The pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) causes the following diseases:
- chronic gastritis - inflammation of the gastric mucosa
- chronic duodenitis - inflammation of the duodenum
- peptic ulcer of the stomach (in 70% of cases) and duodenal ulcer (in 90% of cases)
- helicobacteriosis
- stomach cancer
- lymphoma of the stomach
70% of the population is infected!
The constant presence of a microorganism in the stomach is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain in the stomach after eating or before eating
- occasional nausea and even vomiting
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach
- heartburn and sour taste in the mouth
- bad breath
- bloating
These symptoms not only reduce the quality of life and force you to take medications for a long time, but can also lead to stomach cancer!
Helicobacter pylori can also “trigger” other diseases that at first glance are not associated with the stomach, the permanent habitat of the bacterium. For example, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is a serious disease with a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood and a high likelihood of bleeding.
Therefore, correct diagnosis of a current H. pylori infection is extremely important!
History of discovery
Spiral-shaped pathogenic microorganisms that live in the human stomach were described 100 years ago by Polish professor W. Jaworski. After some time, the scientist G. Bidzodzero discovered the same bacteria on the mucous membranes of the stomach of animals. For many years they turned a blind eye to this infection, unaware of its danger, but in the late 70s of the last century, scientist Robert Warren noted that these bacteria live on the inflamed gastric mucosa.
As it turned out, the life activity of these microorganisms was studied, albeit not completely, and described by German scientists. However, in those days they did not attach much importance to this. Warren, joining forces with Barry Marshall, began conducting research to study in detail the characteristics of these bacteria. For a long period of time, it was not possible to isolate a culture of microorganisms, but scientists were still lucky. During the Easter holidays, laboratory staff accidentally left plates with bacterial cultures for 5 days rather than 2. Thanks to this incident, scientists recorded the growth of colonies of unknown microorganisms.
The bacteria were originally named Campylobacter pyloridis because their characteristics resembled microorganisms belonging to the genus Campylobacter. In 1983, scientists first published the results of their research. However, a little later, the researchers had to refute their previous discoveries, since it soon became clear that the discovered representatives of the pathogenic microflora were not related to the genus Campylobacter. Based on this, the discovered microorganisms were renamed Helicobacter pylori.
To prove the ability of the microorganism to cause ulcerative disease, B. Marshall ingested its culture in 1985. However, it was not an ulcer that developed, but gastritis, which went away on its own. Thanks to this experiment, the scientist was able to prove that the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori is the cause of the development of gastritis. In 2005, Warren and Marshall received the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology for their sensational discovery.
How to detect Helicobacter pylori - modern diagnostic methods
There are various diagnostic options that help detect Helicobacter pylori. These include:
13C-urease breath test
- Credibility. The 13C-urease aerotest has a very high level of sensitivity (up to 95%) and specificity (95-100%), it is recommended by both Russian and European gastroenterologists. Only this test, in addition to the presence of bacteria, also determines its quantity. This test is ideal for quantitatively assessing the level of infection of a patient before and after anti-Helicobacter therapy and drawing conclusions about the effectiveness of treatment.
- Speed. The test is carried out within 40-45 minutes, the patient receives its results within 1-2 days. The result of the 13C-urease test is a conclusion with a graph in which the patient’s data is compared with normal and limit values, the presence and amount of the Helicobacter Pylori bacterium is determined (from the absence or insignificant amount to a pronounced or high level of infection).
- Methodology and conditions. The test is absolutely safe and does not cause any discomfort to the patient. The 13C breath test should be performed in the morning on an empty stomach or in the daytime after 4-6 hours after eating.
- Preparation. Conditions for obtaining an accurate result: conducting the test 6 weeks after using antibiotics and bismuth preparations; 2-3 days before the test it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol; no later than two weeks before the test, you must stop taking proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole) or type 2 histamine receptor blockers (ranitidine, famotidine, nizatidine, roxatidine), in consultation with your doctor.
