Allergy to milk. What is possible, what is not. Table
Sometimes, cottage cheese or milk can cause very unpleasant stomach sensations.
What can you do to feel better when your body reacts poorly to milk? To decompose the sugar contained in milk, that is, lactose, a special enzyme is required - lactase. Some people's bodies don't produce it. Undigested lactose moves into the intestinal tract, where it becomes an excellent environment for the proliferation of bacteria, and, as a result, causes a number of unpleasant ailments - pain, constant bloating, a feeling of fullness, diarrhea alternating with constipation.
These symptoms appear approximately half an hour after drinking milk and can last up to several hours. The more a person has eaten a dairy product that they cannot tolerate, the stronger the sensation.
According to a recent study, 20% of Europeans exhibit the symptom. The cause of lactose problems, paradoxically, is people's avoidance of milk. Lactase is formed, in particular, under the influence of a food stimulus, which is milk sugar. If a person does not drink milk for a long time, then his body does not produce lactase, hence the feeling of unpleasant discomfort after drinking milk. What to do then?
If you suspect lactose intolerance, you should consult a doctor. He will direct you to research and, above all, prescribe an appropriate diet, which is the basis of treatment and well-being. The disease should not be underestimated; it can contribute, for example, to calcium deficiency.
Simple tests can help determine the cause of your symptoms
Depending on the degree of manifestation of the ailment, the therapist will write a referral to an allergist or gastrologist. Doctors will conduct an examination to determine the cause of the problem.
You can do a simple test yourself - eliminate milk from your diet and see if this step causes an improvement.
Provocation testing is performed under the supervision of a physician. You consume samples of dairy products. The resulting food ailments indicate lactose intolerance.
Hydrogen breath test. After the patient consumes a solution containing lactose, exhaled air is examined using a special camera. An increase in hydrogen concentration indicates lactose intolerance.
Internet tests, should you trust them?
There are many home food intolerance tests available online. You should not trust distributors without a certificate.
A dairy-free diet is the best remedy for lactose intolerance
It is worth remembering that lactose intolerance is individual, depends on the amount of product, and can manifest itself under the influence of gradually increasing amounts of dairy products in the diet. However, for a person with severe symptoms, the best way to get rid of the disease is to introduce a lactose-free diet, which means excluding sweet and dry milk from the menu, as well as non-fermented dairy products, such as soft cheeses.
You should avoid products based on sweet milk, that is, puddings, ice cream, cocktails. Often lactose (for example, in the form of milk powder) is added to confectionery products, bars, and bread. Remember that lactose is a popular addition to medications and supplements, so always read the ingredients on packages carefully.
Even if a person is found to be lactose intolerant, people should not give up dairy products because the risk of calcium deficiency increases. And this condition contributes, in particular, to the formation of allergies, sleep and blood clotting disorders, and dental problems. Fortunately, there is virtually no lactose in calcium-rich fermented dairy products (eg, kefir, buttermilk). At the same time, fermented milk drinks and yoghurts contain a lot of fermentation bacteria, which make the products harmless (as they decompose lactose into lactic acid). This type of dairy product is recommended for people suffering from lactose indigestion.
By eliminating milk, a valuable source of D, from the diet, people should consume more other foods rich in the vitamin. By eating fatty sea fish, sardines, egg yolks or avocados three times a week, you will effectively take care of your immunity and strengthen your bones.
How to feed your baby
When a breastfed baby is allergic to dairy products, the nursing mother must adhere to a strict diet. Complementary foods are introduced to allergy sufferers later than to healthy children.
From the age of seven months, vegetable purees are introduced, preferably from soft vegetables (zucchini, cauliflower, squash, etc.). From 8 months, water porridge is added. By 9 months, the baby can be given pureed pork, rabbit, and turkey.
The duration of a dairy-free diet for a baby should be at least 3-4 months, or even more than a year. Only in the presence of stable remission, in consultation with an allergist, can a child be introduced to dairy products in the diet.
How to distinguish intolerance from milk protein allergy?
