Appendicitis in infants and newborns
Less than 2% of appendicitis in children occurs in infancy, and this disease is even more rare in newborns.
There are a number of features and factors that explain and determine the unfortunately late diagnosis of appendicitis in young patients and, accordingly, the high incidence of perforation of the appendix. These factors include: difficulties in examining small children, reduced immunity, small size of the omentum, which prevents the inflammatory process from localizing in the abdominal cavity. If delimitation does occur, an inflammatory infiltrate forms.
The most common symptoms of appendicitis in young children are vomiting and restlessness. Pain, constant or paroxysmal, forces the child to pull up his legs. Refusal to eat, lethargy, and diarrhea are often observed. Sometimes you can notice a restriction in the movements of the right hip.
A small child usually has a febrile fever with appendicitis. Careful palpation of the abdomen may reveal local tenderness in the right lower quadrant, which intensifies when the hand is quickly “lifted” from the abdomen.
Data from auscultation of the abdomen can be varied - bowel sounds can be of normal intensity, and sometimes weakened or even absent. Rectal examination allows in some cases to identify local soreness and infiltration.
In young children, if appendicitis is suspected, an abdominal x-ray should be taken. A characteristic symptom of appendicitis is the presence of calcified fecal matter in the appendix.
Perforation of the appendix in newborns can occur with necrotizing enterocolitis. At the same time, other signs of necrotizing enterocolitis are sometimes observed, in particular pneumatosis of the intestinal wall.
Opinions differ regarding tactics in the presence of appendiceal infiltrate in infants. The delimitation of the process occurs in approximately half of small patients with appendicitis.
Treatment results
Children with uncomplicated appendicitis remain in the hospital for 2-3 days after appendectomy. With perforated appendicitis, the length of hospitalization increases to at least 6-8 days.
When a combination of three antibiotics is used in the treatment of appendicitis, the incidence of postoperative complications is approximately 5%, and these complications are almost evenly distributed between minor and major complications.
Mortality from appendicitis in children over two years of age is less than 0.1%, in infants - 10%, and in newborns, according to some authors, reaches 80%.
K.U. Ashcraft, T.M. Holder
Is there a specific diet after appendicitis in children? There are no special recommendations in this case. This means that there is definitely no difference between children and adults. Basically, the diet should be the same.
But naturally, adults should give up their bad habits. As for children, it is advisable to limit the consumption of sweets so as not to further irritate the intestines.
In general, the recommendations are similar; you should not eat spicy, starchy, sweet or salty foods. Include in your diet as many healthy and light soups as possible, as well as fruits and vegetables. The fact is that diet after appendicitis is the main component of the rehabilitation process.
[13], [14]
Is it possible to replant indoor flowers in October?
Sometimes, when passing by someone else’s pot with a treasured flower, your hands reach out to pinch off a small shoot. But what to do if October 2020 is not the best time for propagating and replanting plants?
Again, it’s worth turning to the characteristics of your favorite flower. For example, geranium is easily propagated by semi-lignified, green cuttings in August - early October... Dichorysandra, oplysmenus, netcreasia, syngonium nofolia or tradescantia will take root no less quickly in October. By the way, the list of plants is far from exhaustive. Maybe the list will be replenished with a new species?
The problem with replanting (transshipment) of your favorite flowers during this period is no less relevant. What to do if the optimal time for replacing the soil is missed, and the plant has grown to enormous sizes? Of course, in some cases it is advisable to postpone the event until early spring. However, for some indoor plants, October 2018 is quite suitable for replanting.
For example, in mid-autumn you can safely refresh the soil of almost all varieties of azaleas; calla lilies (calla lilies); amaryllis; ahimenes; spathiphyllum; petunia; dracaena; Tradescantia; chlorophytum; asparagus and many other plants that were planted in the garden for the summer.
Important! Only healthy flowers that have the strength to recover from the stress of the last sunny days are allowed to be replanted (transferred) in October.
The heating season begins in mid-October, which means severe tests await your pets in the form of dry air and temperature changes. Study the characteristics of your plant in advance to be able to promptly take care of air humidification or choose the right place for the flower to overwinter.
So, caring for indoor plants in October 2020 can be reduced to 4 main actions:
- moderate watering;
- reducing portions or refusing to feed;
- work to humidify the air in the room and maintain optimal temperature;
- following the advice of the lunar calendar.