- Contraindications. There are no absolute contraindications. Consult your doctor about performing the test if you have a history of gastric surgery.
For analysis, the patient's exhaled air is collected 2 or 4 times: the first time as a control sample, and three times every 10 minutes after the patient takes a drug containing 75 mg of 13C-labeled urea. A high-precision infrared analyzer determines the composition of the air and, accordingly, the amount and activity of bacteria.
Breathing Helic test
- Credibility. The helic test provides identification of bacteria. This aerial test for Helicobacter can be prescribed for primary diagnosis.
- Speed. The test takes 15-30 minutes. The conclusion is given to the patient immediately after the test.
- Methodology. The Helicobacter Pylori breath test (Helicobacter Pylori test) is a quick, easy and painless way to diagnose the Helicobacter Pylori bacterium. The test is a non-invasive method, i.e. does not require endoscopic examination or blood sampling, and does not cause any discomfort. It is safe for patients of all ages and for use during pregnancy.
Preliminary preparation is required to carry out the test. The aerotest is taken on an empty stomach; smoking and chewing gum are prohibited before the test. The test is performed 2-4 weeks after the end of antibiotic therapy.
The analysis of exhaled air is carried out twice: on an empty stomach and after the patient drinks a special solution of urea. In this way, the urease activity of the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori is assessed, which indicates the presence of the bacterium.
Test for Helicobacter during FGDS
- Credibility. Taking a biopsy specimen for analysis directly from the stomach is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing Helicobacter pyloriosis.
- Speed. The FGDS procedure lasts 2-5 minutes, and a conclusion on the results and the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection is issued immediately after the study. In general, the examination and conversation with the endoscopist takes 30-40 minutes.
- Methodology. In cases where a gastroenterologist prescribes an FGDS to a patient, especially in the case of gastritis and peptic ulcers, a simultaneous test for Helicobacter will make a significant contribution to the diagnosis. In this case, the patient will receive two conclusions from one study. During FGDS (endoscopic examination - fibrogastroeuodenoscopy), the endoscopist sees with his own eyes the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, identifies the affected areas and takes samples from them for research (biopsy).
Blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori
- Credibility. The presence of antibodies in the blood indicates that the immune system once encountered the bacterium, recognized it and responded. This means that the analysis does not directly detect Helicobacter, but only indirectly indicates its presence in the past or present. Antibodies to the bacterium appear 3-4 weeks after infection, and also remain in the blood for about 1 month after treatment. Sometimes antibodies remain in the blood for life, regardless of the presence of Helicobacter. Therefore, the result of the analysis is not always reliable: it can be either false positive or false negative, and a number of more tests may be needed to clarify the results.
- Speed. The analysis takes 2-3 days.
- Methodology. Blood is drawn from a vein. Blood is donated on an empty stomach; before donation, you should not eat for 8 hours.
Features of the bacterium
The first feature of this microorganism is its ability to withstand a very acidic gastric environment, while most bacteria and viruses simply die. Helicobacter pylori can adapt to the level of gastric acidity using 2 mechanisms:
- When it enters the stomach, the bacterium begins to move through the mucous membranes. She does this with the help of her flagella. Hiding in the mucous membranes of the stomach, the microorganism protects their cells from excess acids. To put it simply, the bacterium “selects” the most optimal habitat for itself.
- H. pylori causes the production of ammonia, which reduces stomach acid. Due to this, the microorganism can be conveniently located on the walls of the organ, remaining in its place for many years.
The second feature of the bacterium is its ability to cause inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. As it multiplies, it causes slow destruction of gastric cells, and the substances it secretes cause chronic inflammatory processes and gastritis. When the mucous membranes of the duodenum and stomach are weakened, ulcers and erosions begin to form, which increase the risk of developing cancer. For this reason, many gastroenterologists rightly consider Helicobacter Pylori to be a provocateur of oncological processes in the stomach.
