Headache is the body’s most common signal about the presence of physiological disruptions or organic problems. Even his one-time appearance deserves attention. People who have headaches regularly or severely need to undergo a thorough diagnosis and identify the causes of the symptom. In 10-20% of cases, the symptom turns out to be one of the secondary consequences of serious disorders in the functioning of organs. Such situations require immediate initiation of adequate therapy. Otherwise, there is a high risk of developing chronic diseases or emergency conditions that can lead to a decrease in quality of life, disability, and death.
Pathology of the cardiovascular system
Nervous tissue is more sensitive to oxygen deficiency than any other tissue. Therefore, the cranial cavity contains a large number of blood vessels and venous plexuses. A disruption of the blood supply or blood flow from the central nervous system immediately leads to pain.
This is the name for an increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. Headaches with hypertension are of a different nature. The typical one is a leaden heaviness in the back of the head, more pronounced in the morning and gradually subsiding in the evening. It occurs due to excess blood flow and stagnation in the venous plexuses of the skull.
Another type of pain syndrome occurs during a hypertensive crisis. In this case, it acquires a bursting or pulsating character; the following are added:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- ringing in the ears;
- flickering of flies before the eyes.
It happens that some types of nervous activity are lost: vision, hearing, speech. All these symptoms disappear after the crisis subsides.
With this disease, cholesterol molecules are deposited in the vessel wall, which leads to the formation of plaques, poor circulation and the formation of blood clots. Symptoms of cerebrovascular disease:
- dizziness, especially when throwing your head back;
- darkening of the eyes or spots before the eyes;
- dull or aching pain in the head;
- noise in ears.
All of them appear in response to a decrease in blood flow to the brain tissue. Atherosclerosis often causes memory and thinking disorders.
Attacks of cephalalgia during pregnancy
While waiting for the baby, the pathological symptoms observed before may worsen. But frequent headaches in pregnant women occur for the following reasons:
- Hormonal imbalance: cephalgia constantly occurs, mood changes, you want to sleep.
- Low pressure: intense headaches, causes and treatment, which are closely interrelated, most often occur in the back of the head, accompanied by dizziness and increased fatigue.
- Problems with sleep, disruption of wakefulness and rest.
- Irritants: with a headache while expecting a baby, the woman becomes very emotional, external factors lead to spasms.
- Changes in the menu: when replacing foods familiar to the body, migraine attacks occur.
- Overstrain, emotions.
Your doctor will be able to tell you how to get rid of a headache after a full examination. But the first thing you need to do is to maintain the correct daily routine and protect yourself from unnecessary worries.
Drug treatment of headaches involves taking antispasmodics: “No-shpy”, “Drotaverine”. Paracetamol will also help relieve cramps, but it can only be used from the 2nd trimester. It is forbidden to take potent drugs that can quickly relieve pain; they are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Pathology of the nervous system
The brain is located in a closed cavity - the skull. The inside is lined with meninges and filled with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. It is produced by the choroid plexuses of the brain, which respond to the disease by increasing fluid secretion.
There are no pain receptors in the nervous tissue itself, so brain diseases lead to pain only when the meninges, which are richly supplied with such receptors, are irritated. Due to the increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid, the pressure inside the skull increases, to which the dura mater reacts. Pain appears, which is bursting in nature, intensifies when the head is tilted down, and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The latter does not bring relief, which is its distinctive feature.
The same symptoms appear with brain tumors, only the pain is constant and gradually progresses.
Streptococcus aureus, which causes rheumatism, often causes damage to the nervous system. Pain in the head with this pathology of a bursting nature occurs periodically. It is accompanied by epileptic seizures, uncontrolled movements of the body and facial muscles, sudden changes in mood, and severe weakness.
One of the causes of headaches in pathologies of the central nervous system is vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Migraine is intense pain that is localized strictly in one half of the head. Before an attack, a person may experience auditory, visual, or olfactory hallucinations. The reasons have not yet been established, but a connection has been noticed with a person’s character: migraines affect people who are motivated and talented.