We wish your home to be filled with flowers, and a luxurious, bright greenhouse to lift your spirits and warm your soul all year round.
Did you like the material? It's easy to say thank you! We would be very grateful if you share this article on social networks:
The lunar calendar, which indicates favorable and unfavorable days for planting and replanting indoor flowers and plants, the time of watering and fertilizing, is very simple and convenient for gardeners. With its help, you can easily plan certain work in accordance with the phases of the moon and zodiac signs.You can look at the 2020 moon phases, full moon and new moon days, as well as information on how they affect plant growth. Here we provide only brief information on days, what work should be carried out in a given month.
Diet by day after appendicitis
What should be the diet after appendicitis removal and what can you eat? Naturally, irritating foods should be excluded. In this case, we are talking directly about sour, salty and spicy foods.
You should not eat a lot of flour, especially in the first days after surgery, as this can cause the stitches to come apart. Therefore, you should listen to your doctor’s advice and do not prescribe your own nutrition; the consequences can be serious.
You should not disturb the functioning of the stomach or irritate the intestines, because all this can lead to excess weight and unpleasant consequences. This is why there should be a diet after appendicitis.
Who can tell me what diet should I follow after removal of appendicitis? This issue can only be decided by the attending physician. You can't do anything on your own. Flour, sweet, salty and spicy foods should be excluded.
It is advisable to eat light soups and vegetables. But even among these products there are things that should be limited. It is advisable to eat less potatoes because they contain a large amount of starch.
It is forbidden to eat fish soups, borscht and okroshka. This can cause a negative reaction in the intestines in the period after appendicitis is removed. The attending physician should provide detailed recommendations. The diet after appendicitis must be followed unquestioningly.
[13], [14]
What should a quality diet menu look like after appendicitis? It is compiled by the attending physician. After all, a lot depends on the situation itself. Therefore, it is worth providing generalized information and recommendations.
So, you should exclude all foods that can cause intestinal irritation. You need to eat only healthy foods. After all, at this stage it is necessary to help the body, recover, and not aggravate the situation.
In general, the daily diet should include soups, cereals and fruits. It is advisable to hold off on eating meat and fish products. Exclude potatoes, sour fruits and pea puree.
Is there a diet for days after appendicitis? Naturally, this exists, but such a menu is compiled only by the attending physician. It is advisable to eat little and sparse food on the first day after removal.
So, light soups that do not contain meat or fish are perfect. These can be broths and vegetable soups. For the first days, it is advisable not to consume anything else. Over time, it will be possible to include porridge in the diet, but not peas.
You should give up sweets until your body is completely restored; you should not irritate your intestines. As for drinks, these may not be sour juices and tea. It is advisable to exclude coffee and other things; there should not be any harmful products. The diet after appendicitis is prepared by day by the attending physician.
Diet after appendicitis in adults
What should the diet be like after appendicitis in adults and are there any specific recommendations? Of course, only the attending physician can answer this question accurately. But there are certain recommendations that should be followed.
So, in the first days after removal, you need to avoid foods that can cause irritation. You can’t eat flour, it contributes to excess weight. This may cause the seams to come apart.
Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol. It is not recommended to eat too hot or cold food. Detailed “instructions” regarding nutrition should be given by the attending physician. It is important that the diet after appendicitis is followed.
Do you know what the diet should be after gangrenous appendicitis? The first step is to eliminate irritating foods. As a first course, you should leave light soups that are full of vitamins.
Fish should be excluded; it is advisable that the soup include vegetables. As for second courses, it can be any porridge except pea porridge. It is not recommended to eat potatoes; they have a high starch content.
If you sort out vegetables and fruits, then in this case you can eat everything except sour ones. No citrus fruits, cranberries, currants, etc. It is advisable to give preference to bananas, apples and pears.
[8], [9], [10]
Are there any special recommendations regarding nutrition or diet after appendicitis with peritonitis? In this case, everything is much more serious, so you need to follow a certain diet. It is better to eat light foods that are not capable of causing irritation and contributing to the development of excess weight.
These should be light vegetable soups, but without potatoes. For main courses, it is advisable to choose porridges such as buckwheat, oatmeal and rice. You should not eat sweets, drink carbonated drinks and eat too spicy and salty foods.
