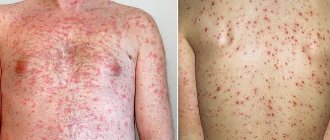
Any type of jaundice indicates an excess of bilirubin in the blood, and a yellow color of the skin and mucous membranes is noted.
Jaundice is not an independent disease, but is only a sign of liver or bile duct disease. In this case, bilirubin, which collects in the liver, is not excreted in the bile, which leads to the manifestation of characteristic symptoms.
There are many varieties of this disease, let's consider those that are most common in newborns and adults.
Photo of hepatic jaundice
Photo of suprahepatic jaundice
Subhepatic jaundice
Jaundice in children and adults
In the first days after the birth of the baby, many mothers may encounter the so-called jaundice of the newborn. This condition is considered normal for an infant, does not require treatment and goes away on its own within a week. But jaundice (symptoms) in adults should be regarded as a signal that a malfunction has occurred in the body’s functioning. Often true jaundice can be confused with false jaundice. Yellowness of the skin can be caused by excessive consumption of vitamins or foods containing carotene (oranges, pumpkin, carrots or beets). It is easy to distinguish true jaundice from carotene jaundice: with false jaundice, only the skin changes color, but the eyes and mucous membranes remain unchanged.
In fact, the manifestations that are usually called jaundice are symptoms. In adults and children, they can occur as a result of a number of pathologies or diseases, and this happens when the body cannot fully clear itself of bilirubin, a product formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin. Under normal conditions, it should be excreted from the body along with feces, but if for some reason this does not happen, bilirubin begins to accumulate in the blood. The body tries to cleanse itself by any other means: through the kidneys or skin, which is why they acquire a jaundiced tint - the color of bilirubin. Such a symptom can be the result of various diseases; it is important to find out the true cause of its occurrence and provide medical assistance as early as possible.
Types of jaundice
In medicine, there are several types of jaundice caused by various diseases:
- hepatitis B and C;
- autoimmune;
- mononucleosis;
- toxic;
- bacterial;
- medicinal.
Experts also use another classification of the disease, which affects the place of its occurrence and shade. Doctors distinguish three classes of jaundice in adults:
- suprahepatic, which manifests itself in blood diseases;
- parenchymal, which develops due to liver dysfunction;
- mechanical, associated with problems in removing bilirubin from the human body.
For these groups with symptoms of emerging jaundice, specific skin shades have been identified:
Yellowish skin color indicates the process of breakdown of blood cells
- a yellowish color with a red tint is characteristic of a liver-related disease;
- a yellowish color with a lemon tint characterizes the process of breakdown of blood cells, as in the photo;
- a dark greenish color indicates problems with the biliary tract.
The incubation period can very often last for a couple of months. The severity of the disease, its chronic consequences and duration will depend on this.
Types and causes of occurrence
For proper treatment, it is important to establish the cause of jaundice (symptoms). In adults, several main conditions can be distinguished:
- Obstructive jaundice - occurs as a result of pathology of the gallbladder or due to blockage of the excretory ducts. It may appear due to helminthic infestation, stone blockage, the presence of tumors or other causes of bile stagnation.
- Parenchymal jaundice is the result of metabolic liver disorders associated with a disorder of hepatocytes. Bilirubin is not converted into a constituent of bile, but remains unchanged. In this form, it enters the bloodstream and is then distributed throughout the body. The cause can be a variety of liver diseases: cirrhosis, hepatitis, cancer, mononucleosis, sepsis, toxic or infectious lesions.
- Hemolytic jaundice occurs as a result of a malfunction in the hematopoietic system, which disrupts the production of bilirubin. May be a consequence of an autoimmune disease, extensive hematomas, lymphomas, anemia, intoxication or hereditary predisposition.