You can get rid of the pathology only after taking a course of antibiotic therapy. With the help of antimicrobial drugs, the level of stomach acidity is regulated. Only a gastroenterologist can prescribe specific medications, after conducting the necessary examinations and referring the patient for additional instrumental diagnostic procedures.
How is H. pylori transmitted?
Infection with this bacterium can mainly be done in two ways – oral-fecal and oral-oral. However, there is an opinion that the microorganism can be transmitted from a cat to its owner, or when the infection is transmitted by flies. Young children are most susceptible to infection.
Transmission from one person to another occurs in 3 ways:
- Iatrogenic when infection is caused by diagnostic procedures. Thus, an infection can be acquired during endoscopy or other poorly sterilized medical instruments that have had direct contact with the patient’s gastric mucosa.
- Fecal-oral. The bacterium is excreted along with the stool. You can become infected with the bacteria through contact with contaminated water or food.
- Oral-oral. Gastroenterologists are confident that H. pylori also lives in the oral cavity. Therefore, the infection can be transmitted by kissing, using someone else's toothbrush or poorly washed cutlery.
Although Helicobacter Pylori is capable of causing histological gastritis in all infected people, signs of pathology appear in rare cases. Less often than gastritis, gastric ulcer develops, and extremely rarely, stomach cancer develops.
How the test is carried out
First of all, to conduct the test and obtain the most reliable data, special preparation is required, including the following measures:
- Antibiotics and antisecretory agents should not be taken for 30 days before the test.
- Avoid any meals 6 hours before the test.
- The examination is carried out only on an empty stomach.
- The use of proton pump inhibitors is prohibited for 14 days before the examination.
- For 72 hours or three days before the examination, you should not eat legumes or drink alcoholic beverages even in minimal dosage.
- Smoking or chewing gum is prohibited 3 hours before the examination.
- The last condition is that on the day of the diagnosis, it is recommended to thoroughly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
The test itself is an easy and completely painless process. However, only a doctor should conduct the examination, because it is very important to do everything as accurately and correctly as possible. The test is carried out in 3 stages, fitting into 12 minutes:
- The patient makes himself comfortable in a sitting position, takes the tube into his mouth (pushing it as deep as possible) and breathes evenly for 6 minutes. At this time, it is important that no saliva gets into the tube; it can be pulled out, swallowed or spat out, then continue the procedure.
- The tube is removed, the patient drinks a special solution, then the tube is placed back into the oral cavity.
- The patient breathes in the same mode for another 6 minutes, and the testing is completed.
During the entire procedure, you need to sit quietly, take a measured breath and exhale the same.
Symptoms of infection
After entering the stomach, the bacterium begins to actively secrete its waste products. They irritate the mucous membrane, resulting in inflammation. Clinical symptoms of Helicobacter Pylori depend on its form.
There are five of them, let’s look at each of them in more detail:
- Latent or asymptomatic form, when an infected person does not experience any alarming symptoms, especially if his immunity is strong enough to resist Helicobacter. But even if the clinical picture does not manifest itself, the person is still a carrier and can infect others. If bacteria remain in the stomach for a long time, severe complications may occur, one of which is stomach cancer.
- Acute gastritis is a disease manifested by epigastric pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. The disease can become chronic with periodic relapses.
- Chronic gastritis. This pathology is one of the main manifestations of helicobacteriosis. During an exacerbation, the patient complains of stomach pain, attacks of nausea, sometimes with vomiting, headaches, loss of appetite. The patient suffers from heartburn, a feeling of bloating, belching, and attacks of flatulence. Nonspecific symptoms also occur in the form of bleeding gums and bad breath.
- Chronic gastroduodenitis, when the pathological process affects the duodenum. The clinical picture resembles the symptoms of gastritis, but with gastroduodenitis, stool disorders, in particular constipation, are possible. The patient loses his appetite, complains of nausea, and has trouble sleeping. Changes in the mucous membranes are detected only during endoscopy. Lesions may be mild, moderate or severe.
