Thiamine chloride instructions for use
Ampoules are administered intramuscularly (deep into the muscle!).
- For adults - 0.025-0.05 g (1 ml of 2.5% or 5% solution);
- For children - 0.0125 g (0.5 ml of 2.5% solution);
The dose is administered once a day. The entire course of treatment takes 10-30 days.
- For Wernicke-Korsakoff encephalopathy - 0.05 - 0.1 g (1-2 ml) 2 times a day. Take until clinical improvement. After prolonged use, allergic reactions are possible.
Vitamin B1 provides hair follicles with proteins, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and biologically active substances. Once in the body, thiamine stimulates the transport of energy substrates into the scalp. A lack of vitamin B1 will quickly affect the general condition of the hair. How to use thiamine chloride for hair?
This leads to the strengthening of side expressions. Long-term use in large quantities will lead to the appearance of the first signs of hypercortisolism, namely:
- Tremor;
- Excitation;
- Headache;
- Increased heart rate;
- Insomnia.
Treatment depends on the symptoms that appear. Stopping the use of the drug brings the body's vital functions back to normal.
The solution is used parenterally, by deep intramuscular injection.
It is recommended to administer the first injection of the drug in a dose of no more than 0.5 ml of solution. Further, if well tolerated, higher doses can be used.
The dose and period of treatment are prescribed by the doctor, taking into account clinical indications.
Recommended dosage: 20–50 mg of thiamine chloride or 0.5–1 ml of solution once a day. The course of treatment can range from 10 to 30 days.
Overdose symptoms have not been established.
How to use and dose the medicine
Thiamine injections can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously or subcutaneously. It should be noted that the administration of vitamin injections should be carried out slowly or by drip method.
During the day, the dosage of the drug is as follows:
- Adult men should take 1.2-2.1 mg of the medicine;
- Elderly men are recommended to take 1.2-1.4 mg of the drug;
- Representatives of the fairer sex can take 1.1-1.5 mg of the vitamin, but women should take 0.4 mg more during pregnancy, and 0.6 mg more during lactation;
- For children, the daily dosage is 0.3-1.5 mg, regardless of age.
The use of the drug for intravenous administration is recommended, starting with a minimum dosage of no more than 0.5 ml of 5-6% substance. And only if the components of the medicine are well tolerated by the body, then the dosage of Thiamine can be increased.
The drug is administered intramuscularly, intravenously, and in rare cases subcutaneously. Upon reaching adulthood, 20-50 mg of the drug (1 ml with 2.5-5% substance) is prescribed once a day, daily, and over time can be used for oral administration. For patients who have not reached the age of majority, a dose of 12.5 mg of vitamin (0.5 ml with 2.5% substance) is recommended every two days.
Vitamins can be taken orally after meals by adults for preventive measures - 5-10 mg during the day, for treatment - 10 mg 1-5 times a day (the daily dose should be no more than 50 mg). The course of treatment lasts 30-40 days.
For children under three years of age, 5 mg of medication is prescribed every two days; from 3 to 8 years – 5 mg three times a day, also every two days. The course of treatment for children is 20-30 days.
Important! If vitamin B1 is used in the form of injections, then the course of treatment will be 10-30 injections, regardless of the patient’s age.
Compound
Dosage form – solution for intramuscular (IM) administration: transparent liquid, slightly colored or colorless, with a characteristic faint odor (1 ml or 2 ml in an ampoule, 10 pcs in a cardboard box; 5 pcs in a blister pack , in a cardboard box 1 or 2 packages)
1 ml of solution contains:
- active ingredient: thiamine hydrochloride – 50 mg;
- auxiliary components: disodium edetate, unithiol (sodium dimercaptopropanesulfonate monohydrate), water for injection.
1 ml of solution contains the active component thiamine (Vitamin B1) - a colorless, slightly yellowish transparent liquid.
Excipients: water for injection, unithiol.
The drug is available in the form of a ready-made injection solution of 2.5% and 5%.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i49Nnk5um7k
Packaged in ampoules of 1 ml. 10 ampoules in a cardboard package.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Thiamine chloride is intended to replenish vitamin B1 deficiency in the body.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) dissolves in water and, through phosphorylation in the body, is converted into cocarboxylase, which participates in many enzymatic reactions as a coenzyme. Vitamin B1 is necessary for the body to ensure normal metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, and the processes of conducting nervous excitation in synapses.
Pharmacokinetics
The level of thiamine concentration in the blood is relatively low; mainly free thiamine circulates in the plasma, and its phosphorus esters circulate in erythrocytes and leukocytes.
