Gonarthrosis of the knee joint (ICD code 10. M17) is a common pathology of a degenerative-dystrophic nature. In most cases, the disease is fundamentally inflammatory in nature, but due to regular friction of bones, this process can occur in the joint. If the symptoms of gonarthrosis are ignored and left untreated, the disease leads to disability and complete immobilization of the lower extremities. What is it and how to cope with the disease?
Myths about gonarthrosis
There are 3 most famous myths:
- “The diagnosis of gonarthrosis is the prerogative of people with increased physical activity, and people with predominantly sedentary work do not suffer from it.” In fact, excessive exercise actually wears down cartilage. During sedentary work, there is a static effect on the knees, and blood supply becomes difficult. In addition, a sedentary lifestyle leads to increased body weight.
- “Gonarthrosis of the knee joint is incurable, the disease progresses every day.” This disease is indeed chronic, but with adequate timely treatment, wear and tear of the cartilage can be prevented.
- “With arthrosis, you need to move as little as possible and lie down more.” A patient with such a pathology is prescribed special gymnastics that strengthens the ligamentous apparatus. Only some sports are truly contraindicated.
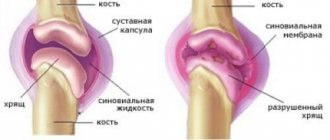
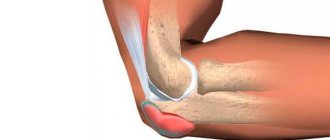
Gonarthrosis is the destruction of articular cartilage in the knee joint and adjacent bone surfaces
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stage, gonarthrosis may not manifest itself, that is, the patient does not experience any special signs. But the destruction of the disease is gradually increasing. Symptoms of gonarthrosis can manifest themselves in different ways, based on the severity of the ailment:
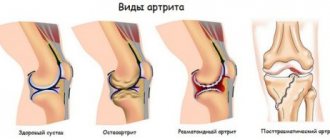
- The first degree is characterized by increased leg fatigue and narrowing of joint gaps, which can only be detected after an X-ray of the extremities. This stage of the disease passes without serious changes in the knee joints, but there is a slight restriction in movement.
- At the second stage of development of gonarthrosis, the patient experiences pain in the joints after a long walk. When moving, you can hear a crunching sound in your knees. The joints stop fully bending and unbending, and x-rays show flattening of the bone edges.
- The third degree is accompanied by severe pain even during complete rest of the joints. The affected area swells, the joint is unstable and often jams. In this condition, a person may develop a high fever.
At the first signs of gonarthrosis, you need to find out which doctor treats such diseases, and then go to the clinic for a thorough examination.
Manifestations of arthrosis of the knee joint
Manifestations depend on the severity of the deformation. The more pronounced it is, the more severe the symptoms.
Gonarthrosis symptoms:
- long asymptomatic period;
- discomfort in the knee area;
- pain syndrome;
- decreased mobility;
- morning stiffness for up to half an hour;
- the presence of a crunch during active movement;
- change in gait.
Bilateral gonarthrosis occurs when the knee joints of both limbs are involved in the process. This is one of the most severe forms. Occurs in elderly people.
Right-sided gonarthrosis appears with excessive static or dynamic physical stress on the right limb. More often among athletes.
Left-sided gonarthrosis occurs in overweight people and athletes when putting weight on the left leg.
Knee pain is the most important symptom of gonarthrosis
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of gonarthrosis do not manifest themselves immediately - they begin to appear gradually, depending on the stage of the disease. For this reason, the clinical picture must be considered in stages.
First stage
At the initial stage of development of the disease, patients complain of mild pain in the knee area, which intensifies with physical activity. They become especially intense during the descent and ascent of stairs.
In addition to pain, the patient feels a certain stiffness of movement, “tightening” in the joint area. It is felt in the popliteal part, and goes away when the knee muscles relax.
Another characteristic symptom is the so-called “starting pain syndrome”. It develops during the patient's first steps. When the knees get used to the load, this anomaly disappears without a trace.
Second stage
At this time, the symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint become more intense and noticeable. The pain intensifies, causing significant difficulty and discomfort when walking. The pain syndrome disappears after a long rest, but with intense exercise it makes itself felt again.
Inflammation of the joint causes swelling of the knee, which is noticeable even to the naked eye. When walking, a strong, unpleasant crunching sound occurs. Movements become more difficult and constrained.
