0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2018.10.13
30
Hip diseases
When a newly born baby is diagnosed with hip dysplasia or congenital hip dislocation, this really frightens parents. Fortunately, it is not a terrible incurable disease. We can say that these words mean an immature hip joint; the pelvic bones are underformed or incorrectly formed. The good news is that if such a problem is detected in time and treatment is started immediately, the child will soon be completely healthy, but if the newborn’s symptoms are not noticed in a timely manner and not treated, then very sad consequences are likely.
Hip dysplasia in children
Hip dysplasia in children is one of the most common orthopedic pathologies. Statistics say that about 3% of newborns are born with subluxations (most often the left joint), and in Europeans the problem is observed more often than in African Americans, and girls are sick ten times more often than boys.
Fortunately, if the situation is not neglected and you are constantly under the supervision of an orthopedist, the joint itself will “mature” to normal.
Newborn
Clinical picture
How to suspect dysplasia in a baby? Doctors identify several main symptoms by which young parents can determine the presence of the disease in their child.
Baby
Hip dysplasia in newborns is expressed by the following symptoms:
- slipping, doctors call this symptom a click. The problem is observed only in the first ten days of life; rarely the symptom persists for up to three months. To determine it, the baby is placed on his back, bent at the knees and hip joints. The bend angle should not be less than 90 degrees. Carefully spread the baby’s legs to the sides, and a characteristic click is heard (the femoral head returns to its rightful place);
- The baby has limited hip abduction. Normally, when the baby’s legs are abducted, it is 90 degrees. With dysplasia, one leg can only move 45 degrees. The symptom does not last long, disappears completely up to three months, then appears with greater force. Trouble signals not only hip dysplasia in a child; sometimes the symptom is the cause of another disease (rickets, spastic paresis of the limbs).
Baby at 2–3 weeks
In addition to the signs described above, at this age, orthopedists identify several other symptoms:
- shortened limb. The sign accompanies a unilateral defect. It is very simple to determine the pathology: lay the baby on his back, place his feet on a flat surface, if one knee is lower, consult a doctor. This symptom characterizes a severe dislocation; delay in treating the disease is fraught with serious complications, even disability;
- asymmetrical folds. Place your baby on his back with his legs bent and spread apart. The skin folds formed on the inside of the thigh should be the same. With dysplasia they are at different levels. Turn the baby over on his tummy, the buttock folds should also be symmetrical, if this is not the case, visit a doctor immediately.
Child over one year old
The main symptom of dysplasia in a one-year-old baby is an uncharacteristic gait. Damage to a joint on one leg causes lameness; if both joints are affected, the baby walks like a duck. It is quite difficult not to notice the problem; detection of pathology is a serious reason to visit an orthopedist and begin treatment.
What it is?
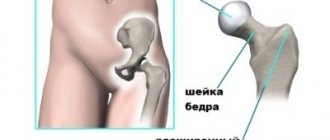
Dysplasia is defined as any abnormal formation of organs in the body. With hip dysplasia (ICD-10 code: Q65.0.), the structure of muscles, ligaments, bones and nerves can be disrupted. The pathology is mainly due to the immaturity of the articular joint, the bones in the joint are physiologically correctly aligned, their physiological formation has simply not yet been completed. This type of dysplasia is considered the mildest. The elements of the joint are easily injured, but the joint itself is not deformed.
The degree of underdevelopment can vary - from severe pathologies (hyperplasia and hypoplasia) to simply increased mobility due to weak ligaments or insufficient connective tissue. The head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis form the actual joint, which has ideal rotational properties. Infants have a peculiarity: their ligaments are very elastic, and the articular cavity is located almost vertically and flatter than in adults.
If for some reason the head of the bone in a baby is not held inside the socket, but begins to shift, then subluxation occurs (partial movement beyond its intended place). If the exit is complete, and contact between the femoral head and the articular fossa is lost, then this is a dislocation (unilateral or bilateral). Lack of treatment can result in a situation where the acetabulum becomes overgrown with fatty or connective tissue, then treatment is much more difficult, if not impossible.
Formation of the vehicle
Changes in the hip joint occur throughout the life of even an adult. But the prenatal period and the first 12 months of infants’ lives are of particular importance for the formation of the connection. At the 6th week of pregnancy, the laying of the tissues of the TS occurs and in the 2nd month one can already notice mobility in the joint.