Cluster crises in men
Women suffer from CG very rarely and only after gynecological operations. Cluster headaches have causes and symptoms that are similar to migraines and have some differences - a series of attacks haunts the patient throughout the day or week only at night.
The crisis lasts from 30 seconds to 2-3 minutes, then the spasms subside for 5 minutes or an hour before returning again. And so on up to 6 times a night for 3-4 days.
The causes of headaches in such cases are not fully established, as is the pattern of development of the syndrome. But doctors suggest that the sources of cluster spasms are:
- Dilation of the artery (carotid).
- Irritation of the nerve endings located behind the eye sockets.
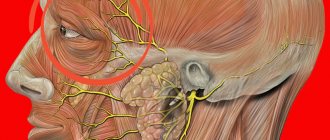
- Hormonal disorders: structural destruction of testosterone.
Headaches in men are accompanied by severe spasms that reach the very “gray matter”. The signs of GKB are quite eloquent:
- the ears are blocked, accompanied by a sharp bursting pain behind the pupils,
- the eyes become red and there is tearing,
- stuffy nose
- the person begins to sweat heavily.
In the first crisis, the spasms are one-sided; in the second crisis, the discomfort spreads over the entire surface of the head. Cluster headaches do not require treatment at home; traditional methods will not give the desired therapeutic effect. To eliminate pathological symptoms, the help of a qualified doctor is required.
Eye diseases
Visual impairment leads to overstrain of the eye muscles, which work hard to ensure visual function. The pain is dull, aching in nature and begins in the frontotemporal region. If the visual load continues, pain affects the parietal areas and spreads all the way to the back of the head. Thus, the pain takes on a girdling character.
The disease glaucoma develops when the pressure inside the eye increases. In this case, overstrain of the oculomotor muscles also occurs, but an additional role is played by reflex irritation of the nerve receptors of the orbit.
Pain in this case:
- occurs against the background of attacks of glaucoma;
- more pronounced on the side of the diseased eye (with a unilateral process);
- not relieved by taking painkillers.
Pain in the forehead with infectious and inflammatory diseases
Inflammation of the frontal sinus (frontal sinusitis) can provoke the appearance of pain in the forehead, which can be dull or acute. One of the common accompanying symptoms is the presence of mucous discharge from the nose. The intensity of pain may increase when the head is tilted forward.
With inflammation of the meninges (meningitis), intense headache is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C, nausea, and vomiting. A rash may appear 2-5 days after the onset of the disease. When the inflammatory process spreads to the brain, psychomotor agitation, convulsions, and disturbances of consciousness may occur.
Another serious infectious disease that may be accompanied by headaches is encephalitis. It should be noted that this is a general name for any inflammatory process in the substance of the brain.
In some cases, encephalitis occurs unrelated to infectious agents and develops by other mechanisms, but in the vast majority of cases, inflammation is provoked by microorganisms.
Encephalitis can be a complication of infections such as influenza (subtypes A1, A2, A3), measles, chickenpox, rubella, and also develop after administration of DPT and DPT vaccines.
In tick-borne encephalitis and neuroborreliosis, the cause of the disease in the first case is a virus, and in the second, a bacterium of the genus Borrelia. What these diseases have in common is that the infection is transmitted by ticks and when a person is infected, the nervous system is affected.
Headache may be the first symptom of tick-borne encephalitis. As with meningitis, there is an increase in body temperature, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions.
With neuroborreliosis, at the first stage of the disease, a bright red spot usually appears at the site of the tick bite, which can reach 10-20 centimeters in diameter. Headache occurs in the second stage of the disease if untreated, when bacteria spread throughout the body.
A headache accompanied by fever, nausea and vomiting requires immediate medical attention! If you have had a tick bite in the previous 1-2 months, you must inform your doctor. The tactics of examination and treatment will depend on this information.
Diseases of the ENT organs
Pain in the head always accompanies ENT diseases, since the affected organs have a direct connection with the bones of the skull.