Diagnosis of the disease
With jaundice there is pain in the right hypochondrium
At the initial stage of development of the disease, a person may not notice how the first signs of jaundice appear. Very often, the patient turns to specialists for help when a yellowish tint to the skin, eyes and mucous membranes appears. also note pain in the hypochondrium area, located on the right side. The normal functioning of digestion is disrupted.
In such cases, specialists first conduct medical research, collect all patient histories, and also study anamnesis. After that, the period of development of the disease and changes in the human body are determined. Pay attention to whether skin itching is present, its characteristics and how long it lasts.
The doctor needs to know whether there was any poisoning from alcoholic beverages or any medications, or whether the sick person had surgery on the gallbladder or liver.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of jaundice in adults are yellowness of the eyeball (sclera) and the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth and tongue. It is easier to identify in good daylight. The color intensity can vary, from lemon to yellow-orange. The skin of the face, especially around the mouth, nose and cheeks, acquires a characteristic tint, and the palms and soles also turn yellow. Over time, yellowness spreads throughout the body, staining the skin, tissues and even bone tissue. The patient notes a deterioration in his general condition, chills, headache and often pain in the liver area (right hypochondrium). Symptoms of intoxication appear: nausea, dizziness, loss of appetite, fever, muscle pain. In some cases, bilious belching and itching appear. The patient noticeably loses weight. Urine becomes dark in color and can foam when shaken and resemble beer. But feces, on the contrary, become discolored.
Diseases that cause jaundice
In order to correctly establish a diagnosis, specialists determine the real cause of jaundice and its stage.
Suprahepatic jaundice in adults is associated with the process of breakdown of blood cells - red blood cells. This helps to increase the volume of bilirubin in the circulatory system. The liver cannot cope with such a large amount of substance, which soon leads to human intoxication.
The main diseases that cause jaundice in an adult are hemolytic anemia, thalassemia, and so on.
The hepatic form of the disease is characterized by the destruction of liver cells and its capillaries. At the time of breakdown in the circulatory system, the volume of bilirubin increases greatly.
The occurrence of hepatic jaundice is promoted by:
- viral hepatitis with acute and chronic form;
- hepatitis with different etiologies;
- changes in the liver associated with chronic intoxication with alcohol, drugs and various toxins;
- mononucleosis caused by infection;
- Gilbert's disease;
- leptospirosis;
- liver cancer;
- autoimmune syndrome, which is aimed at destroying liver cells.
Such jaundice in adults is associated with the causes of the release of bile from the liver ducts. Such a violation indicates the presence of an obstacle in the form of blockage or obstruction.
Can you get jaundice?
This thought usually appears when someone close to you already has jaundice (symptoms). In adults, how is this disease transmitted and is it dangerous for other family members? Jaundice itself is a consequence of other diseases, so every effort must be made to prevent infection of other family members. The only exception may be a disease caused by a hereditary predisposition; this also includes jaundice in newborns and pregnant women, which is the norm and is associated with hormonal changes. And also those types of jaundice that were not caused by a third-party pathogen. Most viral infections are transmitted through close contact, as well as through food and drink, so precautions should be strictly observed. A common cause may be viral hepatitis. This disease is transmitted not only from person to person, but also from animals with hepatitis - dogs or cats. In this case, the virus is transmitted from an animal to a person only through direct contact; food and water are not contaminated in such cases.
In what cases may symptoms of jaundice appear?
By jaundice, people usually understand Botkin’s disease, which in medicine is called hepatitis A. Such a viral pathology leads to general intoxication of the body and disrupts the functioning of the liver. Other types of hepatitis accompanied by jaundice are also known: and. In addition, jaundice can occur in a toxic, bacterial, drug, autoimmune, or mononucleosis form.
Anemia and cirrhosis due to the development of hepatitis or alcoholism often lead to disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gallbladder. Also, jaundice often occurs due to the formation of large stones in the gall bladder and malignant tumors in the pancreas.
Obstructive jaundice occurs due to impaired removal of bile from the ducts due to the occurrence of malignant tumors, cysts or stones. The patient develops a yellow-green complexion and a fever.
