Liver hemangioma is a benign neoplasm of vascular origin that affects one or both lobes of the organ. This tumor is a tangle of blood vessels, the development of which was disrupted during embryonic development. The benign nature of the neoplasm makes it relatively safe, since it is not prone to malignant degeneration. These benign tumors appear more often in women, which is due to hormonal characteristics.
Hemangiomas are often detected in children during the diagnosis of other pathological conditions. In most cases, such tumors do not cause any discomfort. Only when the tumor size is more than 5 cm and there are manifestations of rapid growth, targeted surgical treatment is required.
Classification
There are several approaches to classifying this pathological condition. Depending on the structural features, there are 2 types of such tumors:
- Capillary.
- Cavernous.
Capillary hemangioma is a relatively small benign formation that is formed from venous vessels. Such formations affect both the right and left lobes of the liver with equal frequency. In most cases, these tumors do not exceed 0.5 cm in size and cannot cause any complications. Such hemangiomas have a specific structure: they have chambers filled with blood, separated by septa.
Despite the fact that the prerequisites for the appearance of such tumors are laid during intrauterine development, additional impulses are required for the formation of a visible hemangioma. In adults, the causes of a tumor and its increase in size often lie in taking estrogen-containing medications; in the fair sex, it is in pregnancy.
Cavernous hemangioma is formed from many intertwined small vessels. In most cases, such a neoplasm is located inside the tissues of the right or left lobe of the liver. Such tumors are potentially dangerous because they tend to grow rapidly. They can reach approximately 20 cm in diameter. They are often accompanied by complications caused by ruptures in the walls of the hemangioma.
Depending on the nature of the clinical picture, 4 types of such tumors are distinguished:
- Uncomplicated education.
- Asymptomatic form.
- Complicated tumor.
- Atypical hemangioma.
The last variety is of particular interest. Atypical hemangiomas of the left and right lobes of the liver are formed as a result of other pathological processes in the liver tissue. Gradually, these tumors become overgrown with a hard fibrous membrane, which creates compression of the surrounding healthy tissue. In addition, they can create conditions for malignant degeneration of cells surrounding the tumor. In most cases, hemangiomas of any type are single, but multiple tumor formations also occur.
Form of the disease
In medical science, any benign tumor in the liver is called hemangioma. There are two types of this disease:
- capillary,
- cavernous.
The focus of the disease can be either single or multiple. The first is most often diagnosed, but multiple lesions are not uncommon.
- Capillary hemangioma consists of several autonomous cavities with blood, they have a vessel and are separated by septa. With intense physical activity, during sudden movements, as well as with injuries to this area, there is a danger of rupture, which entails intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
- Cavernous hemangioma occurs when several lesions merge into a single whole, developing into formations with a diameter of over 10 centimeters.
Reasons for appearance
There are several theories regarding the origin of neoplasms such as hemangioma. It is believed that the prerequisites for their appearance are laid during the period of intrauterine development. Some people have a clear hereditary predisposition to such a pathology, since blood relatives in such cases have tumors similar in structure.
In most cases, the size of the tumor does not exceed 3 cm in adults. In infants, such benign tumors are no larger than 0.5 cm. In this case, they do not affect the functioning of the organ.
When it comes to a neoplasm such as hemangioma, the causes of large benign tumors often lie in various additional external and internal factors. These include:
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal medications;
- uncontrolled use of medicines;
- eating foods high in animal fats;
- taking drugs;
- traumatic injury;
- surgical interventions performed on the liver.
Exposure to radiation and toxic heavy metals can be a provoking factor for the formation and growth of hemangioma.