- PUD, which can also occur for other reasons (alcoholism, smoking, frequent stress, hazardous work, etc.). Erosions and ulcers form when the mucous membranes of the stomach are damaged more deeply. The pathology manifests itself with a large number of symptoms: pain in the stomach, nausea, the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, nausea, flatulence, vomiting, indigestion, heaviness in the epigastric region, heartburn, etc.
If we talk about non-gastric symptoms, then a patient with helicobacteriosis will experience the appearance of a subcutaneous or skin rash in the form of small white or pink pimples. As a rule, they are localized on the face. Often this disease causes the development of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, lichen planus, and erythema.
The photo shows the symptoms of Helicobacter pylori: acne on the face.
Why diagnose and treat helicobacteriosis?
Helicobacter pylori promotes the development of:
- stomach cancer
- mucosal atrophy
- peptic ulcer
- non-ulcer dyspepsia
- gastritis.
* % of cases of development of diseases associated with the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori.
Helicobacter Pylori is a gram-negative bacterium that infects the stomach and duodenum. The bacterium secretes toxic enzymes that damage the cells of the stomach and duodenum.
This causes ulceration of the mucous membrane. Helicobacter Pylori delays the healing of ulcers, the unprotected wall of the stomach begins to be exposed to gastric juice, and this contributes to the transition of the disease to a chronic form. The bacterium impedes trophism and microcirculation of tissues, which in turn also interferes with the normal healing of any damage. In this case, therapy that is aimed at eradicating bacteria (their complete destruction) and normalizing regeneration mechanisms can help.
Analysis for Helicobacter pylori
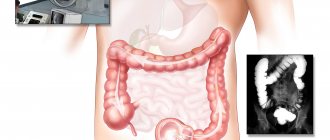
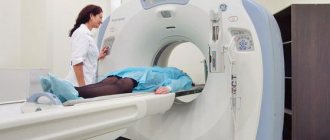
Diagnosis can be invasive (endoscopy followed by biopsy of gastric tissue) and non-invasive (laboratory tests). Of course, the most accurate and reliable method is the invasive method, because by collecting tissue from the gastric mucosa, a medical specialist carefully examines the biomaterial to detect foci of inflammation and the bacteria themselves. In addition to microscopic examination, the gastric tissue sample may be subjected to various laboratory tests.
All laboratory tests are aimed at identifying Helicobacter pylori and assessing its vital activity. During its life cycle, the microorganism breaks down gastric urea into ammonia, thus creating favorable living conditions for itself. If you place a piece of gastric mucosa infected with Helicobacter Pylori in urea, ammonia will be released. This will increase the alkalinity of the solution, but these changes can only be detected using special test strips. Indicators operate on the principle of litmus paper.
But to identify the disease, it is not at all necessary to conduct an FGDS or a biopsy study - you can use another technique. The 13 urea test helps to detect the presence of infection absolutely painlessly and begin treatment immediately.
Recommendations and prevention
After diagnosis and treatment, it is very important to prevent re-infection. If Helicobacter pylori is detected in one of the family members, it is recommended that everyone else be diagnosed, and, if necessary, undergo treatment to avoid the spread of infection.
Prevention measures:
- careful adherence to personal hygiene and the use of only personal hygiene products
- It is important to avoid sharing unwashed dishes
- When eating, do not try food with someone else’s spoon and do not bite off a common piece, but rather put it in, cut it, pour out your portion
- do not let small children eat from someone else’s spoon, keep children’s dishes, pacifiers, and bottles clean
- do not kiss strangers, remember that this is how the infection very easily enters the body
- reconsider your lifestyle, do not drink alcohol, do not smoke, try not to be near another smoking person.
After testing for helicobacter pylori, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is recommended, who will determine:
- need for in-depth examination
- the need for screening of family members
- necessity and regimen of Helicobacter Pylori eradication therapy
- the need and date of follow-up examination after treatment.
