A thrombus is a concentration of platelets, leukocytes, or red blood cells that create a clot that stops the flow of blood. There are blood clots in the veins and arteries of internal organs. They often block a vein or artery, which can cause death. You cannot independently diagnose the presence or absence of blood clots; this can only be done in a hospital after taking tests and undergoing a specialized examination. The final diagnosis is made only by the attending physician.
- Characteristic signs and localization of blood clots
- What diseases are caused by blood clots?
Types of thrombosis
Thrombosis is classified depending on its structure. Highlight:
- Hyaline - formed in small vessels;
- Red ones are characterized by formation in the veins;
- Whites are diagnosed in the arteries;
- Mixed ones occur in the aorta and veins.
The blood clots themselves are divided into:
- Occlusion, formed due to an enlarged wall thrombus. They cause serious disruption of blood flow. The vessel is often half closed;
- Parietal. Blood clots “smear” along the edges of the vessels. Diagnosed in large arteries, veins, heart;
- Progressive is characterized by rapid movement with blood flow;
- Dilatational ones are the most dangerous. They are found in the aneurysm and are large in size. They are characterized by rapid rupture and blockage of the vessel.
Types of thrombosis
A blood clot can form in different types of vessels. According to this principle, pathology is divided into:
- Arterial thrombosis - formed due to the inflammatory process and injuries. A blood clot in the artery is accompanied by intense pain, swelling, redness of the skin, and a local increase in temperature. If one vein is blocked, it is manifested by swelling and minor pain. The general condition does not change. A blood clot formed in the superficial veins is determined by palpation. This indicates the development of thrombophlebitis;
- Venous – formed in individuals with hormonal imbalance, metabolism, or excess body weight. Venous thrombosis causes circulatory problems in the lower extremities. Next, blood flow in the lungs is disrupted. There is a threat of pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of a blood clot
6. Dizziness or fainting
The combination of chest pain and difficulty breathing can make you feel dizzy and lead to fainting.
7. Heart palpitations
If your heart rate increases, this could be a dangerous symptom of a pulmonary embolism. When the clot reaches the lungs, there is a lack of oxygen, and your heart tries to compensate by increasing the heart rate. This is a warning sign that should not be ignored.
8. Unexplained cough
If coughing attacks appear along with a feeling of shortness of breath and an accelerated heartbeat, this may indicate that a blood clot has formed in your body. A cough may be accompanied by blood, and this is a serious reason to consult a doctor.
The cause of such a cough may be a blood clot in the lungs, which leads to congestion in the airways and manifests itself in the form of a cough.
Causes of pathology
The basic reasons for the formation of blood clots in the vessels of the legs are combined into Virchow’s triad:
- Increased blood clotting. Such thrombosis is not associated with genetic predisposition. The disease occurs against the background of chronic pathologies accompanied by elevated body temperature, as well as as a result of alcohol abuse and diets that lead to dehydration of the body. Uncontrolled intake of medications with diuretic effects, oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs, and Viagra contributes to the occurrence of thrombosis. An increase in blood clotting has been noticed during frequent stress, with an active release of adrenaline, which provokes the release of aggressive substances into the blood that cause thrombosis;
- Slow blood flow. This is a problem for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, who suffer from excess body weight, have a history of cardiovascular failure, and varicose veins. Blood clots also appear due to impaired functioning of the valves during pregnancy, varicose veins;
- Injury to the blood vessels of internal tissues is another reason why blood clots form. This occurs after surgery, intravenous injections or injuries.
On a note!
The development of thrombosis is recorded against the background of oncological processes, inflammatory diseases, poisoning with toxic substances, smoking, poor nutrition, when the formation of atherosclerotic plaques occurs, which is explained by high cholesterol.
Causes of blood clots
Blood clot in a vein
11. Warm to the touch skin
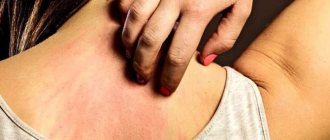
With thrombosis, the temperature of the skin may change, especially in the area where the clot is present. You will feel that this area is warmer to the touch.