Causes of hemangioma
Doctors cannot find the exact cause of hemangioma. It is often congenital, but it can also occur in adults - under the influence of sex hormones, especially while expecting a child. The appearance of a vascular tumor of the liver can be provoked by:
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- bile duct inconductivity;
- bruises;
- hepatitis;
- high cholesterol;
- injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- hormone therapy;
- hypertension;
- poisoning;
- Acute respiratory infections in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Treatment of enterobiasis in children
- How to make rolls - step-by-step recipes. Rolls at home, photos and videos
- How to apologize to a guy
Symptoms of the disease
If the hemangioma does not exceed normal sizes, then no signs of its presence are observed; with liver hemangioma, there are no symptoms of organ dysfunction. Often people throughout their lives do not realize that they have this deviation. In women, hemangioma larger than 6 cm is much more common than in men.
Such formations are extremely dangerous during pregnancy, since an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and the compression effect on the liver by the growing uterus can cause a rupture of the wall of the formation.
Erased symptoms are observed with the growth of large cavernous tumors, reaching 10–20 cm. In this case, the patient may have complaints about:
- liver enlargement;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea;
- flatulence;
- bowel disorders;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating.
In rare cases, large hemangiomas in the liver provoke the appearance of general symptoms, including fatigue, decreased tolerance to physical activity, increased sweating at night, etc.
Hemangioma in children
Such neoplasms can be detected even in newborns. In most cases, a hemangioma in a child does not lead to obvious symptoms. In addition, it is possible to eliminate such a tumor on your own.
In schoolchildren, such benign formations do not manifest significant symptoms, so they are diagnosed extremely rarely.
Features of treatment
The method of getting rid of a tumor largely depends on its size and shape.
Small tumors (up to 5-6 cm in volume) do not require special action. They are monitored and ultrasonic controlled after 3 months from the moment of detection. In the absence of any dynamics, ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed every 6-12 months.
The need for surgical removal is determined individually. This course of events leads to:
- rapid growth of liver hemangioma - more than 50% of the original size per year;
- volume more than 5-6 cm;
- bleeding of atypical tissue;
- aggressive manifestation of symptoms;
- inaccurate determination of the benignity of the tumor.
Possible complications
Active growth of hemangioma is associated with some risks. During physical exertion and bruises, such a formation can rupture, causing extensive internal bleeding. In rare cases, the development of this complication entails severe anemia. If the course is unfavorable, death is possible if surgical treatment is not carried out in a timely manner and the source of bleeding is eliminated. Significant manifestations of the development of this complication are acute abdominal pain and deterioration in general condition.
In addition, there is a high risk of thrombosis of the vessels that form the hemangioma, as well as compression of the veins that feed healthy liver tissue. In these cases, tissue necrosis and sepsis may develop. These conditions pose a danger to the patient's life.
In rare cases, rapid tumor growth provokes severe liver failure.
Liver hemangioma - symptoms
It often happens that liver hemangioma does not bother a person in any way. Small formations can remain “in the shadows” all their lives, but when they begin to grow, problems appear. Due to pressure on neighboring organs, signs of liver hemangioma appear, such as:
- pain and discomfort in the right side;
- nausea;
- vomit.
Sometimes tumors rupture. This happens as a result of sudden movements, abdominal injuries, or too much stress. The rupture of the hemangioma and the associated bleeding are accompanied by sudden severe pain in the abdominal cavity. With this symptom, it is advisable to contact a specialist very quickly. This is because the bleeding is too intense and can even lead to death.
Diagnostics
If this formation is present, you should contact a gastroenterologist. But in most cases, hemangioma is diagnosed accidentally. Since this disease practically does not manifest itself with severe symptoms, examination by a gastroenterologist and taking an anamnesis are not very informative. Such vascular formations in the liver are in most cases diagnosed using ultrasound.
Ultrasound reveals a formation in the parenchyma of the organ with clear contours and a heterogeneous internal structure. To clarify the nature of the existing compaction, an MRI of the liver and biliary tract is often performed. In addition, to identify the structure of the hemangioma, angiography of the celiac trunk is often performed. To determine the benignity of the tumor, static scintigraphy may be prescribed.
