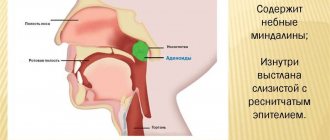
Stomatitis is a disease of the oral mucosa, which is characterized by an inflammatory process in it. This disease causes a feeling of discomfort, and in its acute form, severe pain in the mouth. Stomatitis is especially common in children. This is due to the immature immune system, as well as the habit of babies to taste all objects, as a result of which all kinds of germs and viruses get into the mouth.
The disease in children almost always occurs in an acute form, accompanied by loss of appetite and high fever. Lack of treatment can lead to stomatitis developing into a chronic form , and in the most severe cases, inflammation can affect other organs. Therefore, every parent is obliged to know the symptoms and methods of treating this disease.
Types of stomatitis in children and causes of its occurrence
All types of stomatitis in children can be divided into several types: fungal, herpetic, aphthous.
Fungal stomatitis or candidiasis is caused by a certain type of fungus that attacks the oral cavity. It affects mainly children under three years of age.
The herpetic type of disease is caused by the herpes virus in the active phase. Children under three years of age are also susceptible to it, but even after this age, it can appear in children if their immune system is seriously weakened.
Aphthous stomatitis appears due to mechanical, chemical or physical effects on the mucous membrane. In addition, it may be a consequence of allergic reactions. This type mainly affects children from one to three years old.
The disease in children can occur either in the acute phase, when severe discomfort is felt, or asymptomatically. In rare cases, a child may exhibit several types of disease at once, which significantly complicates the treatment of stomatitis in children.
Advanced stomatitis can develop into a chronic form, when the disease returns with any weakening of the immune system.
Factors influencing the disease in children
The incidence of stomatitis in children is several times higher than in adults. This happens due to the fact that, firstly, the thickness of the mucous layer is very thin , as a result of which it is injured even with little effort. Secondly, not fully formed immunity, which has not yet developed antibodies to fight viruses and bacteria.
Also to blame may be the lack of antiseptic enzymes in saliva, which appear only in adolescence. A reflexive desire to taste objects , which leads to the entry of a large number of bacteria into the oral area. In addition, the presence of foreign objects in the mouth can lead to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. And frequent infection with viral diseases, due to which the immune system is weakened.
Fungal stomatitis in children
Fungal stomatitis in children mainly appears when hygiene rules are violated, when candida fungal bacteria enter the oral cavity with unwashed foods or dirty objects. Infants become infected with this disease either at birth, passing through the birth canal infected with thrush, or through breastfeeding.
In addition, the disease can appear in children after taking antibacterial agents, due to the lack of necessary bacteria in the body that can resist the fungus.
Nuances of therapy for candidal stomatitis
With candidal stomatitis, the oral cavity is covered with a white coating with a light curdled discharge. When removing the film, the damaged surface may bleed. The main reason for the occurrence of this form of stomatitis in a baby is considered to be the immaturity of the microflora in the oral cavity. Provoking factors (dirty objects, toys) easily activate the growth of the fungus. All general methods of treating the disease are relevant.
But a number of antimycotics are added:
- Levorin is an antifungal polyene antibiotic. Available as an ointment and a lyophilisate form (dried and frozen substance) for preparing a solution. Can be used when treating a child over 2 years old. The powder is dissolved in water according to the instructions, rinse the mouth 3 times a day. If the child is small and does not know how to perform such procedures, then a few drops of a liquid composition are injected into the oral cavity or an ointment is used to treat ulcers and the entire mucous membrane.
- Daktarin is a spray/ointment that neutralizes and neutralizes the cells of Candida and Aspergillus fungi. The active components actively act on the surface microflora and almost do not enter the blood.
In addition to specific medications, rinsing with herbal decoctions is recommended; to relieve discomfort, children over 3 years of age can take antiseptics, analgesics in the form of lozenges, and lozenges.
Symptoms of fungal stomatitis
When a fungal infection occurs in children, the following symptoms appear:
- The white coating has a slightly loose consistency, which is easily removed.