In general, it is advisable to wait a while with this. The body is under stress, so it should not be overloaded. That is why the diet after appendicitis should be drawn up by the attending physician.
What should be the diet after purulent appendicitis and is it necessary to follow it? Naturally, after surgery it is imperative to follow a diet. It is prohibited to compile it yourself; this issue is dealt with exclusively by the attending physician.
As after any operation, a certain diet must be followed. So, no harmful products. The daily diet should include light soups and broths. Puree soups are perfect, but only without potato content.
It is advisable that they include carrots, onions, zucchini and beets. Pea puree should be excluded as it can irritate the intestines. In general, the diet after appendicitis should be properly designed.
Proper care of indoor flowers in October 2020, what to pay attention to
Issues of watering and subcortex
Firstly, it is necessary to thoroughly study the characteristics of each specific indoor plant. The variability of care in October 2018 is directly influenced by such characteristics as:
- beginning of the rest period
- flowering time
- general condition of the plant
- other.
With the onset of autumn, most varieties and types of indoor flowers experience a slowdown in metabolic processes. The fading of a flower and the absence of young greenery is a signal to reduce the volume of watering and stop applying mineral or organic fertilizers. The plant is resting. This means that in October it is necessary to minimize soil moisture (so as not to cause waterlogging), and feed the roots less than once every 2 weeks / 1 month. This rule applies, for example, to gerbera and geranium, but crassula (crassula), fragrant callisia, mimosolia jacaranda and many other plants do not need to be fertilized at all in October.
However, it is worth remembering that the resting phase is not the same for all indoor flowers. For example, ginura, azalea, Decembrist or some varieties of clivia in the off-season, on the contrary, prepare for flowering and active growth. Therefore, reducing the amount of fertilizing in October can have a detrimental effect on the appearance and health of buds.
And then there are exceptions! Fertilizing Billbergia blooming in October is strictly prohibited!
Some indoor plants are interesting because they do not have a pronounced dormant period. So, if comfortable conditions are created for abutilon (indoor maple) in September - October, it will continue flowering for many more months. The same applies to drip beloperone. During the flowering period (all year round), the plant needs full feeding with mineral or organic fertilizer.
Use of antibiotics for appendicitis
For several decades, the theory has been supported that for acute appendicitis, the only effective treatment is surgery. Despite this, in some cases, treatment of inflammation of the appendix is possible with the help of antibacterial therapy.
Whether antibiotics can be used to treat inflammation of the appendix should only be decided by a doctor. Independent choice of medications will lead to one result - various complications that may indeed require emergency surgical intervention. Antibiotics are prescribed to patients with suspected appendicitis in the following cases:
- When it is established that inflammation is at the initial, catarrhal stage of its development. With good immunity and early initiation of treatment with antibacterial drugs, in some cases further inflammation can be stopped and the patient will not require surgical intervention.
- At the stage of preparation for surgery. Antibiotic treatment should be started before surgery to avoid serious complications. If during appendectomy it is determined that there are extensive signs of inflammation, then antibiotic therapy should be extended for several days.
- Antibiotics are prescribed if the patient categorically refuses surgery. A sick person should understand that it is not always possible to stop the inflammatory process with antibacterial therapy and therefore one should not assume that replacing surgery with medications will help to recover.
- Antibacterial therapy is used in cases that are difficult to diagnose. Appendicitis is often disguised as other diseases, and if anti-inflammatory treatment is not started at the time of diagnosis, then perforation of the inflamed organ is possible.
The decision on the choice of treatment method for appendicitis must be entrusted to the attending surgeon. Refusal to hospitalize and undergo surgery can result in death. You should especially not show independence if you suspect inflammation of the appendix in young children.
Elderly people have their own characteristics
As for older people, inflammation of appendicitis occurs with a number of characteristic features that complicate the diagnosis of the disease. First of all, this is a mild pain syndrome, which is often absent altogether. Because of this, the determination of appendicitis occurs with a significant delay.