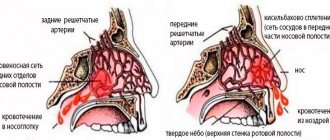
Inside the bones of the skull there are vast voids - sinuses or sinuses. They open into the nasal cavity and are lined with mucous membrane on the inside. During inflammatory processes, the sinuses can fill with mucus or pus, which creates excess pressure in them. Pain receptors in the mucous membrane are irritated and pain appears.
Its localization depends on which sinus is affected:
- Frontitis (inflammation of the frontal sinus) causes pain in the frontoparietal region.
- Sinusitis (inflammation of the maxillary sinus) - in the area of the bridge of the nose, cheekbones, may resemble a toothache.
Sometimes pain affects the entire face. They are of a bursting nature, intensified by tilting the head and lightly tapping the bones of the skull.
Inflammation of the ear (otitis media) causes acute throbbing pain in the temporal region. Increased pain indicates the development of complications. Severe bursting pain behind the ear is a sign of inflammation of the process of the temporal bone; bursting headache is associated with meningitis. If a tumor appears in the ear cavity, the pain syndrome is dull, bursting in nature and increases as the tumor grows.
Inflammatory diseases of the pharynx and oral cavity are usually infectious in nature. Therefore, the pain syndrome with them occurs as part of general intoxication of the body. He:
- does not have a clear localization;
- characterized by aching character;
- intensifies in the evening.
You can learn everything about the treatment of headaches by reading this article. Not only medications, but also folk remedies are effective in treating headaches.
Headache treatment
To stop headaches, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that provoked them.
Traditional medications that are used at home (Paracetamol, Spazmalgon, etc.) help only with one-time pain that is provoked by external factors. Chronic pain requires deeper treatment.
Treatment of persistent pain consists of eliminating the root cause that provokes this effect:
- If the pain is caused by neuralgic diseases of the trigeminal nerve, which is very strong and burning, occurring suddenly (similar to cluster pain), and causing a desire to commit suicide, just not to suffer. In most cases, they are stopped with the help of Phenibut, Carbamazepine, Baclofen and their analogues;
- For the treatment of headaches due to migraine , individual medications are prescribed, since there is no specific treatment regimen, since some patients need to dilate the blood vessels, while others need to narrow them;
- If pain is provoked by high blood pressure, then drugs are used to reduce it, and medications that normalize vascular tone. Massage, proper sleep patterns, proper rest and giving up bad habits are effective;
- If the pain is caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine , and is localized in the forehead and temples, non-steroidal drugs help against inflammation, providing an analgesic effect (Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, etc.), drugs that relax muscles, and also fight spasms.
The above are just some of the possible treatment options.
Since headaches can be caused by a wide range of diseases, what to treat must be selected individually, depending on the primary pathology.
How to relieve a headache with folk remedies?
Treatment for headaches depends not only on the underlying cause, but also on its location. So, during the period of bearing a child, it is extremely dangerous to be treated with medications.
If headaches occur, it is not recommended to drink coffee; it would be better to drink a cup of sweet tea.
To prevent headaches, at home without the use of drug therapy, you can use the following methods:
- Hot shower. It will help dilate blood vessels and reduce blood pressure in them. If it is not possible to put your head under hot water, you can warm only your hands with water;
- A slice of lemon must be peeled and applied with the wet side to the temples until a red spot appears on the skin;
- Decoctions for the head. The most popular are decoctions of mint and oregano. Mix the herbs well and take them as tea;
- A thick woolen bandage will help warm your head and dilate blood vessels;
- Massage of the head and cervical region will relieve tension and improve blood flow;
- Aromatherapy . Rub one or two drops of rosemary or lavender essential oil into your temples;
- Menthol ointment . You need to lubricate the frontal part and temple area with this ointment;
- “Star” balm will help to effectively relieve pain, apply it like menthol ointment;
- Sleep will help you relax and relieve pain.