Stage three
The pain becomes very severe, and the patient cannot do without painkillers. It is difficult for a person to bend his knee, he feels stiffness in the movements of the joint. It becomes deformed and increases in size. In severe cases, the patient cannot move without additional support.
All these signs of arthrosis of the knee joint should not be ignored by the patient. The disease can put a person in a hospital bed for a long time, and sometimes lead to disability.
Reasons for the development of gonarthrosis
Gonarthrosis can be primary and secondary. Primary can occur in childhood and adolescence, which is associated with improper formation of joints, as well as in the elderly due to the natural aging process.
Secondary occurs due to injuries or existing diseases. Main reasons:
- fractures, bruises, dislocations;
- excess weight;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the joint and lack of adequate therapy;
- metabolic diseases that are accompanied by the deposition of salts in cartilage tissues;
- operations;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- hormonal disorders;
- lifting weights;
- some sports (running, hockey, football).
Who is at risk?
Risk groups include:
- professional athletes;
- obese people;
- patients who have undergone trauma or surgery;
- people over 45 years of age;
- patients with varicose veins;
- those who have a family history of arthrosis.
The risk group also includes women who wear shoes with high heels or flat thin soles.
The exact causes of gonarthrosis of the knee joints are unknown
Prevention
It is recommended to adhere to the following principles of a healthy lifestyle:
- balanced diet;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- playing sports;
- healthy weight support;
- prevention of sports injuries (bruises, displacements, fractures).
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint has several treatment options depending on the age and physical condition of the patient. To prevent and control the disease in the early stages, exercise and timely treatment are necessary.
© 2020, Golub Oleg Vasilievich. All rights reserved.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint 1st degree
The first degree is characterized by fatigue, limited mobility is slightly expressed, and a crunching sound is heard. The pain appears after waking up, prolonged sitting and after physical activity.
At this stage there is no deformation yet. The x-ray shows a narrowing of the joint space.
How to treat gonarthrosis?
For treatment, a special group of drugs is used - chondroprotectors. They contain chondroitin and glucosamine, which restore the structure of cartilage and increase elasticity. NSAIDs are used to relieve pain.
Primary gonarthrosis is most often bilateral. Even with the development of a unilateral form of the disease, after some time the second limb is involved in the pathological process.
Early symptoms of gonarthrosis of the knee joints are mild and uncharacteristic
Treatment methods
In addition to drug treatment in the remission phase, the following methods are used:
- physiotherapy;
- massages;
- treatment with leeches;
- ultrasonic influence;
- radon and hydrogen sulfide baths;
- phonophoresis, electrophoresis;
- paraffin wraps;
- use of medicinal mud.
These methods are used regardless of the stage of development of the disease during remission.
Is mud useful for gonarthrosis of the knee joint? One of the indications for mud therapy is diseases of the musculoskeletal system. The course of therapy is carried out twice a year. It includes from 10 to 15 procedures. The method can be used at home, and the mud can be purchased at the pharmacy.
In the first degree, the patient is prescribed orthopedic shoes during an exacerbation to prevent the development of the deforming process. Women are recommended to wear shoes with thick soles of at least 1 cm and heels of 5 cm. They normalize their diet - reduce the amount of salt and spicy foods. The diet includes jellied meat and jelly, as they are natural chondroprotectors.
Another method is weight correction. Reducing body weight to an optimal level for a given patient will reduce the load on the musculoskeletal system.
Diet for gonarthrosis
Proteins help restore intra-articular cartilage. The patient can obtain them from lean meats, cheeses, cottage cheese, fish, lentils, beans, and buckwheat. Jellied meat made from bone broth is useful for gonarthrosis, as it contains a lot of collagen.
Carbohydrates should be obtained by eating vegetables and fruits. Fats should be predominantly vegetable. Small amounts of butter are allowed. Vitamins, especially group B, are of great importance for improving the patient’s condition. They are found in eggs, legumes, bananas, dairy products, cabbage, nuts, and lentils.
It is prohibited to drink alcohol if you have gonarthrosis of the knee joints. It not only has a negative effect on the body as a whole, but also increases appetite, which is undesirable.
When prescribing a diet, patients must comply with important conditions:
- You can eat a small portion at a time, and 5 meals a day are allowed;
- When eating food, you should remain calm and measured;
- The diet must include fresh vegetables and fruits in sufficient quantities, from which juices and salads are prepared;
- you need to sit down for dinner 3-4 hours before going to bed;
- it is important to exclude foods that are harmful to the body from the diet, and you should also refrain from drinking alcohol;
- It is recommended to consume at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day;
- Constipation must be avoided.
