509
0
Parasites will come out like scalded ones if you drink in one gulp...
Mountains of parasites will come out of you if you drink the usual gulp on an empty stomach...
Go to website
People don’t like to talk out loud about diseases caused by parasitic worms. In addition to the fact that diseases provoked by the activity of worms in the body are themselves an extremely unpleasant phenomenon, some of these helminthic infestations can seriously affect human health, and in some cases, can be fatal. One of these diseases is opisthorchiasis. In this informational article we will look at the symptoms and treatment of opisthorchiasis in humans.
First, let's find out the causes of opisthorchiasis in people.
What is opisthorchiasis
Opisthorchiasis is a disease that is widespread in our country. According to some data, today about 2,000,000 people suffer from this disease. The maximum concentration of the disease was noted in the following river basins: Ob, Volga, Irtysh, Kama, Dnieper, Don and others.
Opisthorchiasis is caused by the cat fluke (Opisthorchis felineus), also called the “Siberian fluke”, photo. This type of parasite belongs to digenetic flukes (type of flatworms, trematode class). The cat fluke chooses the ducts of the liver, gall bladder or pancreatic ducts as its “home”. Accordingly, opisthorchiasis is characterized by damage to these locations and subsequent complications, which are caused by destabilization of the functioning of the hepatobiliary system of the human body.
It follows about the Siberian fluke. In other words, this type of parasite can spread to other organs, causing various abnormalities in the functioning of the affected systems, or indirectly contributing to the destabilization of the functioning of these systems and organs.
The cat fluke enters the human body through consumption of lightly salted or undercooked freshwater fish of the carp family (ide, roach, bream, gudgeon, dace and others).
The incubation period for opisthorchiasis varies between 2-4 weeks, depending on the functioning of the immune system. In fact, the disease is divided into 2 stages: acute and chronic.
Adult parasites cause mechanical damage to the walls of the bile ducts or other ducts through movement and attachment. When attached to the walls using specific suction cups located on the body, they can disrupt the integrity of tissues or lead to disruption of local blood circulation. Young parasites have cuticular spines, which they also use to cause damage.
In addition, a large accumulation of egg clutches in the ducts, as well as the parasites themselves, leads to disruption of the normal flow of pancreatic secretions and bile. This process is favorable for the development of various bacteria, which often leads to the formation of secondary bacterial infections.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis involves the use of an integrated approach. If helminthiasis is suspected, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, conducts a visual examination, palpation of the liver and gall bladder, then resorts to laboratory and instrumental examination.
Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis:
- feces on worm eggs;
- Analysis of urine;
- gastroenteroscopy;
- enzyme immunoassay (blood examination);
- Ultrasound of organs.
After diagnosing opisthorchiasis in adults and making an accurate diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
It may take 1-1.5 months to identify eggs in feces.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis in humans
DOCTORS RECOMMEND!
Pinworms, Giardia, tapeworm, helminths, tapeworm... The list goes on for a long time, but how long are you going to tolerate parasites in your body? But parasites are the main cause of most diseases, from skin problems to cancer. But the chief television doctor of Russia, Sergei Agapkin, assures that it is easy to cleanse your body even at home, you just need to drink... Read more »
In initially infected people, after the incubation period, the disease takes on an acute form, which can occur in different ways (mild or severe). However, as a rule, the initial symptoms are less intense and after some time they take on a higher degree of aggressiveness, that is, the mild nature of the disease gradually develops into a severe form.
The chronic form of opisthorchiasis is observed in people living in epidemiological regions of our country, since acute opisthorchiasis cannot go unnoticed and can be treated. The chronic stage is characterized by a decrease in intensity or disappearance of symptoms, but later, perhaps years later, this disease makes itself felt again. In addition, in the chronic form of opisthorchiasis, chronic pathologies are observed in the functioning of the affected organs and their systems.
It is important to understand that the symptoms of this disease, as with many other diseases caused by helminths, are nonspecific and, based only on the symptomatic picture, it is not possible to establish opisthorchiasis in humans.
The symptoms of opisthorchiasis in women are no different from the symptoms of this disease in men, except, perhaps, for one thing – disruption of the menstrual cycle. In all other respects the symptoms are identical.