You can suspect something is wrong by the loss of appetite and tension inherent in the muscles on the right, in the iliac region. You can feel this by palpating an area of the body. However, it is not recommended to examine the body yourself, as you can harm yourself. Also, in older people, various atypical manifestations of appendicitis are observed, which science has not yet been able to systematize. Therefore, it is recommended to visit a doctor if there are any doubtful signs, undergo a check-up and a full range of studies. This will determine whether the appendix is inflamed, as well as identify concomitant pathologies.
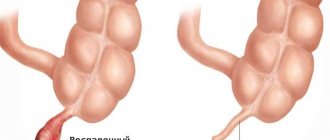
Chronic appendicitis is called chronic inflammation of the appendix or appendix. This disease is not observed very often, and the cause of its development is considered to be acute appendicitis. In such cases, they talk about the residual form of the disease. But sometimes the symptoms of chronic appendicitis occur only periodically, then the patient is diagnosed with a recurrent form of the disease. This usually occurs if, after removal of the appendix, a stump more than 2 cm long remains.
First aid for appendicitis
If symptoms appear that indicate the possible development of appendicitis, you need to behave correctly. First of all, you need to call an ambulance; only a qualified specialist can decide how to treat your disease and whether you need hospitalization in a hospital. Before the doctor arrives, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- You need to lie down in bed and try not to make sudden movements.
- You should not take painkillers or laxatives. The use of laxatives will lead to increased peristalsis, and this may result in rupture of the inflamed appendix and, accordingly, the development of peritonitis. Painkillers smooth out the clinical picture of the disease and thus complicate diagnosis.
- You can place a heating pad with ice on the area of pain. It must be removed after 15-20 minutes and applied again after a short break. It is forbidden to use heat, since in case of acute inflammation this will contribute to the rapid development of a purulent process in the organ.
- It is advisable not to eat and drink less until examined by a doctor and diagnosed.
The cessation of pain is not a good reason to refuse to see a surgeon. Sometimes the cessation of pain indicates a more serious development of a purulent and necrotic process in the appendix. There may be no pain at the beginning of the development of peritonitis.
Contraindications to non-surgical therapy
To reduce the risk of postoperative complications, the patient should follow a gentle regimen. So, you can get out of bed after surgery no earlier than six to eight hours, but only if consciousness and breathing are completely restored.
It is possible that for patients at risk of developing a postoperative hernia, it is necessary to wear a special postoperative bandage.
The patient needs to do dressings every day, always assessing the stage of wound healing and using antiseptics. Depending on the intensity of the pain, painkillers are used.
In cases where there was a need to use drainage to prevent complications of a purulent nature, the administration of such antibacterial drugs from the class of cephalosporins or macrolides is required in the postoperative period.
Sutures are removed seven to eight days after surgery if wound healing is not complicated.
After surgery for phlegmonous appendicitis, heavy physical activity is not recommended for about three months. The doctor can only prescribe exercise therapy or breathing exercises.
For two to four weeks after surgery and discharge from the hospital, to prevent constipation, you need to follow a diet. You can only eat foods grown by a doctor.
For the first two days, you need to eat exclusively liquid porridge and vegetable puree. It is also worth adding jelly or low-fat kefir to your diet. Next, gradually introduce black bread with a small amount of butter.
The transition to regular food that is familiar to the patient can only be done if the patient feels excellent and has normal stools. But do not forget that food should not be spicy, pickled, smoked, fatty, fried or hard.
You need to eat in small portions, about five to six times a day.
[57], [58], [59], [60], [61], [62], [63]
In medicine there is a term “chronic appendicitis”. It is preceded by acute inflammation of the appendix, which did not lead to surgery. The symptoms of the pathology gradually subsided.
In this case, the appendix periodically becomes inflamed and reminds itself of itself with relapses of acute pain. The chronic form of its inflammation responds better to non-surgical treatment. Features of the manifestation of this disease:
- Periodic pain in the right lower abdomen.
- Increased pain with movement.
- In women, pain may be perceived as a gynecological problem.
- Sometimes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea appear, and the temperature rises.
- The attack goes away on its own, although it can go into a critical phase.
Some patients with acute appendicitis are contraindicated for surgery. In such cases, conservative treatment is prescribed. Thus, the group of contraindications to appendectomy includes:
- Inflammatory processes in the digestive organs.
- Disturbances in other organ systems, such as the development of cancer.