If you eat rationally, it will help normalize metabolic processes and lose extra pounds. In addition, thanks to the diet, tissue regeneration is accelerated and joint mobility is restored.
The outcome of treatment will be positive if the patient reacts to the disturbances in time and seeks help.
Gonarthrosis 2nd degree
In the second degree, the pain intensifies, causing movement to be significantly limited. Prolonged walking over long distances causes severe pain. The patient must rest before continuing.
If treatment has not been started (or is ineffective), gonarthrosis of the knee joint progresses further
The crunching becomes loud and lameness appears. The affected joint becomes deformed. An inflammatory process occurs in the inner lining of the joint.
A plain radiograph reveals a narrowing of the joint space and the appearance of spines on the bone (osteophytes).
Treatment
Drug therapy is based on the use of NSAIDs (Butadione, Nimulid, Diclofenac, Movalis and others). They have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Next, chondroprotectors are prescribed.
After the exacerbation has passed, physical therapy and massage are prescribed.
Diet recommendations:
- increase the amount of vegetables;
- include jelly and jellied meat in the diet;
- eat lean fish twice a week;
- give preference to lean meat;
- eat bread with bran.
It is also recommended to include bananas, nuts, eggs, spinach, legumes, liver, and white cabbage in your diet.
In addition to orthopedic shoes, special knee pads are prescribed.
Surgical interventions include arthroscopic removal of deforming tissue. This method has a short-term effect of 2-3 years.
Causes
- heredity or congenital pathologies of the knee joint
- heavy load on joints (both for athletes and overweight people)
- knee injuries
- Previously received leg injuries, the treatment of which was incorrect
- metabolic disorders, endocrine diseases
- circulation problems
Depending on which side the joint is affected, left-sided and right-sided gonarthrosis are distinguished, as well as bilateral gonarthrosis of the knee joint, the treatment of which should be as complete as possible in order to avoid differences between the limbs later.
The most likely causes of the development of knee gonarthrosis:
- age-related changes and natural aging processes of the body, accompanied by metabolic disorders, changes in hormonal levels, deterioration in the nutrition of joint tissues;
- excess body weight, which increases the axial load on the knee joints;
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism);
- injuries;
- infectious diseases.
Next, we will analyze the symptoms and treatment of gonarthrosis of degrees 1, 2, 3 of the knee joint.
Primary gonarthrosis usually develops in older people. Its occurrence is due to:
- metabolic disorders;
- obesity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- taking hormonal drugs.
The primary form affects two knee joints at once and is called bilateral gonarthrosis. But there are cases when the inflammatory process first affects one knee and only a few years later moves to the second.
Secondary gonarthrosis, on the contrary, is always one-sided. He is called:
- heavy physical work and sports that place stress on the right or left knee joint;
- trauma (ligament rupture, dislocation, hemorrhage into the cavity of the knee joint, damage to the meniscus, intra-articular fracture, etc.).
- operations performed on the knee joint;
- inflammation/swelling of the joint.
The best doctors for the treatment of gonarthrosis
8.2 6 reviews RheumatologistTherapistDoctor of the first category
Pushko Anna Aleksandrovna Experience 12 years
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 19001500 The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 1950
8.6 52 reviews
RheumatologistTherapistCardiologistDoctor of the highest category
Yusupova Nozima Asilievna Experience 13 years
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 990
9 14 reviews
RheumatologistDoctor of the highest category
Agapova Lyubov Aleksandrovna Experience 18 years
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 1500
9.5 140 reviews
RheumatologistArthrologistPhysiotherapistDoctor of the highest category
Markus Bronislava Borisovna Experience 43 years Candidate of Medical Sciences
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 18501480
8.9 7 reviews
Rheumatologist
Meshkov Alexey Dmitrievich Experience 9 years Candidate of Medical Sciences
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 5772 The cost is indicated for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 3500
8.9 4 reviews
RheumatologistTherapist
Georginova Olga Anatolyevna Experience 13 years Candidate of Medical Sciences
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 2050
9.2 2 reviews
RheumatologistDoctor of the highest category
Kotsofane Elena Viktorovna Experience 31 years
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 2205
9.5 4 reviews
Rheumatologist
Badalov Nazim Gadzhievich Experience 39 years Doctor of Medical Sciences
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 45003600
9.5 159 reviews
HirudotherapistReflexotherapistNeurologistCardiologistRheumatologistPulmonologistDoctor of the highest category
Safiullina Adeliya Yurievna Experience 29 years Candidate of Medical Sciences
The cost is for the initial appointment. It does not include the cost of additional research and home visits. 1500
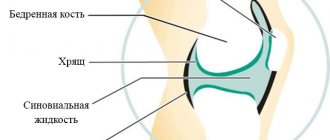
The normal functioning of the knee joint is determined by the presence of cartilaginous plates that cover the surfaces of the tibia and femur. Thanks to the plates, the bone tissue is reliably protected from wear.