Liver tests and blood tests in most cases are uninformative, because they remain normal even with large formations of this type. Carrying out a puncture biopsy for such tumors is dangerous, because it can cause massive bleeding. Differential diagnosis for hemangioma involves excluding cysts that have developed as a result of an increase in the number of certain parasites, and tumors of other types, including malignant ones.
Diagnosis – liver hemangioma
As practice shows, in most cases, patients learn about education by chance - during a general examination. An ordinary physical examination for small tumors is ineffective because they cannot be felt, and blood and urine tests in almost all cases remain absolutely normal. How to diagnose the problem? Liver hemangioma is noticeable on ultrasound. Such tumors are usually echogenic, but it is better to perform color Doppler mapping. In addition, hemangioma can be detected using:
- computed tomography with contrast agent;
- magnetic resonance imaging with contrast;
- single-photon emission CT;
- biopsy (this method is recommended only as a last resort, because it is associated with a very high risk of bleeding when collecting materials for analysis);
- arteriography (the presence of a formation can be determined by the displacement of the hepatic artery).
Treatment
If the presence of a large hemangioma is confirmed, specific therapy is not required, since such formations have a low risk of developing complications and do not cause any discomfort to patients. If the tumor is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, is growing rapidly, or if its wall has ruptured, removal of the tumor is required.
In addition, for multiple liver hemangiomas, operations are often prescribed to reduce the risk of total damage to the organ. However, surgical treatment of hemangiomas also has contraindications, which include:
- Presence of hepatic hepatoma.
- Large-vascular organ damage.
- Pregnancy.
- Cirrhosis.
Several types of surgeries are performed to eliminate tumors. In the presence of small tumors, embolization of the hemangioma can be performed, which involves blocking the veins feeding the tumor. This measure helps prevent its growth. Such manipulations often trigger the process of reducing formation until its complete disappearance.
Often this operation is performed if there are contraindications to more radical interventions in the treatment of hemangioma. In addition, embolization is the only effective method of treating multiple forms of pathology, when removal of part of the organ will not completely solve the problem. At the same time, with such an intervention there is a higher risk of relapse.
Minimally invasive methods for eliminating such tumors include:
- sclerosis;
- exposure to microwave radiation;
- radiotherapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction.
If such gentle methods of therapy do not achieve the desired result and manifestations of liver damage persist, radical excision of the tumor is required to prevent its further growth. When large or rapidly growing hemangiomas are identified, segmental resection is most often performed. In this case, part of the organ is removed. In rare cases, when the tumor has damaged the entire liver, impairing its function, an organ transplant may be necessary to save the patient's life.
Drug treatment
Since hemangioma can be effectively treated only with the help of surgical interventions, the attending physician may prescribe a course of hormonal medications. This allows the tumor to be reduced in size and subsequently reduce the amount of surgical intervention. The dosage and duration of the course are selected individually. The use of other medications is ineffective for this pathological condition.
How to treat and how to handle liver hemangioma?
In most cases, the tumor is small and can persist for a long time, so surgery is not required.
The patient is under the supervision of a doctor and undergoes regular examinations. The first examination is scheduled 3 months after the tumor is detected, then it is enough to be examined once a year. The disease is also treated conservatively. Treatment with medications involves hormonal therapy. They also resort to minimally invasive methods (exposure to low temperatures, radiotherapy, etc.). In medicine, there have been cases where the hemangioma disappeared on its own.
Removal surgery is performed if :
- The size of the neoplasm exceeds 50 mm;
- If the tumor grows quickly;
- The hemangioma has ruptured;
- There is a suspicion that the formation has degenerated into cancer.
The surgeon removes a segment or lobe of the liver. This is necessary when unpleasant symptoms not only interfere with the patient’s normal life, but also pose a danger to his life. A safer method of surgical excision of liver hemangioma is enucleation. This method reduces the risk of large blood losses and also helps to preserve liver tissue as much as possible. The procedure is carried out through the gap between the hemangioma and the surrounding liver parenchyma.