The use of traditional medicine is allowed only for one-time pain after exposure to obvious external factors.
If headaches appear regularly, they are associated with pathological conditions and require a medical examination.
Infectious diseases
Most pathogens produce toxins that damage the vascular wall. Its permeability increases, so blood plasma and its cells escape into the surrounding tissues. So, they appear:
- swelling;
- hemorrhages;
- in the case of the brain, the secretion and volume of cerebrospinal fluid sharply increases.
Many infectious diseases cause inflammation of the dura mater - meningitis. The pain with it is bursting in nature and covers the entire head. Without treatment, it constantly increases, reaching unbearable intensity. Nausea and vomiting like a fountain are a frequent companion to irritation of the meninges.
When you can't put off visiting a doctor
- For an acute headache that suddenly arose and resembles “a blow to the head.” This may be a symptom of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Call an ambulance immediately.
- The pain intensifies when lying down and goes away half an hour after getting out of bed. This is a sign of impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, increased intracranial pressure, and a tumor.
- If the headache appears regularly, is intense, is associated with changes in body position and changes with movement.
Traumatic brain injuries
Head injuries cause headaches for several reasons:
- The formation of a hematoma in the cranial cavity is a limited hemorrhage that increases intracranial pressure. Painful sensations of a bursting nature occur in the first days after injury and can be of varying intensity.
- Stretching and deformation of the vessels of the brain lead to stagnation of venous blood in the skull. The pain is pressing, intensifies with changes in the position of the body in space, and occurs in paroxysms. May be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. If persistent changes have occurred in the blood vessels, such pain will torment the person for years.
- Swelling of the brain due to injury. Painful sensations appear immediately after restoration of consciousness, are more pronounced at the site of injury, and tapping on the bones of the skull intensifies them.
As you can see, not only brain diseases lead to headaches. There are many reasons for it and each requires specific treatment. To ensure that the therapy is adequate and leads to recovery, consult a doctor to prescribe it. In many cases, headache is a sign of serious illnesses, waiting for which worsens the future prognosis.
Headache is considered a symptom that is known to every person. This symptom accompanies many pathological conditions. One example is intoxication syndrome, which causes headache. Based on this, this symptom can accompany any inflammatory pathology. However, there are certain head diseases. There are many of them. These ailments refer to pathological processes occurring in this particular part of the body. Among such diseases are damage to the brain and its membranes, blood vessels, problems with the skin of the face, and hair. In addition, mental disorders can be attributed to this group of pathologies.
Diagnostics
Features of the manifestation of diseases allow the doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis. Then various research methods are used to confirm or refute suspicions. Only after this is a treatment regimen developed, aimed not at cephalgia, but at its cause.
Diagnosis of headache may include the following measures:
- MRI and/or CT;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck;
- EEG, REG;
- X-ray of the head and neck;
- Lumbar puncture.
Which is better than MRI or CT, read about it here.
General and biochemical blood tests are mandatory. They help evaluate the composition of biological material, its viscosity, cholesterol level, and eliminate the presence of infection in the body.
Description of head diseases
Human head diseases are a broad group of pathologies that include many ailments. Most often they are associated with damage to the central nervous system. However, pathologies in this area include dermatological diseases, oncological processes, injuries, and developmental anomalies. As you know, there are many causes of pain. However, not all pathological conditions of the head are accompanied by this symptom. In some cases, manifestations of such diseases include neurological and psychological disorders. Sometimes symptoms such as decreased cognitive function and sleep disturbance indicate the development of pathology. Head diseases are equally common among children and adults. Gender also does not matter in these pathologies. In some cases, the diseases are congenital and are detected already in the newborn period. Examples are hydrocephalus, intrauterine growth retardation, and developmental anomalies. Sometimes diseases are diagnosed during early childhood. However, this does not mean that the pathology was not genetically determined (Down syndrome, cerebral palsy). In the adult population, acquired head diseases predominate. Most often they develop from vascular damage, trauma, or neoplasms. Some pathologies are hereditary, and the cause of their occurrence is unknown. Although genetically determined, they can appear at any age. Such illnesses include most mental disorders (schizophrenia, multiple personality syndrome), some neurological pathologies.
