Features of biomaterial collection
To assess the acid-base state of the body, blood is needed:
- Arterial.
- Venous.
- Capillary.
Arterial blood is the most suitable biomaterial for assessing gas composition. This is due to the fact that its study allows the most complete assessment of the degree of lung functioning.
Types of access:
- Radial artery puncture. The method is considered the simplest. After it is performed, the risk of developing a hematoma is less than 1%. A puncture of the radial artery is not performed if there is pronounced atherosclerosis in this area, as well as with a negative Allen test. The latter is carried out as follows: the patient must clench and unclench his fist several times until the skin of the hand turns pale, after which the vessel is pinched. If the natural color of the cover is restored in less than 5 seconds, this is considered normal. A longer process indicates a violation of blood flow.
- Femoral artery puncture. Disadvantages of the method: high risk of loss of liquid connective tissue, thrombosis, arm ischemia, vessel occlusion, infectious complications. Biomaterial collection is not carried out in the presence of a vascular prosthesis in this area, in case of aneurysm and local thrombosis, or taking anticoagulants. The complexity of the method lies in the fact that it is not always possible to puncture the artery on the first try.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, which is the end product of metabolism in tissues, is higher in venous blood. In this case, the amount of oxygen, on the contrary, is lower. If you analyze the acid base of venous blood, it becomes possible to evaluate the indicator of systemic metabolism. Collection is extremely rarely carried out from peripheral vessels, since the result of such a study is not clinically significant. The most common puncture is the pulmonary artery.
When collecting blood for acid-base balance (if it is carried out from a limb vessel), a tourniquet is never applied. This is explained by the fact that against the background of local blood circulation disturbance, the result of the study is significantly distorted and becomes uninformative.
If biomaterial is collected from a catheter installed in a central vein, the physician should avoid the channel through which electrolytes and glucose are administered. Blood acid-base level in such a case will also be considered uninformative due to falsely high values.
In terms of gas composition, capillary liquid connective tissue is closer to arterial tissue. Nevertheless, its analysis is considered the least informative. It is taken, as a rule, when it is necessary to assess the main indicators of the acid-base state of the blood in newborns.
Indications for studying ASL-O
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus is a spherical bacterium that causes pharyngitis, sore throat, scarlet fever, erysipelas, and endocarditis. Complications of streptococcal infections often include rheumatism, vasculitis, and glomerulonephritis. After penetration into the body, microbes release toxins that damage the tonsils, heart, kidney tissue and skin, and massive hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells also occurs.
After 10 - 20 days from the moment of infection, cells of the immune system produce antibodies (ASL-O), which reduce the activity of toxins.
Based on the degree of change in the titer of these protective compounds, one can determine the relationship with streptococcal infection of the following symptoms:
- recurrent pain in the knees or elbow joints;
- labored breathing;
- new long-term pain in the heart;
- swelling in the ankles and under the eyes;
- arterial hypertension in children, adolescents, young people;
- violation of urine excretion, the appearance of blood in it;
- elevated body temperature of unknown origin (37.1 - 37.5 degrees);
- sudden onset of fever up to 39 degrees or higher;
- burning or bursting pain in the legs, facial skin, redness, swelling, blisters and ulcers in this area;
- twitching of limbs in children with nervousness, tearfulness;
- circulatory disorders (shortness of breath, tachycardia, swelling of the extremities) with myocarditis and heart defects.
Culture for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Characteristic manifestations of streptococcal infections usually do not require confirmation by ASL-O testing, but atypical forms of the disease are also common. If antibacterial therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, autoimmune inflammatory processes occur, since streptococcal antigens are very similar to the components of vascular cells, cardiac muscle tissue, articular surfaces, and neurons.
A referral for analysis can be issued by cardiologists, nephrologists, dermatologists, otolaryngologists to select a treatment method, determine its effectiveness, and indications for surgery. The examination is usually prescribed over time (for example, every week) along with the determination of rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, and ESR.
If there are no clinical manifestations, no increase in acute phase indicators of inflammation, and the titer remains stable, then this indicates that the person is a carrier of streptococcus; he can infect others without showing signs of illness.
Antistreptolysin-O (ASL-O)
Synonyms:
ASL-O, ASLO, Antistreptolysin-O, ASO.
Streptococci are bacteria that, when they enter the human body, produce special enzymes. One of them is streptolysin-O, a protein that destroys red blood cells. It is in response to this that the immune system begins to produce anti-streptolysin-O (ASL-O), which can protect the body from the action of both streptococci themselves and their toxins.
Testing for antistreptolysin-O allows for timely detection of diseases caused by streptococci and their waste products. However, this analysis has the greatest diagnostic value for identifying acute rheumatic fever, since it is one of the laboratory criteria for rheumatism.
General information
Streptococci are divided into groups according to the type of effect and their characteristics. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is the most dangerous, as it is the causative agent of serious pathologies:
- scarlet fever (a highly contagious (infectious) infectious disease);
- glomerulonephritis (damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys);
- tonsillitis and tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils);
- erysipelas (skin infection);
- rheumatic fever – rheumatism (inflammation of connective tissue);
- osteomyelitis (purulent-necrotic process in soft tissues, bone and bone marrow);
- bacterial endocarditis (damage to the inner lining of the heart muscle);
- pyoderma (purulent skin lesion), etc.
Different types of toxins released by bacteria cause different pathological symptoms or syndromes. One of these components is the protein streptolysin, which damages red blood cells - erythrocytes.
In response to the release of streptolysin, the body secretes antibodies (Anti-streptolysin-O). Their concentration begins to increase 1-5 months after infection with streptococcal infection.
The ASL-O indicator returns to normal only after six months to a year.
Indications
The ASL-O analysis can be deciphered by an immunologist, an infectious disease specialist, as well as any general practitioner (general practitioner, pediatrician, family doctor, etc.).
The following reasons may be indications for analysis:
- Recurrent diseases of the heart, kidneys, joints and nervous system (mainly in children);
- Diagnosis of rheumatism - an acute form of rheumatic fever;
- Monitoring the effectiveness of antistreptococcal therapy;
- Monitoring the treatment of purulent-inflammatory pathologies;
- A prolonged increase in temperature in a patient for no known reason;
- Diagnosis of chronic diseases.