For certain reasons, thinning and separation of the cartilage occurs, it cracks, and then completely disappears. As a result of such degenerative processes, the exposed bone area becomes denser, followed by the formation of spines. Due to joint deformation, the limb becomes crooked. Therefore, the second name for gonarthrosis is deforming arthrosis of the knee joint.
Pathology is provoked by:
- Injuries (for example, meniscus injuries, joint dislocations, tibia fractures). Due to trauma, a deficit in motor activity appears, which leads to deterioration of blood circulation in the knee and the occurrence of stagnation.
- Excessive overload on the knee, especially after 45. The disease is usually diagnosed in those who play sports.
- Having extra pounds. In obese people, the meniscus is often damaged. Severe gonarthrosis is often observed in patients suffering from excess weight and varicose veins in the legs.
- Inflammatory diseases (arthritis, rheumatism).
- Congenital weakness of the muscles and ligaments of the knee.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Prolonged nervous tension. Due to regular overstrain of the nervous system, the load on joints and muscles increases.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint, symptoms and treatment of 3 degrees
The most severe degree. Pain occurs during movement and at rest. Mobility in the knee is extremely limited and sometimes impossible. Deformation is pronounced. The radiograph shows virtually no joint space.
The progressive destruction of cartilage and bone in the final stages leads to the development of disfiguring deformities of the knee, which increases in size
Treatment
At this stage, in addition to NSAIDs, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs. They are administered intravenously or inside a joint. Severe pain is relieved with painkillers.
At stage 3, surgery is already indicated - endoprosthetics. Either individual bone elements or the entire joint as a whole are replaced. Contraindication: osteoporosis.
Complications of endoprosthetics:
- marginal skin necrosis;
- prosthesis rejection;
- neurovascular disorders (paresis, thrombosis).
In addition to endoprosthetics, there is an arthrodesis operation - removal of deformed tissue and joint. It is rarely used.
Osteotomy is excision of the edges of bones to redistribute the load.
Diagnosis of gonarthrosis
To diagnose a patient with gonarthrosis, a combination of collecting complaints, examination, and X-ray examinations is necessary.
An X-ray image of a joint today is the simplest and most easily accessible research method, with the help of which it is possible to diagnose the patient with a sufficient degree of accuracy, observe the development of the process over time, and determine the tactics of further treatment. Among other things, an x-ray allows you to make a differentiated diagnosis, for example, to exclude a tumor process in the bone tissue of the thigh or lower leg or an inflammatory one. Also, to diagnose gonarthrosis, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used, which can show changes not only in bone structures, but also in soft tissues.
In old age, everyone has certain signs of gonarthrosis, so a diagnosis can be made only after a complete collection of anamnestic data, complaints and visual examination, as well as instrumental research methods.
Physiotherapy
Exercises for gonarthrosis of the knee joint can relieve pain, strengthen the muscular system, and stimulate blood flow to them.
Exercise No. 1. The patient lies on his back, lifts his straight leg up and holds it for at least 30 seconds, then the other. The execution time should be increased to 2 minutes.
Exercise No. 2 “Bicycle”. Lying on your back, imitate riding a bicycle with your legs. Repeats from 20 to 50 times.
To develop the knee and restore its function, it is necessary to constantly and systematically perform exercises with dosed, gradually increasing loads
Exercise No. 3. The patient lies on his stomach, alternately bends his legs, trying to reach the buttock with his heel. Repeats 20-50 times.
Exercise No. 4. It is done in the same way as the previous one, only statically. That is, the patient fixes the limb in this position for 20-30 seconds.
Patients are advised to stretch:
Exercise No. 1. In a standing position, bend over, trying to reach the floor without bending your knees. Hold for 20 seconds, inhaling air through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
Exercise No. 2. Sitting on the floor with straight legs, try to clasp your feet with your hands, while keeping your knees straight. Stay in this position for up to 30 seconds. Perform 2-3 approaches. If there is not enough flexibility to reach the feet, take the leg by the shin and try to pull the body as close to the legs as possible.
