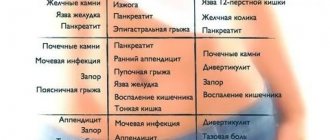
Abdominal pain and painful urination can be a cause of serious concern. These symptoms may occur due to common medical problems such as cystitis. Less often, more dangerous diseases are responsible for them.
The cause of abdominal pain is difficult to determine because the abdominal cavity contains many vital organs. Often, problems such as inflammation or infections cause pain in this part of the body.
Diagnosing painful sensations when urinating is a simpler task, since their cause usually lies in the urinary tract.
In any case, it is important to find out the true causes of the types of pain in question.
Reasons for women
Cystitis
Possible causes of abdominal pain and pain when urinating include pelvic inflammatory disease and cystitis
People suffering from cystitis or a bladder infection may experience pain in the lower abdomen and a burning sensation when urinating.
Other signs of cystitis include the following:
- frequent and urgent urge to urinate;
- frequent urination at night;
- unpleasant smell of urine.
Most cases of cystitis and other urinary tract infections (UTIs) are caused by bacteria, and doctors typically prescribe antibiotics to treat them. It is extremely important to treat UTIs because without treatment they can spread throughout the body and lead to serious consequences.
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is characterized by irritation and inflammation of the bladder. Like traditional cystitis, this condition develops more often in women.
Interstitial cystitis leads to hardness of the bladder lining. As the organ fills with urine, this hardness can cause pain, which later goes away.
Interstitial cystitis can lead to other problems in addition to pain. For example, people may experience a frequent urge to urinate, but produce only small amounts of urine when they empty their bladder.
Scientists have not yet been able to determine the exact cause of the development of interstitial cystitis. Treatment for this condition usually involves managing symptoms and doing exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. In addition, people often benefit from techniques aimed at reducing stress.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) develops under the influence of infections in different parts of the female reproductive system. In particular, such infections can occur in the following structures:
- uterus;
- ovaries;
- cervix;
- fallopian tubes.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services estimates that PID affects approximately 5% of women.
Other symptoms of PID include the following:
- painful sex (dyspareunia);
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- menstrual irregularities.
PID is usually caused by sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Treatment for this condition involves a course of antibiotics. In most cases, oral medications help, but in particularly severe situations, doctors may prescribe hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
Uterine (endometrial) cancer
This happens quite rarely, but endometrial cancer can lead to painful sensations in the abdomen and pain during urination.
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. Malignant transformations in this tissue can cause symptoms such as pain and inflammation.
Treatment for uterine cancer involves radiation (radiation) therapy or chemotherapy. Some patients require a total hysterectomy, which is a surgical procedure in which the entire uterus is removed.
Why does it hurt to go to the toilet "small times"?
Most often, these unpleasant sensations in girls and women are caused by the following reasons:
- Cystitis,
- Infections,
- Urethral injuries after sex
- Inflammatory processes
- Condylomas, papillomas,
- Foreign body
- Urolithiasis disease
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Tumors
- Pregnancy
Most girls complain that it hurts to pee, and this is often associated with various diseases. Sometimes these unpleasant symptoms are accompanied by frequent urges, the appearance of blood and pus in the urine, abdominal pain, etc. The most common cause of pain when urinating in women is a lower urinary tract infection with the development of diseases such as urethritis and/or cystitis. Also, the risk of such infections increases significantly when a young girl becomes sexually active - they are very often a consequence of recently completed defloration. Therefore, when planning to start an intimate relationship, visit a gynecologist and make sure of your health!
WHAT IS CYSTITIS
Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) can develop acutely, but more often the symptoms increase gradually. Usually this is a feeling of discomfort, burning sensation, itching in the perineum and urethra during urination, especially at the end. Unpleasant sensations above the pubis and in the perineal area often persist even after urination. The urge to go to the toilet in women with cystitis is frequent, painful, and the amount of urine with each trip may decrease. Eventually, blood-colored urine may come out. Sometimes urinary incontinence occurs. In acute cystitis, body temperature, as a rule, remains normal, rarely elevated.
WHAT IS URETHRITIS
With urethritis, inflammation of the urethra (urethra), it hurts a girl to pee most at the beginning of the process or equally throughout it. In addition, the urethra can hurt constantly, without any connection with urination at all; this is often accompanied by discharge from the external opening of the urethra. Cystitis and urethritis in women often occur simultaneously. At the same time, their symptoms may be equally expressed, or the manifestations of one of the diseases may predominate.
