feces through the digestive organs, making them more viscous and dense. These medications are indicated for increased peristalsis.