Also, inflammation of nearby lymph nodes often occurs and severe pain appears in the liver area. With this type of jaundice, the patient experiences severe itching on the skin, so he scratches it to the point of wounds. The stool becomes lighter and the urine becomes darker.
Newborns often develop conjugation jaundice, which is caused by a sharp increase in bilirubin content in the body. In some cases, this form of jaundice is also observed in adults. This is due to the impact of various negative factors on the liver. One of them is the use of medications. In rare cases, conjugation jaundice refers to congenital pathologies, in particular, Gilbert-Meulengracht syndrome.
Diseases such as lymphocytic leukemia, anemia, lymphosarcoma and tropical malaria lead to the development of hemolytic jaundice. As a result of disturbances in bilirubin metabolism and immaturity of the enzyme system, physiological jaundice occurs in many premature and weakened newborns. It manifests itself in yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and drowsiness.
Sometimes a baby develops neonatal jaundice immediately after birth. It may be associated with the accumulation of high amounts of bilirubin in the blood and insufficient ability of the serum to bind it. Another cause of such jaundice is the enzymatic immaturity of hepatocytes. This pathology may require immediate treatment, since indirect bilirubin is a neurotoxic poison. It can cause damage to the cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei.
Disruption of the structure and functioning of hepatocytes can lead to parenchymal jaundice. This disease occurs due to acute viral hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. The patient is usually diagnosed with an enlarged liver. In this case, the skin acquires a yellow and subsequently a slightly reddish tint. Spider veins – telangiectasia – appear on the patient’s body.
The disease can be caused by drug-induced liver damage, cirrhosis, viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and the presence of malignant liver tumors. As a result of the development of the disease, loss of appetite, nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium, change in the color of urine and feces, and icteric discoloration of the skin are observed. Drug therapy is selected depending on the cause that led to the development of hepatic jaundice.
Prehepatic jaundice in adults develops due to the rapid breakdown of red blood cells in the body - hemolysis. In human blood, bilirubin levels quickly rise to a maximum. The liver does not have time to process the pigment and it quickly enters the blood, turning the skin, mucous membranes and whites of the eyes yellow. Typically, such jaundice is the result of hereditary diseases or poisoning of the body with certain poisons.
Symptoms of the disease can also include:
- pale skin;
- darkening of stool;
- a significant decrease in red blood cell and hemoglobin levels;
- an increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
- the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium.
Carotene jaundice does not pose a risk to human health. It is caused by consuming large amounts of foods with carotene, such as pumpkin or carrots. With this type of jaundice, the feet and palms are usually stained. It is very easy to cure such jaundice. By reducing the consumption of these products, the body is cleansed and quickly gets rid of pigmentation.
Establishing diagnosis
Correct diagnosis is extremely important. It is necessary to establish the cause of jaundice (symptoms) in adults. Treatment will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, and a course of therapy will also be prescribed that will help cleanse the body of bilirubin. The specialist will conduct an external examination, prescribe a series of tests and determine the root cause. The patient will need to have blood, stool and urine tested. Additionally, an ultrasound may be prescribed to determine the condition of the liver, bile ducts and spleen. For parenchymal jaundice, liver laparoscopy is performed.
In case of severe diseases requiring surgical intervention, as well as hepatitis, a liver biopsy and additional scanning (celiacography and splenoportography) are prescribed. Other types of tests may be prescribed. A correct diagnosis and timely treatment will help not only cure, but also reduce the risk of dangerous complications. And this is what jaundice itself looks like (symptoms in adults), the photo allows you to compare the color of the sclera of a healthy person and a patient with a high level of bilirubin in the blood.