Consult a gastroenterologist if characteristic symptoms appear or if you have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Don't self-medicate!
Possible complications
With timely initiation of therapy, dangerous consequences can be prevented. In addition, the risk of infecting other people will be completely eliminated.
If we talk about complications, they can manifest themselves through the development of:
- chronic or atrophying gastritis;
- JAB and DPC;
- stomach oncology;
- endocrine pathologies caused by atrophy of the epithelial lining of the stomach.
To avoid such consequences, self-medication is strictly not recommended. It is better to entrust this issue to a qualified gastroenterologist.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori
Before starting treatment with Helicobacter Pylori, the degree of damage to the stomach and the contamination of its walls is assessed. The fact is that in some people, over time, these microorganisms become one of the varieties of opportunistic microflora, and therefore may not manifest themselves in any way.
If the bacterium does not harm the health of its carrier, manipulation to remove it is not carried out. But to cure the infection, you will need to use powerful antibacterial drugs. They, in turn, can significantly weaken the immune system and cause the development of intestinal dysbiosis.
On a note. You cannot resort to using folk remedies to treat helicobacteriosis. The use of decoctions and infusions can only temporarily “lull” the symptoms of the disease, forcing the patient to postpone a visit to the doctor. In the meantime, the disease will only progress, which in the future can cause serious complications.
Analysis results and normal indicators
If we talk about the results, the norm is a urease indicator of 0 or less. These data are calculated by assessing the ratio of the results of the first and second stages of the survey. This means that Helicobacter is absent in the patient’s gastrointestinal tract, that is, the test is negative.
It is important to understand that decoding will give results even if the size of the Helicobacter colony is minimal, and the indicators may be as follows:
- 1.5-3.5 – the bacterium is inactive;
- 3.5-5.5 – low level of damage;
- 5.5-7 – moderate level;
- 7-15 – the bacterium is active;
- anything above 15 indicates a high degree of damage.
In each of the above points, the test is considered positive, which means the person requires appropriate treatment.
Therapeutic regimens
The treatment regimen for Helicobacter pylori requires an integrated medical approach. Usually the patient is prescribed 2 drugs, which are selected individually. Plus, one drug from the group of proton pump inhibitors is mandatory.
The duration of treatment is determined by the gastroenterologist after a thorough examination of the patient and assessment of the severity of the disease. The duration of the course of therapy is 14-21 days. After its completion, the doctor conducts repeated laboratory tests to confirm the patient’s complete recovery.
Helicobacter breath test results
If the indicators correspond to weakly expressed urease activity, additional studies should be carried out to confirm or refute the presence of H. pylori in the stomach.
Based on the examination data, medical history and condition of the patient, the gastroenterologist individually selects a treatment regimen and, if necessary, prescribes additional examinations.
In the case of a helic test, a specialist evaluates the results of the study visually - using the color indicator of the device. Test systems do not provide quantitative parameters. They indicate a positive or negative diagnostic result.
Antibiotics
Despite the fact that Helicobacter Pylori belongs to the group of pathogenic bacteria, not all antimicrobial drugs are able to destroy it.
The microorganism quickly develops resistance to antibacterial substances, which significantly complicates the healing process. Sometimes the doctor has to combine several medications at once in order to achieve positive dynamics; moreover, the acidic environment of the stomach can prevent the activation of drug components and slow down the therapy process.
Antibiotic therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection involves the use of the following drugs:
- Clarithromycin
- cephalosporin drugs;
- Azithromycin;
- Levofloxacin.
The drug Amoxicillin and its analogue Flemoxin Solutab have the highest effect in the treatment of inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and ulcers formed on it. It is possible to use other antibacterial drugs - Augmentin and Amoxiclav. They contain clavulanic acid, which prevents the production of specific enzymes by microorganisms. This, in turn, prevents H. pylori from developing resistance.
Diagnosis: How to detect Helicobacter?