This sensation occurs due to impaired blood flow and may also be accompanied by throbbing and itching.
12. Red veins in the veins
Blood clots can cause red streaks that run the length of the veins and are often warm to the touch. When you touch them, they are warmer than the skin around them and are quite noticeable. You may mistake them for a skin rash or bruises, but if they feel warm to the touch, it's worth checking with your doctor.
13. Pain in calves
When a blood clot forms in the legs, one of the common symptoms is pain in the calves. Pain is often confused with a muscle spasm or cramp, and for this reason, a dangerous symptom is often ignored.
However, unlike a cramp, which comes on suddenly and lasts a few minutes, calf pain from a blood clot comes on gradually and may persist for days or weeks.
14. Change in skin color
Redness is one of the most common symptoms associated with a blood clot, and it usually appears at the site where the clot is present. However, you should be wary of any other change in skin color. For example, the area of the blood clot may appear pale due to decreased blood flow.
As the condition worsens, the skin may take on a bluish tint and feel colder to the touch. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
15. No symptoms
One of the reasons why thrombosis is so dangerous is the fact that there are often no symptoms that precede it. At least, there are no obvious signs that require prompt attention to a doctor, and before we have time to find out about them, something irreparable happens.
For this reason, it is important to take preventive measures to prevent this from happening. Avoid sitting in one place for a long time, engage in physical activity, regulate your weight and watch your diet so that you never find out what thrombosis is.
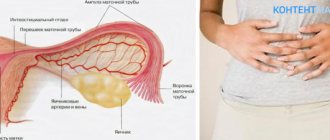
If blood clots form in the vascular cavity, this disease is called thrombosis. The accumulation of blood clots interferes with normal blood circulation, contributes to blockage of vascular lumens, and is fraught with the development of infarction of internal organs and gangrene of the extremities. Treatment of thrombosis should follow immediately.
Mechanism of thrombus formation
Many patients have a question about how a blood clot forms. Its formation goes through a number of stages:
- Stage of platelet agglutination. Damage to the walls of blood vessels occurs. Platelets stick together. Attached to the damaged area. At this time, the active substances are released;
- At the next stage, fibrin is formed. Platelets become the basis for further formation of a blood clot in the veins. The protein contents become denser;
- Red blood cells and leukocytes are captured by the thrombus;
- Precipitation stage. At this time, blood protein settles on the formed clot and becomes denser.
Blood clots attach to the damaged area. But a fragment of a blood clot can break off at any time. It enters the bloodstream, causing circulatory problems. Thromboembolism is dangerous because of a heart attack that develops against the background of a blocked vessel. A blood clot can break off as a result of various factors:
- Fast speed of blood movement through the veins;
- Large size of the formed blood clot;
- With progressive vascular diseases;
- Inflammatory process of veins;
- Excessive physical activity.
What are venous thrombosis and thrombophlebitis?
Thrombosis – literally translated from Greek means a clot. Blood clots form inside the blood vessels, which impede the normal flow of blood throughout the circulatory system.
When a blood vessel is damaged, the body begins to release fibrin and platelets, which help form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. There are situations when the vessel is not damaged, but there is a clot, and it can circulate throughout the circulatory system. These clots are called emboli.
There are several types of thrombophlebitis:
- Thrombosis affecting superficial veins (varicose veins);
- It can damage the deep vein;
- Thrombophlebitis of the lower legs;
- A disease affecting the portal or vena cava.
Risk group
Any person is susceptible to blood clots. But there is a risk group for this disease, which includes:
- Cancer patients;
- People who drink little fluid;
- Persons who make frequent and long flights;
- Patients who frequently undergo surgery;
- Women protected by hormonal contraceptives;
- Athletes taking anabolic steroids;
- Patients who have suffered spinal injuries;
- Disabled people who are bedridden;
- Obese patients.