- Bleeding and redness of the mucous membrane in areas of inflammation.
- At the initial stage, the inflammation is localized in a small area of the oral cavity and over time affects the entire mucous membrane.
- Burning, itching, pain in the mouth when eating, dryness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Restless sleep.
With this type of disease, the temperature usually does not rise and the lymph nodes do not enlarge. Intoxication of the body is not observed.
Symptoms: common points for all types of stomatitis
Each diagnosis has a number of specific symptoms. But doctors identify several common signs characteristic of any type of stomatitis:
- The baby suddenly complains of weakness, a headache, muscle discomfort appears - these symptoms indicate intoxication of the body.
- On the second day, subfebrile temperature rises. Range - from 37.5 to 39-40o.
- Regional submandibular lymph nodes enlarge: the formations harden and are easily palpated, the skin in these areas may be reddened.
- The mucous membrane becomes hyperemic.
- As a result of inflammatory processes (depending on the cause and type of pathogen), erosions are formed.
- In 60% of cases, there is varying degrees of redness of the gum arch around the teeth, rashes along the edges of the lips, and on the adjacent skin.
Ulcers can be single or merge together. Placers of small erosions, small and shallow, often form. In 30% of children, the disease begins acutely, and in other cases the primary symptoms are blurred.
The chronic form of stomatitis with periodic remissions and relapses is characterized by less intoxication, the general condition deteriorates slightly, and the temperature does not rise. The remaining symptoms coincide with the traditional ones.
Treatment methods for stomatitis caused by fungus
The tactics for treating stomatitis in children with candida fungus is based on the use of antiseptic and antifungal drugs and alkalization of the environment inside the oral cavity.
For non-advanced forms of the disease, only local therapy is often prescribed, which includes:
- Rinse or wipe with a solution of water and baking soda 2-5 times a day after meals. Prepare the solution at home - take 1 tbsp. soda per 200 ml. water. This product is used in a warm state.
- Treatment of foci of the inflammatory process with boric acid, “Blue” and borax in glycerin, which is available in the form of a solution.
- Use of topical products that have an antifungal effect - Clotrimazole ointment, Imazol cream paste, Candide for external use.
In advanced and severe forms of the disease, it is necessary to use systemic antifungal drugs - Diflucan, Clotrimazole, Flucanazole.
These medications are prescribed only by a doctor, as they have a number of serious side effects. In addition, their frequent or incorrect use can lead to fungal microorganisms becoming resistant to the active substance of the drugs.
If the baby gets sick from breastfeeding, the mother's nipples must be treated with local antifungal drugs. This is necessary to prevent re-infection of the infant.
In addition to the direct impact on fungal lesions, it is necessary to strengthen the immunity of children. For this purpose, vitamin complexes and immunomodulatory drugs are used.
During treatment of fungal stomatitis, it is worth transferring the child to a certain diet , which provides the following:
- Exclusion from the diet of spicy and salty foods, which can cause irritation of the oral mucosa.
- Rough food, which can injure the mucous cavity, is not allowed.
- Food is consumed only in a warm state.
- Temporarily remove vegetables, some types of fruits and soda from the menu, as they create greenhouse conditions for the growth of fungal microorganisms.
If treatment is started on time and the child has a strong immune system, only local therapy is sufficient. Children should rinse their mouths at the first sign of stomatitis. This will help you avoid resorting to potent drugs.
Treatment
The main directions of treatment of childhood stomatitis are represented by local therapy, correction of the daily diet and strengthening of the body's defenses. The basis of therapy is the use of local drugs. Only a specialist who can select medicinal formulations taking into account the nature of the pathology knows exactly how to cure stomatitis.
To treat ulcers that are localized in accessible areas of the oral cavity, you can use antiseptic solutions, ointments, and gels. For the aphthous form of stomatitis, antibiotics should be used, for thrush - ointments and creams with antifungal effects, and for the hermetic form of the disease - special antiviral drugs.
Attention! If the formations are located in the throat or tonsils, you can use the appropriate medicinal formulations available in the form of sprays.