OTHER CAUSES OF PAIN WITH URINATION
Urolithiasis disease. Against this background, it becomes painful to go to the toilet for one simple reason: salt crystals appear in the urine, which irritate the urinary tract. This disease, in addition to uncomfortable urination, in women is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the lumbar area;
- renal colic during movement, shaking, heavy physical activity;
- bloody impurities in the urine (at an advanced stage of the disease).
Sexual infections. More often it is herpes, trichomoniasis, vaginitis pathogens, chlamydia. With such diseases, it not only becomes painful for girls to pee, but other symptoms may also appear depending on the nature of the pathogen:
- various rashes on the external genitalia;
- “bad” vaginal discharge - leucorrhoea, its pungent odor;
- the appearance of foamy discharge;
- pain in the vagina during intimacy, etc.
What to do if it hurts to go to the toilet “little by little”?
Which doctor should you go to if it hurts to write? Considering the possible variety of reasons causing this situation, girls and women need to promptly consult a gynecologist for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
WHEN YOU NEED TO CONTACT A GYNECOLOGIST URGENTLY:
- With severe cutting pain after emptying the bladder, constant deceptive urges, cramps in the lower abdomen;
- If there is a burning sensation in the urethra, the pain radiates to the perineum, vagina;
- It is painful to write after gynecological operations, abortion or after cesarean section;
- If there is a device in the uterus or taking contraceptive medications.
You should pay attention to the time of day when urination becomes more frequent, and also determine the amount of fluid released and its approximate characteristics (color, presence of impurities, foreign elements, smell) - the specialist will definitely ask all these questions at the appointment.
MINIMUM EXAMINATION: Examination in a chair, smears for flora, PCR tests for “hidden” infections, bacterial culture of the vaginal flora, general urine test, urine test according to Nechiporenko, urine culture for sterility, ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, general blood test.
ACCORDING TO INDICATIONS: Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, blood tests (biochemistry, clinical analysis), consultation with a urologist or nephrologist, cystoscopy.
TREATMENT METHODS
Treatment for painful urination can only be prescribed by a gynecologist. If it hurts to go to the toilet in a small way, treatment will depend on the cause of this symptom:
- in case of an inflammatory process (cystitis, urethritis) or sexually transmitted infections, doctors must prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- urolithiasis requires taking medications that help remove stones from the kidneys and urinary tract;
- To relieve pain when urinating, antispasmodics and painkillers may be prescribed;
- The most suitable diet and plenty of warm drinks are recommended.
In each specific case, treatment for pain when urinating for a woman is selected individually depending on the characteristics of her body, the course of the disease, etc.
Don't self-medicate! Our paid clinic employs highly qualified gynecologists who will conduct the necessary diagnostics, determine the cause of frequent urination without or with pain, make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment! Timely contact with a specialist will help avoid possible complications. Chronic problems with the genitourinary area are much more difficult to treat and require a lot of money and time.
DOES IT HURT TO WRITE? WHERE TO GO TO A DOCTOR IN MOSCOW
| "Clinic of Gynecology and Women's Health." Contacts: Kutuzovsky Prospekt, 35 Moscow. Telephone |
- WHAT IS WORRIING: There is discharge
- Itching and burning
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Intimate pain
- Delay of menstruation
- Pain when urinating
- Vaginal odor
- Pain during menstruation
- How not to get pregnant
- See a gynecologist
- EXAMINATION BY A GYNECOLOGIST: Examination
- TEST: Flora smear
- TREATMENT BY A GYNECOLOGIST: Inflammation of the appendages
- TREATMENT METHODS IN OUR GYNECOLOGY: Physiotherapy
- Gardasil
- INTIMATE AESTHETICS: Intimate plastic surgery
- Appointment with a gynecologist
- HPV in women
Copying or reproducing materials from this site is prohibited. The website of the gynecology clinic was updated on 01/17/2020
source
Reasons for men
Prostatitis
In men, prostatitis can cause painful urination
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. This condition may cause pain in the lower abdomen and discomfort when passing urine.
Inflammation can spread to those areas of the body that are located near the prostate gland. As a result, people experience the following symptoms:
- lower back pain;
- fever;
- difficulties when trying to start the process of urination;
- difficulty trying to hold the flow of urine.
Treatment for prostate inflammation depends on the cause of the problem.
Sometimes prostatitis goes away completely without any therapy. In other cases, the inflammation requires a course of antibiotics to kill the harmful bacteria that are causing the infection.
Even if the doctor was unable to immediately identify the cause of the inflammation, he can prescribe treatment to relieve the symptoms of prostatitis and at the same time perform diagnostics.