Pain in the forehead due to injury
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the main causes of mortality and disability in the population. About 80% of all TBIs are concussions. With a concussion, as a rule, there is a short-term depression of consciousness from several seconds to several minutes. Although in some cases it can be quite difficult to record or evaluate this, since the patient may have amnesia about the circumstances of the injury.
Other accompanying symptoms may be nausea, vomiting, increased breathing and pulse; headache, dizziness, tinnitus, sleep disturbance, and sweating may appear somewhat delayed.
In case of a concussion, no specific changes are found on CT or MRI, but the very fact of injury requires a computed tomography to exclude skull fractures, brain contusions, and intracranial hemorrhage.
Patients with a concussion are prescribed bed rest for 1-3 days and outpatient treatment for 2 weeks. It is advisable to spend the first day after the injury in a hospital under the supervision of a physician, since a delayed appearance of an intracranial hematoma is possible, requiring neurosurgical intervention.
In 20% of cases of traumatic brain injury, a brain contusion of varying severity is detected. In this condition, there is a long episode of loss of consciousness from several tens of minutes to several weeks. In this case, emergency hospitalization of the patient in a hospital is necessary.
The basis of diagnosis is computed tomography (CT). During this study, areas of brain contusion, hemorrhages, skull fractures, and cerebral edema are identified. The severity of the patient’s condition and the need for transfer to the intensive care unit are jointly assessed by a neurologist and a resuscitator.
The prognosis for recovery is based on the degree and duration of depression of consciousness and the extent of brain damage. Headaches due to brain contusion can be caused by increased intracranial pressure, trauma to the soft tissues of the head, and reflex tension of the suboccipital and neck muscles.
Causes of head diseases
The cause of the head disease depends on what kind of pathology occurs in a given patient. There are the following unfavorable factors that contribute to the development of diseases:
- Infectious agents. In most cases, microorganisms cause inflammatory diseases. These include pathologies of the brain and its membranes. In addition, bacterial and viral particles are the cause of the development of skin diseases.
- Fungal infection of hair follicles.
- Hereditary predisposition. Many head diseases are genetically determined. This is especially true for mental pathologies. For example, a disease such as schizophrenia is often inherited or observed in close relatives. It is now known that in some diseases the genetic code changes. Similar pathologies include Alzheimer's, Pick's, Parkinson's, Huntington's chorea, etc.
- Bad habits.
- Atherosclerosis of arteries and hypertension.
- Obesity.
- Oncological processes in the brain.
- Benign neoplasms.
- Bites of tropical insects, encephalitis tick.
- Specific pathologies: syphilis, AIDS.
- Vasculitis.
- Head injuries.
In some cases, the cause of the disease cannot be determined. Congenital pathologies develop as a result of fetal ischemia during pregnancy, infectious lesions in the mother, bad habits, chemical and ionizing effects.
Common Causes
Before we figure out what to do if you have a headache, let's find out what causes it.
To determine the exact cause of this phenomenon, you need to consider the accompanying symptoms. Based on additional signs, the doctor most often determines that the headache is due to some illness or under the influence of environmental factors.
Causes of pain on the left side
So, let's find out why there may be soreness on the left, more precisely, on the left side of the forehead.
Here are some reasons that may contribute to this:
- osteochondrosis;
- sensitivity to weather influences;
- migraine;
- stroke;
- infectious diseases;
- cold;
- muscle strain;
- neck and head injuries.
Causes of pain on the right side
Here are the causes of pain on the right side of the forehead:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- injuries;
- stroke;
- tonsillitis;
- Costen's syndrome.
Causes of childhood headaches
Headaches are a common occurrence in children, especially teenagers. Most often, such symptoms do not last long.