Detecting the presence of Helicobacter pylori is not a difficult task. Blood tests and studies of gastric secretions will help make a diagnosis in the initial stages of diagnosis:
- laboratory research methods;
- A breath test for Helicobacter
is a modern, fast and highly informative research method. It is based on a single dose of a suspension with labeled carbon molecules, which are broken down by specific Helicobacter pylori enzymes. After some time, the labeled carbon in carbon dioxide is determined in the exhaled air using a special device.
The advantage of the urease test is that it is non-invasive, that is, the patient does not have to deal with blood sampling or FGDS.
- serological test (search for antibodies against Helicobacter in the patient’s blood). The normal level in the blood is the complete absence of antibodies to the bacteria. The method is notable because it helps make a diagnosis at the earliest stages;
- stool analysis. Using polymerase chain reaction,
laboratory specialists can find traces of bacterial antigens in stool; - general blood analysis. Chronic infection may be indirectly indicated by such signs as anemia, increased white blood cells;
- instrumental research methods;
- FGDS is an endoscopic method for examining the stomach and duodenum. Helps you see the signs. When performing an FGDS, the doctor performs a biopsy of the gastric mucosa, and the smallest piece of tissue is sent to the laboratory, where it is examined by specialists.
The biopsy material is stained with special substances and examined under a microscope to determine the presence of bacteria.
- a study of gastric secretion by probing the stomach will help establish the fact of increased acidity of gastric juice;
- X-ray of the stomach. A contrast research method that is rarely used in diagnostics. It will help to carry out a differential diagnosis with cancer and stomach polyps, as well as establish the localization of the smallest ulcers and erosions.
Preparations of bismuth tripotassium dicitrate
Most often, the drug De-Nol, which contains the active substance tripotassium dicitrate, is used to treat diseases caused by helicobacteriosis. Due to this, there is a significant reduction in the production of biological compounds that promote the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
De-Nol's action is aimed at:
- disruption of cell membrane permeability;
- change in the membrane structure of cells.
During the chemical interaction of tripotassium dicitrate with protein compounds in the gastric mucosa, the formation of high-molecular complexes occurs. Thanks to this, a strong protective film is formed on the surface of ulcers and erosions, which prevents gastric juice from entering damaged areas of the gastric mucosa.
After completing the full course of therapy with De-Nol, the resistance of the gastrointestinal mucosa to pepsin and hydrochloric acid increases.
Proton pump blockers
To effectively and quickly get rid of Helicobacter Pylori, proton pump blockers are included in the treatment regimen. Due to the components included in their composition, complex biological processes are launched, which lead to a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid by the stomach.
The most effective proton pump blockers (inhibitors) include the following drugs:
- Omeprazole (Omez, Ultop).
- Rabeprazole (analogues - Khairabezol, Bereta).
- Pantoprazole (analogs - Controloc, Nolpaza).
When the acidity of the stomach decreases, the process of repairing damaged tissue begins. It creates unfavorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and in particular H. pylori.
In addition, proton pump inhibitors significantly increase the effectiveness of antibiotics used to treat diseases caused by this bacterium. Taking this into account, gastroenterologists often reduce the dose of antimicrobial drugs. This has a beneficial effect on the state of the intestinal microflora and the general immunity of the patient.
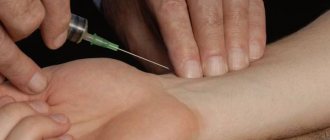
Blood tests
If the patient complains of pain in the stomach, any discomfort, with functional digestive disorders, with gastritis and peptic ulcers, a blood test is taken for Helicobacter pylori. Antibodies to helicobacter pylori in the blood are an indicator of human infection with the bacterium helicobacteriosis.
It is recommended to donate blood for Helicobacter bacteria if:
- weak immunity
- hereditary predisposition to stomach cancer
- as a preventive diagnosis
- to evaluate the treatment received for the infection.
How to prepare for the analysis?