Symptoms of opisthorchiasis:
- Increased body temperature, first reaching 38 degrees. This can continue for about 2 weeks, then (after 2-3 weeks) the temperature rises to 39 degrees and even higher. In fact, the rise in temperature itself indicates the activation of the body's defense system. With opisthorchiasis, an increase in temperature is observed quite often, but, as a rule, the initial temperature is subfebrile;
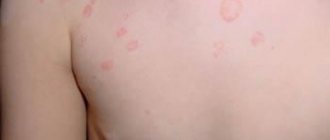
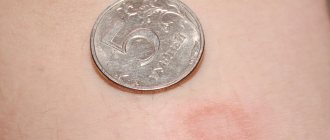
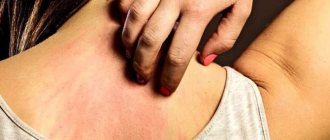
- Skin rashes, in particular urticaria;
- Weakness and general malaise are a consequence of high intoxication of the body, provoked by the cat fluke. During their life, this type of trematode releases characteristic substances classified by the human body as potentially dangerous;
- A disorder of the nervous system, manifested in irritability, increased excitability, depression, is another consequence of toxic poisoning;
- Disorder of the normal rhythm of sleep/insomnia is a consequence of an irritated nervous system due to intoxication and the activity of parasites in the body;
- Pain in muscles and joints throughout the body;
- Headaches/dizziness. Dizziness appears due to intoxication, and headaches are the result of damage to the nervous system;
- The appearance of allergic reactions during opisthorchiasis is caused by the production of specific immunoglobulins (antibodies) of the IgE class, which further contribute to the release of histamine (a mediator of allergic reactions) and serotonin, which is also called the “hormone of happiness”, into the blood;
- A sharp decrease in appetite is the result of the same toxic substances;
It is important to understand that opisthorchiasis spreads to various organs and tissues, provoking the appearance of specific symptoms:
- If the liver is damaged - jaundice, enlarged nodes of the lymphatic system, pain in the right side;
- If the digestive tract is affected, frequent and persistent pain in the right side, under the ribs, bloating, diarrhea, nausea (vomiting is possible). There may also be attacks of coughing, pain that occurs in the chest during breathing;
- Heart damage – pain or discomfort in the heart area, destabilization of the heartbeat rhythm;
- Damage to the gallbladder - pain can radiate to the left shoulder, back and chest (left side);
In chronic opisthorchiasis, symptoms characteristic of the following diseases or the direct development of the diseases themselves are often observed:
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Hepatocellular carcinoma. Simply put, a malignant tumor of the liver;
- Chronic hepatitis;
- Feeling of bloating/immediate distension in the epigastric region of the abdomen;
- Duodenal or stomach ulcer;
- Chronic gastritis;
- Cholangiocarcinoma (malignant tumor of the bile ducts);
- Duodenitis;
- Cholecystitis;
- Cholangitis, including purulent cholangitis;
- Nutritional deficiencies and so on;
Treatment of opisthorchiasis in humans
To begin with, we note that the treatment of opisthorchiasis is quite labor-intensive, lengthy and does not always end positively. For most patients, treatment is provided on an outpatient basis; for other infected members of the public, hospitalization is provided. Treatment at home or placement in a hospital, under the supervision of a qualified specialist, is directly related to the severity of opisthorchiasis and the individual characteristics of the patient (liver/kidney failure, neuropsychiatric disorders, etc.)
Therapy is carried out using highly effective antiparasitic drugs in combination with medications that help restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system of the body, and also involves the use of drugs that help restore the depressed immune system. The therapeutic process can be divided into 3 stages:
- The primary stage of treatment is aimed at eliminating the consequences of the activity of the intestinal fluke in the human body and stabilizing the general condition of the patient. This includes: intestinal cleansing procedures, elimination of intoxication of the body, normalization of liver function, elimination of blockage of the bile ducts, elimination/reduction of allergies, relief of inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and bile ducts. Drugs used during the preparatory stage: sorbents, choleretic agents, antihistamines, enzymes, painkillers, and antibiotics;
- Therapy using specific antiparasitic drugs;
- Rehabilitation therapy;
For 6 months after the end of the therapeutic course, patients are observed by a doctor.
Statistical data indicate a high percentage of effectiveness of drug treatment of opisthorchiasis. The positive outcome of the therapeutic course is more than 80%. This figure directly depends on the quality of the preparatory stage.
The mechanism of pathology development
To understand what opisthorchiasis is in humans, it is necessary to consider the mechanism of development of the pathology.
The causative agent of this type of helminthiasis is the fluke. This microscopic worm, which reaches a length of 8 mm, lives in fresh water. It enters it in the form of an egg along with human feces. The helminth in an open environment retains its viability for 1.5 years.
For the formation of the intermediate form of opisthorchis, it is necessary that their eggs be swallowed by a mollusk from the genus Candiella. In his body, the helminth is transformed and re-enters fresh water.