Lactose indigestion is not the same as a milk protein allergy. An allergic reaction is an excessive immune response that occurs as a result of contact with an allergen. The body considers the milk component (most often its proteins) to be an enemy and fights it, causing unpleasant ailments.
It is worth knowing that symptoms of a milk allergy develop immediately after drinking it, and not, as in the case of food intolerance, only after some time.
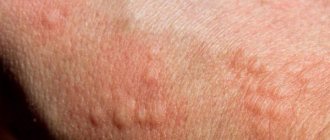
One of the most common manifestations of allergies are skin lesions such as urticaria or atopy.
Suitable diagnostic methods
Conducting timely and accurate diagnosis is extremely important, since the disease can lead to a number of serious complications.
Moreover, good diagnosis is the key to proper treatment.
Any diagnosis begins with collecting an anamnesis.
Much depends on the patient himself, who must provide complete information about when the first symptoms appeared and how they manifested themselves.
After collecting the anamnesis, a visual examination follows.
The presence of symptoms on the body will only make the diagnosis easier.
Then a laboratory test is carried out, which involves:
- clinical studies: general analysis of urine and blood. A general blood test is characterized by eosinophilia and leukocytosis, as well as increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. There may be protein in the urine, as well as high levels of red blood cells, and casts may even be present. This occurs if the process affects the urinary system;
- biochemical research. This examination may reveal elevated levels of immune complexes, as well as C-reactive protein;
- carrying out an immunogram. Immunoglobulins E predominate.
In addition to laboratory diagnostics, provocative tests are performed.
Scratches are applied to the forearm or back with a scarifier.
A drop of milk is applied to this place.
For a more accurate diagnosis, several scratches are made and a specific component of the product is applied to each of them:
- proteins;
- fats;
- or carbohydrates.
If there is hypersensitivity to any component, inflammation will form at the site of the scratch.
Read how an allergy to honey manifests itself. What are the symptoms of an allergy to antibiotics? The answer is here.
Allergy to milk
Signs of allergies may appear as early as the first week of a child’s life.
- A baby with allergies may suffer from flatulence or unpleasant colic, often defecating with mucus or streaks of blood.
- Most often, these symptoms are accompanied by skin changes, mainly atopic dermatitis.
Many babies develop symptoms between 3 and 6 months of age. Changes appear on the cheeks, resembling a blush.
- The affected skin becomes rough and scaly.
- In more severe cases, a rash in the form of follicles and scabs appears on the child’s body.
- The disease is accompanied by constant itching, therefore, the baby is restless, irritable and often cries.
Therapy for food allergies is carried out under the supervision of an allergist and consists mainly of eliminating dairy products. At the same time, treatment for skin syndrome is applied using creams with steroids and emollients.
Lactose intolerance
In addition to abdominal pain, a problem with lactose in children is indicated by frequent episodes of bloating and a change in the consistency of stool to a more loose and foamy one (the so-called fermentation stool). Similar symptoms occur after treatment with antibiotics. If the intolerance is temporary, then you should simply not give your child milk for a while (he can eat cheeses, yoghurts and kefir). If lactose intolerance is constant, then it is necessary, together with the doctor, to set up a special diet for the baby to eliminate calcium deficiency.
How to recognize a milk allergy?
Milk intolerance lies in the fact that the immune system perceives this product as a harmful substance. This protein enters the blood through the stomach, and from there it spreads throughout the body. Therefore, the reaction to an allergen can be very different. Among the most common signs of the disease are the following symptoms of milk allergy in children:
- Bloating, diarrhea, constipation, excessive regurgitation in infants, the presence of undigested food residues in the stool.
- Hives, especially in the elbows and knees, milky scabs on the scalp, eczema.
- Sneezing and runny nose, cough, which turns into asthma if left untreated.
Most often, milk allergy manifests itself in children under three years of age. By the age of three, even a persistent allergy to milk protein may go away. But this disease also occurs in older children, up to adulthood.
The source of the disease can be various factors, most often it is heredity. Allergies can also be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, insufficient development of the digestive system, or excessive addiction to dairy products during the perinatal period.
Treatment
Treatment does not always progress well, so allergy sufferers must take a responsible and conscious approach to their health.
But patients often underestimate the severity of the disease, as well as the risk of possible complications, which is why they may be negligent in treatment.
It is worth remembering that increased sensitivity to this product is not a death sentence, the disease can be cured, everything depends primarily on the patient’s attitude towards himself and his health.
But patients often underestimate the severity of the disease, as well as the risk of possible complications, which is why they may be negligent in treatment.
Treatment first begins with lifestyle changes and the absolute exclusion of contact with the antigen.
Let's consider the main components of proper treatment:
- medications. The use of antihistamines, local and systemic corticosteroids, adrenergic agonists, antispasmodics, and enzyme preparations in combination helps combat clinical symptoms;
- decreased sensitivity of the body to the allergen. Two methods are used to carry out sensitization. The first option is to introduce a concentrated solution of the antigen itself into the body parenterally. At first glance, it seems that a reaction should immediately develop, but this does not happen.
The thing is that the immune system is simply shocked and paralyzed for some time as a result of such a huge amount of allergen.
But if you calculate the dosage incorrectly, you can only make things worse. The second method is slightly different from the first. It is proposed to administer small doses of antigen.
In this case, the immune response will be weak, but anaphylactic shock will not develop;
- change of lifestyle. Throughout your life you should avoid any contact with the allergen.
Which foods are more allergenic?
A dairy allergy can occur to any type of milk, but most often it occurs to cow's milk. When proteins enter a child’s body, the immune system perceives them as a threat to health. As a result of the immune system fighting an imaginary danger, health problems arise - colic in the tummy, rash, gas, etc. If this condition does not cause problems in an adult, then it can cause anxiety in a child. Decreased appetite and weight loss are harmful to babies, so it is better to consult a doctor.
Important! If you are breastfeeding, you should remove from your diet not only pure milk, but also fermented milk products. The same applies to a child if he already eats on his own.
When purchasing any food product, pay attention to its composition. If there are traces of lactose in a product, it is better to refrain from purchasing it. If a child is allergic to milk only due to cow's milk protein, you can replace it with goat's - it causes an allergic reaction less often, and is also tasty and very healthy. Be sure to consult your doctor and also find out how to support your immune system.
Be healthy!
Milk allergy, one of the most common types of food allergies in children, is an abnormal response of the body's immune system to milk and products containing it. Cow's milk is usually the cause, but milk from sheep, goats, buffalo and other mammals can also cause a reaction.
An allergic reaction usually develops within minutes or hours after drinking milk. Signs and symptoms of a milk allergy can vary in severity and include shortness of breath, vomiting, hives and digestive problems. Sometimes a milk allergy can lead to anaphylaxis, a severe, life-threatening reaction.
Avoiding milk is the main way to treat allergies. Fortunately, most children outgrow their milk allergy. Those who do not outgrow the allergic reaction may have to continue to avoid dairy products for life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a milk allergy can vary greatly and occur within minutes to hours after consuming milk or dairy products.
Immediately after drinking milk you may develop:
- Hives
- Dyspnea
- Vomit
After some time the following may appear:
- Loose stools, possibly containing blood
- Diarrhea
- Spastic abdominal pain
- Cough or wheezing
- Runny nose
- Tearing
- Itching, skin rash, often localized around the mouth
- Colic in babies
Milk allergy or milk intolerance?
A true milk allergy is different from milk protein or lactose intolerance. Unlike milk allergy, intolerance does not involve the immune system. Milk intolerance has different symptoms and requires different treatment than milk allergy.
The most common symptoms of milk protein or lactose intolerance include digestive problems, such as bloating, flatulence, or diarrhea, that occur after drinking milk or products containing milk.
Anaphylaxis
A milk allergy can occur as anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction in which the airways narrow and respiratory failure develops. Milk is the third most common cause of anaphylaxis after peanuts and tree nuts.
If you or your child has an allergic reaction to milk, tell your doctor, even if the allergy symptoms are mild. Special testing can confirm the diagnosis so you can avoid future problems and anaphylaxis.
Anaphylaxis is an emergency condition that requires emergency administration of epinephrine (adrenaline) and hospitalization. Symptoms of anaphylaxis appear soon after drinking milk and may include:
- Narrowing of the airways, including swelling of the throat, making it difficult to breathe
- Facial skin hyperemia
- Itchy skin
- Shock with marked drop in blood pressure
When to see a doctor
Contact your general practitioner or allergist if you or your child has a milk allergy. If possible, see your doctor during an allergic reaction to help your doctor make a diagnosis. Get emergency help if you or your child develop signs of anaphylaxis.
Causes
All true food allergies are caused by abnormal reactions of the immune system. Your immune system identifies certain proteins in milk as harmful and produces immunoglobulin E (IgE) to neutralize these proteins (allergens). Upon subsequent contact with milk proteins, IgE antibodies recognize them and signal your immune system to release histamine and other chemicals that cause allergic reaction symptoms to develop.
There are two main proteins found in cow's milk that can cause allergic reactions:
- Casein, which is found in cottage cheese
- Whey that remains after milk has been curdled
You or your child may be allergic to only one milk protein or both. It is quite difficult to avoid them because they are found in many processed foods. And most people who are allergic to cow's milk will also react to sheep, goat and buffalo milk, and less commonly to soy milk.
Food protein –induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES
Food allergens sometimes cause a condition called delayed food allergy or food protein-induced enterocolitis. It can be caused by any food; milk is one of the most common causes. The reaction, usually vomiting and diarrhea, occurs several hours after eating the food.
Unlike food allergies, FPIES goes away over time. FPIES can be prevented by avoiding milk and dairy products.
Risk factors
Risk factors for developing milk allergy:
- Other types of allergies. Many children with milk allergies also have other allergies. Milk allergies are often the first to develop.
- Atopic dermatitis. Children with atopic dermatitis are much more likely to develop food allergies.
- Family history. The risk of developing a food allergy increases if one or both parents have a food allergy or another type of allergy, such as hay fever, asthma, hives or eczema.
- Age. Milk allergies are more common in children. As they grow older, their digestive system matures and their sensitivity to milk decreases.
Children who are allergic to milk often also have other health problems:
- Allergies to other foods such as eggs, soy, peanuts or even beef
- Hay fever is a common reaction to pet dander, dust mites, grass pollen and other substances.
what can you do
If you experience mild allergy symptoms, taking an antihistamine may help relieve discomfort. Remember that more severe symptoms may require medical attention. If you or your child develop symptoms of anaphylaxis, seek emergency medical help immediately.
Treatment
The only way to prevent an allergic reaction is to avoid milk and milk proteins. This can be difficult because milk proteins are found in many foods. In addition, some people with a milk allergy may be able to tolerate some milk-containing foods, such as milk-based baked goods, or some processed foods, such as yogurt. Talk to your doctor about which foods you should avoid.
If you or your child accidentally consume milk and have a mild allergic reaction, you should resort to antihistamines.
If you or your child has a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), you may need an emergency injection of epinephrine (adrenaline) and hospitalization.
If you or your child are at high risk for a severe allergic reaction, you should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector (eg, EpiPen, Auvi-Q, others) with you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a demonstration on how to use this device so you are prepared in an emergency.
Prevention
You can avoid developing an allergic reaction if you do not consume foods that cause allergies. If you know that you or your child has a milk allergy, you should avoid drinking milk and dairy products.
Read food labels carefully. Casein, one of the proteins found in milk, can be found in a wide variety of foods, including non-dairy products, such as canned tuna. Ask what is included in a particular dish before ordering at a restaurant.
Products containing milk
Obviously, milk proteins are found in dairy products such as:
- Whole milk, skim milk, buttermilk
- Oil
- Yogurt
- Ice cream
- Cheese and anything containing cheese
- Mixture of milk and cream for cocktails
Milk can also be used as an ingredient in some products, including baked goods, processed meats and breakfast cereals. In such cases, it may be more difficult to determine that the product contains milk proteins.
“Hidden” sources of milk are:
- Serum
- Casein
- Ingredients with the prefix "Lact" - such as lactose and lactate
- Candies such as chocolate, nougat and caramel
- Protein powders
- Artificial butter flavor
- Artificial cheese flavor
- Hydrosolate
Even if a product is labeled "milk-free" or "nondairy", it may contain allergy-causing milk proteins - so you should read the label carefully. If in doubt, contact the manufacturer to ensure that the product does not contain any ingredients that may be harmful to you.
When eating out, ask how the food was prepared. Maybe there's melted butter on your steak? Maybe the seafood is dipped in milk before cooking?
If you are at risk of developing a serious allergic reaction, talk to your doctor about using an epinephrine (adrenaline) auto-injector. If you have already had a severe reaction, it is advisable to wear a medical bracelet or necklace to let others know you have a food allergy.
Milk Alternatives for Babies
Some studies suggest that breastfeeding for the first four to six months of a baby's life, instead of using standard cow's milk-based formulas, may help prevent allergies. For children with milk allergies, breastfeeding and using a hypoallergenic formula may help prevent allergic reactions.
- Breastfeeding is the best type of nutrition for your baby. Breastfeeding is recommended for at least the first four to six months of life, especially if your baby is at high risk of developing allergies.
- Hypoallergenic formulas are made using enzymes that break down (hydrolyze) milk proteins such as casein or whey. Further processing may include heating and filtration. Depending on the degree of processing, products are divided into partially or highly hydrolyzed. Or they may be called elemental formulas.
Some hypoallergenic formulas are made not based on milk, but on the basis of amino acids. Like highly hydrolyzed formulas, amino acid-based formulas are less likely to cause allergies.
- Soy-based formulas contain soy protein instead of milk protein. Soy formula contains a variety of additives to enhance its nutritional value, but unfortunately, some infants with a milk allergy may also have a soy allergy.
If you are breastfeeding and your baby has a milk allergy, it may be due to cow's milk proteins passing into breast milk. If this is the case, you may need to eliminate all foods that contain milk from your diet. Contact your doctor if you know or suspect that your baby has a milk allergy and symptoms begin after breastfeeding.
If you or your child does not drink milk, your doctor or dietitian can help you eat a balanced diet. You may need to take supplements to make up for the calcium and nutrients found in milk, such as vitamin D and riboflavin.
Diet for allergies to cow's milk protein
Naturally, if an allergy is suspected, it is necessary to adjust the child’s menu in such a way as to remove the allergen product from the diet. In this case, cow's milk. If you are breastfeeding, and one of your relatives suffered from an allergy to milk protein, it is better to immediately refrain from eating it or be extremely careful.
Important! If a child is on IV, he may also develop allergies. Most formulas use the milk protein casein. But there is also a special hypoallergenic mixture on sale.
To monitor a child’s nutrition, doctors advise keeping a food diary, noting the menu and the baby’s condition. Obviously, if an infant is allergic to cow's milk protein, the mother's nutrition is indicated in the diary. It is also recommended to build a special menu based on hypoallergenic products:
- vegetable, fish broths, with caution - chicken broth;
- lean meat, liver;
- beans, peas, beans;
- cereals;
- pasta;
- potato;
- dull fruits and vegetables;
- juices from soft fruits;
- tea, water.
If you are definitely not sure which product is causing a negative reaction, you can gradually add one type of product to the menu. If there is no deterioration within a few days, the product is safe.
If you are not ready for milk, today you can buy different types of milk substitutes:
Any of them can be used to prepare food for a child, for example, porridge, and soybean is even suitable for making homemade kefir, cheese, and cottage cheese.
And most importantly, always remember that everything will be fine! Follow the menu prescribed by your allergist. Soon you will forget about the problem, and the baby will simply outgrow it!
Allergy to cow's milk protein: replacement options
From an early age, my children have been allergic to cow's milk protein: if they consume products containing them regularly, their atopic dermatitis worsens (this is an extremely common and very unpleasant disease in children now, manifested as an allergy, but not limited to it). Avoiding this allergen in everyday life is not so easy, because it is found not only in milk and its obvious derivatives, but also in many ready-made products and dishes where dairy components are present completely unnoticeably (baked goods, sauces, candies and chocolate, ice cream, meat and fish semi-finished products, etc.). I would like to share our experience of surviving in a culture where a glass of milk is traditionally considered a guarantee of health (remember parental stories about “milk is bad for you”?), and where the standard children's diet includes a lot of dairy and milk-containing products.
Figures and facts
Allergies to cow's milk protein are considered one of the most common in the world - both in children and adults. In Russia, it is diagnosed in 2–5% of formula-fed children and 0.5–1.5% of breastfed children during the first year of life. In children with atopic dermatitis (according to the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, this is 10-15% of children under 5 years of age and 15-20% of schoolchildren, incidence statistics are steadily growing from year to year), intolerance to cow's milk proteins reaches 75-80%.
These numbers are inaccurate due to diagnostic problems. A typical story: a child is covered with “diathesis”, a local pediatrician or dermatologist prescribes a “hypoallergenic” diet for him and his nursing mother - without tangerines, red fish, smoked meats, caviar, blue cheeses, eggs, honey (as if nursing mothers and babies do nothing but that they eat caviar!). Plus, a cocktail of medications that relieve skin manifestations and other symptoms. The allergy does not go away - the list of exceptions (and with it the stress for everyone who cares for the child) grows, and now the family is “on buckwheat, turkey and kefir.” If they are lucky, they will come across an allergist who will refer them for tests to identify specific allergens to which this particular child reacts. And there you go! - it turns out that you shouldn’t drink kefir, but you can drink caviar and chocolate. The Association of Children's Allergists and Immunologists of Russia recommends treating food allergies and atopic dermatitis this way, but this tactic has not yet become a pediatric standard.
Symptoms and treatment of allergy to cow's milk protein, replacement of dairy products
Cow's milk is a common food allergen. An infant is more likely to suffer from allergies than an adult. Another feature of the disease in a child is that it can go away on its own with age, but an adult needs to fight it. An allergy to cow's milk protein can lead to swelling of the larynx, and then suffocation, so it is important to recognize the symptoms in time and begin treatment.
What in milk provokes an allergic reaction?
Cow's milk is considered a strong allergen. It contains about 40 types of proteins, 7 of which are recognized as strong allergens. The milk of other animals is somewhat different in its composition and size of protein molecules from cow's.
For example, goat milk has a finer composition and is more easily absorbed by the body of children. Camel milk is devoid of lactoglobulin, which makes it a hypoallergenic product.
All cow's milk proteins can be divided into 2 large groups:
- casein (80%).
- whey (20%).
Casein is less digestible than whey protein. Among whey products, the championship in intolerance in children is given to beta lactoglobulin and alpha lactalbumin. Not only cow's milk, but also its processed products can cause allergies.
Cow's milk protein intolerance can develop into cross-reactivity in the body.
This is when an allergic reaction in children develops not only to whole milk, but also to products containing closely related allergens - beef, cheeses, cottage cheese, fermented milk products.
Allergy to milk, causes and methods of development
What is a milk allergy called?
Milk allergy is considered a food allergy and is called DMA.
This type is widespread and can occur in adults and children. Milk is considered an obligate product that contains many allergens for the body. Such a product contains a large amount of useful nutrients, but the body does not digest them, which means that it must be completely abandoned and, if possible, replaced. There are several types of milk allergies:
- Lactose intolerance - lactose is the name given to milk sugar - a carbohydrate;
- Allergy to milk proteins - casein, globulins, albumins.
Allergens are most often found in cow's milk, but if a person is allergic to this product, then it will also be when consuming goat's or mare's milk and others.
Lactase deficiency
There is another name for lactase deficiency - lactose intolerance. This disease is associated with the inability to digest dairy products, namely lactose. Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose and is secreted in the intestines. In patients with lactase deficiency, it is not produced, which means lactose is not processed and absorbed. At the same time, water accumulates in the intestines, causing diarrhea - loose stools.
The main symptoms in an adult with lactase deficiency are:
- Bloating – flatulence;
- Sharp pain in the abdomen;
- Intestinal disorder - diarrhea.
In a baby, symptoms may include constipation, nervousness, moodiness, crying and tucking his legs to his stomach after eating.
Symptoms appear immediately after eating; the disease can be cured by eliminating allergens from the diet. Such patients are prescribed a special diet, which can include small amounts of lactic acid products.
Kefir, cheese and other “fermented milk” do not contain lactose, but lactic acid, which is well absorbed in the body.
Features: condensed milk and ice cream contain, in addition to lactose, also sucrose, which increases its absorption, so they can also be consumed.
Lactase deficiency is not treated, but rather prevented with a lactose-free diet. That is, the patient will get rid of it if he stops consuming dairy products containing lactose. Pathology often accompanies a person throughout his life.
Allergic reaction to protein
An allergy is the body's reaction to specific components that enter the body and cause specific symptoms. Such components are called allergens, and an allergic person is hypersensitive to them. In this case, the allergen is cow's milk protein, which can come in the following forms:
- Casein;
- Beta-lactoglobulin;
- Alpha lactoglobulin;
- Lipoproteins.
Allergies in adults occur when consuming cow's milk. A baby can get it through artificial feeding or complementary feeding, as well as through breastfeeding if the mother has previously drank cow's milk.
Important: if you are allergic to alpha-lactoglobulin in milk, a complication may occur in the form of an allergic reaction to cow meat protein.
Most often, an allergy to protein occurs in an infant between the ages of 1 month and 1 year, and until the age of 3-5 years the body becomes stronger and “outgrows” the disease; it rarely progresses into adulthood.
What to do for prevention when the allergic reaction passes?
The main prevention for allergy sufferers can be an adapted diet and strengthening the immune system. When breastfeeding, the mother should not consume products containing cow's milk. Prevention also includes periodic examinations with a doctor and occasional preventive courses of treatment.
Dietary food includes food without milk proteins, which are found in many foods. Therefore, it is very important to carefully study the composition of products and avoid components such as: cow's, whole, baked, powdered, condensed milk. Milk can also be found in products such as baked goods, bread, sweets, cookies and others.
You can replace them with fermented milk products, but in small doses. You can also eat eggs, nuts, beans, soy, any meat and fish.
Infants who are artificially fed or complementary foods are prescribed a special diet with an adapted mixture that does not contain an allergen.
The best way to strengthen your baby's immune system is to breastfeed until the time specified by your doctor. Also, both children and adults are prescribed gymnastics, proper nutrition - a formula or diet, sports, hardening, and most importantly - more walking in the fresh air.
Allergy to cow protein is a common food reaction. It is especially common in children under one year of age, and later at 3-5 years of age, the body itself “outgrows” the disease. And sometimes the disease remains for life. You should not confuse milk allergy with intolerance - these are completely different diseases, with different consequences. Intolerance is much easier to tolerate.
Allergy symptoms are pronounced, diagnosis is not difficult, but treatment is difficult and lengthy. During an acute occurrence, urgent medical attention is needed, so it is important to have the right first aid kit for allergy sufferers. The best prevention of allergies is diet and strengthening the immune system.
- The body's reaction to one of the proteins - milk allergens;
- Lactose intolerance;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Cross-allergy (for example, to a cat);
- Enzyme deficiency;
- Inflammatory bowel diseases.
In other words, in some cases the cause of the reaction is food intolerance - pseudo-allergy, in others it is a true allergy.
I propose to understand in more detail cow's milk as a source of true allergies.
Milk, like any allergen, contains proteins - allergens that provoke an allergic reaction in the body.
Thermal treatment of milk (boiling) or milk-containing products (baking) can lead to changes in the properties of proteins - allergens.
Casein is very resistant to high temperatures and can cause allergy symptoms after 90 minutes of boiling at temperatures above 90°C.
Whey proteins lose their allergenic properties after 15-20 minutes of boiling at temperatures above 90 ° C.
Therefore, in a conventional milk allergen panel, several indicators are used: cow's milk and boiled cow's milk.