- Inflammatory appendiceal infiltrate, which develops 24 hours after the development of appendicitis. In such cases, abscesses and ruptures may develop.
Refusal to undergo surgery if prescribed by a doctor can lead to a ruptured appendix, peritonitis, abscesses, sepsis and even death. Contraindications to conservative therapy:
- pronounced adhesive process in the abdominal cavity;
- progression of chronic appendicitis;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- acute appendicitis, if there are no contraindications to surgery.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostics includes the use of the following laboratory and instrumental methods:
- Palpation. Initially, the doctor examines the patient, using his hands to determine the source of pain. The exact position of the inflamed process is difficult to identify, but the starting point can be recorded.
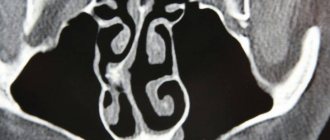
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Can diagnose appendicitis with a probability of no more than 50%.
- Laparoscopy. Allows you not only to detect the inflamed appendage, but also to remove it immediately.
If after ultrasound and laparoscopy there are still doubts about the diagnosis, then deep microwave radiothermography is performed, which accurately determines the presence of the disease even in the early stages. This technique makes it possible to non-invasively diagnose destructive phlegmonous appendicitis.
- General and biochemical blood tests, blood glucose, RW, ELISA. Particular importance is given to the white blood formula, where in case of phlegmonous appendicitis a large number of young forms of neutrophils (the main types of leukocytes in human blood) are present.
- General urine analysis. Patients exhibit increased levels of red blood cells and white blood cells.
Differential diagnosis
Phlegmonous appendicitis is differentiated from the following diseases:
- ectopic pregnancy (for women);
- right-sided renal colic;
- acute cholecystitis (for elderly people);
- acute pancreatitis;
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- perforated gastric ulcer;
- acute inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs;
- torsion of cysts and other tumors;
- mesadenitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- exacerbation of gastroenterocolitis;
- pleurisy.
Diet recipes after appendicitis
Do you know any recipes for a diet after appendicitis? There is no need to create something special. The diet should be familiar, but without fatty meat and fish. Carbonated drinks and sugary foods should be excluded.
If we are talking about soups, then they should contain only healthy ingredients. These include carrots, beets, zucchini, peppers and onions. You should wait a bit with potatoes; a high starch content can have a detrimental effect on a recovering body.
If we are talking about main courses, then it is advisable to give preference to porridge, but exclude peas. In fact, there are quite a lot of recipes, but only the attending physician can give his recommendations, which will need to be followed. A diet after appendicitis should help the body recover, and not cause harm.
Methods of treatment for inflammation of the appendix
In case of acute appendicitis, surgery will help to avoid complications and quickly stabilize a person’s general well-being. To be sure that the person seeking help is developing inflammation of the appendix, the surgeon must conduct a series of tests, analyzes and instrumental examinations.
Appendicitis in its clinical manifestations is similar to a number of other diseases, some of which can be treated conservatively. Some pathologists with symptoms similar to appendicitis also require emergency or planned surgery.
The correct diagnosis depends on the professionalism of the surgeon, the accuracy of all studies, and examinations of other specialists. Difficulties in diagnosis are associated with the atypical location of the appendix, which changes the typical clinical picture of the disease.
It is especially difficult to determine developing inflammation in young children and older people. The first cannot describe exactly what changes in well-being bother them. In elderly patients, symptoms of acute inflammation of the appendix are usually smoothed out; in older people there is often no pain syndrome.
Only a doctor should decide how to treat a patient with suspected appendicitis. If surgery is proposed, you cannot refuse it, as this can lead to serious complications.
During surgery, you can accurately establish the diagnosis and, if necessary, remove the appendix or during the operation make a decision on resection or further treatment of other abdominal organs.
Treatment of appendicitis in the acute development of inflammation is only possible through surgery. But there are also forms of appendicitis for which antibiotic therapy may be suggested. It is also necessary not to forget that the likelihood of developing severe complications depends on what kind of care is provided to the patient in the first hours of the disease.
If acutely developing appendicitis is diagnosed, the operation is not delayed. It is believed that performing surgery within two hours of a patient with appendicitis being admitted to hospital is the optimal treatment.
With this approach, the least number of complications are recorded, and the recovery period does not take much time. Removal of an inflamed appendix can be done traditionally and using endoscopic equipment.