Risk group
Diagnostics
In order to identify a blood clot and check the vessels, several effective methods for diagnosing veins and arteries are used.
Medical examination
Before the external examination, the specialist interviews the patient. Clarifies the location of pain, determines the type of pain, collects anamnesis and indicates the individual characteristics of the patient.
The external examination also includes an indication of concomitant diseases that are provoking factors.
The initial examination is limited to superficial palpation and a presumptive diagnosis. However, a final diagnosis can be made by conducting a series of hardware studies.
Hardware diagnostics
The most accurate and effective diagnostic method used by phlebologists and vascular surgeons.
- Ultrasound of the intended area. Ultrasound diagnostics gives a complete picture of the pathological process, accurately describes the disorders and stages of the disease. But, despite its effectiveness, ultrasound is not a fundamental method of thrombosis.
- Angiography is a specific research method, the results of which provide a “verdict”. The method is radiography using a contrast agent. Using the resulting images, the doctor accurately determines the location of the clot and the degree of blockage of the veins (arteries).
- Duplex scanning is an equally effective method that allows you to identify the disease at the primary stage
- Dopplerography is a method for assessing the blood supply to organs and determining the degree of blood flow disturbance. Often used in conjunction with ultrasound examination.
To check blood vessels for patency, a modern method called electroencephalography is used.
This method is applicable to identify the pathological process in the vessels of the brain.
Laboratory research
- Biochemical blood test. The concentration of substances that aggravate the course of the pathology will be determined.
- General blood analysis. Necessary to detect possible inflammation, as well as to determine the level of hemoglobin and platelets. With thrombosis, hemoglobin and hematocrit are often increased and thrombocytosis is observed.
- Coagulogram is the main laboratory method. The purpose of the analysis is to determine blood clotting time, partial thromboplastin time activity, prothrombin index and fibrinogen concentration. Based on the data obtained, the clinical picture of the disease is supplemented and treatment tactics are selected. The analysis time is about 2 hours.
Forecast
The prognosis for thrombosis of the lower extremities can be favorable or unfavorable. It will be favorable when the blood clot resolves and blood flow in the vein is restored. There are known cases of blood clot canalization. Provided the blood clot has a loose structure and high pressure in the vessel, the blood makes a channel in the vein. Complete or partial restoration of blood flow occurs.
With an unfavorable prognosis, the following occurs:
- Thrombus tissue growth. It attaches tightly to the walls of the veins, disrupting blood circulation;
- Transformation of a thrombus into an embolus as a result of separation;
- Infection of a blood clot with pus, which causes the microorganisms to spread throughout the body;
- The formation of thrombosis in multiple microvessels, causing hemorrhage of the veins.
The development of a heart attack is a defect in the body’s perception
A harbinger of a heart attack is the development of edema, and defects appear on the plaque. The body perceives these defects as holes in the vessel that need to be “patched”, and to prevent blood loss, platelets and fibrin are produced, which form a blood clot - a thrombus. It narrows the lumen of the vessel even more than the plaque, which leads to pain - angina pectoris and the subsequent development of a heart attack.
A blood clot is the cause not only of heart attacks, but also of other equally serious diseases: deep vein thrombosis in the legs, thrombolic stroke, thrombosis of arteries that carry blood to the kidneys, intestines, and other organs.
Prevention of thrombosis
You can avoid blood clots by following these simple recommendations:
- Physical inactivity leads to stagnation of blood in the veins and worsens metabolic processes. Staying in one position for a long time should not be allowed. When working sedentarily, you should take regular breaks and do some exercise;
- It is important to drink more water, at least 1.5 liters. in a day. Water is an excellent blood thinner;
- You should protect yourself from injuries, increase your immunity;
- Avoid alcohol abuse, quit smoking;
- Control your weight;
- Avoid stress if possible;
- Stick to proper nutrition.
Knowing why blood clots form, you can avoid the development of thrombosis and its complications, which without adequate timely treatment can lead to death.