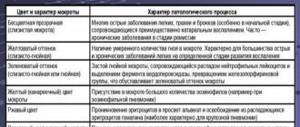
Various indicators of impurities in the analyzes of the tested urine can vary over a fairly wide range. And these deviations are due to various natural (physiological) and pathological reasons. Deviations due to physiological reasons are acceptable variants of the norm, and fluctuations of a pathological nature reflect the development of pathological processes.
Deviations from the norm in urine tests cannot be assessed unambiguously, accurately determining the probable cause. They only indicate the possible genesis of pathological processes that are at the stage of a certain syndrome or the formation of a disease. What can mucus in urine tell you?
Mucus in a urine test - what does it mean?
The urinary system of the human body itself creates conditions for its protection. The epithelial cells of the urethra synthesize urethral mucus, which protects the ureter from aggressive influences, urine passing through it and infectious effects. Under normal conditions, the concentration of mucosal epithelial cells in urine is practically unnoticeable.
If the tests reveal an increased content of mucus in the urine, this means that the doctor has additional information that allows him to determine the possible development of the pathology and carry out an accurate diagnosis. The epithelium that settles in the urine along with the mucous urethral secretion helps determine the nature of the development of pathological processes.
- Sedimentation of mucus with flat epithelium into urine is a sign of the development of inflammatory processes in the ureters or urethral canal.
- The settling of the renal epithelium with mucous secretion is the first symptom of the development of glomerular nephritis with damage to the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys (inflammation of the renal glomeruli).
- The presence of transitional epithelium and mucus in the urine is noted during the development of urolithiasis, during the acute course of pyelonephritis and cystitis, or during the formation of tumor neoplasms in the urinary system.
Thus, if mucous discharge is not the result of careless urine collection for analysis, its presence in the urine is a compelling argument for visiting a urologist.
Small amounts of mucus in urine: what does it mean and what are its functions?
In a healthy person, a small amount of mucus is produced by special goblet cells in the epithelial layer of the urinary tract. Mucus secretions are an important defense mechanism of the body. They protect the inner surface of the organs involved in the process of removing urine from the body from the negative effects of urea and the acidic reaction of urine.
Mucus is secreted in small quantities only to neutralize the aggressive effects. It is excreted from the body along with urine during urination. It is transparent, odorless and should be absolutely invisible to humans. Its content in urine is determined using laboratory urine tests.
What reasons contribute to the formation of mucus?
A small amount of mucus (lumps, flagella) is a normal process. This is explained by the fact that with constant secretion, especially in women, the urethral secretion is mixed with vaginal discharge, which justifies its small presence in female urine tests.
The natural structure of urine found in the bladder is sterile. Mucus and bacteria in the urine change its structure, entering the urethral canal due to various functional pathologies of the urinary system. The reasons are due to:
- The development of inflammatory reactions in the renal pelvis caused by pyelonephritis.
- Inflammatory damage to the internal tissue structure in the bladder, with bacterial penetration from foci of inflammation.
- Bilateral renal pathology caused by chronic nephropathy.
- Damage to the ureters and kidneys due to urolithiasis.
- Stagnation of urine, causing inflammation and accumulation of large amounts of mucus in the urine.
- The influence of sexually transmitted infections.
Often mucus appears in urine due to common household reasons. This is especially true for women, when before collecting urine for analysis, their genitals are poorly washed. Almost none of the women cover the vaginal opening with a tampon, which must be done before collecting urine. This also applies to children, when mothers do not check whether the child has washed his foreskin before collecting urine for analysis.
The cause of cloudy urine may be an insufficiently clean container, or prolonged storage of collected urine exceeding certain periods.
Mucus in baby urine
When mucus is detected in a child’s urine, the parents’ anxiety is understandable. Its loss into the urine is largely due to the failure of the immature children's urinary system, which is due to:
- Imperfect system of muscular innervation of the bladder organ;
- Poor muscle development and lack of tissue elasticity;
- Nephroptosis, manifested by increased kidney mobility;
- Insufficient ability of muscle contraction of the ureter;
- Vulnerable and weak mucous structure of the urethra.
