Modern high-tech diagnostic methods make it possible to identify diseases that were previously considered difficult to diagnose. CT scanning of the lungs and bronchi helps to detect and determine the degree of pathology in the organs of the respiratory system. This is an innovative technique based on the interaction of X-ray radiation and computer technology. The information on the pages of our portal will help you evaluate the benefits of computer lung examination and find out the exact addresses of clinics.
Short description:
Time: from 30 seconds. up to 1 minute, with contrast – 15-20 minutes.
The need to use a contrast agent: necessary for almost every examination.
Contraindications: yes.
Limitations: patient weight no more than 200 kg.
Conclusion preparation time: from 15 to 30 minutes.
Diagnostics for children: from 14 years old.
What is a computer examination of the respiratory organs?
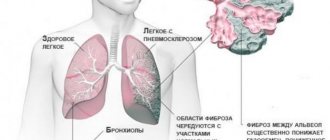
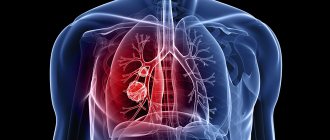
Computed tomography of the lungs and bronchi is an ultra-precise way to diagnose and study almost all diseases of the tissues and structures of the respiratory system. Using a tomograph, you can study the lungs, bronchi and surrounding tissues in detail. The unique capabilities of this device make it possible to identify many pathologies at a stage when they are not yet diagnosed by traditional examination methods.
The operation of a computed tomograph is based on X-ray pulses. The waves emitted by the beam tube pass through the patient's body and are captured by the scanner's sensors. Darkening in the lungs visualized on X-ray layer-by-layer images will indicate the presence of pathology. Information from the scanner is processed by a computer and as a result, the patient receives a sheet with layer-by-layer images of the organ being examined.
What diseases are diagnosed
Spiral computer examination diagnoses the following pathologies:
- Inflammatory processes in the bronchopulmonary system.
- Benign neoplasms.
- Tuberculosis, including focal.
- Vascular pathologies.
- Traumatic injuries and contusion of the lungs and bronchi.
- Subpleural lesions in the lungs.
- Abnormal changes in the structure of lung tissue.
- Emphysema.
- Oncology.
- Fibrosis.
- Sarcoma.
For a more accurate study of oncological pathologies, PET CT of the lungs is prescribed. This computer diagnostic method identifies cancer foci and places where metastases are localized. In this case, a positron emission study not only detects oncological tumors, but also accurately determines the boundaries of the tumor focus, as well as the degree of its malignancy.
Who is diagnosed?
A computer examination of the bronchopulmonary system is prescribed if it is necessary to establish the state of the respiratory organs over time and if it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis using other diagnostic methods.
Indications for undergoing CT scanning:
- Pathological neoplasm of any nature in the lungs, pleura, bronchi, mediastinum, chest.
- Increased amount of pleural fluid and pleural effusion.
- Signs of pulmonary emphysema.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the examination area.
- Traumatic injuries to the lungs and bronchi.
- The bronchi and lungs have changes in structure.
Contraindications for the study
There are no absolute contraindications to conventional computer examination. As relative contraindications, doctors identify:
- The patient is young. A CT scan of the lungs is prescribed to children when they reach 12 years of age, but in some cases the study can be performed regardless of age. If the child is unable to lie still during the procedure, he will be examined under anesthesia;
- Psychoneurological diseases and claustrophobia in a patient.
- Pregnancy throughout.
- Some forms of allergies.
In any of the above cases, the doctor prescribing a computer examination of the lungs individually understands the advisability of the procedure, and if there is no alternative, the study will be carried out.
Indications for virtual bronchoscopy:
- Suspicion of the presence of tumors of the respiratory organs;
- Examination of the lungs of smokers;
- Diagnosis of rare diseases (for example, Kaposi's sarcoma);
- Inflammatory diseases of the lungs, bronchi and mediastinum;
- Syndrome of lobar and segmental opacities identified by x-ray examination (to clarify the diagnosis);
- Surgery planning;
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of the respiratory system (including after surgery).
How to prepare for a CT scan of the lungs
No preparation is required for a CT scan of the lungs and bronchi without contrast. Before the procedure, the patient must remove all jewelry and metal objects from clothing. Then, if there are no relative contraindications, the procedure is performed in the prescribed manner.