Modern medicine does not exclude the use of a method called endovascular embolization. This method is based on blocking the venous vessels through which the tumor is fed.
You should adhere to certain rules when you are sick, namely follow a diet and avoid heavy physical activity.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative treatment is used if surgery is not practical. The most common means are:
- Oat tincture. A glass of oat grains is poured with a liter of water and kept under a closed lid for about 10 hours, after which the tincture is boiled, simmered for half an hour and again allowed to brew for 10-12 hours. Another liter of water is added to the resulting broth. This product should be used before meals, 3 times a day, 100 ml. The course of treatment is one and a half months, after which a month's break is taken. The duration of treatment is a total of one year;
- Raw potatoes. It must be consumed before meals three times a day, 50-100g;
- Tincture of wormwood. Wormwood flowers are poured with vodka and left in the dark for a month. The medicine is used three times a day, 15 minutes before meals, 15 drops. The duration of the course is 2 months, followed by a month break. It is necessary to complete 3 courses.
Folk remedies should not be used without consulting a doctor.
Nutrition and diet
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of liver hemangiolipoma.
Poor nutrition can trigger tumor growth, leading to bad consequences. Contraindications for hemangioma: alcohol, various sodas, chocolate, hot spices, egg yolks, pears, fresh bread. It is not recommended to overuse salty, fatty, smoked and various kinds of canned food. But foods such as fish, dairy products, liver, cereals, crackers, honey, fruits, vegetables, herbs, and citrus fruits are considered healthy. They restore normal functioning of the liver and the entire body as a whole. Consumption of dairy products and fish, which contain vitamin B12, which has a beneficial effect on the liver, will also benefit.
Diet principles
A special diet can reduce the risk of fatty liver and aggravation of disorders such as hemangioma and its complications. To improve the patient’s condition, it is necessary to exclude alcoholic beverages from the diet, as well as dishes high in animal fats and easily digestible carbohydrates. Foods that need to be limited or excluded from the diet include:
- pickles;
- smoked meats;
- fried foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- ice cream;
- strong tea and coffee;
- dishes with a high content of spicy seasonings.
Nutrition for hemangioma involves including the maximum amount of protein in the diet. Must be used:
- lean meats;
- fish;
- eggs;
- porridge;
- butter;
- low-fat cheeses;
- dairy products.
In addition, the menu of a patient suffering from hemangioma should include as many vegetables and fruits as possible. They are rich in plant fiber, vitamins and minerals. Among drinks, preference should be given to linden decoction and herbal tea.
Following a diet allows you to avoid problems with stool and ensure the systematic removal of bile from the ducts into the intestines.
Symptoms and signs
Most often, hemangiosal tumors develop asymptomatically, but if they begin to grow and put pressure on nearby tissues, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome in the area of the right hypochondrium - dull, pressing pain;
- In the epigastric region there is a bursting sensation of fullness and heaviness;
- Nausea and vomiting symptoms;
- Most patients experience a feeling of discomfort, unpleasant painful symptoms, high gas formation, flatulence, etc.;
- Increased liver size;
- Patients often complain of heartburn, belching, problems with stool, and lack of appetite;
- You may be concerned about general weakening of the body, hypersweating at night, inability to do physical labor, and fatigue.
Prognosis and prevention
For small hemangiomas that are not characterized by rapid growth, the prognosis is favorable. Even with bruises, in this case, heavy bleeding is extremely rare, posing a danger to human life. Large and multiple tumors are considered more dangerous, which can cause severe complications or liver failure. In this case, the prognosis may worsen in the absence of timely surgical intervention.
Specific prevention of the development of this pathological condition has not yet been developed. Considering that the prerequisites for the development of hemangioma in the liver tissue are laid during the fetal development of the baby, the expectant mother needs to carefully plan her pregnancy, adhering to a healthy lifestyle during this important period and following all the doctor’s recommendations.