All these shortcomings taken together are a provocative factor predisposing to the development of infections in the urinary system of children. In girls, a predisposition to infections is associated with the special structure of the urinary system - the urethral canal is wider, unlike that in boys, it is located closer to the anal outlet, which makes it easier to get infected through the ascending route. Provocative causes of mucus in the urine of a child are due to:
- Inflammatory infectious pathologies;
- Kidney diseases caused by an unhealthy diet and a small amount of fluid to drink;
- Vulvovaginitis, manifested as a result of streptococcal, fungal and intestinal infections in girls;
- Phimosis, which does not allow free exposure of the foreskin, which contributes to the accumulation of mucous secretion in its folds, which subsequently falls into the urine;
- Manifestation of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis (in rare cases).
Possible inflammatory diseases
If mucus is detected in a urine test, this means that there is an inflammatory process in the urinary system. It must be remembered that the norm of laboratory parameters in adults and children may include a slight content of mucus and bacteria as a result of the study, since errors in the collection of material are allowed. Under the influence of bacteria, the mucous membrane of the urinary organs becomes swollen, edematous and congested, as a result of which the goblet cells are activated and produce a significantly larger amount of the mucous component. This process is launched as a protective mechanism against the damaging effects of bacteria, as well as viruses and fungi. The largest amount of mucus in a urine test is detected in cystitis, urethritis, and urinary tract infections.
Urethritis: features
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra - the urethra. This process can be acute or chronic. Urethritis is usually caused by saprophytic bacteria (staphylococcal flora, E. coli) or specific bacteria transmitted during sexual contact (mycoplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, trichomonas).
So the combination of mucus, blood, and leukocytosis in the urine in men speaks in favor of acute specific urethritis. Less common causes of inflammation in the urethra are viruses or fungi of the genus Candida. Clinically, such changes in urine will be accompanied by itching, a burning sensation in the urinary tract, pain at the beginning of urination, and a frequent urge to urinate. Urethritis in men can develop against the background of prostate pathologies.
Cystitis and factors of its occurrence
Cystitis is an acute or chronic disease of the bladder that occurs with an inflammatory process. The most common causes are damage to the body by E. coli. Women develop cystitis more often than men. The establishment of a hemorrhagic form of cystitis means infection of the urinary system by viruses, which occurs in adults and children.
Clinically, this disease is manifested by pain above the womb (intensified during urination, as well as at the end), frequent urination, and a false urge to go to the toilet. A urine test for cystitis determines a significant amount of mucus, leukocytes, bacteria, as well as red blood cells (typical for a hemorrhagic type of disease).
Urinary tract infection and its symptoms
This is a disease characterized by inflammation in the urinary tract, which develops against the background of increased aggressiveness of saprophytes. This condition may manifest itself as symptoms of cystitis or urethritis, but instrumental examination does not reveal morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the urinary system.
Antibiotic treatment is quite effective in combating this pathology. It occurs more often in women of childbearing age than in men.
The mucous component can be detected in urolithiasis, as well as in chronic diseases of the urinary system . In men, the causes of this pathology may be associated with disorders in the prostate gland (hyperplasia).
Mucus in the urine of pregnant women
Apart from the general reasons given above, the presence of mucus in the urine of women during pregnancy can be the result of many provocative factors. The very fact of their manifestation in tests indicates problems in the urinary system caused by an infectious lesion. This unpleasant symptom appears in the second half of pregnancy. It is during this period that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the urinary tract.
Increased stress on the kidneys contributes to the manifestation of gestational pyelonephritis. The disease develops due to the combination of the presence of an infectious focus and obstructed processes in the outflow of urine from the ureter, caused by compression by the enlarged uterus. As a result, mucous inclusions with epithelial flakes appear in the urine.
In addition, urethral mucus in the urine of pregnant women may appear as a consequence of inflammatory processes caused by sexually transmitted infections, which can result in dangerous complications not only in the woman, but also in the fetus. Errors in diet can cause cloudy urine:
- high presence of fatty foods in the diet;
- hobbies for sweets and baked goods;
- dishes made from pork and poultry.
By eliminating these errors and replacing a harmful diet with a balanced diet, the normal structure of urine is restored without consequences.
What do bacteria and mucus in a child's urine indicate?
Children's urine should not contain mucous secretions at all. If tests show their presence, then an inflammatory disease is occurring in the child’s body. Most often, organs such as the ureters, kidneys, and bladder are affected.
Mucus formations in the urine of boys are sometimes associated with abnormalities in the structure of the genital organ. If the head of the penis does not partially or completely open, dirt and discharge accumulate under the skin of the foreskin. If the rules of personal hygiene are violated, laboratory tests will show that the content of mucous formations is exceeded. Therefore, parents should monitor the hygiene of little boys and explain the importance of keeping the genitals clean to older adults.