Parenchymal jaundice
Parenchymal (hepatic) jaundice is true jaundice that occurs with various lesions of the liver parenchyma. It is observed in severe forms of viral hepatitis, icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis, poisoning with hepatotoxic poisons, sepsis, chronic aggressive hepatitis, and so on. Due to damage to hepatocytes, their function of capturing free (indirect) bilirubin from the blood, binding it with glucuronic acid to form non-toxic water-soluble bilirubin glucuronide (direct) and releasing the latter into the bile capillaries is reduced. As a result, the bilirubin content in the blood serum increases (up to 50-200 µmol/l, rarely more). However, not only the content of free but also bound bilirubin (bilirubin glucuronide) increases in the blood due to its reverse diffusion from the bile capillaries into the blood vessels during dystrophy and necrobiosis of liver cells. A icteric discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes occurs. Parenchymal jaundice is characterized by skin color - saffron-yellow, reddish (“red jaundice”). Initially, the icteric color appears on the sclera and soft palate, then the skin becomes colored. Parenchymal jaundice is accompanied by itching of the skin, but less pronounced than mechanical jaundice, since the affected liver produces less bile acids (the accumulation of which in the blood and tissues causes this symptom). With a long course of parenchymal jaundice, the skin can acquire, as with mechanical jaundice, a greenish tint (due to the conversion of bilirubin deposited in the skin into biliverdin, which has a green color). The content of aldolase and aminotransferases, especially alanine aminotransferase, usually increases, and other liver tests are changed. Urine acquires a dark color (the color of beer) due to the appearance of bound bilirubin and urobilin in it. Feces become discolored due to a decrease in the content of stercobilin in it. The ratio of the amount of stercobilin secreted in feces and urobilin bodies in urine (which is an important laboratory sign for differentiating jaundice), which is normally 10:1-20:1, is significantly reduced in case of hepatic cell jaundice, reaching up to 1:1 in severe lesions.
The course depends on the nature of the liver damage and the duration of action of the damaging principle; in severe cases, liver failure may occur. Differential diagnosis includes hemolytic, mechanical and false jaundice; it is based on the history, clinical features of parenchymal jaundice and laboratory data.
Treatment
Treatment methods can be completely different and depend on the clinical form of the disease. The main therapy is aimed at eradicating the main cause of the disease and eliminating the consequences.
- In case of an infectious disease, antiviral drugs are prescribed, as well as medications aimed at maintaining and restoring liver function. Such jaundice (symptoms in adults) can provoke infection in people who come into contact with the patient. Therefore, treatment is carried out in infectious diseases departments of hospitals with limited access to visitors.
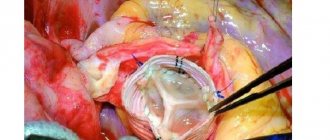
- If the disease is caused by a mechanical factor (obstructive jaundice), then radical treatment is prescribed. Tumors or stones are removed surgically, drainage of the excretory ducts is ensured for normal outflow of bile.
- For hemolytic jaundice, hormonal therapy with glucocorticoids is prescribed. In some cases, surgical removal of the spleen is indicated.
Bilirubin, which is present in excess in the tissues of patients, breaks down well under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, phototherapy (herbal medicine) may be prescribed. For jaundice, split meals and a gentle diet are recommended.
Treatment with home remedies
Traditional medicine offers a wide variety of treatment options for this disease. These are mainly herbal preparations that have a diuretic effect and also disperse bile. These include infusions or decoctions of plantain, dandelion, St. John's wort, calendula, yarrow, birch leaves and many others. But remember, before starting such treatment, you should definitely consult with your doctor, because only he can determine the real cause of jaundice and give effective recommendations. You need to choose a treatment method based on the diagnosis, otherwise irreparable harm can be caused to your health.