During the treatment of stomatitis, the child should be excluded from eating any food that causes irritation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity . Restrictions apply to salty, sour or hot foods. In this case, it is better to give preference to food in liquid or semi-liquid form in order to avoid causing new damage and exacerbation of pain.
The development of stomatitis focuses attention on the fact that the defenses of the child’s body are quite weakened. In order to avoid relapse of the pathology, as well as to speed up healing, it is imperative to strengthen the baby’s immunity. To prescribe vitamin complexes, you should contact your pediatrician.
How to rinse your mouth for stomatitis?
Regular rinsing of a child’s mouth is an important component of successful treatment. For these purposes you can use:
- Stomatidin is a strong antiseptic solution that has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. It is recommended to rinse your mouth 2 to 4 times daily, maintaining an interval of 4 hours between repetitions of the procedure. The optimal duration of treatment, according to expert recommendations, is about seven days.
- Miramistin. This drug is available both in aerosol form and in the form of solutions for rinsing the mouth. The procedure should be repeated about three times a day. The medicinal composition is quite effective in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms.
- Chlorhexidine is a well-known solution that has an antiseptic effect and helps suppress pathogenic microflora and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. The use of undiluted solution is allowed only if the child is over five years of age. Younger children should rinse their mouths with a composition prepared by mixing equal amounts of antiseptic with boiled water.
- Furacilin is another well-known composition that belongs to the category of antiseptics with a wide spectrum of effects. The solution is prepared by dissolving one tablet in boiled water (500 ml). It is recommended to repeat the rinsing procedure at least 3 times a day.
- Stomatophyte is a herbal preparation that has bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effects. To prepare an effective medicinal solution, it is recommended to dilute about 10 ml of the drug with boiled water in the amount of ¼ cup. You should rinse your mouth with the prepared mixture about 4 times a day.
Stomatophyte
How to treat stomatitis in the mouth in children: solutions, ointments and gels
The basis of therapy for stomatitis is the treatment of damage to the mucous membrane in the mouth in order to suppress the activity of the pathogen, eliminate pain, normalize the microflora, accelerate the regeneration of tissue structures and prevent the appearance of new lesions.
Important! Today, there are many medicinal formulations that can effectively and quickly cope with the listed tasks, but experts most often give preference to:
- Cholisal is a drug that has a good analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. It comes in the form of a gel, which is recommended to be applied to damaged areas three times a day before or after eating.
- Kamistad is a medicinal composition based on lidocaine and chamomile infusion. It is characterized by a good analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. It is recommended to use the medicine three times a day to achieve a quick therapeutic effect.
- Kalgel is a gel-like combination drug that has an antimicrobial and analgesic effect. When the question arises of how to smear stomatitis in a child’s mouth to reduce pain, most often the attending physicians choose this gel, which can also be used in the fight against gingivitis and other inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity. The composition should be used up to six times a day.
- Hexoral is a composition with pronounced activity against pathogenic microorganisms. It comes in the form of a spray, which should be used after eating food. The quick effect lasts up to 12 hours, so it will be enough to use the composition twice a day, evenly spraying it in the child’s mouth.
- Solcoseryl - a paste that stimulates the epithelization of damaged tissue structures and promotes rapid healing of existing ulcerative defects associated with stomatitis. It is recommended to use the composition three times a day. The treatment procedure must be preceded by rinsing the mouth with any antiseptic composition and removing excess moisture using cotton swabs. The composition should be used at least 3 times daily.
- Inhaliptom is a combined drug, the composition of which is a soluble form of streptocide and essential oils. It has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and to a certain extent analgesic effects. The procedure for irrigating the oral cavity with this spray should be repeated three times a day.
- Yodonil is a medicinal composition based on iodine. This product is characterized by low toxicity and high effectiveness against many pathogenic microorganisms. Can be used for rinsing the mouth in children over 1.5 years old. The medicinal solution is prepared by mixing 5 ml of medication with warm water in a volume of 50 ml. The rinsing procedure should be repeated about 4 times a day for a treatment duration of no more than 5 days.