Patients with hemangioma should take measures to prevent its growth and development of complications. To prevent deterioration of the condition in the presence of hemangioma, you should:
- Avoid physical and emotional overload.
- Adhere to a gentle diet.
- Get rid of all bad habits.
Treatment in a sanatorium-resort environment can be of great benefit. This strengthens the immune system and reduces the negative impact of stress and poor environment on the entire body, including the liver.
During pregnancy
As is known, in the presence of a hemangiosal tumor in the liver tissue, pregnancy is considered one of the factors provoking the active growth of the tumor.
After all, as long as the tumor is small and does not grow further, it is safe and benign. But if active growth begins and neighboring tissues are drawn into the tumor processes through infiltration, then the benign nature of the formation becomes conditional.
If the size of the hemangioma is above 6.5 cm, then there is a risk that the cavity structures of the tumor will rupture. This factor can cause the death of the fetus or the pregnant woman. This is due to the influence on the growth of the formation of estrogens, which are normally responsible for increasing the uterine cavity and relaxing the pelvic muscle tissue.
Clinical manifestations and diagnosis
The progression of the tumor can lead to disruption of a number of liver functions:
- bile duct (by squeezing the bile ducts);
- detoxification (if a significant amount of tissue is affected);
- hematopoietic;
- synthetic;
- total liver failure;
Early diagnosis provides time for attempts at conservative treatment of liver hemangioma. It becomes possible to plan an effective surgical intervention.
For diagnosis, the most important role is played by ultrasound, computer and magnetic resonance imaging, and angiogram.
The data from these studies provide a knowledgeable doctor with a complete picture of the disease (localization, features of the tumor structure, extent). This information is extremely important for choosing the optimal treatment method for hemangioma and prognosis for liver health in the short and long term.
Classification of neoplasms
There are multiple versions of the classification of hepatic hemangiomatosis. The most common of them classifies hemangiomas into the group of vascular and stromal-vascular (mesenchymal) neoplasms.
According to the clinical picture, liver hemangiomas are divided into four forms:
- form of asymptomatic course;
- uncomplicated forms, but with clinical manifestations;
- complicated forms;
- atypical forms occurring against the background of concomitant diseases.
The clinical course of hemangiomatosis often manifests itself in a combination of cirrhosis, but there is no single version - hemangioma provokes the formation of cirrhosis or, conversely, the development of connective tissue with vascular deformation, giving impetus to the formation of hemangioma tumors.
The histological structure characterizes hemangioma as a tumor of multiple cystic wells that are filled with blood. Fibrous tissue, of various layers, separates the cystic wells.
The structure of a hemangioma depends entirely on the number of wells and fibrous tissue. Liver cells around and under the wells are deformed, located in a chaotic state, or completely absent. The structure of neighboring tissues does not change.
Differential diagnosis
Benign liver tumors must be differentiated from malignant tumors and alveococcosis. In malignant tumors, rapid tumor growth, a characteristic ultrasound picture and progressive cachexia are observed. Alveococcosis is characterized by slow growth, rocky density of the parasitic node, and positive immunological reactions. The final diagnosis is reliable only after a morphological examination of the biopsied material.
Alperovich B.I.
Published by Konstantin Mokanov
Liver adenomas
Clinical diagnosis
Clinical diagnosis of liver adenomas is quite simple in the presence of a palpable tumor. It is dense to the touch, has a round shape and is slightly painful on palpation.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of liver adenomas does not help make a diagnosis, since blood counts hardly change. Only with large tumors are signs of anemia and nonspecific changes in the blood coagulation system observed.
Needle biopsy
A needle biopsy provides some diagnostic information, but its results should be treated with caution. B.I. Alperovich reported on a patient in whom a puncture biopsy was diagnosed with liver cancer, and examination of the resected specimen gave a diagnosis of adenoma.