The process of vitamin phosphorylation occurs in the liver. The phosphorus ester thiamine diphosphate has coenzyme activity. Thiamine accumulation mainly occurs in the liver, brain, heart, kidneys, and spleen. The myocardium and striated muscles contain 50% of the total amount, and the internal organs contain 40%.
Excreted through the kidneys and intestines.
Cofermentation of the most important enzymes is impossible without this drug. With their help, carbohydrate metabolism is catalyzed. The vitamin product has a positive effect on the nervous system, reduces agitation by affecting the area of neuromuscular synapses. Responsible for protecting the cell membrane, which is toxically affected by oxidation products.
What is Thiamine
Thiamine is a synthetic product similar to vitamin B1, which is characterized by good solubility in water. In the human body, thanks to a process such as phosphorylation, the vitamin preparation becomes a cocarboxylase, a coenzyme for many enzymatic reactions.
According to the pharmacopoeia, Thiamine chloride, Thiamine Vial, Thiamine bromide, Thiamine hydrochloride are analogues of vitamin B1. All of the above products are available in the form of crystallized white powder, capsules, tablets or solution for injection.
The medicine is characterized by a light, specific aroma, good solubility in water, and resistance to acidic solutions, although it can easily be destroyed by an alkaline or neutral environment.
When administered intravenously, the drug quickly penetrates the bloodstream and is distributed fairly equally throughout the body.
The active component is phosphorylated near the liver. The vitamin accumulates in the renal, liver, cardiac systems, as well as the spleen and brain. The active ingredient is excreted through the liver and kidneys.
Thiamine (vitamin B1) is needed by the human body for the complete metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, as well as for the normal functioning of the nervous, digestive, endocrine and cardiovascular systems.
Indications for use
The use of Thiamine chloride is indicated for vitamin deficiency and hypovitaminosis B1 and as part of complex therapy for the following diseases:
- violation of coronary circulation;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- radiculitis, neuritis of various origins, neuralgia;
- peripheral paresis, paralysis;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- intestinal atony, anorexia, atonic constipation;
- eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, lichen planus and other dermatological pathologies associated with metabolic disorders and neurotrophic changes.
- pregnancy period;
- breast-feeding;
- childhood;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Thiamine chloride should be prescribed with caution in Wernicke's encephalopathy, in the premenopausal and menopausal periods.
Prescribed for:
- Vitamin B1 deficiency;
- Neuralgia, radiculitis, neuritis, peripheral paralysis;
- Gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- Liver problems;
- Wernicke-Korsakoff encephalopathy.
- Myocardial dystrophy;
- Pyoderma;
- Eczema;
- Psoriasis.
- High sensitivity to Vitamin B1;
- Allergic manifestations;
- Idiosyncrasy;
- In the climatic and pre-climatic periods in the weaker sex.
Take with caution when:
- Increased nervousness;
- Ulcerative disease of the duodenum.
Indications
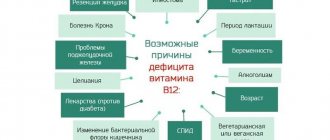
The main indications for taking vitamin B1 include the following conditions:
- Deterioration in the quality of night sleep and insomnia;
- Tingling in fingertips;
- Numbness of hands and feet;
- Deterioration of hair condition;
- Feeling of chilliness, even in a warm room;
- Deterioration of mood, depression;
- Frequent headaches, causeless anxiety, tearfulness;
- Rapid physical and mental fatigue;
- Increase in normal blood pressure levels;
- Increased heart rate, shortness of breath, mild nausea;
- Intestinal disorders.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Absorption - high percentage of absorption throughout the small intestine. Digestive enzymes are pre-released before the drug is absorbed. The concentration of the drug product in the blood is low.
Distribution - free thiamine is released in plasma, and phosphorus esters in leukocytes and erythrocytes. Half of the substance settles in muscle tissue and only 40% on internal organs.
Metabolism - the phosphorylation reaction occurs in the liver. This may be due to coenzyme activity. The largest amount of the drug accumulates in the internal organs, as well as in the brain.
It is excreted passing through the kidneys and intestines.
Side effects
Thiamine chloride may cause allergic reactions:
- Itching;
- Hives;
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- Quincke's edema.
In rare cases:
- Tachycardia;
- Sweating;
- Collapse;
- Angioedema;
- Anaphylactic shock is very rare.