- Metrogyl Dent is a combination remedy used to combat inflammatory diseases in the oral cavity. It is produced in the form of a gel, which is recommended to treat the affected areas at least three times a day for a treatment duration of up to 1 week.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
The appearance of herpetic stomatitis in a child is always associated with a serious weakening of the immune system , in which the herpes virus, without encountering resistance from the immune system, affects the oral mucosa. Such weakening is often associated with past illnesses or an incorrect diet, which is poor in vitamins.
Herpetic stomatitis is especially difficult in children for the first time, when the immune system is not yet adapted to fight pathogenic bacteria. In this case, stomatitis in children causes high fever and intoxication of the body.
Bacterial stomatitis: specifics of the disease
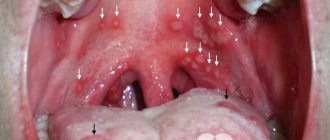
This form of the disease often occurs against the background of tonsillitis, sinusitis, other diseases of the ENT organs or upper respiratory tract caused by bacteria, often staphylococci or streptococci. With this type of stomatitis, a yellowish, drying, crust-like formation often appears on the lips. This type of illness in children is accompanied by high fever. The immune system is already weakened, resistance to developing pathogenic microflora is minimal.
For bacterial stomatitis, it is mandatory to take antibiotics and compounds that have bactericidal activity against cocci. Bioparox is prescribed locally - the affected areas of the mucous membrane are irrigated, bacteria lose their ability to multiply, and inflammation decreases. Systemic antibiotics are also indicated, the dose of which is determined by the dentist, taking into account the medications already taken by the child.
Chlorophyllipt oil is effective in combating bacterial infections. An alcohol solution is not recommended - using it can cause additional irritation of the mucous membrane. Chlorophylls isolated from eucalyptus leaves are active against staphylococci and act as powerful antiseptics. The drug is not recommended for preschool children. Children are prescribed Miramistin and other “mild” and hypoallergenic antiseptics.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis
The herpetic type of stomatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of small red spots on the mucous membrane , in place of which bubbles with a clear or whitish liquid inside appear within one to two days. As the disease progresses, the number of blisters increases, and they appear on the outer surface of the lips, nasolabial triangle and in the nasal passages.
- High temperature , which appears on the second or third day. It is practically not affected by antipyretic drugs.
- Enlarged lymph nodes located in the jaw and neck area.
- Severe intoxication of the body , which may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, chills, headaches, weakness, etc.
- Loss of appetite due to discomfort in the oral cavity.
- Sleep disturbance.
In mild forms of the disease, the number of bubbles usually does not exceed 2-3 pieces, which are located on the inner surface of the lips. Body temperature does not exceed 38 degrees and is easily removed with antipyretic drugs. There is no intoxication.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
To cure stomatitis in children, the following set of measures is used. Firstly, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin can be used to dry and cauterize the blisters on the mucous membrane. After several days, the solutions are replaced with decoctions of chamomile and sage.
To disinfect the oral cavity, solutions of Miramistin, Lugol, Chlorhexidine or other antiseptic drugs for similar purposes are used. To reduce pain, anastatic drugs are used, which are often also antiseptics. Among the most common are Inhalit and Tantum Verde.
To accelerate the transition of herpes to the latent stage, antiherpetic drugs are used - Acyclovir, Oxolinic ointment, Bonafton . To restore the tissues of the mucous membrane, regenerating preparations are used - Shostakovsky balm, sea buckthorn or rose hip oil.
Childhood herpetic stomatitis in severe forms requires mandatory hospitalization of the child, since in this case there is severe intoxication of the body, which can lead to dire consequences. This form of stomatitis is treated with systemic antiherpes drugs.
In addition, during treatment it is necessary to adhere to a diet that excludes spicy and sour foods from the daily diet. Food is consumed only warm, so as not to injure the mucous membrane.