Exercise No. 3. The same position as when performing the previous one. The patient takes the leg by the foot, tries to straighten it and holds it as high as possible above the floor. If the exercise is difficult to do, then take the leg in the shin area. Hold the position for 10-30 seconds, then do it with the other leg.
Contraindications are periods of exacerbations and the presence of an acute inflammatory process. Patients are prohibited from running, long walking and squats.
After physical therapy, it is useful to massage the muscles of the thigh and lower leg on the affected limb. The joint itself should not be affected, as this will increase inflammation.
Treatment with modern methods
Conservative
It should be noted that treatment of gonarthrosis using conservative therapy is possible only in the first two stages of the process. The patient is prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Recommended for relieving pain and inflammation in the joint and periarticular tissues. The drugs are used only as symptomatic therapy. Long-term use of drugs can lead to exacerbation of gastritis or peptic ulcer. Can be used in combination with gels or ointments.
- Chondroprotectors. Helps in the restoration of cartilage tissue. Should be taken for a long time. They help only if the cartilage is preserved, so in the last stage of gonarthrosis their use does not make sense.
- Glucocorticoids. Severe inflammatory process in the knee joint is stopped with the help of intra-articular injections. Steroid drugs have a number of side effects, so at the present stage of development of medicine they are rarely used.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage and manual therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
Surgery
Recently, arthroscopy of the joint has been successfully performed with the removal of damaged parts of the cartilage. Such operations are minimally invasive and do not require long-term rehabilitation. The indication for such an intervention is the patient’s young age, the second stage of gonarthrosis and the absence of indications for endoprosthetics.
At the last stage, the patient is offered endoprosthetics to preserve joint function. The operation consists of removing all damaged tissue and installing a prosthesis made of special materials.
Stem cell treatment
German doctors have demonstrated successful treatment experience with cell transplantation. This technique allows you to stop the destruction process and postpone radical intervention for an average of ten years.
However, this method of treating gonarthrosis is used only by a few of the most influential and largest orthopedic centers in Germany.
Disease prevention
This disease is not hereditary, so its development can be prevented. To do this you need:
- avoid injuries while playing sports;
- do stretching and joint exercises, yoga;
- Healthy food;
- maintain normal body weight;
- If you experience any discomfort in the knee area, consult a doctor;
- drink enough water;
- after 40 years, take prophylactic chondroprotectors;
- do not overcool the joints;
- in the presence of early stages of the process and during the period of remission, do not increase physical activity, do not run;
- wear orthopedic shoes;
- Use knee pads when playing sports.
Changes that occur in a joint with arthrosis
When a person experiences various physical activities, his subchondral bone thickens and grows. As a result, the articular cartilage is subject to increased trauma. Substances that form after microtrauma in destroyed cartilage end up in the synovial fluid.
However, the synovial membrane tries to reject them, since they are foreign to it. As a result, the inflammatory process begins. The formation of synovial fluid becomes more complicated, although before this the process was continuous and represented work to cleanse and enrich the blood.
In addition, the amount of hyaluronic acid in the joint fluid is significantly reduced. This provokes negative consequences, since with the help of hyaluronic acid the synovial fluid acquires viscosity. With its help, a lubricating effect is created between the bones, due to which the friction of the bones from each other is reduced. The consistency of the joint fluid does not resemble water, but egg white.
Another important importance of hyaluronic acid is that it ensures the delivery of nutrients to the articular cartilage, because it has nowhere else to feed from - the blood vessels do not fit into it. Waste substances enter the joint fluid from the cartilage also with the help of hyaluronic acid.
Gonarthrosis of the knee is a very common disease
When all these processes are disrupted, the bone becomes increasingly dense, and the articular cartilage finds itself in unbearable conditions. However, he begins to adapt to these conditions and change. This process is called remodeling. It causes the elasticity of the cartilage to decrease. In advanced stages of the disease, the bone becomes stiffer and more fragile, and the cartilage becomes calcified and absorbs calcium on its own.
Main symptoms of the disease
Those who have a predisposition to this disease need to know what arthrosis of the knee joint is and what its main symptoms are. Its development occurs slowly, over months and even years. In most cases, there are no obvious signs in the initial stages, so people do not even suspect that the disease is progressing. In some cases, only slight discomfort is felt in the knees. Over time, the symptoms become more noticeable.
Grade 1 gonarthrosis is characterized by increased fatigue of the limb
The main ones are:
- The appearance of pain is observed at the very beginning of the development of the disease due to irritation that occurs when sliding on uneven surfaces of the joint. At first, pain appears from time to time, mainly when walking. The patient feels it especially in the morning and during physical activity. Pain is often felt when walking up stairs or after doing squats.
- Stiffness of movements. In the initial stages, motor function is limited due to pain and stiffness in the morning due to synovial effusion. Subsequently, the resulting deformities reduce the ability of extension and flexion, which leads to the development of lateral instability in the knees.
- The appearance of crepitus and clicking is observed during the second and third stages of the disease during movements. Accompanied by pain.
- Developing synovitis causes swelling of the knee joint, which is accompanied by stiffness and pain. Excessive accumulation of synovial fluid and protrusion of the membrane into the back of the knee is the cause of cyst formation.
- The destruction process that affects the cartilage in the inner part of the condyles of the tibia and femur leads to deformity. Subsidence of the surface of the joints and varus deformation of the leg occurs. In some people, the outer condyles are affected first, causing valgus at the knees. Angular deformations significantly increase the load at the site of destruction. If both knees are affected by arthrosis of the knee joint, the shape of the legs changes and becomes O- or X-shaped.
- The occurrence of bursitis, tendovaginitis, tendonitis and venous insufficiency occurs in advanced forms of the disease, when para-articular tissues are involved in the pathology.
- Muscle atrophy is explained by forced limitation of activity in the case of arthrosis of the knee joint. In this case, the quadriceps femoris muscle atrophies and the stability of the ligamentous apparatus is disrupted.
Chondroprotective drugs
At the next stage, chondroprotectors are connected. This group is symptomatic and has a prolonged effect. Most often prescribed are Structum, Dona, Artra, Teraflex, Alflutop. They are used in complex therapy and prevention of degenerative disorders. The main active ingredients are glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate - important components of cartilage tissue.
The purpose of chondroprotectors is associated with their ability not only to eliminate signs of pathology, but also to have a positive effect on cartilage tissue, increase the production of synovial fluid, and slow down the process of destruction.
Such drugs are considered indispensable in the treatment of arthrosis of the first degree, but their capabilities should not be exaggerated.
At the third stage, their use will be inappropriate. The last stages of gonarthrosis are characterized by large-scale destruction of cartilage tissue, so even the most expensive and modern drug will not be able to restore it or eliminate the deformation.
Also, chondroprotectors have delayed results. They act slowly and several courses are needed for real results. In unadvanced cases, it is possible to restore damaged areas of cartilage, return the joint to its previous range of motion and relieve pain. Chondroprotectors will not change the deforming changes.
Development mechanism
| Factors | Pathological changes |
| Mechanical reason | These include injuries. Changes in the cartilage are observed, and if left untreated, its destruction. |
| Disturbances in the process of microcirculation | When nutrition is disrupted, connective tissue loses elasticity and begins to dry out. |
| Negative changes in the nutrition of cartilage tissue | There is a decrease in glucosamine and chondroitin, the main building material of cartilage. |
| Changes in synovial secretion | Its content decreases and the lubricating function is lost. |
Classifications of the disease
The International Classification of Diseases divides gonarthrosis into seven subcategories:
- Primary gonarthrosis is bilateral. The diagnosis is most often made in women aged 70 to 74 years and men aged 60 to 64 years. This places the disease in the “older” category.
- Other primary gonarthrosis. Pathology of one knee joint, due to natural wear and tear or due to other diseases.
- Post-traumatic gonarthrosis is bilateral. People of different age groups with serious leg injuries are susceptible.
- Other post-traumatic gonarthrosis. Unilateral, due to injuries and bruises of the limb.
- Other secondary gonarthroses are bilateral. They are the result of old, not fully cured bruises, fractures or dislocations. Most often it is diagnosed in athletes who have heavy loads on both legs - football players, athletes, figure skaters.
- Other secondary gonarthroses. Unilateral development of pathology associated with the profession. For example, miners, metallurgists, fishermen.
- Gonarthrosis, unspecified. Diagnosed when the etiology of the disease is not clear, after excluding age, occupational and genetic predisposition.
According to medical statistics, more than 10 million people of different age categories suffer from gonarthrosis of one type or another. Every year, about 3 thousand people with an established diagnosis die.