Here are some possible reasons:
- Psychological – aggression from relatives or classmates, stressful situations and fear of separation from loved ones.
- Infections may be accompanied by symptoms such as cough, vomiting, runny nose, muscle tension and lethargy.
- Hunger and general fatigue of the body.
- Bruises. If after bruises the condition worsens and you feel sick, you should go to the doctor. It could also be a concussion.
Classification of head diseases
Some patients ask the question: “What is the name of the disease when you have a headache?” As mentioned above, many pathologies can lead to this symptom. Let's consider those associated with diseases of the head area:
- Meningitis. This group of pathologies occurs due to inflammation of the meninges. Bacterial (purulent) meningitis is considered the most dangerous. Regardless of the etiological factor, with inflammation of the meninges, severe headache is observed.
- Encephalitis. This group of diseases is distinguished by the fact that the inflammatory process covers the substance of the brain itself. The main symptom of encephalitis is the occurrence of severe neurological symptoms.
- One of the pathologies accompanied by pain is migraine. The cause of this disease has not yet been clarified.
- Acute and chronic diseases of the blood vessels of the head. This group of diseases belongs to the most common neurological pathologies. Thrombosis and bleeding from cerebral vessels (stroke) are considered especially dangerous, since acute ischemia often leads to disability and mortality.
- Degenerative pathologies of the nervous system. In some cases, you can see the following picture: the patient’s head is shaking. What kind of disease is characterized by this symptom? Most often, degenerative pathologies develop in old age. To a greater extent, they are manifested by motor and neuropsychiatric disorders. An example is Parkinson's disease, which causes tremors of the hands and head, memory impairment, and changes in gait.
- Atrophic pathologies of the central nervous system. Characterized by a gradual decrease in the number of brain cells. Examples are Pick's disease and Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's chorea. These pathologies are characterized by progressive memory impairment and movement disorders.
- Tumors of the central nervous system. Often accompanied by pain in a certain area of the head.
- Mental pathologies.
- Damage to the skin and its appendages.
Therapy for cephalalgia at home
Various types of headaches and the causes of the pathological condition can be eliminated with the help of medications prescribed by a doctor after examination. Independent ways to combat the syndrome and prevent it include:
- Light exercises for the muscles of the neck and back that soothe tense tissues.
- Breaks during work.
- Reducing the amount of caffeine consumed.
- Correct daily routine with walks in the fresh air and relaxation.
- Sleep for 8 hours in a ventilated room.
- A balanced diet that will cleanse the body of toxins.
- Warm baths with the addition of a decoction of medicinal herbs will help quickly relieve headaches.
- Physical activity: swimming, roller skating.
- Refusal from “recreational” cocktails and tobacco products.
- A doctor can tell you how to quickly relieve pain caused by osteochondrosis, but a special orthopedic mattress and pillow will help reduce tension in the muscles of the neck and back.
Preventive measures have a beneficial effect on the blood vessels of the brain and the functioning of internal organs in general. But before you start doing them, you need to find out why your head hurts.
Non-drug therapy for spasms involves silence, complete rest in a dark, ventilated room. The use of tinctures and herbal decoctions is permissible only after consultation with a doctor.
If the syndrome does not go away and becomes more intense, you should not decide on your own how to quickly get rid of a headache, but consult a therapist. The pathological condition can be a symptom of a dangerous disease - a malignant brain tumor, stroke.
Vascular diseases of the head
Vascular pathologies of the head are a group of diseases characterized by impaired blood supply to the brain. They can occur at any age, but are more common in older people. There are acute and chronic vascular disorders. The first include strokes. Acute ischemic cerebrovascular accident is a disease that occurs due to obstruction of the lumen of a vessel by a thrombus or embolus. In most cases, this type of stroke has a more favorable prognosis. The cause of the development of ischemic stroke can be atherosclerotic damage to the cerebral arteries, cardiovascular and oncological pathologies, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and prolonged immobilization (staying in one body position). Hemorrhagic stroke is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate surgical treatment. The etiological factors of this disease are complicated hypertensive crisis, malformation and vascular aneurysm. Chronic pathologies include discirculatory encephalopathy. DEP often occurs in older people. The main reason for the development of encephalopathy is the gradual narrowing of the lumen of cerebral vessels due to atherosclerosis. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is also considered an etiological factor.