The hip joint is not stable enough even in a baby born without pathology. The surface of the pelvic bones, which form the acetabulum, partly has a soft structure. And in the area of their articulation there is a cartilaginous layer, in the language of specialists called the Y-shaped plate.
The head and a small section of the neck of the femur bone also have a cartilaginous structure. As for the size of the acetabulum, it is somewhat smaller than in adults. Therefore, only a third of the head of the bone enters it (in an adult – 2/3), and its angle of inclination reaches 60˚ (in an adult – 40˚).
This structure hardly fixes the head of the femur in its natural position. Its retention is achieved due to tissue tension in the ligamentous apparatus and articular capsule. Upward displacement is prevented by a limbus located at the edges of the acetabulum. This structure, so characteristic of newborns, causes general weakness of the joint, which becomes the main cause of instability of the joint.
Causes
In modern medicine, there are several theories about the occurrence of dysplasia in infants. What can cause such a pathology? Obstetricians claim that pregnancy pathologies, difficult childbirth, infections, or the environment are to blame, while other experts are confident that the main factor is a hormonal factor, since girls make up 80% of children with pathology, they are much more sensitive to changes in the mother’s hormonal levels.
The bottom line is that a pregnant woman’s body intensively produces hormones necessary for childbirth (especially for the first). Oxytocin increases muscle tone, but can contribute to fetal dislocations. Relaxin prepares a woman for childbirth, makes her femoral-sacral joints as elastic as possible and gives flexibility to the pelvic bones. Unfortunately, hormones, while helping the mother, can sometimes harm the child; by acting on the mother, they also affect the baby’s bones.
The joints of the fetus are very weak and easily deformed, and if the soft head of the femur jumps out of the socket, the weak ligaments will not be able to return it back. This is why many babies develop dysplasia immediately after birth.
Pregnancy
Also risk factors include:
- Difficult labor, post-term or premature baby
- Posterior position of the fetus before birth. When the baby comes out with his butt forward, the pelvic bones experience extreme stress, which increases the possibility of developing the problem tenfold. The bones are still too plastic, the articular head falls out of the socket and is unable to return to its place on its own.
- Magnitude. The larger the fetus (3500 and above), the more uncomfortable it is for it to actively move in the womb, which prevents the joints from fully developing.
- Tight swaddling. In countries where it is not customary to tightly swaddle newborns, dysplasia practically does not occur. When Japan officially banned traditional swaddling, the incidence rate dropped sharply, from 3 percent to 0.2 percent. If a child is constantly wrapped tightly, this can easily cause the joint to fall out of its proper place.
- Genetics. Hip dysplasia is 4 times more likely to affect children whose relatives had a similar pathology, mainly on the mother’s side.
- Ecology. Pathology occurs five times more often in environmentally polluted regions.
Reasons may also include poor nutrition of the pregnant woman, lack of foods with vitamins E and B, and poor supply of calcium, iron, phosphorus and iodine to her body. Various infectious diseases, gynecological diseases (fibroids or adhesions), bad habits, some medications, severe toxicosis - all this can lead to intrauterine deformity.
Types of hip dysplasia in infants: preluxation, subluxation, dislocation
Table 1. Types of dysplasia in infants
| Type of dysplasia | How does it manifest? |
| Pre-dislocation of the hip (precedes subluxation and dislocation of the hip). | The hip joint capsule is stretched. The head of the femur is displaced, but can be easily returned to its correct anatomical position. May progress and lead to more severe forms. |
| Hip subluxation | Incomplete displacement of the head of the hip joint relative to the socket. The ligament in the femoral head stretches and loses its inherent tension. |
| Hip dislocation | There was a failure in the process of joint formation. Improper connection of the femurs: The femur does not sit in place. It can be either congenital or acquired. |
Development options
If the disease was diagnosed in a child before six months, then it responds well to treatment and goes away very quickly. If the child is already walking, long-term treatment may be necessary, and further complications are possible. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner and is not treated, an adult will most likely have difficulties with walking and health in general (arthrosis, neoarthrosis, coxarthrosis), and may have no idea what the cause was. Dysplasia in adults, as a rule, is diagnosed accidentally, for example, during an X-ray or ultrasound, and it can only be eliminated surgically, since the body has long been fully formed.