Consequences of the disease in adults
With timely and correct treatment, the prognosis is positive. But in the case of serious pathologies (liver cancer, cirrhosis or hepatitis A and C), jaundice can take a chronic form and even cause death. You can often come across the misconception that jaundice (symptoms) experienced in childhood in adult men can cause problems with reproductive function. This statement is not entirely true. A man who has had jaundice may well become the father of a healthy child. But with a disease such as hepatitis, caution should be exercised. At the time of conceiving a baby, both parents must be healthy, and this applies not only to the father, but also to the mother of the unborn child. To prevent hepatitis, people in contact with a sick person are given an injection of immunoglobulin. If the expectant mother is healthy and has this vaccination, then her baby will be born completely healthy.
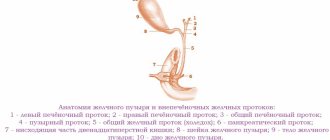
Biliary tract disease and its symptoms
Diseases associated with the gallbladder lead to symptoms of severe mechanical jaundice. It is characterized by a violation of the excretion of bile into the intestine. Such a malfunction may be associated with cholelithiasis, cancer, problems with the pancreas, as well as human worms and much more.
Obstructive jaundice is characterized by increased body temperature and large areas of scratched skin. Human feces are colorless, while urine, on the contrary, is dark in color. In a sick person, experts note increased abdominal bloating, flatulence, diarrhea or prolonged constipation. Often, such symptoms can be caused by a malignant neoplasm. In most cases, it occurs in elderly people.
Signs of the disease in pregnant women
Most girls don’t know: why is jaundice dangerous during pregnancy? Experts note that for representatives of the fairer sex in an interesting situation, jaundice can cause severe heartburn, itchy skin, and attacks of nausea. In such cases, doctors distinguish between mild and moderate forms. Most often, this disease occurs in girls with their first child.
Pathogenesis can be of two types. In the first case, the expectant mother may experience the first signs of jaundice in the first or second month of pregnancy. Symptoms at this point are:
Jaundice is dangerous for pregnant women
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- attacks of severe nausea;
- severe heartburn;
- vomiting reflex;
- sudden loss of body weight.
In this case, this disease manifests itself in the form of kidney failure or abnormal liver function.
Jaundice in adults during pregnancy is one of the most dangerous diseases. Since at this moment a large amount of fluid accumulates in the serous compartment, which causes severe swelling, bleeding and even the death of the child.
Any form of illness during pregnancy must be detected in time.
After all medical examinations, the specialist will be able to prescribe the correct and necessary treatment, regardless of what month the expectant mother is in labor.
Features of the disease in old age
In old age, this disease can appear in its most acute form and be particularly severe. Jaundice manifests itself over a long period of time, which has a detrimental effect on the body of a person over 60 years of age. Experts note that severe symptoms of the disease can lead to death in a sick patient. Scientists noted that there are about 27 deaths per thousand people. In most cases, an elderly person dies from kidney failure.
Consequences of jaundice in childhood
In the case of babies who developed “newborn jaundice” after birth, but it did not go away after two weeks, or intrauterine infection occurred from mother to child, immediate treatment should be prescribed. This course is called “kernicterus” and it is a serious pathology. The main danger of the disease is the effect of bilirubin on brain cells, which can subsequently affect the child’s mental development or disruption of certain functions: speech, hearing, vision or coordination. The mortality rate of children with nuclear flow is very high and reaches about 50%.
Diet: what you can and cannot do?
It is very important to stick to your diet if you develop jaundice (symptoms). In adults, nutrition should be gentle and not burden the gallbladder and liver.
Do not eat: fried, stewed meat, as well as poultry, fish and products using them (soups, cereals, stewing vegetables and preparing broths). Any types of canned food, pickles and marinades are contraindicated. Confectionery and bakery products, chocolate, tea, ice cream, as well as sour fruits or vegetables and eggs. It is necessary to exclude fatty foods and those containing coarse fiber; alcohol and spices are contraindicated. Food should not be hot or cold.
You can eat: light vegetable dishes, porridge, spaghetti, crackers and brown bread, vegetable oils and low-fat dairy products. In moderation, you can eat steamed or boiled poultry, fish and lean meat. Fresh fruits are good for you.