Epididymitis
The epididymis or epididymis is a paired organ of the male reproductive system, which is located behind the testicles and serves to transfer sperm to the urethra. Inflammation of the epididymis, or epididymitis, can result from infection or injury.
Symptoms of epididymitis include the following:
- pain or swelling of the testicles;
- pain and swelling in the pelvic area;
- pain during sexual activity;
- soreness of the penis;
- unusual discharge from the penis.
Causes of pain when urinating
There are at least three reasons for this pain.
- The inflamed mucous membrane of the urethra or bladder reacts to the passage of urine with pain. This can also happen during urination, but at the end, when the bladder muscles contract, the pain intensifies.
- With urinary tract lining, the appearance of pain can be explained by the presence of stones or what happens with urolithiasis. When emptying the bladder, these inclusions injure both it and the urethra, causing pain.
- With a healthy mucous membrane and the absence of stones and sand in the urine, pain may occur if there is an obstruction to the outflow of urine. This can occur when the urethra is narrowed due to a tumor, prostate adenoma, or prostatitis. In this case, pain occurs due to the fact that the bladder muscles contract with greater force.
Causes for men and women
Urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can affect both men and women, although they are more common in the fairer sex.
Most UTIs originate in the bladder, although they can affect any part of the urinary system, including:
- kidneys;
- ureters;
- urethra.
When a UTI develops, women most often experience pain in the pelvic area, while men experience pain in the rectal area. Other symptoms of urinary tract infections include the following:
- more intense urge to urinate;
- change in urine color;
- change in urine odor;
- blood in urine.
In most cases, UTIs develop under the influence of bacteria, so doctors use antibiotics to treat them.
STI
All sexually active people are at risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. Such infections can cause a burning sensation when urinating, pain in the lower abdomen, and other symptoms.
Some people also experience urethral discharge, although STIs often do not cause any visible symptoms.
Genital herpes
This STI also causes blisters that ooze fluid. However, many people begin to feel pain even before the appearance of such formations.
Genital herpes is an incurable disease, so doctors' therapeutic efforts usually focus on easing outbreaks.
Stones in the kidneys
Stones are excess accumulations of minerals. Such growths can cause pain as the body tries to get rid of them through the urinary tract.
The pain can be very severe, especially during urination. In some cases, stones can completely block the urine passage.
Treatment of stones depends on their size and composition. With the help of some drugs, doctors are able to break the stones into small fractions and provide easier passage. In addition, patients may be prescribed medications to relieve pain.
Urethral stricture
Urethral stricture is a medical condition characterized by narrowing of the urethral outlet and reduced urine flow. This problem can lead to abdominal pain and painful sensations during urination.
Narrowing of the urethra usually results from inflammation or scarring of the tissue. Scarring can occur after injury, surgery, or the use of medical instruments such as a catheter.
The doctor may try to widen the urethra. In some cases, surgery is required to achieve this goal.
Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is a less common cause, but it can also cause pain in the abdomen and when urinating.
Bladder cancer can develop in both men and women, but much more often this problem affects the stronger sex.
Other symptoms of bladder cancer include the following:
- lower back pain;
- frequent need to urinate;
- difficulty urinating;
- blood in urine.
Doctors may treat bladder cancer in different ways, but treatment typically involves removing cancer cells and managing symptoms.
What to do if there is blood in your urine and your lower abdomen hurts?
If blood is detected in the urine, you should consult a doctor. The doctor will ask about the amount of blood that appears during urination. He will also want to know how often the process of urination occurs, what kind of pain occurs during this process, and what medications the patient uses.
The doctor will then perform a physical examination and suggest a urinalysis.
Your doctor may suggest a CT scan, which uses radiation to create an image of the human body.
Another possible test that the doctor may suggest is a cystoscopy. This is a procedure that uses a special tube with a camera to view the urethra and bladder. This allows you to view the internal area and determine the cause of blood in the urine.
source
When should you see a doctor?
Pregnant women should consult a doctor if they experience abdominal pain or pain during urination.
Abdominal pain and pain when urinating are often cause for concern, but if these symptoms are mild, you can wait a few days before seeing a doctor.
If the problems under consideration appear in pregnant women or in people suffering from diseases of the immune system, then in this case, seeking medical attention should not be delayed.
In addition, people who know that they have problems in the urinary tract or have experienced pain in the abdomen and when urinating more than once should not postpone a visit to the hospital.
Associated signs that may indicate the presence of hidden medical conditions include the following:
- pain in the kidney area;
- fever or chills;
- presence of immune system disorders;
- recent use of medical devices such as a catheter.