When dysplasia is cured and left behind, the child is healthy and can lead exactly the same life as his peers. The only thing that doctors do not recommend is to play sports professionally. The exceptions are water sports and skiing, they are very useful and well stabilize the muscles of the lower extremities. Another recommendation is to maintain normal weight; excess body weight is a danger to joints.
Dislocation
Symptoms
In the early stages, pathology is difficult to identify, since signs of hip dysplasia are very mild, so all newborns are immediately carefully examined to look for possible pathologies. Immediately after childbirth, a first examination is carried out, followed by regular examinations by a pediatrician and an orthopedist, and in addition it is necessary to do a planned ultrasound at one month, three months, six months and a year. If the disease is not pronounced, then it is difficult for parents to identify its presence; this should be done by a doctor; treatment here is most effective precisely in the initial stages.
Signs of hip joint pathology in children under one year of age can be clearly visible even visually, but more often they are so hidden that they can only be determined by the close gaze of an experienced doctor, who can notice distortions in the angles of the child’s bones on an x-ray. A visit to the doctor is mandatory if symptoms described below are noticeable:
- Different knee heights. You need to lay the baby on his back, straighten his legs and bend them at the knees, one knee may be slightly higher than the other.
- Marx-Ortolani sign. Laying the baby on his back, you need to bend his legs at the knees and gently spread them in both directions. Infants have increased flexibility, and flexed legs will easily touch almost completely to a horizontal surface. If you feel a clicking sound during extension or the child “does not allow” you to move your hips, consult a doctor.
- Measuring skin folds. You need to lay the baby down with its legs extended and examine the inguinal folds of skin and folds under the butt - they should look similar and be located at the same angle. If there is pathology, there will be more folds on one side.
Baby
It should be noted that the above symptoms also exist in 40% of completely healthy babies; during the process of growth they disappear without a trace. The presence of visual signs is not enough to accurately diagnose, and if necessary, the doctor will conduct a more detailed examination.
How to identify the disease in a newborn?
Mild hip dysplasia usually does not appear in the baby after birth. However, at an older age, the occurrence of pain and the appearance of intolerance to heavy physical activity indicate that the joint was underdeveloped in utero. In the case when such changes in the articular surfaces lead to joint failure, its subluxation or dislocation develops, the following signs of which can be identified in a newborn:
- When trying to separate the baby's legs, there is a feeling of limited movement of the limb, which is accompanied by pain. Since the femoral head does not fully contact the articular surface of the acetabulum, the amplitude of abduction of the leg is reduced.
- A symptom of hip slipping, which is also determined when trying to separate the baby’s legs. In this case, the femoral head automatically moves into the joint (a characteristic click is felt), and then leaves it again due to the underdevelopment of the structures of this anatomical region.
- Misalignment of the femur, causing the limb to become shorter. This is also manifested by visual asymmetry of the inguinal folds of skin in a newborn.
Every neonatologist and obstetrician-gynecologist knows how to identify the symptoms of the congenital form of hip dislocation that accompanies dysplasia. It is these specialists who, after identifying signs of pathology, invite a pediatric orthopedist for consultation after childbirth. Having examined the newborn, he can not only confirm the disease, but also prescribe a set of examinations to accurately determine the degree of hip dysplasia.
The pediatric orthopedist fully evaluates all segments of the lower limb, the length of both legs, and the angles at which the child’s leg can flex, abduct, or adduct. It is also assessed whether there is indeed a “clicking” symptom and an insufficient angle of abduction of the limb. To establish a final diagnosis, a specialist prescribes an ultrasound of the hip joints for a child in the first year of life, and less often, an x-ray of this area of the body. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will be able to select the most effective method of treating this pathology in a newborn.
Hip dysplasia in a newborn is detected by the results of an objective examination, as well as ultrasound (or radiography).
Diagnostics
Even if there are some symptoms, this does not mean that the baby is at risk of dysplasia, and vice versa, there are many options for the manifestation of the problem in children (about 20%), in which there are no known symptoms, so the diagnosis can only be accurately established using hardware research.
- Ultrasound is indicated for all infants up to three months. This method is practically harmless to the baby’s body and at the same time quite informative. However, the ultrasound technique has a drawback: the results are not accurate enough, then doctors additionally use x-rays to obtain the necessary information.