General treatment recommendations
- Depending on the pathogen, the main drug is prescribed. Its dosage is calculated depending on the weight and age of the baby. For most types of stomatitis, antiseptic rinses are necessary. We recommend decoctions of chamomile, sage, ready-made solutions: Rotocan, Chlorhexedine bigluconate, prepared solution of Furacilin. The wounds are treated with oil Chlorophyllipt. You can use tampons soaked in medications: such compresses alleviate symptoms and relieve inflammation.
- It is easy to clean wounds from protein deposits using pharmaceutical hydrogen peroxide - this treatment is recommended to be carried out immediately after detection of primary ulcers in the mouth. This option is not suitable for infants and children with hypersensitive mucous membranes.
- Rinsing the mouth with a soda solution (usually a concentration of half a teaspoon per glass) should be used for no more than 3 days, since the tissues of babies are vulnerable, and this composition loosens the structure of the surface integument and prevents epithelialization. Infants can treat the pacifier with antiseptic solutions or inject 2-3 drops from a pipette onto the tip of the tongue or cheek.
- As anesthetics for children, it is recommended to use paste-like preparations, sprays or lozenges with a combined disinfecting and analgesic effect. For children over 12 months old, Cholisal is suitable. This gel is universal: it can be prescribed for all types of stomatitis. It has an anti-inflammatory effect, acts as an analgesic and a disinfectant.
- After 4 years, you can dissolve Hexoral lozenges, which will relieve pain and speed up recovery. This remedy is considered an excellent antiseptic and mild analgesic. Hexaliz - lozenges - are indicated from 6 years of age.
- Lidocaine Asept spray is recommended for teenagers. Inhalipt can be used for different age categories. Babies are prescribed a gentle dose, and the drug is sprayed gently onto the front of the tongue or cheek.
- Dentists advise treating the mucous membrane with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, which promotes epithelial regeneration: the microflora is restored in the affected area, and wounds heal faster. Antihistamines are also indicated to help reduce swelling and alleviate the general condition.
After acute symptoms have been relieved, special attention should be paid to stimulating the immune system, which will allow the body to effectively fight viruses and bacteria found on the mucous membrane and prevent the development of pathogenic fungal microflora. For example, the drug Imudon promotes the development of phagocytosis, activates the creation of immunocompetent cells, increases the level of immunoglobulin in saliva, and protects the mucous membrane from damage. There are special toothpastes that increase local immunity: “PRESIDENT Baby 0-3” from 0 to 3 years, “LACALUT baby” from 0 to 4 years.
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis in children occurs when damaged areas of the mucous membrane appear in the oral cavity . Pathogenic bacteria enter these areas, after which inflammatory processes begin. It is worth noting that with strong immunity, minor wounds do not develop into stomatitis. It is the weakening of the immune system that leads to the body being unable to defeat bacteria.
Damage to the mucosa during aphthous stomatitis can be divided into mechanical, chemical and physical. Mechanical injuries include injuries caused by objects (pens, toys with sharp edges, forks, etc.) and body parts (fingernails, sharp fragments of teeth).
Chemical damage occurs due to contact with the mucous membrane of toxic or active substances (acids, detergents, etc.). Physiological damage includes injuries to the mucous membrane caused by thermal means. In addition, allergies can be the cause of this type of stomatitis.
Clinical manifestations
The initial stage of aphthous stomatitis has similar symptoms to the common cold. This is why diagnosing the disease becomes difficult and the doctor will not be able to quickly prescribe treatment. In children, their body temperature rises sharply, they become lethargic, their appetite decreases, irritability and tearfulness appear, salivation increases, there is bad breath, and a white coating forms on the surface of the tongue.
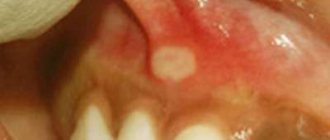
Ulcers are easily detected during oral examination. In most cases, aphthae occur on the moving parts of the mouth - tongue, cheeks, lips and gums. At the initial stage, the neoplasms look like oval tumors, which increase in size after 2-3 days.