X-ray diagnostics
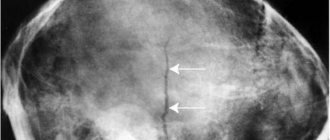
X-rays usually reveal larger tumors. In addition to a local enlargement of the liver, which has a round shape, quite often in the liver shadow it is possible to identify a round shadow, different in intensity from the surrounding tissues.
X-ray. Liver adenoma. Shadow of a tumor on an x-ray
Unlike the hydatid cyst, calcification was never noted along the periphery of the shadow.
Angiography
The angiographic picture of liver adenomas is quite characteristic. In the tumor area there is a level of vascularization different from normal liver parenchyma. In this case, hypovascularization is characteristic, in contrast to liver hemangiomas. There is deformation and displacement of the intrahepatic arteries along the periphery of the zone of perverted vascularization with amputation of small branches in the tumor area.
Large trunk trunks go around the tumor in the form of a hand holding a ball. Unlike liver hemangiomas, hypervascularization is not observed in the tumor area, and there are no vascular “lakes.” In a number of patients, it is possible to observe the tumor capsule on angiograms.
Liver adenoma. Angiography. Tumor capsule visible
The sensitivity of the method reaches 100%. We did not use venous angiography of the liver to diagnose liver adenomas.
Ultrasonography
For adenomas, the effectiveness and sensitivity of the ultrasound diagnostic method was 100%. All patients studied were diagnosed with liver tumors and the topography of the pathological process was accurately established. As for the specificity of the method, all patients were found to have a space-occupying formation in the liver of a round shape and varying sizes from 3 to 30 cm. The contour of the formation is clear, but not marked, as with echinococcosis or a cyst.
A tumor capsule was identified in a number of patients, which serves as a differential diagnostic feature distinguishing adenomas from malignant tumors. Particularly valuable in the ultrasound diagnosis of adenomas is the possibility of preoperative visualization of large vascular trunks of the liver and clarification of the relationship of tumors with them (elements of the portal and their branches, the trunk of the inferior vena cava) without the use of angiographic examination and computed tomography.
Radionuclide research
For adenomas, the method makes it possible to identify a lesion in the liver that does not accumulate radioactive drugs. This defect in isotope accumulation helps to establish the presence of a neoplasm in the liver, but does not allow us to determine its topography and nature. V.L. Gannota believes that the effectiveness of the method for adenomas is 72.4%. The method is significantly inferior in accuracy to ultrasound examination.
CT scan
CT allows you to determine the presence of a tumor in the liver, its size and topography. According to V.L. Gannot (1991), the efficiency of the method is 100%, and the sensitivity is 93.75%.
Liver adenoma. Computer tomogram
Therapy
Treatment of liver hemangioma is not required if the tumor is small. When it grows, serious symptoms may occur, which require surgical removal of the tumor to eliminate.
The following criteria serve as indications for surgery:
- hemangioma of the right lobe of the liver, as well as its superficial location;
- the tumor begins to put pressure on the internal organs and continues to grow;
- the neoplasm can infect the main veins of the liver.
When hemangiomas in the liver are localized on both lobes of the organ, but surgery is prohibited.
Effective medicines
The essence of this therapy is to take hormonal drugs. The dosage and duration are determined individually by the attending physician.
The following non-surgical methods can be used to treat hemangiomas on the liver:
- Microwave radiation;
- radiotherapy;
- exposure to a laser beam;
- use of liquid nitrogen.
Proper nutrition
When the development of hemangioma on the liver is accompanied by a small tumor, a diet is used in combination with the main treatment. Its main principles:
- limit or completely forget about alcoholic drinks;
- the diet should include lean fish and meat;
- monitor the amount of fat consumed;
- the diet prohibits the consumption of smoked and fried foods;
- limit the consumption of salty, canned foods;
- the diet must contain carbohydrates, the amount of which should not exceed the permissible limit;
- Meals should be portions and fractions.