- X-ray and ultrasonography. The technique is used for older children. The fact is that the bones of newborns are not dense enough and do not show up well on X-rays; it is also not recommended to load the body with additional radiation. The importance of the image is that its decoding helps to recognize the holistic picture of the problem and the stage of the pathology.
Important! It is best for parents to go for an x-ray while the baby should be sleeping (if he does not move, the picture will come out much clearer).
Properties of massage
To treat hip dysplasia, physical exercises in the form of massage are used, which is appropriate at all stages of the disease. Massage should be performed only by a qualified specialist, since the effectiveness of the procedure largely depends on the professionalism of the massage therapist. Massage should not be used without a doctor’s prescription, as this may negatively affect the baby’s health. However, if the need for a massage is obvious, but for some reason it is not possible to contact a professional, you can carry out the procedure yourself.
Child massage is divided into two separate stages: general and local. The general massage has a light structure and prepares for deeper effects. This approach helps to establish psychological contact and calms the child before the main procedure. The local part of the massage has a direct effect on the affected area and creates a therapeutic effect. The duration of the exercises is no more than twenty minutes, of which five are for the general impact.
A general massage involves lightly stroking the entire body using circular, spiral movements. This is followed by more vigorous rubbing. The entire procedure is carried out using the fingertips, without excessive pressure and excessive energy. The second part of the exercises is characterized by a transition to the buttocks area and directly to the dysplastic joint. The pathological area is rubbed with a slight tingling, then the hip joint is fixed, and the leg makes a spreading movement, while holding the child’s leg by the knee.
Massage movements should be like a fun game with a child.
Consequences
A defect that is identified at the very beginning of life goes away quickly because it has not yet become a serious problem. However, without proper correction, dysplasia already in adolescence can cause lameness, osteochondrosis, disorders of posture and gait; it can lead to pain in the joints and back, curvature of the spine, distortion of the pelvis and even to a wheelchair.
Therapy
Treatment
Before the age of one year, articular dysplasia is not considered a disease as such; despite this, its correction is mandatory. The main task of the correction is to properly secure the femoral head in the articular cavity for a certain time and allow the ligaments to strengthen so that displacement does not occur during movement. The desired physiological position is considered to be a pose when the baby’s bent legs are further spread apart. For correction use:
- Orthopedic devices that fix the lower limbs in a bent and spread position. Such devices include a variety of leg braces, splints, corsets made of plastic, fabric and leather.
- Pavlik stirrups are a popular brace, named after a doctor from the Czech Republic who came up with the idea of securing the lower limbs with a special bandage made of straps and fabric. This design rests on the chest and does not allow the legs to be moved. You need to wear the retainer around the clock without removing it, this is the only way to achieve a positive effect.
Stirrups
- The Freika pillow, a soft design, also fixes the legs in the desired position, and can be removed to bathe or feed the baby. Sometimes more rigid fixation is required, then plaster is used.
- Wide swaddling. With this method, only the baby’s arms are swaddled, but the legs can move freely and “swing.” Advice! If you constantly use a diaper a couple sizes larger than necessary, this will also be a wonderful prevention of dysplasia.
- Massage and exercise therapy are the most pleasant and effective methods of therapy. To begin with, parents should undergo several sessions with a massage therapist and a specialist in therapeutic exercises, and then do everything on their own; most often, children perceive the exercises as an exciting game.
Massage
- Surgical treatment is indicated when conservative methods do not help. Laser exposure and prosthetic installation operations are used.
Gymnastics
Trying to cure hip dysplasia using traditional methods is useless!
Methods and general rules of treatment
The method and nature of treatment for hip dysplasia in children depends on the degree of damage and the age of the baby. If the child is six months old, in most cases conservative treatment is used; older children are allowed surgical intervention. The choice is made by an orthopedist after consultation with a pediatrician or pediatric surgeon.
Useful tips for parents
The baby subtly senses your mood; any worries and worries negatively affect the child’s health and slow down the healing process.
Follow some recommendations from pediatricians:
- behave normally, do not pay attention to medical devices;
- buy new toys, keep your baby occupied with them, walk in the fresh air more often;
- regularly check your baby’s skin under the tires for an allergic reaction, inflammation, or diaper rash;
- carefully study the rules for using tires and stirrups;
- no matter how difficult it is, don’t panic, learn to cope with emotional stress.