Side effects of the drug also include:
- Intestinal hemorrhage;
- Damage to the optic nerve;
- Symptoms of bronchial asthma;
- Blood pressure surges;
- Cardiac arrhythmias;
- Malfunction of the nervous system.
When using Thiamine chloride, increased sweating, tachycardia, and the development of allergic reactions in the form of skin itching, urticaria, Quincke's edema, and anaphylactic shock are possible; at the injection site there is a feeling of pain.
special instructions
It is recommended to prescribe the drug parenterally only in cases where the patient is unable to take vitamins orally (including the period before and after surgery, nausea, vomiting and malabsorption syndrome).
It should be borne in mind that high doses of thiamine may distort the results of studies using the spectrophotometric method for determining the level of theophylline in blood serum or when using the Ehrlich reagent to determine the content of urobilinogen.
Anaphylactic reactions more often occur during intravenous administration of high doses.
According to the instructions, Thiamine chloride for Wernicke encephalopathy should be administered only after the use of dextrose.
Not recommended to be taken with:
- Other vitamins, for example: B12 and B6
- Combine with solutions of the sulfate group. Such actions will lead to complete disintegration of the drug.
Thiamine chloride in ampoules is actively used for hair; it is not recommended to apply it to hair in its pure form. Allergic consequences may occur. The drug should be added to masks, hair balms, etc.
To avoid a decrease in the level of vitamin B1 in the body, it is worth reviewing your daily diet. The most beneficial components are found in fatty meats, oatmeal, buckwheat, peas and nuts. Don't forget about wholemeal flour, rice bran, and green vegetables.
Contents in preparations
If an insufficient amount enters the body, it is recommended to use synthetic forms of vitamin B1.
Injection form - this injection should be injected intramuscularly;
Tablets – the drug Benfogamma. Used to prevent thiamine deficiency in the body;
The pills of the combined drug Milgamma contain, in addition to thiamine, also vitamin B6 and benfotiamine.
You can inject vitamin B1 intramuscularly in a medical facility, or you can do it yourself. If you inject at home, it is recommended to be in an upright position. Or someone at home can help you give an intramuscular injection.
For children, it is more difficult to inject thiamine intramuscularly, therefore it is recommended to use this drug in tablets.
Before using any drug there must be instructions for use.
To know whether your diet contains a sufficient amount of vitamin B1, you must also take into account the necessary daily requirement for this substance.
To better study the properties of this substance, we will consider the instructions for using vitamin B1.
Interaction
The simultaneous use of Thiamine chloride with other medicinal components leads to the following consequences:
- Pyridoxine complicates the absorption of the drug, and Cyanocobalamin, on the contrary, enhances its effect.
- The drug weakens the effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants on the body
- Long-term treatment with phenytoin, phenobarbital and carbamazepine can cause thiamine deficiency.
- Consumption of caffeine, as well as substances containing sulfur or estrogens, increases the need for vitamin B1.
- The drug should not be taken together with analogues that contain sulfites, penicillin-based drugs, or nicotinic acid. Under their influence, thiamine is destroyed.
With simultaneous parenteral administration with Thiamine chloride:
- pyridoxine (vitamin B6): complicates the process of converting thiamine into a biologically active form, increases the risk of developing allergic reactions;
- cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12): enhances the allergenic effect of thiamine;
- phentolamine, suxamethonium iodide, propranolol, hypnotics, sympatholytics (reserpine): reduce their pharmacological activity.
The drug should not be mixed in the same syringe with benzylpenicillin, streptomycin, nicotinic acid and solutions containing sulfites.
It is not recommended to prescribe thiamine in combination with barbiturates, carbonates, citrates, and copper preparations.
The drug is unstable in neutral and alkaline solutions.
THIAMIN
Drug: THIAMINE Active substance: thiamine ATC code: A11DA01 KFG: B vitamin Reg. number: LS-000960 Registration date: 08.18.06 Owner reg. credential: VEROPHARM (Russia)
DOSAGE FORM, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING
| Solution for intramuscular administration | 1 ml |
| thiamine hydrochloride | 25 mg |
1 ml - ampoules (10) - cardboard packs.
1 ml - ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs. 1 ml - ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (2) - cardboard packs. 1 ml - ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (2) - cardboard packs. 1 ml - ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs. 2 ml - ampoules (10) - cardboard packs. 2 ml - ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs. 2 ml - ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (2) - cardboard packs. 2 ml - ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (2) - cardboard packs. 2 ml - ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs. DESCRIPTION OF THE ACTIVE SUBSTANCE.