Such a diet will allow you to better digest food, improve intestinal motility and promote the introduction of bile and regular bowel movements.
simptomer.ru
Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that can be located in different places in our body: on the skin, on the mucous membranes, in the liver. Liver hemangioma occurs in approximately 7% of the world's population. This formation is often single, small in size and does not bother its “owner” during life. But sometimes large hemangiomas up to 20 cm are found in the liver. It also happens that several tumors of this type are formed at once. In this case, surgery may be necessary.
Source likar.info
Table of contents
Causes Diagnostics Treatment Folk remedies
Causes
Doctors cannot name the exact causes of liver hemangioma, but there are suggestions that this tumor may be congenital, since it has been detected more than once in children at an early age. There is another assumption about the appearance of benign tumors on the liver - their occurrence can be stimulated by female hormones, since it is the fair sex that is more susceptible to this defect.
Source gepaten.ru
Diagnostics
Plain radiographs show a calcified capsule.
Ultrasound reveals a solitary echogenic formation with smooth, well-defined contours. Characteristic is the amplification of the acoustic signal as it passes through the blood located in the cavernous sinuses.
CT scan with contrast shows accumulation of contrast agent in the venous bed of the tumor in the form of puddles. It diffuses from the peripheral parts to the center, and after 30-60 minutes the darkening becomes homogeneous. Dynamic CT scan after intravenous jet injection of contrast agent shows globular areas of opacification. Calcification may be present due to previous bleeding or blood clot formation.
On magnetic resonance imaging, the tumor appears as an area of high signal intensity. Relaxation time T2 exceeds 8 ms. MRI is especially valuable in diagnosing small hemangiomas.
Single-photon emission CT with 99mTc-labeled red blood cells reveals long-term persistence of radioactivity over the tumor due to blood retention in it.
Source ilive.com.ua
Treatment
Liver hemangioma, which does not require treatment if the tumor does not reach a significant size, can cause serious consequences if it grows. If tumor growth is accompanied by complex symptoms, then surgical intervention and complete removal of the hemangioma is indicated.
liver hemangioma surgery. Drug and non-surgical treatment is also possible. In the first case, we are talking about standard hormonal therapy, the dosage and duration of which is determined strictly individually. Non-surgical treatment involves microwave radiation, radiotherapy (treatment using ionizing radiation to eliminate atypical cells that provoke the development of hemangioma), laser technology (affected liver vessels are sclerosed), cryodestruction and the use of liquid nitrogen (painless exposure to low temperature), electrocoagulation , which is based on the use of high-frequency and direct electric current.
Before the operation, an examination is required. Surgery is required if the hemangioma reaches a size greater than 50 mm in diameter. In addition, the tumor must be located superficially and compress internal organs, grow, infect, or degenerate into cancer. Biopsy for hemangioma is prohibited, because the procedure causes bleeding.
The operation is prohibited if the tumor has affected the main veins of the liver, as well as if the patient has cirrhosis. In addition, it is prohibited to remove hemangioma in case of large hematomas located on both lobes of the liver, because in this case, it will be necessary to remove the entire liver, which, in itself, is absurd.
Source gepatito.ru
Folk remedies
Treatment of liver hemangioma with home remedies is more extensive and aims to minimize symptoms and prevent tumor growth and surgery. Once the disease is detected, the following means are used:
1. Collection of medicinal herbs.
yarrow and tansy flowers, blackroot leaves, 15 g each; St. John's wort, cat's paw, celandine, calendula flowers and cherry stalks 30 g each; coltsfoot (leaves) 45 gr.; plantain 60 gr.
The ingredients are mixed and the infusion is prepared according to this recipe: 1 table. l. The components are ground and filled with cold water (0.4 l.), brought to 100 and simmered for another 5 minutes. After this, the brew is allowed to cool completely and brew, filter, divide into 4 equal parts and take in 20 minutes. before meals throughout the day. The herbal mixture is taken for 21 days. Then they stop for 2 weeks, and during this period of time 3 p. chew thistle (milk thistle) seeds a day, ground into powder. After finishing the course of taking milk thistle powder, take a week-long time-out, and then repeat the cycle. The duration of taking the drug collection is measured in years, but noticeable changes towards improvement occur after the 5-6th course.