Look at a selection of didactic games for developing memory and attention in children.
The rules for the use and dosage of Tizin drops for children for a runny nose are described in this article.
On the page https://razvitie-malysha.com/novorozhdennye/aksessuary/kolyaska-osen-zima.html read tips on which stroller is best to choose for a newborn for the winter.
Conservative therapy
Simple defects are corrected by medical manipulations without surgical intervention. These methods include:
READ ALSO: What to do and what to do if your child often suffers from colds: methods of strengthening children's immunity
- wide swaddling for hip dysplasia. The method is used as a prevention and treatment of the disease. Use cloth diapers, the fabric located between the legs fixes the hips in the desired position. Wide wrapping allows the legs to move freely. For children under three months of age, in most cases this treatment is quite sufficient;
- gymnastics. Repeat the exercises from the first days of your baby’s life. Such manipulations have a positive effect on the rapid recovery and general condition of the child. The manipulations are quite simple: bend and spread the baby’s legs, make circular movements with your hips. Do all exercises with special care, do not harm the baby;
- use of medications. The medications are prescribed exclusively by the doctor; the baby is prescribed corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid injections. This treatment is used in difficult cases and almost always has a positive effect on the baby’s health;
- therapeutic massage for hip dysplasia. The course is prescribed by an orthopedist, initially the exercises are performed by a specialist, then parents can perform therapeutic procedures on their own;
- use of special devices (Pavlik stirrups, Freik pillow). They help fix the child's legs in the correct position.
The orthopedist determines which method to use; it is strictly prohibited to carry out any medical manipulations independently without consulting a doctor.
Surgical intervention
The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- conservative treatment did not produce any results;
- the child has a severe form of hip dysplasia; it cannot be corrected without surgery;
- the pathology was discovered late, the child’s age exceeds six months;
- re-dislocation of the joint is observed after treatment.
The operation is allowed only for one-year-old children. Carrying out manipulations at an earlier age is fraught with serious complications.
Types of surgical intervention:
- minimally invasive operations. They are performed not on joints, but on nearby muscles;
- openly reduce the femoral head. Sometimes an additional operation is performed to correct the depression and build up roofs;
- Salter or Pemberton osteotomy. The angle of the hip harness is changed, and special plates are installed for one year.
All operations are stressful for a child’s body and require a qualified specialist. Be prepared for a long recovery period, but the results will be worth it.
Prevention
To prevent and prevent the problem, it is necessary to create the best conditions for pregnant women, eliminate the influence of harmful exogenous and occupational factors, medications, and eat right.
If there is a risk of dysplasia, for example, an ultrasound shows that the baby will be a girl, and the fetus will be delivered head up, then to prevent problems with the joints, doctors recommend a cesarean section.
To avoid the development of dysplasia, the child must be worn correctly. There are special backpacks for carrying and a variety of slings on sale. In those countries where mothers carry their offspring, tying them to their backs or stomachs with their legs wide apart, no cases of hip dysplasia have been recorded at all. Although it is not recommended to carry the baby on the side of an adult, then the child does not sit symmetrically.
Do not miss appointments at the clinic and show your baby to an orthopedic specialist as soon as possible. Timely diagnosis and correction of pathology eliminates expensive, lengthy and hazardous treatment in the future.
Main symptoms
Diagnosis and determination of the degree of development of hip dysplasia is carried out by an orthopedic doctor, since only a specialist can correctly interpret the existing symptoms. Despite the fact that the final verdict on the presence or absence of a disease is made by the doctor, there are a number of symptoms by which parents can determine whether to sound the alarm. To notice the manifestations of the disease at home, you should pay attention to the following signs:
- asymmetrical structure of the buttocks and gluteal folds;
- one baby's leg is shorter than the other;
- the child spreads his legs asymmetrically while lying on his back;
- the appearance of an additional fold on the thigh;
- When bending the legs, a click is heard in the hip or knee joints.
These symptoms are not guaranteed signs of the presence of dysplasia. However, it won't hurt to see a doctor. With timely treatment, the severe consequences of the disease can be avoided, while the slightest delay will aggravate the course of the disease with inevitable complications.
The presence of certain signs should be a reason for an immediate visit to an orthopedic doctor from the first years of a child’s life.