Important! Diseases caused by group A streptococcus often cause serious complications in internal organs (heart, liver, kidneys), joints, bone and nervous systems.
And since the concentration of ASL-O increases only a few weeks after infection with a streptococcal infection, this study allows us to identify only the relationship between residual symptoms and the activity of bacteria in the body.
Thus, analysis for ASL-O makes it possible to predict and prevent the development of severe complications.
Norms of antistreptolysin-O
| Patient age | ASL-O indicator, U/ml |
| 2 days – 7 years | less than 100 |
| 7 – 14 years | less than 250 |
| Over 14 years old | less than 200 |
Note: The peak concentration of ASL-O is reached no earlier than 1-1.5 months after the start of their production. It should also be taken into account that antibodies remain in the patient’s blood for several months.
Factors of influence
- A false positive result is possible in healthy people who themselves are carriers of group A streptococcus.
- Tests performed on patients with liver disease give false positive results.
- A false negative result can be obtained by taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs (Coldrex, ibuprofen, aspirin, etc.), steroids and corticosteroids, as well as hormones.
- A false negative result is possible in the very early stages of streptococcal infection (up until the maximum concentration of ASL-O is reached).
With local infection of the skin by streptococci, a high level of antibodies is detected only in 1/4 of all cases. Additionally, a test for antibodies to deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNase B) is prescribed.
Increasing ASL-O
An increase in the concentration of antistriptolysin-O is observed in the following diseases:
Note : determination of the ASL-O indicator is necessary for diagnosing streptococcal infection during remission.
However, the analysis is not informative enough, since an increase in the level of ASL-O antibodies in patients is possible only in 75% of cases.
Therefore, diagnosis in the presence of certain symptoms characteristic of streptococcal diseases is necessarily supplemented by other laboratory tests.
An excess of ASL-O concentration by 3-4 times may indicate a recent illness caused by streptococcus.
Important! A high concentration of antibodies in pregnant women does not affect the formation and development of the fetus, the course of pregnancy or the general well-being of the expectant mother.
Low antistreptolysin-O
A negative test result (low concentration of antibodies or their absence) excludes infection with streptococci. To confirm the result, it is advisable to repeat the test after 2 weeks. If the disease has existed before and any complications are possible in the future, then the level of antistreptolysin-O will rapidly increase.
Preparation
The biomaterial for the study is venous blood, which is taken from the ulnar vein according to the standard venipuncture algorithm.
- Manipulation time is morning hours (from 8.00 to 11.00).
- A prerequisite is that blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach. It is allowed to drink clean drinking water without gas.
Recommendations:
- 30-40 minutes before the manipulation, eliminate physical and emotional stress;
- half an hour before - do not smoke or consume nicotine-containing products (tobacco, chewing gum, spray, patch, etc.).
There are no special diet requirements for this test.
Other rheumatology screening tests
Source: https://www.diagnos.ru/procedures/analysis/aso
How to prepare for analysis
To avoid mistakes, you need to properly prepare for your visit to the laboratory. Since this test is part of a biochemical analysis, preparation for it is carried out according to general rules:
- It is advisable to donate blood in the same laboratory. Especially if the analysis showed a deviation from the norm.
- Venous blood is required for determination. But in exceptional cases, material can be collected from a finger.
- The collection of material for research should be carried out strictly on an empty stomach. The “hungry” period should be eight to twelve hours. On the morning of the laboratory visit, you are allowed to drink only clean water without gases.
- You need to donate blood in the morning, but no later than 11 o’clock.
- Before visiting the laboratory, you must eat as usual for three days, but exclude/limit fatty, fried and spicy dishes/foods.
- Sports and other active physical activities should be avoided, as they can change the quality of the blood.
- It is advisable to stop taking medications unless they are vital. Otherwise, you will need to inform your doctor about the treatment being performed.
- Before donating blood, you need to sit in the waiting room and calm down.
Preparation carried out in accordance with the given recommendations allows you to obtain the most reliable results.
Diagnostics
A blood test for ASO is carried out in conjunction with the study of markers of immunological disorders. Rheumatic tests are prescribed if the patient has symptoms of rheumatism, autoimmune reactive arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune prostatitis, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis. This blood test is also prescribed for those who are often susceptible to diseases caused by the activity of streptococcus: scarlet fever, tonsillitis, including acute form, tonsillitis, erysipelas (erysipelas).
So, for example, if the protein content is low, then this indicates the presence of rheumatoid arthritis, and if there is increased protein in the blood, then this is most likely rheumatism.
An increase in antibody titer in the blood, characterized by short duration, may indicate the presence of infectious diseases. Typically, this increase lasts no more than two weeks. If the level of ASO in the blood persists for more than two weeks, this may indicate an acute form of the disease or the presence of a chronic systemic disease. A longer increase in ASO titer may indicate the development of rheumatism.
What is antistreptolysin O (ASLO)?
ASLO are specific antibodies that are produced by the body to neutralize enzymes secreted by group A streptococci. When a pathogen enters the body, the antibodies recognize their antigens and immediately react with them. As a result of this, the toxins secreted by streptococci are neutralized and then eliminated from the body.
An increase in the number of bacteria also causes an increase in the volume of antibodies in the blood. Because of this, the indicators are diagnostic, allowing one to assess the stage of the disease and the intensity of infection.
Streptococci
Reasons for high levels of ASLO
After streptococci have been identified by ASLO analysis, the first thing to do is to search for the cause, and only then begin treatment of the patient.
A slight deviation in the amount of antistreptolysin O from the norm is a sign of recent infection. A significant increase in antibody levels is a sign of prolonged infection of the body. A gradual decrease in the indicator is a consequence of the correct treatment.
High levels of ASLO do not pose a direct threat to human health. This indicator is only a source of information about a recent illness caused by streptococcal infection. Therefore, there are no specially developed methods for reducing the value of antistreptolysin O.
ASLO is elevated after the bacteria enters the body only for 3-5 weeks; until this moment it remains within normal limits. A decline after an illness is possible only after six months at best, or even after 12 months.