At the next stage of development, the parasite infects the body of carp fish, penetrating under the skin or into the muscle layer. Further, they reach a state that is dangerous for humans. It is important to note that parasites do not affect the condition of the fish in any way, so it is impossible to externally distinguish an infected freshwater fish from a healthy one.
After opisthorchises have entered the human body, they lose their shell under the influence of the acidic environment of the stomach and intestines. At the end of the development cycle, helminths enter the bile ducts of the liver, parasitizing them.
Within about one month, opisthorchis reaches sexual maturity and begins to actively lay eggs, which again penetrate into the environment along with feces.
Diet for the treatment of opisthorchiasis
Along with taking medications and various procedures, dietary nutrition is prescribed. The importance of such nutrition should be noted, since without strict adherence to the diet, the likelihood of a positive result of drug therapy is reduced.
The number of meals per day is 5; it is advisable to prepare meals in a double boiler. Meals may include the following:
- Vegetarian dishes;
- Low-fat milk soups and porridges;
- Low-fat dairy and fermented milk products;
- Compotes from fresh or dried fruits and berries (not sour), jelly, juices, weak coffee with milk, rosehip decoction, weak tea;
- Lean varieties of meat and fish;
- No more than 1 egg per day (preferably boiled);
- Honey, jam and sugar are allowed in small quantities;
- Rye bread and other flour products based on unleavened dough;
- Vegetables, herbs, fruits, dried fruits;
- Vegetable fats are allowed no more than 50 grams per day;
Tablets for opisthorchiasis
Warning
Herman Gandelman: “Halitosis is a very bad signal, 98% that you have parasites! To drive them out, you need a regular…” Read more »
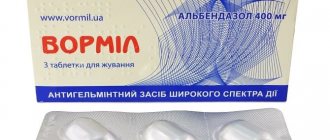
As a rule, tablets based on praziquantel and albendazole are prescribed for the treatment of opisthorchiasis.
What drugs are these:
- Praziquantel (Biltricide);
- Albendazole (Nemozol);
- Chloxyl can be used;
Preparations based on praziquantel have specific activity against trematodes. Praziquantel causes sustained contraction of the cat fluke muscles (paralysis) by increasing the permeability of the cell membrane to calcium ions. In greater quantities, it contributes to the disruption of the integrity of the upper protective layer of parasitic worms, which leads to the vulnerability of parasites to the body’s natural defense system and enzymes. Praziquantel is highly effective against larvae and adults.
Biltricide is used for opisthorchiasis according to the following regimen: 25 mg of the drug/1 kg of body weight, number of doses per day - 3. The duration of therapy is prescribed individually. The original instructions indicate a period of up to 3 days;
Preparations based on albendazole have a wide spectrum of action and are also active against the Siberian fluke. Albendazole selectively inhibits the formation of microtubules by disrupting the polymerization of beta tubulin (protein). This leads to destructuring of the cells of the digestive system of the cat fluke. Helps suppress the process of glucose utilization, which causes depletion of glycogen stores. It provokes a decrease in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphoric acid, which contributes to the inhibition of biochemical processes occurring in parasite cells. Among other things, it causes a block in the movement of various organelles in muscle cells. This drug works on larvae and adults.
In addition, drugs based on albendazole are less toxic compared to drugs based on praziquantel; however, albendazole is believed to be less effective for opisthorchiasis. The treatment regimen for opisthorchiasis with Nemozol is as follows: 10 mg of the drug/1 kg of body weight. The number of appointments per day is 2. The duration of therapy is also prescribed individually. As a rule, the course lasts no more than 7 days.
Chloxyl, today, is rarely used for opisthorchiasis, since it is less effective in comparison with drugs based on praziquantel and has a greater degree of toxicity. Moreover, Chloxyl has long been discontinued for reasons of irrelevance due to the availability of more effective alternative medicines.
Prevention
Simple prevention rules help reduce the risk of possible invasion. All efforts should be directed towards proper preparation and use of fish:
- You should not eat fish that has not undergone heat treatment or a raw product.
- Avoid lightly salted foods.
- Wash knives and board after cutting the carcass.
- Effectively freeze the product.
Due to possible infection through animals, it is necessary to limit contact with cats and dogs and feed them only well-processed foods.
Opisthorchiasis is a serious disease that leads to serious complications and consequences. If medical assistance is not refused, death may occur. Compliance with the rules of prevention helps to cope with helminthic infestations and reduce the risk of possible infection.
From the video you will learn about the symptoms and treatment of opisthorchiasis: