Scrotal injuries
Pain in the right testicle is often a consequence of injury. Due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure, these male glands are very poorly protected - only by the soft tissue of the scrotum.
Throughout life, situations arise when the right or left testicle is injured. An accident, a fall, a fight, riding a bicycle, playing sports, hunting - this is a small part of the list of dangerous activities. They can cause various degrees of bruises, testicular strangulation or dislocation. Particularly dangerous injuries that cause severe pain on the right or left include ruptured membranes or puncture wounds.
If there is a bruise, the right testicle swells, the scrotum changes color (redder or bluer, becomes purple), swells, and hurts . The intensity of the sensation depends on the nature of the damage. Painful shock may be accompanied by loss of consciousness, difficulty breathing, and the appearance of signs of tachycardia. With strong blows or exposure to cutting objects, the wound may be open - in this case, heavy bleeding is added to the symptoms. When dislocated, the right testicle may take on an unusual location for it - it may move to the groin, under the skin of the abdomen or leg.
The man should be provided with emergency assistance - provide him with peace, stop the bleeding. Painkillers are used to relieve severe pain in the right testicle. If serious symptoms are observed - dizziness, nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness, emergency help should be called.
In the hospital, the patient is required to be examined by a urologist or andrologist or surgeon. It is necessary to undergo examinations - ultrasound of the right and left testicles, evaluate the vessels using Doppler sonography. Treatment involves tissue drainage, restoration of the natural position of the organ, and sometimes surgical intervention is indicated. In the subsequent period, physiotherapy is recommended.
Causes of pain
Pain in the left testicle can appear for various reasons, but in any case, such an alarming symptom cannot be ignored.
This is a consequence of a pathological process in the body. The structure of the organ itself is very delicate; any even slight damage can affect reproductive functions. The structure of the organ is also quite complex; there are vas deferens, ducts, and blood vessels. They are also covered by appendages. The problem can occur in any part of the organ; even skin trauma or sperm stagnation is a sufficient reason for discomfort.
But more serious diseases can be diagnosed based on such signs. Therefore, scheduled examinations cannot be rescheduled or cancelled. And any persistent pain for several days is a sufficient reason for an unscheduled visit to a doctor or urologist.
Pain in the left testicle in a man: causes and how to treat?
Much depends on the nature of the pain; based on such signs, not only the disease is diagnosed, but also the methods of treatment and the stage of development of the disease are determined. The symptom can be aching or pulling, not just acute. But the aching one also causes significant inconvenience, because attacks appear periodically, at the most inopportune times.
Other symptoms are often observed along the way: redness, swelling, fever. What does the appearance of such signals mean, why does the left egg hurt? A number of diseases can be diagnosed, or only mechanical damage to the skin may be detected.
Consulting a doctor won’t hurt; it’s better to diagnose it right away and identify the disease at an early stage. If the testicle on the left hurts, the reasons can be varied, but the most common ones are not too many. Let's list the main ones, why the left testicle hurts, the reasons and how to treat it.
Mechanical damage and injury
Mechanical damage is possible, for example, with a strong blow to the scrotum area. A bruise is possible for other reasons, but such situations occur much less frequently. The blow leads to a sharp attack and significant hemorrhage. Sometimes cases of loss of consciousness were even recorded.
It may happen that the impact causes significant damage. You need to be guided by the situation; if there are no visible signs of serious injury, but the pain does not subside for several hours, you need to see a doctor.
A nagging pain in the left testicle may occur due to injury. Over time, the discomfort disappears. But if the damage, or the factors causing it, remains, the injury is permanent, then under certain circumstances the symptom may arise again, seemingly without any reason.
This is possible in the following cases:
- A man prefers tight underwear, which compresses the genitals;
- Unpleasant sensations may occur after long cycling;
- Long horse rides or regular horse riding;
- Damage caused during training or sports competitions.
For any injury to the scrotum, you should consult a specialist, urologist, therapist or surgeon. And if the damage is accompanied by blood loss, you need to urgently go to the emergency room and then visit a urologist. The remaining nagging pain in the left testicle is a reason to visit the clinic again. Immediately after the injury, the doctor may not have taken into account any damage.
This is necessary even in cases where the symptom after injury remains insignificant or subsides gradually. It is necessary to check the organ and eliminate the possibility of hidden damage. In some cases, severe injuries may require surgery to correct the consequences.
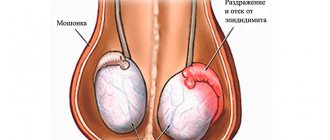
Inflammation in the appendages
If the epididymis of the left testicle hurts, most often this means the occurrence of a focus of inflammation in this organ. The disease is called epididymitis and is accompanied by a number of other symptoms. The general body temperature increases, discharge from the penis appears, the patient complains of frequent visits to the toilet. In this case, unpleasant sensations arise gradually, but then the left testicle hurts and radiates to the leg. The discomfort becomes extremely intense. In some cases, it is impossible to even touch the scrotum.
Why does pain appear in the left testicle and radiate to the leg? In other words, what factors cause inflammation itself?
Experts identify several groups of such factors:
- Diseases of the genitourinary system (urethritis, prostatitis is also very common lately). If they are not treated correctly, the inflammation can spread to neighboring organs. Therefore, the treatment plan must be strictly followed, do not skip medications and do not end treatment prematurely;
- Infections, sexually transmitted diseases;
- Neglect of basic hygiene rules;
- Hypothermia;
- Diseases of the pelvis, congestion that appears against their background.
Testicular torsion
An extremely dangerous condition when the right testicle hurts is torsion. The patient experiences a sharp turn in his position relative to the conventional line - vertical or horizontal. There is compression of the spermatic cord and the vessels, nerves, and vas deferens located inside it. If medical care is not provided to the patient on time, there is a high probability of developing necrosis of the gland tissue, which can lead to the loss of the right testicle. Torsion of the testis on the right is provoked by sudden movements, bruises or abdominal tension, congenital or acquired pathologies.
Symptoms help to understand that torsion of the right testicle has occurred:
- pain in the stomach and testicle on the right;
- the scrotum has acquired a bluish color and is very swollen;
- urination is difficult and painful;
- body temperature rises, nausea and vomiting occur.
The location of the testis changes noticeably; it can be noticed when examining the groin area - the right testicle has become significantly higher than the left. The right testicular cord hurts.
The patient requires hospitalization . At the clinic, the doctor examines the patient, palpates the scrotum, asks about the nature of the pain and other manifestations. A general urinalysis is prescribed, a Doppler ultrasound is performed, and the diagnosis of orchitis is excluded. Sometimes torsion of the right testicle is eliminated by external manual detorsion - the testis returns to its natural position, the pain subsides and then disappears. In other cases, surgery is indicated. The operation involves cutting tissue and assessing the extent of testicular damage. The surgeon then rotates it or removes it completely.
Orchitis
Symptom - pain in the right testicle is characteristic of orchitis. This male disease is infectious in nature, it is provoked by bacteria and viruses. May be a complication of mumps, influenza, gonorrhea, syphilis, tuberculosis, typhoid. Sometimes the causes of the disease cannot be reliably established. A sedentary lifestyle, significant physical or mental stress, severe hypothermia or overheating of the body, decreased immunity due to diseases, pathologies of the kidneys or genitourinary system increase the risk of developing orchitis.
A sudden increase in body temperature against the background of pain in the right testicle characterizes the onset of the pathological process . Each patient’s testicle can hurt differently – they describe sensations of different duration and character. It is noted that the pain radiates to the lower back, groin, and perineal area. They intensify with changes in body position and any physical activity. The right testicle becomes larger in size, feels denser to the touch, and its skin becomes smoother due to swelling. Chills appear accompanied by a headache.
When examining the patient, the doctor notices that his right testicle is enlarged and hurts greatly when pressed. The diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory research methods - urine tests (general and bacterial cultures), urethral smears, and general blood tests are required. The instrumental diagnostic method used is ultrasound of the scrotum. Sometimes a testicular biopsy is necessary.
To treat orchitis and relieve pain in the right testicle, complex treatment is prescribed . It is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and is anti-inflammatory and antibacterial in nature. The patient is prescribed bed rest. Good results are observed when using physical procedures - magnetic, electrical and laser therapy, acupuncture, therapeutic baths (mud or mineral).
Disease symptoms and diagnosis
Epididymitis , that is, inflammation of the epididymis, manifests itself in swelling of the scrotum. Slight hyperemia may also be observed. In this case, severe, sharp pain occurs in the male genital organ. The testicle increases in size and becomes sensitive if you touch it. There is also a burning sensation and spontaneous urination. Very often the temperature rises to high values.
When the spermatic cord of the left testicle is torsed, severe pain can occur and blood circulation is impaired. The testicle does not receive oxygen and essential nutrients, which leads to its death.
With prostatitis , that is, inflammation of the prostate gland, pain in the testicles also often occurs. It is by this symptom that doctors can make the correct diagnosis.
Orchitis is characterized by an acute onset: fever, pain in the lower back and groin. The affected testicle becomes larger in size, and the skin of the scrotum becomes smooth. The pain is especially worse when walking or during physical activity. In some cases, chills and pain in the head are felt.
With ureaplasmosis , that is, infection with pathogenic microorganisms, testicular diseases and pain in them also occur. This virus is transmitted to the child during the mother's pregnancy and often does not manifest itself for a long time. The disease becomes apparent when a certain concentration of the virus in the body is reached.
Dropsy
Another pathology when the right testicle may hurt is hydrocele or dropsy. It can be primary in nature, that is, it can arise “on its own” or due to the presence of secondary causes. These include testicular injuries, orchitis, infections, scrotal tumors, heart and liver failure, and conditions after surgical interventions. Factors that provoke dropsy are significant force loads.
The first symptom of the pathology is that the man notices that the right testicle has suddenly become significantly enlarged and a sharp pain has appeared. Body temperature may rise, signs of intoxication of the body, weakness, and loss of appetite appear.
To confirm the disease, you need to contact a urologist, or, if he is not available, a surgeon . They examine the patient and evaluate symptoms. The doctor uses palpation of the testicle, scrotum, groin area, diaphanoscopy, ultrasound, and differential diagnosis. How to treat a patient determines the characteristics of the pathological process. Medicines used are decongestants, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory. The threat of atrophy of the right testicle and severe pain in it are grounds for choosing a surgical method of treatment.
Basic treatment methods
Treatment of pathologies that manifest as pain in the testicle is carried out by a urologist or andrologist-urologist. The choice of treatment method depends on the disease that caused pain in the testicles.
In case of severe pain, a blockade is performed with painkillers, after which it is necessary to wear special underwear for some time, which, as it were, tightens the scrotum. After eliminating the pain syndrome, it is necessary to begin treatment of the underlying disease.
Let's consider what methods are used for various pathologies:
- For minor acute injuries or chronic compression of the testicles by tight underwear, you can deal with the problem yourself; in the first case, you will need to apply ice, and in the second, stop wearing inappropriate underwear. But after the pain has passed, it is still recommended to consult a urologist.
- Severe injuries may be accompanied by hemorrhages or damage to the integrity of the organ, so you should consult a doctor. In some cases, surgical treatments may be required.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases are treated mainly with antibiotics, and it is not superfluous to determine the sensitivity of the causative agent to the action of the drug.
- Testicular torsion, inguinal hernia, varicocele, the presence of neoplasms, and hydrocele require surgical intervention.
Varicocele
Dilatation of the veins of the pampiniform plexus of the spermatic cord characterizes another male pathology in which the right testicle may hurt - varicocele. In the first stages it is asymptomatic and is detected already with a developed clinical picture. Signs of varicocele usually appear in adolescence.
At the beginning of the disease, pain is mild. It intensifies with physical activity and during sex. The patient may notice that his right testicle is swollen, and the scrotum on this side appears to be drooping . Sometimes pain is felt in the groin, leg, neck. The scrotum in the area where the affected veins are located becomes strongly tuberous. The pain is described as burning, pulling, itching of the skin in the problem area. Sweating, difficulty with potency, a decrease in the volume of ejaculatory fluid are observed, and infertility is suspected.
For diagnosis, examination of the patient and analysis of his complaints are used. The doctor prescribes an ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound of the scrotum and renal veins, and diaphanoscopy. Treatment is aimed at restoring the structure and function of blood vessels; in most cases, the surgical method is used.
Inflammation of the appendage
Epididymitis develops due to an infection that occurs as a result of the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the body. It is also caused by Trichomonas, gonorrhea or tuberculosis infection. This disease can occur in men at any age, but men between 20 and 40 years of age are especially susceptible to it. The clinical picture of epididymitis first manifests itself in the form of pain in the groin area. The pain may radiate to the side or abdominal cavity. During the illness, swelling of the scrotum, painful urination, and sometimes blood appears in the urine. In the advanced stage, purulent mucus is released from the urethra.
An inflamed appendage is treated with antibacterial drugs, which can be taken either orally or by injection. In advanced cases, antibiotics, bed rest, fixation of the scrotum upward are prescribed, and cold compresses are recommended to relieve swelling. If you are ill, you should exclude spicy foods, alcohol, and intimacy from your diet.
Prescribing treatment on your own is strictly prohibited, because the doctor prescribes an antibiotic based on laboratory tests, which reveal the sensitivity of the infection to a particular drug. When self-treating, the drug may be chosen incorrectly, which will lead to further development of the disease and serious consequences.
Traditional medicine recommends the following preparation for epididymitis: per liter of boiling water, take half a tablespoon of corn silk, herbs and violet roots, finely chopped green beans and bearberry leaves. Brew the mixture, let it brew for half an hour, then take 3 spoons 3 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely.
Spermatocele
A common disease of the right testicle, accompanied by pain, is spermatocele. Its development is characterized by the accumulation of seminal fluid in the epididymal duct . A small cyst forms here; the process is not accompanied by significant manifestations. As the tumor grows, the manifestations become noticeable. The disease can be congenital or acquired.
In the area of the right testis there is a bursting, pulling pain. A lump appears in the scrotum; it can be noticed by palpation. They have a clear shape. If you press on it, the pain will not increase. Pain from spermatocele becomes acute and constant when the tumor becomes significant in size. The formation has a round shape, elastic to the touch.
The main diagnostic methods for confirming spermatocele are diaphanoscopy and ultrasound examination of the scrotum. To get rid of an epididymal duct cyst, only minimally invasive surgery is used - spermatoceleectomy. Physiotherapy complements treatment measures and is used during the patient’s recovery period.
Anatomical features
Testicles are the paired external male reproductive glands located inside the scrotum and covered with seven membranes. In the area of the upper pole, each of them is approached by a spermatic cord, consisting of testicular membranes, as well as vessels (arteries, venous plexus), and the vas deferens, enclosed in these membranes. Along the entire lateral surface there is an epididymis, which in the lower part passes into the vas deferens.
Normally, the male gonads have a round shape, elastic consistency and are easily palpable through the skin of the scrotum, one of them is located slightly lower than the other. On palpation, the appendages are felt as dense ridges, and the vas deferens as thin cords.
The main functions of the gonads in men
- synthesis of testosterone – the main “male” hormone;
- the formation of gonads (spermatozoa) that fertilize the egg.
Main functions of the epididymis
- ensuring complete maturation of sperm;
- transport of sperm from the testicle to the vas deferens.
With the development of diseases manifested by pain in the testicle, problems with conception, disorders in the sexual sphere (including erectile dysfunction), and disturbances in general well-being may occur.
Other causes of pain in the right testicle
In addition to the main diseases and situations discussed, pain can occur in the right testicle in men for other reasons. Experts often call these :
- diseases of a sexually transmitted nature – gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia;
- inguinal hernia located on the right side;
- the appearance and development of tumors of various types, the formation of cysts on the egg itself or nearby tissues;
- cystitis and urolithiasis;
- congestion in the scrotum;
- prolonged abstinence from sexual intercourse or its irregular nature;
- hormonal imbalances;
- inflammation in the prostate;
- hypothermia of the body.
Why the symptom cannot be ignored, prevention of testicular pain in men
Only a specialist doctor can reliably determine why a patient’s right testicle hurts. This symptom is alarming, because the diseases that cause it can significantly worsen a man’s quality of life, cause serious complications, lead to organ loss, decreased libido and infertility. To prevent the development of such situations, doctors recommend undergoing annual examinations with specialized doctors. It is prohibited to engage in self-diagnosis and self-therapy if there are signs of acute or chronic genitourinary diseases. For any injury to the testicles, especially if pain occurs after sex or increased physical activity, you should seek emergency medical help.
Found an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
The left testicle hurts - men often turn to a urologist with such a complaint, experiencing real panic, since the pain symptom is quite strong, and its cause has no objective, visible reason.
The testicles are small organs that should be evenly distributed in the scrotum on both sides. The upper part of each testicle has a cord, which in turn is quite complex in structure - it contains an artery, veins and the vas deferens. Each testicle is enclosed by appendages, which connect below and pass into the vas deferens. The testicles are responsible for the production of an important male hormone - testosterone, and also contribute to the production of sperm, without which the process of reproduction and fertilization is impossible. [1]
Differential diagnosis
Radionuclide scanning in patients allows us to diagnose acute and chronic persistent pain in the testicles, including:
- testicular torsion (negative predictive value 96 to 100%; positive predictive value 75%). False positives (“cold” scans) can be caused by hydroceles, hematomas and hernias involving the intestine;
- testicular abscess;
- testicular rupture or torsion from injury;
- epididymo-orchitis (“hot” scan);
- distinguish testicular torsion from testicular abscess.
Also, evaluate the testicle in patients with a normal physical examination and associated emotional problems. Radionuclide scanning may show no damage ranging in size from 1 to 1.5 cm
Modern ultrasound examinations have better resolution and can detect lesions smaller than 1 to 1.5 cm. Thus, radionuclide angiography can detect cases of torsion (cold scan) or epididymo-orchitis (hot scan). A hydrocele, hematoma, or hernia may cause decreased isotope uptake and mimic testicular torsion. [8]