Which specialist should I contact?
If the pain continues for a week, then you should consult a specialist.
Depending on the specifics of the pain, the following specialists can provide assistance:
- The therapist conducts an initial survey and then may refer you to a more specialized specialist.
- A neurologist will be needed for neuralgic disorders. You should go to such a specialist if the pain bothers you frequently.
- A psychotherapist will help with migraines, mental stress and depression.
- A reflexologist treats by applying pressure to specific points on the body.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Depending on the expected diagnosis, the following diagnostic options are prescribed:
- X-rays are performed to rule out ENT diseases.
- Dopplerography is used to determine the condition of cerebral vessels.
- MRI is used to examine tissues of the cervical, spinal and brain structures.
- Blood and urine tests will help identify infectious processes.
I hope you find the information in my article useful. If you want to add something, write in the comments.
Well, that's all I have for today. Goodbye, dear friends!
Atrophic diseases of the brain
Atrophic pathologies are conditions in which a decrease in brain activity occurs due to a breakdown in connections between neurons. The reasons for this phenomenon have not yet been fully elucidated. It is believed that atrophic pathologies are caused by changes that occur at the gene level. Therefore, such illnesses are often observed among members of the same family. One of the most striking examples of brain atrophy is Alzheimer's disease. Often this particular memory disorder can be seen in various films. With such a pathology, a person gradually loses orientation in his own personality. The patient does not remember events that happened recently in his life. However, the years that have passed long ago remain in his memory. Thus, a progressive violation of the patient's personality occurs. A similar disease is Pick's disease. The differences between these pathologies are in the preservation of the ability to write and speak. Another atrophic disease is Huntington's chorea. This pathology is characterized by a movement disorder, that is, the inability to control one’s activity. Later, other signs of head disease appear. Among them are mental disorders, memory impairment, aggressive behavior, etc. The first signs of the disease are noted in middle age.
Pain in the forehead associated with changes in intracranial pressure
The term “increased intracranial pressure” is used quite widely, but pressure levels can only be measured by performing a lumbar puncture. To do this, you need to insert a needle into the spinal canal in the lumbar region, with a pressure gauge connected.
The procedure is extremely unpleasant for the patient and carries a risk of complications. Since an increase in intracranial pressure is accompanied by certain complaints, it is enough for the doctor to conduct an examination and prescribe a range of non-invasive examinations to clarify the cause of this condition, only in rare cases resorting to a lumbar puncture.
It is incorrect to believe that blood pressure is directly related to intracranial pressure. A hypertensive crisis in most cases is not accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure and, conversely, an increase in pressure inside the skull does not always lead to the development of arterial hypertension.
Headache in the forehead with increased intracranial pressure can occur due to a tumor, abscess, or intracranial hematoma, which are localized in the frontal lobes of the brain.
At first, the pain may occur only in the morning, but gradually becomes constant and increases in intensity, intensifying when coughing, sneezing, or tilting the head. In 70% of cases, hypertensive headaches are accompanied by congestive optic discs, which are detected during examination by an ophthalmologist.
Separately, there is benign intracranial hypertension, which mainly affects women. The main manifestation of this disease is headaches, which occur in 90% of patients.
When performing an MRI of the brain, no volumetric intracranial processes are found. The cause of increased intracranial pressure is not always possible to establish.
In some cases, it increases with obesity, pregnancy, menstrual irregularities, vitamin deficiencies, anemia, and taking certain medications (oral contraceptives, corticosteroids, psychotropic drugs).
Benign intracranial hypertension resolves on its own in 60% of cases. However, patients with this diagnosis should be observed by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist, since in some cases the chronic course of the disease leads to the development of optic nerve atrophy and blindness.