A similar situation is observed in the following diseases:
- Rheumatism, especially in the acute course of the disease;
- some liver diseases;
- with myocarditis;
- Erysipelas;
- Scarlet fever;
- Various streptococcal infectious diseases, for example, sore throat.
There are cases when an increase in antibody concentration is observed in a completely healthy person. Therefore, the interpretation of the analysis is carried out taking into account the overall clinical picture. The level of total protein content (should be high) and whether paraproteins (light and heavy chains of immunoglobulins) are present are taken into account.
If the patient delays seeking medical help, then other organs may also suffer. The risk group includes:
- Heart;
- Nerve fibers;
- Joints (TEST “Are the joints of your legs okay?”);
- renal parenchyma.
Tumormaker NSE - norm and interpretation of results
The level of neurospecific enolase is determined in venous blood. The normal level of the NSE is up to 16.3 ng/ml. If the level of the substance is within normal limits, this can be regarded as the absence of cancer. However, we must remember that in the initial stages of cancer the tumor marker may not increase.
The reasons for an increase in NSE are the following conditions:
- Small cell form of lung cancer;
- Neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma;
- Thyroid cancer;
- Pheochromocytoma;
- Neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas;
- Seminoma;
- Brain damage (stroke, head injury);
- Non-oncological lung diseases (for example, benign neoplasms, tuberculosis).
Accept that if the NSE is slightly elevated, this most likely speaks in favor of a non-malignant process. While a significant increase in tumor markers in the presence of alarming symptoms may well indicate an oncological process. One way or another, the doctor deciphers the analysis, and the results of other studies are necessarily taken into account.
Valeria Grigorova, doctor, medical columnist
4, total, today
( 51 votes, average: 4.78 out of 5)
Spermogram: preparation, decoding, indicators and deviations
Tests for STDs in men: list, deadlines, preparation
Related Posts
What happens with a streptococcal infection?
Gram-positive streptococci bacteria produce enzymes that lead to tissue damage. Streptolysin is one of these enzymes. It has a toxic effect on the heart, disrupts the conduction of impulses, and blocks the respiration of myocardial tissue. When streptococci penetrate the body, the production of antibodies to streptolysin, antistreptolysin O, begins. Its level in the blood begins to increase one to three weeks after infection, after three to five weeks it reaches maximum values, after which it begins to decrease. A small level of ASL-O in the blood can persist for six months or even a year.
If ASLO remains high for a long time, there is a chance that acute rheumatic fever will develop, which is a complication of streptococcal infections such as strep throat. In this case, the indicator returns to normal after 4-8 months with a favorable course. Treatment usually shortens this period.
ASL-O is a marker of streptococcal infection in the body
In rheumatic fever, ASLO does not increase in all patients. For 10-15% this does not happen. A slight increase in antistreptolysin O can be observed in rheumatoid arthritis, but its level in this case is much lower than in rheumatism. Therefore, this analysis is carried out for differential diagnosis of joint damage due to rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis. During the recovery period, the level of ASL-O decreases compared to the acute phase, so it is used to monitor the dynamics of the disease and the continued activity of streptococci in rheumatic fever.
If within six months after the onset of the disease caused by streptococci, the level of ASL-O does not decrease, we can assume the likelihood of relapse.
Streptococcal infection cannot be excluded in the absence of antistreptolysin O in the blood. ASL-O levels remain normal in approximately 15% of patients.
When is an analysis scheduled?
A biochemical blood test for ASLO is prescribed in the following cases:
- to confirm a recent streptococcal infection;
- to assess the likelihood of complications after a recent streptococcal infection;
- as a differential diagnosis. If you need to differentiate between rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis caused by acute rheumatic fever.
An ASLO test is also prescribed two weeks after the start of therapy for rheumatism or glomerulonephritis. The analysis allows us to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
Analysis for ASLO is most often prescribed in childhood, when a child is diagnosed with kidney pathologies, heart disease, nervous system or joint diseases. It is necessary to confirm the cause of the disease - a streptococcal infection. The study is not prescribed in the following cases:
- when diagnosing streptococcal skin lesions;
- with scarlet fever;
- during the period of streptococcal endocarditis. In this case, a bacterial test gives a faster result;
- with osteomyelitis.
Advice! A blood test for ASLO in the acute period is not of diagnostic interest, since the production of antibodies begins only one to two weeks after infection.
Blood test for thyroid hormones
Tests for thyroid hormones are carried out in laboratories and help a medical specialist determine whether a very important endocrine organ in our body is functioning correctly. There are several parameters by which malfunctions of the thyroid gland are determined.
Tests for thyroid hormones:
- TSH is a thyrotropic hormone. It is produced in the human brain and controls the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Norm: 0.45 – 4.10 mU/l.
General TZ – triiodothyronine. This analysis is carried out when the thyroid gland is overactive.
Normal: 1.05 – 3.15 nmol/l.
In older people, the rate decreases.
TT4 – total thyroxine.
For women: 71.2 – 142.5 nmol/l.
For men: 60.74 – 137.00 nmol/l.
Deviation is a decrease or increase in metabolism in the body.
TG – thyroglobulin.
Indicator: should not exceed 60.00 ng/ml.
AT-TPO - antibodies to thyroid peroxidase.
Norm: 5.65% units/ml. and no more.
Interpretation of clinical blood test
After receiving the results of a laboratory test, the question arises of how to decipher the blood test. For this purpose, hematological determinants are used, the range of which is 24 different parameters. Among them are the hemoglobin concentration, the number of leukocytes, the volume of erythrocytes, the average level of hemoglobin concentration in an erythrocyte, the average volume of platelets, the size distribution of erythrocytes and others.
Automatic decryption involves precise determination of the following parameters:
- WBC – white blood cells, leukocyte content in absolute values. The normal amount is 4.6 – 9.0 cells/l, necessary for recognizing and destroying foreign agents, stimulating the body’s immunity, and eliminating dead cells.
- RBC - red blood cells, the content of erythrocytes in absolute value at a norm of 4.4 - 5.8 cells/l in elements that include hemoglobin, which is a transporter of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- HGB is the level of hemoglobin in the blood at a normal level of 133-174 g/l. The analysis is carried out using cyanide. Measurement is in moles or grams per liter.
- HCT is hematocrit, which determines the ratio of the volumes of blood elements in plasma: leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets.
- PLT - blood platelets, platelet content in absolute value at a norm of 151-401 cells/l.
Research results and their possible dynamics
Blood tests for ASLO are explained in different laboratories with some differences. The average transcript is presented in the table.
Note!
The norm and deviations in the ASLO level are determined using 2 methods: latex test and turbidimetric study. Using the first method, titers are additionally detected, but some clinics place greater confidence in the second method, which requires the use of additional equipment.
Let us recall that the study is of diagnostic value if it monitors the dynamics of changes in antibody levels. For this purpose, they are carried out several times.
Let's look at how to decipher the results of laboratory tests as they are carried out.
- The peak of elevated rates is recorded a month after infection. Then it begins a slow and steady decline, which indicates that the body is coping with the pathology.
- A persistent increase in antigen levels is classified as a course of the rheumatic process. A similar complication can also be diagnosed after a sore throat.
- The success of rheumatism treatment is indicated by even a slight decrease in titers 2 months after the onset of the disease.
- The absence of downward dynamics within six months indicates the presence of a relapse.
What to do if abnormalities in the blood test for ASLO are detected? Inflated digital indicators of this laboratory study record the past pathology associated with streptococci. However, high titre values do not pose a danger to human life and health. Therefore, measures aimed at normalizing ASLO are not being taken, while continuing to monitor the dynamics of possible changes.
ASLO during pregnancy
A biochemical blood test during pregnancy is a mandatory laboratory test. At the same time, a slight increase in ASLO indicators in this case does not pose any threat to either the expectant mother or her baby, so treatment is not prescribed. However, the doctor makes such conclusions if the streptococcal infection suffered did not leave behind complications.
Laboratory testing to determine the level of ASLO is more informative in children. This is due to the correct determination of the nature of the disease. Thus, identifying the streptococcal nature of a sore throat requires the use of antibiotics, while other types do not require their use. Incorrect therapy will cause dangerous complications associated with disruption of the functioning of vital internal organs. Such a diagnosis will help determine the advisability of prescribing a specific treatment.
It should be remembered that it makes no sense to decipher the results of the research on your own. This issue is resolved by qualified doctors.
Basic rules for preparing to take the UAC
It is recommended to donate blood early in the morning, after 12 hours of fasting. In exceptional cases, you can drink unsweetened tea. In addition you should:
- in agreement with the doctor, stop taking medications the day before the test
- do not donate blood after physiotherapy or x-ray examination
- do not donate blood directly after mental and physical stress
- 1 hour before the procedure, refrain from smoking
- Avoid fatty and spicy foods and alcohol 48 hours before the procedure
- go to bed at your usual time, get up no later than one hour before blood sampling
Repeated examinations should be carried out at the same hours, since the morphological composition of the blood is prone to daily fluctuations. I suggest watching a video of how a general blood test is done:
Do not neglect the rules of preparation for the research procedure, and you will not be afraid of false results!
So, now the reader knows what a general blood test shows, the purpose of its use, what indicators the general analysis includes. How to prepare for the test procedure, and what factors influence the results. We learned about normal values and how they change under various conditions and diseases of the body.
ESR
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate shows how quickly the blood separates into two layers - the upper (plasma) and lower (formed elements). This indicator depends on the number of red blood cells, globulins and fibrinogen. That is, the more red cells a person has, the slower they settle. An increase in the amount of globulins and fibrinogen, on the contrary, accelerates erythrocyte sedimentation.
Reasons for high ESR in a general blood test:
- Acute and chronic inflammatory processes of infectious origin (pneumonia, rheumatism, syphilis, tuberculosis, sepsis).
- Heart damage (myocardial infarction – damage to the heart muscle, inflammation, synthesis of “acute phase” proteins, including fibrinogen.)
- Diseases of the liver (hepatitis), pancreas (destructive pancreatitis), intestines (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), kidneys (nephrotic syndrome).
- Hematological diseases (anemia, lymphogranulomatosis, myeloma).
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis).
- Injury to organs and tissues (surgeries, wounds and bone fractures) - any damage increases the ability of red blood cells to aggregate.
- Conditions accompanied by severe intoxication.
- Lead or arsenic poisoning.
- Malignant neoplasms.
An ESR below normal is typical for the following body conditions:
- Obstructive jaundice and, as a consequence, the release of large amounts of bile acids;
- High levels of bilirubin (hyperbilirubinemia);
- Erythremia and reactive erythrocytosis;
- Sickle cell anemia;
- Chronic circulatory failure;
- Decreased fibrinogen levels (hypofibrinogenemia).
ESR, as a nonspecific indicator of the disease process, is often used to monitor its progress.
ASLO results in dynamics
Testing blood for ASLO levels allows you to monitor the course of the disease. For this purpose, the analysis is scheduled at intervals of seven days. The following options are possible:
- an increase in ASLO levels is recorded a week after infection. Maximum indicators are diagnosed in the third to fifth week. If the body’s immune system copes with the pathogen, then the level of ASLO begins to decrease and reaches normal levels within six months;
- a persistent increase in enzyme levels should be alarming. Because it becomes a sign of a developed complication - rheumatism (rheumatic fever). The pathological process can develop after a sore throat. In this case, long-term and persistent ASLO activity is observed;
- a decrease in the ASLO titer by the end of the first month of the disease becomes a sign of a favorable course of rheumatism, i.e. the heart is not involved in the pathological process. When selecting adequate therapy, treatment periods may be reduced;
- Steadily increased ASLO indicators within six months from diagnosis of the disease indicate a high probability of developing a relapse of the pathology.
It is worth remembering that the level of ASLO in the blood during the development of rheumatism in some people remains normal. Such patients account for approximately 15% of all diagnosed cases of pathology.
A consistently high level of ASLO can be recorded in the absence of pathological symptoms typical of rheumatism. In this case, a person can be suspected of having the following diseases in a chronic form:
- tonsillitis;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition, a similar result can be observed in carriers of streptococcal infection. The infectious agent is dormant and can be activated at any time.
Streptococcal infection can provoke the development of a rheumatic process and cause acquired heart disease in a child. For this reason, after any infection, it is necessary to check the child’s blood for the ASLO value. This will help determine the true cause of the illness.
A blood test for ASLO can also be prescribed to an adult to confirm rheumatoid arthritis. The interpretation of the results obtained should be carried out by a qualified specialist. Independent interpretation of blood biochemistry indicators is unacceptable.
Complete blood count in adults
A general blood test in adults is mandatory whenever you visit a doctor due to illness or deterioration in health. It allows you to assess the general condition of the body and make the correct diagnosis. Women during pregnancy take the OAC upon registration, at 12, 20, 30, 36 weeks of pregnancy.
For an accurate interpretation of the results of the CBC, the age of the person is important, since the norms of some blood parameters differ somewhat in accordance with this factor
| Indicators | Hemoglobin | Red blood cells | ||
| age | women | men | women | men |
| 20-30 | 110-152 | 130-172 | 3,5*1012-5,0*1012 | 4,2*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 30-40 | 112-150 | 126-172 | 3,5*1012 -5,0*1012 | 4,2*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 40-50 | 112-152 | 128-172 | 3,6*1012 -5,1*1012 | 4,0*1012-5,6*1012 |
| 50-60 | 112-152 | 124-172 | 3,6*1012 -5,1*1012 | 3,9*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 60-65 | 114-154 | 122-168 | 3,5*1012 -5,2*1012 | 3,9*1012 -5,3*1012 |
| Over 65 | 110-156 | 122-168 | 3,4*1012 -5,2*1012 | 3,1*1012 -5,7*1012 |
Features of changes in blood counts during pregnancy:
- By increasing the total volume of blood, its viscosity decreases. As a result, pregnant women have a decrease in hemoglobin and a decrease in the number of platelets.
- The leukocyte formula changes: the concentration of leukocytes increases to 10*109/l, the numerical value of band neutrophils increases, and the content of lymphocytes decreases.
- The ESR value during pregnancy can be increased to 45 mm/h.
ASLO blood test: explanation
Not all patients understand what a positive and negative ASLO result means. A negative test does not have important information content, since such a result has no significance in diagnosis. When the blood test for ASLO is higher than normal, the doctor begins a detailed study of the patient’s medical history.
Doctors diagnose elevated ASLO when:
- rheumatism (a positive rheumatic test in the form of analysis for CRP and RF is diagnosed in 85% of patients);
- chronic pharyngitis, otitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- scarlet fever;
- pyoderma;
- diffuse glomerulonephritis,
- erysipelas inflammation.
Important! A table with high ASLO scores indicates recent infection. If the indicators are close to normal, but are still too high, then this condition indicates a long-standing infection.
There are several indications for donating blood for ASLO if a person is sick with tuberculosis, has liver disease or high levels of bad cholesterol (LDL). A relatively low level of antistreptolysin-O in a blood test can be found in children from 6 months to 2 years.
Hematocrit
Hematocrit is the percentage ratio of the volume of the blood being tested to the volume occupied by red blood cells in it. This indicator is calculated as a percentage.
A decrease in hematocrit occurs when:
- anemia;
- fasting;
- pregnancy;
- water retention in the body (chronic renal failure);
- excess protein content in plasma (myeloma);
- drinking plenty of fluids or administering large amounts of intravenous solutions.
An increase in hematocrit above normal indicates:
- leukemia;
- polycythemia vera;
- burn disease;
- diabetes mellitus;
- kidney diseases (hydronephrosis, polycystic disease, neoplasms);
- fluid loss (excessive sweating, vomiting);
- peritonitis.
Normal hematocrit values: Men – 40-48%, women – 36-42%.
Purpose of the study
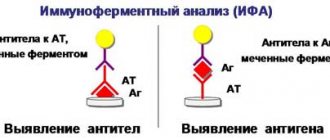
When an antigen meets an antibody, a reaction occurs. The interaction occurs in 2 stages:
- The first phase is the identification of the antigen and its combination with antistreptolysin O;
- The second phase proceeds similarly to the gluing of particles (agglutination)
The first phase involves insoluble particles, that is, the bacteria themselves. The second stage is the reaction for soluble toxins. The goal of the whole thing is to neutralize and remove antigens out. In the process of interaction of ASLO with streptolysin (an enzyme secreted by streptococci), a third party also appears - complement proteins (globulins).
ASLO analysis helps determine the amount of antibodies and deviations from generally accepted standards. Based on the results obtained, you can not only identify the presence of infection, but also find out how long a person has been a carrier of streptococcal infection. The study allows us to answer the questions:
- Whether the person is currently sick or not;
- Assume the limitation period for infection.
For this purpose, a latex test is used in medical practice. It does not require expensive equipment and is carried out quickly. It shows what concentration and titer of antibodies is present in the body.
A more expensive alternative to latex analysis is the turbidimetric titration method. It is carried out using measuring instruments: a photometer and a spectrophotometer.
This approach to research helps to make quantitative measurements of ASLO in the blood.
You can learn more about ASLO in our article “Antistreptolysin O (ASLO) in the blood: what it is, the norm by age, interpretation of results, therapy.”
Checking the sample helps to determine the presence of autoimmune and rheumatic diseases and assess the existing inflammatory process.
When conducting a complex of immunological studies, the following indicators are checked:
- Total protein;
- C-reactive protein;
- Uric acid;
- Circulating immune complexes (CIC)
- Antistreptolysin O.
Antistreptolysin O is elevated: what does it mean, causes, treatment
If a blood test for antistreptolysin (another name for the ASL-O, ASLO, ASO examination) showed an increase in normal values, this means that there is an infection in the body caused by group A streptococcus. The main purpose of this analysis is to search for the cause of purulent-inflammatory diseases and associated complications (for example, erysipelas or myocarditis).
The action of specific antibodies (antistreptolysin) is aimed at combating antigenic substances and pathogenicity factors secreted by group A streptococcus.
Their number increases as the concentration of waste products of streptococci increases.
Streptococcus can cause the development of other diseases, this is its main danger (glomerulonephritis, rheumatism)
Purpose of the study
When an antigen meets an antibody, a reaction occurs. The interaction occurs in 2 stages:
- The first phase is the identification of the antigen and its combination with antistreptolysin O;
- The second phase proceeds similarly to the gluing of particles (agglutination)
The first phase involves insoluble particles, that is, the bacteria themselves. The second stage is the reaction for soluble toxins. The goal of the whole thing is to neutralize and remove antigens out. In the process of interaction of ASLO with streptolysin (an enzyme secreted by streptococci), a third party also appears - complement proteins (globulins).
ASLO analysis helps determine the amount of antibodies and deviations from generally accepted standards. Based on the results obtained, you can not only identify the presence of infection, but also find out how long a person has been a carrier of streptococcal infection. The study allows us to answer the questions:
- Whether the person is currently sick or not;
- Assume the limitation period for infection.
For this purpose, a latex test is used in medical practice. It does not require expensive equipment and is carried out quickly. It shows what concentration and titer of antibodies is present in the body.
A more expensive alternative to latex analysis is the turbidimetric titration method. It is carried out using measuring instruments: a photometer and a spectrophotometer.
This approach to research helps to make quantitative measurements of ASLO in the blood.
You can learn more about ASLO in our article “Antistreptolysin O (ASLO) in the blood: what it is, the norm by age, interpretation of results, therapy.”
Checking the sample helps to determine the presence of autoimmune and rheumatic diseases and assess the existing inflammatory process.
When conducting a complex of immunological studies, the following indicators are checked:
Proper preparation for analysis
You need to donate blood for antistreptolysin in the morning (before 11 o’clock). For the study, blood is drawn from a vein. The procedure is performed using a disposable syringe. The following factors may influence the results of the examination:
- Physical exercise;
- Bad habits;
- Certain medications;
- Liver dysfunction;
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hemolysis is the decomposition of red blood cells, with the release of hemoglobin;
- Nephrotic syndrome.
The following recommendations should be followed to exclude falsely elevated ASLO levels in the test results:
- Blood donation is done on an empty stomach. Dinner should be 8-12 hours in advance;
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited per day;
- The last cigarette should be smoked at least one hour before visiting the laboratory;
- It is necessary to stop taking “accidental” medications that may affect the result, and the doctor who ordered the study must be notified of all prescribed drugs;
- The day before, you need to take care of yourself, avoid strength exercises and physical activity.
What results should there be?
The normal value is considered to be the absence of ASLO, or a very low value. But even if a low level of antibodies was detected, this is a normal condition. By the way, a child’s low concentration of antistreptolysin is observed between the ages of six months and 2 years. Below is the ASLO norm by age:
- In children under 7 years of age, the maximum value is 100 U/ml;
- The group 7-14 years old was assigned a standard of up to 250 U/ml;
- In adolescents over 14 years of age, the level should be up to 200 U/ml.
In adult women and men, the level of antibodies in the blood should be a maximum of 200 U/ml.
Aslo is above normal
If antistreptolysin O is elevated, what does this mean? First of all, this indicates the presence of streptococcal infection in the body. This indicator is also checked for the following diseases:
- Rheumatism;
- Sore throat;
- Myocarditis;
- Scarlet fever;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Otitis;
- Glomerulonephritis.
Unfortunately, it is not practical to use this indicator for emergency diagnosis of infections.
This is because after contracting a streptococcal infection, the level of ASLO remains within normal limits for another week.
Only on the 8th day the number of antibodies begins to increase, reaching a maximum value a month later. After the patient recovers, the blood condition returns to normal after 6-12 months.
You need to take the test at least 2 times to track the dynamics of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method. The interval between blood donations should be 1.5-2 weeks.
An increased value of ASLO indicators is, for example, a consequence of rheumatoid arthritis and streptococcal rheumatism. This is very important when selecting a course of therapy.
Antistreptolysin analysis is also important in confirming streptolysin in the serum, that is, the presence of bacteria in the body. The course of treatment is based on taking antibiotics. If the moment is missed, then the recovery process will be accompanied by relapses and complications (rheumatic fever, glamerulonephritis).
Reasons for high levels of ASLO
After streptococci have been identified by ASLO analysis, the first thing to do is to search for the cause, and only then begin treatment of the patient.
A slight deviation in the amount of antistreptolysin O from the norm is a sign of recent infection. A significant increase in antibody levels is a sign of prolonged infection of the body. A gradual decrease in the indicator is a consequence of the correct treatment.
High levels of ASLO do not pose a direct threat to human health. This indicator is only a source of information about a recent illness caused by streptococcal infection. Therefore, there are no specially developed methods for reducing the value of antistreptolysin O.
ASLO is elevated after the bacteria enters the body only for 3-5 weeks; until this moment it remains within normal limits. A decline after an illness is possible only after six months at best, or even after 12 months.
A similar situation is observed in the following diseases:
- Rheumatism, especially in the acute course of the disease;
- some liver diseases;
- with myocarditis;
- Erysipelas;
- Scarlet fever;
- Various streptococcal infectious diseases, for example, sore throat.
There are cases when an increase in antibody concentration is observed in a completely healthy person. Therefore, the interpretation of the analysis is carried out taking into account the overall clinical picture. The level of total protein content (should be high) and whether paraproteins (light and heavy chains of immunoglobulins) are present are taken into account.
If the patient delays seeking medical help, then other organs may also suffer. The risk group includes:
What to do if the readings are high?
Before prescribing treatment for elevated levels of ASLO in the blood, you need to undergo an additional examination to look for rheumatic pathology and take additional tests. A test for glomerulonephritis is carried out, for which a series of tests are prescribed, the Rehberg test, creatinine and urea levels and other studies. A kidney biopsy is possible.
To confirm the diagnosis of myocarditis, the following is carried out:
Most often, when confirming the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes penicillin therapy. Treatment involves taking antibiotics, Extencillin and Bicillin. In addition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticosteroids are prescribed.
For myocarditis, antibiotics are prescribed, Elcar and Mildronate.
If glomerulonephritis is diagnosed, the patient is hospitalized and treated in the nephrology department. A salt-free diet is recommended for such patients. Drinking regime is also controlled. A daily diuresis diary is kept. It indicates the volume of liquid drunk and urine excreted. Blood pressure is measured every day.
Antibiotics are mainly used for etiotropic therapy and elimination of streptococcus. The patient's diet should be enriched with various fermented milk products to maintain the intestinal microflora in a normal state (kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese). Don’t forget about drugs that strengthen the immune system.
Phytotherapy
As a preventative measure, you can use onions and garlic without additional processing. They cope well with bacteria, including streptococcus, at the initial stage of infection, before the infection spreads throughout the body.
To lower ASLO levels, specially selected decoctions, teas and infusions are used. Raspberry leaves, cranberries, and rose hips have a diuretic effect and help remove germs. Cranberries and rose hips can be used both natural and dried.
Fresh hop cones are a powerful remedy in the fight against infection. Here is one recipe for a healing decoction based on them:
- 8-9 hop cones are poured into ½ liter of boiling water;
- Cover with a lid;
- Let it brew for 4 hours;
- Drink 3 times a day before meals (10-20 minutes). The decoction should be consumed warm.
Keep in mind that the healing properties of the decoction last only 12 hours, so you will have to brew the “healing elixir” every day.
Source: https://MyAnaliz.ru/blood/antistreptolizin-o-povyshen/
When the analysis is not carried out
There is a period when streptococcal infection gives vivid manifestations - damage to the skin, tonsils, pharynx, other ENT organs, temperature reaction, serious condition of the patient, but antibodies to the microbial toxin have not yet appeared in the blood. Therefore, in the acute period of tonsillitis, laryngitis, otitis or scarlet fever, the ASL-O test is not prescribed. Its result will be negative, or a low titer of antibodies will not give an idea of the activity of inflammation.
Infection of the tonsils with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus
The second situation with unreliable antistreptolysin values is possible in case of skin diseases (streptoderma, erysipelas). Antibodies to streptolysin in this case are destroyed by phospholipids of skin cells.
Streptococcal infection - what is it, why is it dangerous?
- Streptococcal infection is infection of the body by pathogenic microbes streptococci
- Streptococci are spherical bacteria that cause many human diseases.
Today, 21 groups of streptococci are known (A, B, C, G, V...)
The causative agents of most human streptococcal diseases are group A hemolytic streptococci (in particular the β-hemolytic streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes)
Penetrating into the body, streptococci release toxic extracellular enzymes into the human blood, causing poisoning, acute inflammation, cell destruction and tissue damage.
Toxic factors of group A streptococcus
| Substance released | Harm |
| Streptolysin-O (hemolysin) | Destroys red blood cells under anaerobic conditions (without oxygen) |
| Streptolysin-S | Destroys red blood cells under aerobic conditions |
| C5a peptidase | Suppresses protective immune responses |
| Pyrogenic toxins | Indirectly stimulate the development of acute inflammation and fever. Cause cytotoxic effects with damage to vascular walls, myocardium, and other connective tissues |
| Cardiohepatic toxin | Damages the myocardium and diaphragm. Causes the appearance of giant cell granulomas in the liver |
| Streptokinase (fibrinolysin) | Indirectly induces the dissolution of fibrin fibers of connective tissue |
| Streptodornases (DNases) | Promote the breakdown and dissolution of DNA structure |
| Hyaluronidase | An enzyme capable of breaking down mucopolysaccharides of connective tissues, including hyaluronic acid |
Analysis structure
The result of the analysis is usually presented in the form of a general table, which displays the names of the indicators, the threshold value of the norm, the current indicator, as well as units of measurement.
Indicators determined through analysis:
- Total protein (norms in adults - 63–83 g/l, in newborns - 49–69 g/l, in children under 14 years old - 57–82 g/l). Based on the level of total protein in the blood, one can draw conclusions about the health of vital organs such as the liver and kidneys.
- Albumin level (normal in adults and children - 35-52 g/l, in newborns - 34-44 g/l). A decrease in this protein may indicate the presence of kidney, liver and intestinal diseases. An increase occurs when the body is dehydrated.
- Glucose (normal - 3.3-5.5 mmol/l, in newborns - 1.7-4.7 mmol/l). Glucose levels are directly related to such a serious disease as diabetes. Therefore, detection of glucose levels is present in almost all blood tests. An increase may indicate the presence of not only diabetes mellitus, but also hormonal disorders, pancreatitis, chronic kidney and liver diseases.
- Bilirubin (total, direct, indirect). Normal levels of total bilirubin are 8.5–20.5 µmol/l in adults. Elevated levels of bilirubin and its forms reflect the functioning of the liver and gallbladder. In newborns in the first days of life, bilirubin concentrations may increase to 50 µmol or higher (newborn jaundice).
- Gamma-Gt (norms: in men -
- Total cholesterol (normal values: in adults - 3.5-5.5 mmol/l, in newborns - 1.6-3.0 mmol/l, in children under one year - 1.8-4.9 mmol/l) . It is one of the main lipids that enter the blood mainly with food. An elevated level is a provoking factor in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. A level below normal may indicate impaired absorption in the intestines and acute forms of disease.
- Triglycerides (in adults the norm is 0.41-1.8 mmol/l, in newborns - 0.2-0.86 mmol/l). These substances belong to neutral fats that reflect lipid metabolism.
- Lipid profile indicators: low, very low, high density lipoproteins, their ratio (atherogenic coefficient), used for diagnosing atherosclerosis. The normal LDL level in men is 2.2–4.8 mmol/l, in women – 1.9–4.5 mmol/l; the norm for HDL is 0.7–1.8 mmol/l in men and 0.8–2.2 mmol/l in women.
- Indicators that change during inflammation: C-reactive protein, seromucoid, sialic acids.
- Some blood clotting indicators, such as fibrinogen. Its normal level in adults is 2-4 g/l, in newborns - 1.25-3 g/l.
- Uric acid (in men - 210-420 µmol/l, in women - 150-350 µmol/l). A higher than normal level of uric acid may indicate the presence of gout and uric acid diathesis.
- Iron (in women - 8.95-30.43 µmol/l, in men - 11.64-30.43 µmol/l). It is one of the most important microelements that make up hemoglobin. A deficiency of this element indicates a violation of oxygen metabolism in cells.
- Creatinine (men - 62-115 µmol/l, women - 53-97 µmol/l). The level of this substance is a criterion for diagnosing kidney function. It also allows us to draw conclusions about energy metabolism in tissues.
- Chlorine (normal - 98–107 mmol/l), sodium (136–145 mmol/l), potassium (3.5–5.5 mmol/l). These substances are electrolytes. Their performance directly affects the functioning of muscle, nervous and other cellular tissues. These substances also help regulate metabolic processes throughout the body.
- ALT (norm for women - up to 34 U/l, for men - up to 45 U/l). One of the enzymes synthesized in the liver. A higher than normal level of this enzyme is characteristic of serious diseases of the liver, blood, and heart failure.
- AST (norm for women - up to 31 U/l, for men - up to 37 U/l). Another enzyme that is synthesized in the liver. The level of its concentration above normal is typical for hormonal imbalance, as well as for cardiac dysfunction.
This analysis can be expanded; additional studies are carried out at the discretion of the attending physician. The duration of laboratory research, as a rule, is no more than one day. After which the biochemical blood test is interpreted.
Decoding a blood test for HIV
The final diagnosis of the presence of the immunodeficiency virus can only be established when at least three months have passed after contact with an infected patient.
A repeat analysis for the reliability of the diagnosis is carried out six months later. The results of the tests obtained will be reliable only in cases where there has been no further contact with the infected patient.
The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is used to determine the DNA of the virus. If the presence of infection is detected, the result is indicated as a “positive reaction.” If the presence of HIV infection is not detected, the result is indicated as a “negative reaction.”
There are times when “false positives” are present. This happens when the laboratory worker is poorly qualified or when using outdated equipment. To confirm or refute such an analysis, an F 50 test is prescribed, which can find antibodies if HIV infection enters the body.
Where to take blood for testing: from a vein or from a finger
The results of laboratory research are significantly influenced by the location and technique of collecting biological material. In medical practice, blood from capillaries is more often used. Usually it is taken from the pulp of the ring fingers, in difficult cases - from the earlobe.
The puncture is made on the side, where the capillary network is thicker. The blood should flow by gravity so that there is no admixture of tissue fluid, which will distort the result. For testing, capillary blood should be taken:
- for extensive burns of the body, especially the hands
- if the veins are small or inaccessible, if you are obese
- in patients prone to thrombosis
- in newborns
Currently, blood from the venous bed is considered the best material for general clinical analysis. This is due to the use of hematology analyzers. With their help, in our time, OAC is carried out. They are designed and standardized for the processing of venous blood.
When taking blood from a vein, you also need to follow some rules. The best place to take blood is the cubital vein. Do not apply a tourniquet for more than 2 minutes, this will lead to an increase in cellular elements in the bloodstream.
Proper preparation for analysis
You need to donate blood for antistreptolysin in the morning (before 11 o’clock). For the study, blood is drawn from a vein. The procedure is performed using a disposable syringe. The following factors may influence the results of the examination:
- Physical exercise;
- Bad habits;
- Certain medications;
- Liver dysfunction;
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hemolysis is the decomposition of red blood cells, with the release of hemoglobin;
- Nephrotic syndrome.
The following recommendations should be followed to exclude falsely elevated ASLO levels in the test results:
- Blood donation is done on an empty stomach. Dinner should be 8-12 hours in advance;
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited per day;
- The last cigarette should be smoked at least one hour before visiting the laboratory;
- It is necessary to stop taking “accidental” medications that may affect the result, and the doctor who ordered the study must be notified of all prescribed drugs;
- The day before, you need to take care of yourself, avoid strength exercises and physical activity.
Specifics of the study
To understand what an ASLO analysis is, you need to understand the specifics of infections caused by streptococci.
When a dangerous microorganism enters the systemic bloodstream, it begins to secrete streptolysin. This substance has a toxic nature, due to which it is capable of destroying red blood cells, causing damage to the main “pump” of a person - the heart.
As the disease progresses, toxic substances become more and more numerous, so the immune system begins to repel their attack with the help of antistreptolysins. These are antibodies aimed at neutralizing the action of streptococci. The more antibodies are formed in the bloodstream, the easier it is for the body to win the fight against infections. In this case, an increase in antistreptolysin is observed 1-2 weeks after infection. Its concentration reaches peak values after a month. Then there is a gradual decrease in antibodies, although their presence may remain in the blood for another six months.
Carrying out a biochemical blood test allows you to determine the number of protective bodies. Thanks to this indicator, doctors diagnose the stage of streptococcal disease and its severity. The lack of qualified assistance leads to pathological changes in the heart and joints. Damage to the kidneys and nervous system is observed.
Note!
If the level of ASLO in the blood is high for a long time, rheumatoid fever will develop. With such a complication, normal laboratory test results can be expected no earlier than after 4 months.
Despite the high diagnostic performance of the analysis, it should be noted that in 15% of patients experiencing an infection of streptococcal origin, the levels of antigens in the blood do not exceed the norm.
How to prepare for the analysis?
In order to avoid distortions in the results, it is recommended to comply with the following requirements:
- for dinner on the eve of blood donation, you should not drink coffee, strong tea, fatty foods and alcohol, and it is better to exclude the latter from the diet 3 days before the test;
- for a day you should refrain from visiting the sauna and heavy physical activity;
- It is not recommended to take the test immediately after you come from the street to the office, especially if you had to rush, it is better to sit for 10 minutes in front of the office;
- two weeks before the test, you should stop taking medications that reduce lipid concentrations, before taking the test - hormonal drugs, antibiotics, diuretics; Cancellation is carried out only on doctor's orders.
The norms of indicators in each laboratory may differ significantly. It is for this purpose that the standards are indicated on the result form. However, you should not make a diagnosis on your own based on the tests obtained.