If a tomography with contrast is prescribed, the patient must refuse to eat 6 hours before the examination. This is due to the fact that in some cases, the introduction of a contrast marker can cause nausea and vomiting in the patient.
CT scan of the lungs - what it shows
CT scan of the lungs is a method designed to clarify the characteristics of the pathology, which is revealed on the X-ray of the chest, but does not allow making a diagnosis. An X-ray image is obtained by summation of shadows located along the path of the X-ray beam. Behind the sternum there is a whole complex of organs that are not diagnosed on a chest x-ray. More precisely, minor anatomical changes and enlarged intrathoracic lymph nodes are visualized when performing a CT scan of the chest. It is rational to perform a computed tomography scan if hilar lymphadenopathy is suspected. The radiologist can visualize a lumpy enlargement of the roots of the lungs in the image. This is where the capabilities of the traditional x-ray method are limited. A CT scan of the lungs and mediastinum allows a thorough study of the size and structure of enlarged lymph nodes. With tuberculosis of the intrathoracic lymph nodes in children, radiography does not show pathology due to the projection overlap of the sternum and heart. Computed tomography clearly indicates the pathological nature of the lymphadenopathy. It is not always necessary to do a CT scan of the lungs. Due to the high radiation exposure of the patient, it is necessary to be selective in prescribing the diagnostic method. In case of traumatic injury to the chest, a computed tomography scan is often prescribed. There are clinical studies regarding the irrationality of prescribing the procedure for blunt chest trauma. Researchers from California and Massachusetts conducted thorough studies to evaluate the possibility of not using computed tomography for this nosology. CT scans increase the likelihood of cancer in young people due to the mutational effects of ionizing radiation on cells. The cost of analysis is not cheap. Professor, MD R. Rodriguez from San Francisco (University of California) conducted a study involving about 11 thousand people over 14 years of age. About 5,000 people had an unknown diagnosis. Sorting of injuries was carried out according to the following gradation:
- Fracture of the thoracic spine
- Blood in the pleural cavity;
- Lung collapse;
- Diaphragm rupture;
- Injuries of the bronchi, trachea, esophagus;
- Fractures of several ribs.
Minor injuries, a fracture of one rib without displacement, do not require surgical intervention, so careful verification of the diagnosis does not play a big role. During the study, 2 types of diagnostics were performed: Detailed CT of the chest, CT of the lungs with maximum sensitivity for chest injuries.
Application of contrast
A contrast marker is a special drug that can accumulate in affected cells. Intravenous contrast makes the image clearer. The slightest changes in tissue structures become visible in the image. Depending on the chosen diagnostic technique, the marker is introduced either before the start of the procedure or in drops throughout the entire research process.
The contrast allows the diagnostician to better examine the segments of the lungs on a CT scan, determine the exact boundaries of the cancer focus, even if its size does not exceed a few millimeters, and accurately determine the onset of the development of metastases. The marker is safe for the patient’s body and is quickly eliminated naturally through the urinary system.
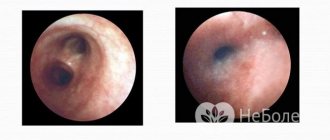
How is virtual bronchoscopy performed?
CT is an absolutely painless and fast diagnostic method.
During the examination, the patient is in a horizontal position on the tomograph table, which can move.
One of the main conditions for the effective behavior of the procedure is the immobility of the subject, therefore, if necessary, the upper part of his body can be fixed.
Before scanning, the doctor must determine the area of study and correctly set the operating mode of the device.
Next, the patient must listen to the doctor’s commands and periodically hold his breath.
How to do a CT scan of the lungs and bronchi: technique
The method of computer examination of the lungs itself consists of a detailed study of the respiratory organs using X-rays. Depending on the diagnostic mechanism, there are three methods for its implementation:
- Simple sequential tomography of the lungs - the tomograph tube stops after each full revolution around its axis. A new scanning cycle will begin only after the couch with the patient moves deeper into the tube.
- Spiral diagnostics - the tube of the device is in continuous rotation, and the couch gradually enters inside the tomograph at an arbitrary speed.
- MSCT (multilayer tomography) - the tube of the device rotates in an accelerated mode, and the device itself has several independent beam tubes and receiving sensors. The scanning process produces a three-dimensional image of the organ, which allows you to examine it entirely.