2. Raw potatoes are useful for treating this disease. It is eaten 3 times before the main meal.
3. Once every six months it is necessary to organize a morning tea party (the course is designed for 2 months)
Now it becomes more clear what liver hemangioma is, how it manifests itself and how to treat it. You should not rely solely on alternative medicine treatments, but if you are on the verge of surgery, it would be foolish to completely exclude them.
Source pro-medvital.ru
liver-up.ru
Liver hemangioma is a benign focal formation in the form of a small tumor. It occurs quite often, but women are more susceptible to this disease than men. According to general statistics, hemangioma occurs in approximately 7% of healthy people.
Possible causes:
- Congenital malformation (defect) of vascular development.
- The female sex hormone estrogen.
At the moment, the exact causes of tumor formation have not been established, so the first factor listed is considered the most likely. In accordance with this, treatment of liver hemangioma is prescribed, usually without taking into account the hormonal balance.
Types of disease:
- Lymphangioma.
- Benign hemangioma.
- Capillary or juvenile hemangioma.
- Cavernous hemangioma.
- Racilic hemangioma.
- Benign hemangioendothelioma.
Diagnostics
The presence of a tumor can be determined during an ultrasound examination or magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Increased liver size.
How to treat liver hemangioma?
The usual treatment for liver hemangioma is diet. Small tumors do not require complex medications or surgical intervention. Most often, the tumor does not grow, but rather decreases. Over time, the hemangioma tissue undergoes scarring and does not cause unpleasant symptoms.
Liver hemangioma - diet
The patient's diet does not change significantly. The following recommendations must be observed:
- limit alcohol consumption;
- give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish;
- control fat intake;
- give up fried foods and smoked foods;
- It is advisable not to eat pickles and preserves.
If the tumor size is less than 5 cm in diameter, then special nutrition for liver hemangioma may not be observed. It is only necessary to monitor normal digestion, intestinal functions, proper motility and general health.
Liver hemangioma: surgery
Indications for surgery (liver resection):
- tumor more than 50 mm in diameter;
- hemangioma puts pressure on surrounding internal organs;
- the neoplasm is superficial;
- danger of tumor rupture;
- severe symptoms of the disease;
- growth of hemangioma by more than half in 1 year;
- inability to determine the nature of the formation (benign or malignant).
Before surgery, studies of the liver vessels are carried out, and less often - a biopsy. Then sclerosis of the hemangioma is performed, i.e. blocking blood access to the tumor. After the necessary preparation, the tumor is excised.
Surgical treatment of liver hemangioma – contraindications:
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Damage to large veins of the organ.
- Pregnancy.
- Liver hematoma.
- Hormone replacement therapy.
Why is liver hemangioma dangerous?
In fact, this disease does not pose a threat to human health if it is asymptomatic and does not grow. But, in rare cases, the tumor can mutate into a malignant formation. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately contact a therapist and undergo an examination.
Treatment of liver hemangioma with folk remedies
Naturally, you should not rely on intuition or the advice of others and prescribe treatment for yourself. An integrated approach, coordinated with the attending physician, is required. Traditional treatment for liver hemangioma involves gentle cleansing of the body and detoxification.
womanadvice.ru
Reviews about the treatment
Elena:
Fortunately, I myself have not encountered such tumors. But my friend practically got rid of hemangioma with the help of wormwood tincture. Her hemangioma has shrunk to the size of a small pea, although it was almost 6 cm. The tumor has not grown for many years and has stopped developing.
Maria:
My hemangioma was surgically removed. I was terribly afraid, but everything went well. I haven’t remembered the disease for more than 6 years now.