Treatment of pain when urinating
Depending on what type of cause has become the provoking factor for the appearance of pain when urinating, the specialist prescribes a course of therapy, which includes:
- Taking antimicrobial drugs - the course of treatment lasts from 7 to 10 days.
- Antiviral drugs.
- Antifungal.
- Non-hormonal agents.
- Sedatives.
- Medicines that relieve spasms.
- Teas for pain relief.
- Herbal preparations.
- Immunostimulating drugs.
In addition to conventional medications, traditional medicine is used, which include:
- herbal decoctions - bear ears;
- infusions from lilac inflorescences or marshmallow root;
- decoctions of cucumber seeds;
- decoctions of cherry branches.
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent pain when urinating and abdominal pain, but in some cases people are able to do so using the following steps.
- By drinking large amounts of water, you can maintain fluid balance, cleanse the urinary tract and flush out toxins from the body.
- Washing your hands before touching your genitals and regularly washing your genitals with mild soaps are measures that can help prevent irritation and infections.
- When visiting the toilet, women should wipe from the pubic area to the back to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Avoiding the use of harmful chemicals around the urethral opening may also help.
- Before sexual activity, you can ask your partners to shower. This will prevent some health problems. In addition, during moments of intimacy, you should use condoms, which effectively protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Psychological factors
Pain and burning when going to the toilet can be caused not only by various pathologies, but also by elementary mental disorders. Doctors make this diagnosis based on the patient’s general state of mind. Often, girls who do not have any pathologies or health problems go to the hospital with similar symptoms, but the symptom is there, and there is no escape from it. Neurosis, depression or prolonged prolonged anxiety may be to blame.
In this case, the burning sensation occurs sporadically or from time to time. It is not accompanied by pain or pain, or any discharge from the genitals. An interesting feature is that such pain based on a psychological breakdown is typical only for girls; this happens very rarely in men.
Non-pathological causes
Pain does not always indicate that you are sick, even if it is quite acute. Among the most common non-pathological risk factors are:
- Injuries to the genital organs. This happens to women when they have unsuccessful sex or wear the wrong underwear.
- Allergies to fabrics, detergents or pads.
- Neoplasms and tumors.
- Malfunctions of the reproductive system or menopause. This often happens in women after childbirth, because hormones have not yet begun to be produced correctly and the body itself provokes frequent urination with pain.
Treatment of the disease
If the cause of your poor health is precisely problems with the genitourinary system, then the doctor will prescribe antibiotics and antiviral drugs. In this case, therapeutic drugs and tablets for pain during urination in women will also be effective. If the cramps appear due to sexual diseases, then your treatment will consist of antibiotics and specific drugs that are prescribed to eradicate a specific disease. If you have an allergy after a general examination, you will be prescribed an antiallergic drug. Sometimes therapy consists of taking hormonal drugs if the pain was caused by a malfunction of the reproductive system.
You can enhance the effect of medications prescribed by your doctor using various folk remedies that were used by our grandmothers and great-grandmothers. Moreover, it cannot be said that such treatment was not successful.
One of the most popular remedies is bear ears. To prepare the infusion, you need to take 1 tablespoon of this herb and pour 250 ml of boiled water into it. After this, the broth comes to readiness in a water bath for half an hour and is filtered. It should be taken 100 ml three times a day. Lingonberry leaves are also called a medicinal remedy. Preparing the decoction is very simple. You need to take 1 tablespoon of leaves and pour 2 cups of boiling water. After this, the broth is left to infuse at room temperature for an hour.
After this time has expired, you need to boil the infusion for at least 15 minutes. Cool the finished product and take one tablespoon three times a day. Small dill seeds have healing properties. To use them, you need to prepare them according to this recipe: take 2 teaspoons of seeds and pour a glass of hot water. Leave this mixture to steep for a quarter of an hour. After this, the infusion is ready for use. Take it 3 times a day.
Treatment tips
Please take into account that folk remedies can be taken only after the diagnosis has already been made, otherwise the symptoms may not be accurate and the disease will be determined incorrectly. The fewer self-confident actions you take before going to the doctor, the better for your health.
As you already understand, pain during urination in women can be triggered by various factors. They often occur in women after childbirth, and acute pain and blood when urinating in women are characteristic of diseases that are sexually transmitted: gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia.
We hope that this article was useful to you, and you were able to find in it all the information you were interested in about pain and how to treat it. If some aspects are not sufficiently highlighted, use the link to this thematic video:
Pain when urinating in women: processes that cause discomfort
Rate this entry