Before the analysis, you must not eat food, coffee, tea, alcoholic drinks, or smoke 8 hours before the test. This test for Helicobacter pylori determines the amount of immunoglobulins. When a certain toxin enters the human body, a virus, microbe, immunoglobulins interact with them and neutralize these harmful substances. The analysis shows the interaction of the pathogen and immunoglobulins, which makes it possible to determine whether Helicobacter pylori is in the stomach or duodenum.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of this test:
- the diagnostic procedure is not expensive;
- high accuracy of the result;
- analysis is available to everyone.
The test for Helicobacter pylori has its drawbacks:
- there are factors that influence the result of the analysis;
- some patients experience fear when taking blood;
- thorough results are obtained in 4-6 days.
Analysis transcript
Deciphering the result of a blood test for Helicobacter pylori can be done without medical skills. Antibodies are divided into categories A, G, M. Opposite each category there is a result on the form. If all blood test parameters for Helicobacter pylori do not exceed the norm, then there is no bacteria in the body:
- immunoglabulin LgG is absent or significantly lower than normal: bacteria are absent in the body;
- LgG detected: helicobacteriasis is present or has been previously experienced;
- immunoglabulin LgM was not detected or below the norm: conditional norm for Helicobacter pylori;
- LgM class detected: initial stage of the disease;
- immunoglabulin LgA is not detected in the blood: this may indicate an early stage of the disease, recent antibiotic therapy, or the patient is in the recovery stage.
Contraindications
A blood test for Helicobacter is not performed:
- for convulsions
- with increased excitability of the patient
- if there is skin damage at the injection site.
A blood test for antibodies is also not prescribed for venous phlebitis.
Therapeutic diet
To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract throughout the course of treatment and after its completion, the patient must follow a special therapeutic diet. It implies the following rules:
- Meals should be fractional, that is, you need to eat little, but often.
- Exclude fried, fatty, spicy, spicy foods, baked goods and confectionery products.
- Maintain drinking regime.
- Avoid alcohol and low-alcohol drinks.
- Eliminate marinades, pickles, carbonated water, fast foods and other junk foods from your diet.
It will not be easy to follow such a strict diet at first, but the patient must do it to take care of his health. Over time, he will get used to this diet and will not notice food restrictions.
Here is a sample menu for patients with Helicobacter Pylori:
- Breakfast consists of oatmeal porridge, fresh cottage cheese pancakes and fruit compote.
- For afternoon tea, you are allowed to eat cottage cheese soufflé and drink a cup of chamomile tea.
- For lunch, you can eat soup based on chicken broth with lean meat, steamed fish cutlets and stewed or fresh vegetables.
- For the second afternoon snack - fruit or milk jelly with baked apples.
- For dinner you can eat steamed turkey and boiled potatoes.
- For a late dinner, you are allowed to consume kefir or a decoction of rose hips.
Dishes are selected individually, depending on the stage of the disease. The risk of exacerbations, as well as other factors, are also taken into account.
Prevention
To avoid infection, you must follow the simplest rules:
- wash your hands thoroughly before eating and after using the restroom;
- use only your own hygiene products and items (towels, toothbrushes, soap, etc.);
- completely cure gastrointestinal pathologies;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- It is mandatory to undergo routine preventive medical examinations.
To consolidate the results of treatment and strengthen the immune system, the doctor will prescribe vitamin complexes, as well as medications that include microelements necessary for a person. But the patient himself must help his body get stronger after the illness by giving up alcohol and smoking, and reviewing his lifestyle.
(Visited 62,572 times, 29 visits today)
Contraindications for carrying out
The beauty of this examination method is the complete absence of any contraindications. The procedure is carried out non-invasively; the maximum inconvenience it can cause is a gag reflex if the tube is inserted too deeply.
Otherwise, a breath test can be performed on everyone, without exception, from pregnant women at any stage of gestation to small children. But remember, you need to prepare for the procedure carefully, because the reliability of the results depends on this.