- Traditional surgery involves making an incision in the abdominal wall in the area of the inflamed appendix. After making an incision into all soft tissues, the surgeon examines the appendix and surrounding tissues, removes the organ, treats the wound and stitches it up. After an uncomplicated operation, recovery takes two to three weeks; patients usually easily tolerate such surgery.
- Endoscopic surgery involves making small incisions in the abdominal wall. An endoscope is inserted through these incisions, the surgeon examines the area of pain from the inside and decides to remove the organ. After endoscopic intervention, the recovery period takes only a few days and the patient does not have the difficulties associated with the recovery period after a traditional appendectomy.
In case of acute appendicitis, ordinary hospitals can most often only offer a conventional operation; it is performed free of charge. If possible, doctors also suggest endoscopic intervention, although there are also some contraindications to it.
The vermiform appendix of the cecum is a digestive organ that is also part of the immune system. Its removal is not so harmless. No surgeon will remove the appendix unless it is inflamed.
- Drug treatment also requires consulting a doctor, since antibiotics for appendicitis are administered intravenously.
- According to statistics, the drugs helped 63% of patients, and 37% still required surgery.
- In patients who took a course of antibiotics, complications occurred 31% less often.
Please note once again that conservative treatment for inflammation of the appendix should only be prescribed by a doctor. It has certain indications:
- Catarrhal stage of appendicitis development. Drug treatment helps stop the mild inflammatory process.
- The patient's categorical refusal to undergo surgery. This is dangerous for the patient, but the doctor cannot force the operation.
- Difficulties in diagnosis. Inflammation of the appendix can mask other diseases, such as myocardial infarction.
The basis of conservative treatment is antibiotics: macrolides, fluoroquinolones, penicillins, tetracyclines, carbapenems. Commonly used antibacterial drugs:
- Metrogil;
- Dalatsin;
- Zinacef;
- Tienam;
- Meronem;
- Imipenem.
Additionally, the patient may be prescribed symptomatic therapy to alleviate the condition. It includes the following pharmacological groups of drugs:
- antispasmodics;
- immunomodulatory;
- anti-inflammatory;
- improving blood circulation.
When positive dynamics are observed from the use of medications (symptoms of abdominal muscle tension, pain, and temperature decrease), treatment of chronic appendicitis is continued for 10 days. Conservative treatment regimen:
- For the first 2 days, patients are administered 2 antibiotics intravenously: the first - every 12 hours, the second - every 8 hours.
- Then for another 7 days the patient takes antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets.
Treatment of appendicitis with folk remedies is unacceptable. They are used only after the approval of a doctor and exclusively in combination with the main treatment. If a specialist allows it, you can use the following recipes at home:
- For 1 liter of boiling water, take 1 tbsp. l. dry wormwood, keep the infusion for 1 hour in a thermos. Drink 50 g in one sip, as the product tastes bitter.
- Mix equal parts of yarrow, strawberry and raspberry leaves. Brew 1 tbsp. l. collecting a liter of boiling water. Leave for 15 minutes. in a water bath. Drink the decoction throughout the day.
Pain is the first signal
When highlighting the signs of inflammation of appendicitis, pain is first mentioned. It appears in the area near the navel. It feels dull, does not go away over time, and is permanent. Sometimes about halfway through. Less often, painful sensations cover the entire abdomen. Sometimes pain is felt on the right in the iliac region.
Increased discomfort occurs when a person walks or bends over. There are sharp unpleasant sensations when coughing and laughing. It is very painful to sneeze. But older people tend to have no pain syndrome.
Please note that with an atypical location of the appendix, pain may be felt in an unpredictable place. Sometimes it hurts on the right under the ribs, near the pubis or in the area of the kidneys and ureters. Painful sensations may radiate to the hips or lower back. In some cases, it is noted that pain is felt in the external genitalia. A vague area on the left side of the body may hurt.
A few hours after the initial appearance of pain, sensations shift toward the appendix. These signs of inflammation of appendicitis in women are very important: if you suddenly stop feeling pain, there is a high probability that the disease will transform into a gangrenous form, which is associated with the death of nerve endings in the affected area. You can’t delay: you need to urgently call a doctor!