The scientific information provided is general and cannot be used to make a decision about the possibility of using a particular drug. PHARMACHOLOGIC EFFECT
Vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin. In the human body, as a result of phosphorylation processes, it is converted into cocarboxylase, which is a coenzyme of many enzymatic reactions. Vitamin B1 plays an important role in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism, as well as in the processes of nerve excitation at synapses.
PHARMACOKINETICS
After oral administration, it is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Before absorption, thiamine is released from its bound state by digestive enzymes. After 15 minutes, thiamine is detected in the blood, and after 30 minutes - in other tissues. The content of thiamine in the blood is relatively low, while predominantly free thiamine is found in plasma, and its phosphorus esters are found in erythrocytes and leukocytes.
The distribution in the body is quite wide. A relative predominance of thiamine content in the myocardium, skeletal muscles, nervous tissue, and liver was noted, which is apparently associated with an increased consumption of thiamine by these structures. Half of the total amount of thiamine is found in striated muscles (including myocardium) and about 40% in internal organs.
The most active of the phosphorus esters of thiamine is thiamine diphosphate. This compound has coenzyme activity and plays a major role in the participation of thiamine in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates.
Excreted through the intestines and kidneys.
INDICATIONS
Hypovitaminosis and vitamin B1 deficiency (including in patients on enteral nutrition through a tube, on hemodialysis; with malabsorption syndrome). Neuritis, radiculitis, neuralgia, peripheral paresis and paralysis; intestinal atony, impaired absorption in the intestine, severe liver dysfunction; myocardial dystrophy; thyrotoxicosis; chronic alcoholism; starvation; increased body need for vitamin B1 during pregnancy.
DOSING REGIME
Injected deeply intramuscularly or slowly intravenously 1 time/day. A single dose for adults is 25-50 mg. The course of treatment varies from 10 to 30 days.
When taken orally for moderately severe chronic hypovitaminosis, use 10-25 mg 1 time / day or in divided doses. For severe hypovitaminosis, the daily dose can be up to 300 mg.
SIDE EFFECT
Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, Quincke's edema; in isolated cases - anaphylactic shock.
Other: sweating, tachycardia.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to thiamine.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
Can be used during pregnancy and lactation according to indications in recommended doses.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
Allergic reactions to the administration of thiamine occur more often in individuals predisposed to allergies.
SC (and sometimes IM) injections of thiamine are painful due to the low pH of the solutions.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
With simultaneous parenteral administration, pyridoxine makes it difficult to convert thiamine into a biologically active form.
With simultaneous parenteral administration, cyanocobalamin enhances the allergenic effect of thiamine.
Reviews of Thiamine Chloride
Thiamine chloride is a fairly discussed drug on the Internet. Most reviews talk about its beneficial effects on the body. On women's forums, various recipes for using thiamine chloride for hair are actively shared.
Reviews about Thiamine chloride are only positive. They indicate the high effectiveness of the use of a vitamin preparation in the treatment of neurological diseases, exacerbation of gastric ulcers, coronary circulation disorders and skin pathologies. Its use as part of complex therapy helps provide the body with the necessary energy and activate recovery processes. Women share their impressions of the positive effects of the drug when used for hair care.
Thiamine chloride - what vitamin is it?
Thiamine chloride is better known as vitamin B1. Its analogue is thiamine bromide. The difference between these drugs is only in the salts combined with thiamine, which is what every human body needs.
Once in the body, thiamine is converted into another form - thiamine pyrophosphate. With its help, all nerve cells receive the necessary nutrition. It is involved in the formation of acetylcholine, which is responsible for the transmission of impulses between neurons and between neurons and muscles. Thiamine pyrophosphate takes care of brain cells, which makes it possible to have good memory, concentration and the ability to learn.
B1 is sometimes called the “optimism vitamin.” It helps strengthen the nervous system, making it more resistant to stress and tension, making it easier to get rid of depression and anxiety.
In addition, thiamine promotes better absorption of carbohydrates, which provide energy for the whole body, as well as proteins and fats, which are responsible for the growth and development of tissues.
B1 stimulates the proper functioning of the stomach and intestines, strengthens the heart and reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Another important role in the body that thiamine chloride plays is helping in the formation of the thyroid hormone thyroidin. This hormone regulates many energy processes, improves glucose absorption and much more.
Thiamine takes an active part in the breakdown of lactic and pyruvic acid, and in combination with other B vitamins, neutralizes toxins that have entered the body.