All three methods can be used either without contrast or with the use of a contrast agent. A CT scan of the lungs with contrast is performed to identify pathology of the pulmonary vessels and study the circulatory system of the lungs, bronchi and surrounding tissues.
Indications and contraindications
It is possible to understand why such research is needed by characterizing the main areas within which it is applied. Using a CT scan of the lungs you can:
identify where tumors are located, establish their size and consistency features;- distinguish between foci of tuberculosis and neoplastic processes;
- make a diagnosis in doubtful cases;
- analyze the condition of lymph nodes and blood vessels;
- determine the stage of development of the disease;
- Based on the established features, make a forecast for the further development of the disease.
There are several types of computed tomography of the lungs. One of them is spiral CT. This variety is the most modern. With its help, it is possible to obtain the most accurate images of the organs under study due to the spiral rotation of the emitter.
If a spiral tomograph has a large number of detectors, then the procedure performed on such a device is called multislice computed tomography of the lungs (MSCT). During this process, doctors receive even more accurate and detailed information about the patient’s condition.
Another method of examination is a CT scan of the lungs with contrast. It is used much less frequently, since there is not always a need for its use. In this case, the patient is given a contrast agent intravenously. Typically, a CT scan of the lungs with contrast is performed in order to establish the exact boundaries of pathological foci.
The use of CT is necessary for differential diagnosis (if the patient has signs of two diseases and it is not possible to make a diagnosis). Sometimes a CT scan of the lungs is performed instead of a traditional X-ray.
This is done if the formation of the following diseases is suspected:
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- lung tumors, malignant and non-malignant;
- metastasis;
- emphysema;
- thromboembolism;
- pericardial pathology;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the respiratory tract.
This study of the lungs has certain contraindications.
During X-ray scanning, the patient's body is exposed to UV rays, and their dose is much higher than in the case when the result is a regular X-ray. Therefore, this diagnosis is not suitable for all patients.
Most often it is prohibited in the following cases:
pregnancy;- severe diabetes mellitus;
- thyroid diseases;
- serious condition of the patient;
- presence of mental illness;
- renal failure;
- serious heart disease.
It should be said that not all of these contraindications are strict. Sometimes, if the use of a CT scan is warranted, doctors perform it.
Decoding the research results
Deciphering a CT scan of the lungs and bronchi makes it possible to almost accurately detect tuberculosis and inflammatory pathologies in the early stages. Having a diffuse nature. Such diseases are not always diagnosed by traditional examination methods (x-ray or fluorography).
The screening study clearly shows nodules with areas of decay on CT scan of the lungs. Deciphering the images and drawing up a conclusion takes about half an hour. Upon completion of the description, the patient is given pictures and a sheet reflecting the diagnostic results. Based on these results, the patient is given recommendations on which doctor to contact to treat the identified pathology.
Frequently asked questions from patients
• How often can a CT scan of the lungs be done?
– Computer scanning is no more dangerous than conventional radiography. Thanks to the advent of modern models of tomographs, the radiation dose received by the patient during the procedure is minimal. Therefore, the doctor determines the number of studies for a particular patient based on the severity of the disease, taking into account the total annual radiation exposure.
• MRI or CT scan of the lungs – which is better?
– In simple terms, a computed tomograph “sees” better the pathologies of the bone structure of the thoracic region, and a magnetic tomograph “sees” soft tissues better. However, CT almost accurately detects cancerous foci and metastases in the lungs. MRI is better at diagnosing inflammatory diseases. Therefore, the choice of referral for a CT or MRI will be up to your attending physician.
• Which is better, CT or X-ray of the lungs?
– Radiography gives a flat image of the organ and in such a “picture” it is difficult to recognize pathological foci and it is almost impossible to assess the degree of damage to adjacent tissues. A tomograph can provide a three-dimensional image of the lungs and bronchi, and layer-by-layer images will “show” the slightest changes in the anatomical structures of the lung. It is impossible to say unequivocally which is better. Each type of diagnostic was developed for a specific range of studies.
• How much does a CT scan of the lungs and bronchi cost?
– The cost of diagnostics starts from 3000 rubles. The maximum price threshold is 5900 rubles. The price depends on the purpose of the study, the model of diagnostic equipment and the qualifications of medical personnel.