The cause of excess mucus in urine may be prolonged retention of urine in the body. When a person feels the urge to urinate, but constantly puts off visiting the restroom, stagnant urine irritates the epithelial layer, the cells of which begin to produce mucous secretions in an intensified mode.
To eliminate the possibility of violation of hygiene rules during urine collection, it is scheduled to be repeated. If the second time the indicators exceed the norm for mucus content, specific tests are prescribed to specify the disease and its further treatment.
About the treatment of possible diseases
The detection of urethral mucus in urine tests is not a disease, but only a sign of the development of various diseases. In this regard, a treatment protocol is drawn up according to the results of further diagnostics and the identified disease. A diagnosis cannot be made based on mucus alone.
Even a small amount of urethral secretion in urine with the addition of sediment of proteins, bacteria and leukocytes indicates urological pathologies. Example of treatment regimens:
- Identified cystitis is treated with antibiotic therapy with the prescription of the drugs Augmentin, Nolitsin, or Norbactin and water therapy, which involves daily fluid intake of at least 3 liters in the form of decoctions, herbal teas, or compotes and fruit drinks.
- In case of renal pathologies, medications from the group of uroantiseptics - Furazidine, Nitrofurantoin, Canephron or Urolesan - are added to antibiotic therapy. The painful syndrome is relieved with the drugs “No-shpa” and “Drotevarina”.
- Neoplasms in the prostate, if drug treatment fails, are removed using TU resection (transurethral).
- Urolithiasis are removed using various surgical techniques, or by crushing.
The detection of urethral mucus in the urine is a symptom that warns the patient about the possibility of developing various chronic diseases and complications. Therefore, examination and treatment should not be postponed “until better times.”
Tags:
urinary system analysis
Is treatment necessary if mucus is found in the urine?
The doctor decides whether to prescribe treatment if pathological inclusions are detected in the urine. To do this he needs:
- make sure that the analysis is made from correctly collected urine;
- find out the patient's complaints;
- examine the patient, check for symptoms of kidney disease;
- if necessary, order additional examination.
There is no special treatment against mucus. To improve the cleansing of the epithelium and stop the irritating effects of toxins and pathogenic microorganisms, the following is prescribed:
- drinking plenty of water;
- herbal and vegetable decoctions (rose hips, lingonberry and currant leaves, cranberries, chamomile, oats);
- Canephron is used as a herbal uroseptic.
Specific treatment involves:
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- removal of intoxication;
- strengthening the immune system with vitamin complexes;
- normalization of metabolism with diet and special preparations for dissolving salts;
- medications that normalize the tone of the muscles of the ureters and bladder;
- surgical removal of stones and tumors to eliminate congestion.
An identified disease may require:
- relieving pain symptoms in renal colic, cystitis, acute pyelonephritis;
- specific treatment for kidney tuberculosis, sexually transmitted diseases;
- simultaneous treatment of gynecological diseases in women and pathologies of the genital area in men.
The patient must learn to follow the rules of hygiene.
During treatment, the doctor prescribes control urine tests to check the effectiveness. The reduction or disappearance of mucous discharge confirms the restoration of epithelial cells and normal secretion production.
The full prognosis depends on the stage of the disease at which the patient consulted a doctor and began treatment. People with venereal inflammation should remember that it is not limited to the external genitalia, but can spread to the urinary organs and cause severe damage.
Therefore, it is necessary to fully comply with the doctor’s requirements and complete the course of treatment and stage-by-stage examination confirming a complete cure. Recovery is indicated by the absence of mucus and other inflammatory cells in a urine test.
source
Causes of bacteria in urine during pregnancy
During pregnancy, even healthy women can have bacteria in their urine. This phenomenon is caused by hormonal changes, a physiological decrease in immunity and the activation of opportunistic flora associated with these conditions.
Often, bacteria in the urine is found in expectant mothers suffering from candidiasis (thrush).
In addition, bacteriuria in pregnant women is a direct consequence of congestion in the pelvis. The enlarging uterus begins to put pressure on the bladder, preventing it from completely emptying.
The retention of urine in it leads to the proliferation of bacteria, often coming from areas adjacent to the rectum. As you know, during pregnancy the intestines and bladder shift and are closer than usual.