If they are opened, their surface is covered with a thin crust of white or yellowish tint. The rim is bright red. A mild form of aphthous stomatitis can heal on its own.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
The following signs of stomatitis in a child are common :
- Foci of inflammation are small ulcers with a yellowish or grayish coating.
- Fever.
- The appearance of pain in the oral cavity, especially when eating.
- Sleep disturbance in a child.
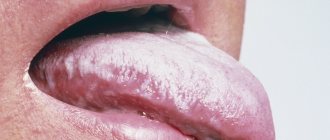
During an allergic reaction, a child develops a “geographic tongue,” when a large number of small watery blisters appear on this organ, as well as a white coating.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Initially, in order to treat stomatitis in a child, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence. To do this, you should consult with a dentist, allergist, therapist and gastroenterologist . After examining the oral mucosa and determining the etiology, suitable medications are prescribed.
Before prescribing medications, general-purpose solutions are used - Rotokan, Hexicon, Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin, etc., which have antibacterial and antiseptic properties.
It is strictly prohibited to treat aphthous stomatitis in children without consulting a specialist, since an error in determining the cause of the disease can lead to the disease becoming acute.
Prevention of stomatitis
Like any disease, it is better not to treat stomatitis, but to prevent its occurrence . To prevent this disease, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations and rules:
- Breastfeeding mothers need to wash their breasts at least twice a day to prevent thrush.
- During pregnancy, a woman must be examined for the presence of thrush in the genital area and, if detected, be sure to treat it.
- It is imperative to maintain the child’s immune system at a high level. To do this, you should periodically give the child vitamin complexes or immunomodulatory drugs. Such therapy is especially important after viral diseases.
- The child's diet should include a large amount of vegetables and fruits , which contain many useful vitamins and elements, which improves immunity.
- Before giving food to your child, you should check its temperature. Food should be neither hot nor cold.
- Feed children only from personal dishes , since bacteria that do not harm an adult can easily break a child’s immunity.
- Strictly monitor the sanitary condition of the child's toys . If they are used outside, then when you come home, you need to wash them thoroughly. Soft home toys must be washed at least once every two months, as they accumulate a huge amount of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms.
- Strictly observing personal hygiene measures is necessary for both the child and the parents. It is especially important to strictly control the cleanliness of the hands of children from 6 months to one and a half years, since during this period they are almost constantly in the baby’s mouth.
- Buy toys for children without sharp and rough surfaces so that they cannot injure their oral cavity while playing.
- Monitor household chemicals in the house. Keep it out of the reach of children.
- Supervise the child's play with pencils , pens or other objects that have a pointed shape.
- Feed children only from special cutlery that does not have sharp edges. Typically, forks or spoons for children are made of plastic or hard rubber.
- When introducing new products into the diet of children, it is necessary to first monitor the body’s reaction . Children often develop allergic symptoms. In this case, you should immediately use specialized drugs.
Diagnosis and therapy of childhood stomatitis – video
Stomatitis in children is one of the most common diseases. For children, this disease brings pain and discomfort in the mouth. There are many reasons for the appearance of the disease, but almost always the disease occurs against the background of a weakened immune system. The doctor talks more about the disease in this video.
Pathogenic bacteria that multiply in the oral cavity can easily move to other organs, and then the disease simply turns from unpleasant to dangerous. Therefore, parents should periodically examine the oral mucosa of their children and, if any deviations from the norm are detected, immediately contact a doctor who will prescribe correct and effective treatment.
Drugs
Young patients are prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as rinsing with ready-made antiseptic solutions. For rinsing, you can use the following drugs, which are sold in pharmacies:
- Chlorhexidine . This is the most effective antiseptic. This remedy helps destroy harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity. Chlorhexidine should be used after each meal for 7-10 days. Pain and discomfort disappear after the first use.
- Hydrogen peroxide . The presented remedy will help relieve pain, swelling and excessive itching. To prepare the solution, you need to take one tablespoon of hydrogen peroxide and dilute it in 100 ml of water. The oral cavity is treated three times a day for 10 days.
- Iodinol . This is an effective and efficient antiseptic, which is a must during the treatment of aphthous stomatitis.