Much less common are headaches associated with decreased intracranial pressure. This occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the dura mater during a lumbar puncture or non-compliance with the technique of spinal anesthesia.
The decrease in pressure occurs due to the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid through the membrane defect. The headache gets worse when standing up and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and tinnitus.
Psychosomatic pain
This type of pain is a very complex problem that requires joint treatment by a neurologist, psychiatrist, and psychotherapist. The reason for the appearance of psychosomatic headaches lies in the sphere of psychological conflicts, and the fact of a traumatic brain injury or a previous illness can only be a trigger for the “somatization” of a psychological problem.
Often the patient denies the relationship between soul and body in the formation of his chronic headache, which complicates the treatment process. The patient hopes for recovery with the help of painkillers or alternative medicine, wants to overcome pain at all costs, firmly believing that the cause of his suffering is “muscle tension”, “poor circulation”, “osteochondrosis”, “vegetative dystonia” or other abstract diseases.
He begins to uncontrollably use analgesics, which in itself can lead to the development of abuse headaches, while he requires complex treatment with the mandatory participation of a psychotherapist and pharmacological support provided by a neurologist or psychiatrist.
Diseases of the scalp
In addition to diseases of the head itself, this group of pathologies also includes dermatological pathologies. Among them is damage to the skin and its appendages, in particular, the hairline. This issue especially worries the female half of the population. Indeed, such disorders as fragility and hair loss, loss of shine and silkiness are common. To fix this, women make various masks and use special shampoos. However, scalp disease also occurs in men. In these cases, a symptom such as alopecia is often observed. This disease is characterized by pathological hair loss, leading to baldness. There are diffuse and focal (areas) alopecia. Baldness can develop not only in men, but also among the female population. The exact causes of this symptom are not known; it is believed that it occurs under the combined influence of several damaging factors. Most often, diffuse alopecia develops with chronic anemia and diseases of the adrenal glands. Patchy baldness can be caused by a fungal infection. In most cases, it develops after contact with infected pets (cats). Also causes of alopecia areata are pathologies of the thyroid gland, chronic stress, helminthic infestation, etc.
Head diseases: symptoms of ailments
Considering that there are a lot of head diseases, their symptoms can be different. This is especially true for CNS pathologies. The clinical picture depends on the type of head disease. Symptoms of illnesses:
- Neurological disorders. They are found in inflammatory, oncological, vascular, degenerative and atrophic processes. Symptoms of neurological disorders depend on the location of the pathological focus. When the right side of the brain is affected, disturbances are observed in the left limbs (and vice versa).
- Headache. It is observed in inflammatory processes (encephalitis, meningitis), neoplasms, and cerebrovascular accidents. The most severe headache occurs due to migraine.
- Cognitive disorders (decreased memory, perseverance, sleep disturbance). It is observed in the initial stages of degenerative and dystrophic pathologies, with dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
- Decrease in intelligence. Occurs at the last stage of DEP (senile dementia). In some cases, mental retardation is congenital and develops due to chromosomal abnormalities.
- Mental disorders.
- Convulsive syndrome.
Symptoms of dermatological diseases include skin peeling, rashes, itching, and alopecia.
Treatment without pills
How to cure headaches without pills? There are situations when it is not possible to purchase medications or there are contraindications to their use.
In this case, you need to fight the headache yourself.
To reduce symptoms without the use of medications, it is recommended to follow these tips:
- Lie down on a comfortable bed in the most comfortable position so that your whole body is in a relaxed state.
- Turn off the lights or close the curtains. Strong lighting irritates the eyes and provokes new migraine attacks.
- Place a warm compress on your head.
- Ask a loved one to give you a light neck and head massage. Massaging the back of the head, frontal lobes and temples will help reduce the duration of the attack.
- Try to sleep. During sleep, the brain rests, the body relaxes and spasms stop.
- Ventilate the room, as lack of oxygen can cause headaches.
If the pain does not go away on its own, consult a doctor.