Bovine serum albumin is structurally identical to human albumin and the albumins of beef, cats and dogs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jJiLmMYIb0c
Thus, allergy sufferers who are sensitive to albumin proteins, such as cats, may react if they eat a small piece of beef.
Bovine serum albumin is also responsible for the clinical manifestations of cross-allergy between cow's milk and raw beef.
If the human body is sensitive to serum albumin, which is found in milk, it is highly likely to react to thermally poorly processed beef.
There is a strong cross-reaction between the proteins of cow's milk, goat's milk and sheep's milk.
In contrast, little cross-reaction was observed between cow, buffalo, donkey, mare and camel milk.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with which maternity hospital to go to give birth
It is important not to confuse milk allergy and the concept of “lactose intolerance” (or other milk components).
An allergy to cow's milk is caused by the body's immune system, which perceives one of the milk proteins as a threat and initiates a protective reaction.
Manifestations of the reaction can be very diverse, from gastrointestinal disorders and skin rashes to anaphylactic shock from just a drop of milk.
If the body does not tolerate lactose, only the stomach will react. In this case, you can be sure that the allergy is caused by an enzymatic deficiency, most often a deficiency of the enzyme lactase.
After the first two years of life, in most children the amount of lactase produced begins to decrease, and in some cases the body stops producing it completely (this especially often happens to those who, for some reason, have not drunk milk for a long time and who have relatives with lactose intolerance ).
At the same time, fermented milk products can be consumed, since lactose there is decomposed by enzymes, without the participation of body enzymes.
It is interesting that lactose intolerance has a clear ethnic dependence: up to 80% of adults in Asia and Africa cannot drink milk, while among Scandinavians, for example, only 3-4% of the population are forced to avoid this product.
Thanks to molecular diagnostics, you can find out exactly what the cause of the reaction is, whether it is a true allergy or a lack of enzymes.
If a molecular analysis shows that the body does not react to cow's milk proteins, then you need to seek help from a nutritionist, not an allergist.
Why do allergies to dairy products occur?
When allergens enter the body of an allergic person, the immune system perceives them as a foreign body and produces antibodies in large quantities, which causes a protective reaction in the body.
Swelling of the mucous membrane, tearing, skin rash and other allergic symptoms will appear. Most often, the patient may suffer from the disease due to heredity, when one or both parents also have allergies. The difficulty of diagnosing the pathology is that it does not cause sharply manifested reactions of the body in the form of an obvious rash on the skin after the first consumption of milk.
Causes of milk intolerance
Lactose is not digested due to a deficiency of the lactase enzyme, which is produced in the duodenum and intestinal mucosa. There are two reasons for intolerance:
- The primary reason is that the lactase enzyme is produced, but with very low activity, so lactose is still not broken down. More common in infancy. When the age reaches thirty years, lactose in the body also begins to break down worse, so an adult should not abuse cow's milk;
- The secondary reason is when the mucous tissue in the intestines is damaged, the secretion of the enzyme decreases or stops completely. Also secondary causes are dysbiosis, infection and other food allergies.
Risk factors
There is a group of risk factors under which allergies can develop, these include:
- Hypersensitivity of the immune system to allergens;
- Genetics, heredity;
- Milk intolerance, which is associated with a deficiency of enzymes that break down components involved in digestion;
- Weak immune system due to concomitant allergies, chronic diseases, past illnesses or poor environment.
The essence of the disease
An allergy occurs when a substance enters the human body, which he perceives as unnecessary and extremely dangerous. As a result, the immune system forms a “response” to the allergen, trying to remove it from the body as quickly as possible. This reaction is called an allergic reaction.
People at risk of becoming a victim of allergies include:
- with a hereditary predisposition (there are allergy sufferers among close blood relatives);
- leading an unhealthy lifestyle;
- with parasitic lesions of the body;
- survivors of psychological stress;
- suffering from intestinal dysbiosis.
Important: Even minor allergic manifestations must be treated. Severe diseases such as eczema, hay fever, and bronchial asthma begin with allergic reactions. As a rule, allergies are accompanied by increased fatigue and decreased immunity.
In recent decades, doctors around the world have noted a steady increase in the incidence of allergies.