Author of the article: Alexey Alexandrovich Zubkov, otolaryngologist of the first category, member of the European Rhinologic Society
Pharyngitis is a chronic inflammatory process that develops in the pharynx, first affecting the mucous membrane, and later deeper tissues, including the soft palate and lymph nodes. This disease, even with serious complications, cannot be life-threatening. However, it is very common, and certain forms of pharyngitis can be extremely difficult to completely cure.
Signs and symptoms of pharyngitis
The first sign of the possible development of pharyngitis is the appearance of painful and unpleasant sensations in the throat: burning, soreness, tickling, tingling. In the morning, a person gets rid of the accumulations of mucus that accumulate during the night by expectoration or coughing, this is a common procedure. If pharyngitis occurs, it can lead to nausea and further vomiting. In addition, people begin to complain of pain while swallowing food.
The severity of the signs of the disease largely depends on the form of pharyngitis, as well as its etiology. In most cases, the pathology is accompanied by such symptoms? How:
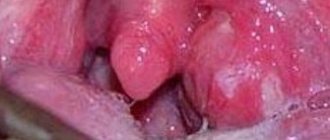
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the throat in human pharyngitis;
- granularity of pharyngeal lymphoid fluids;
- also on the back of the pharynx, on the palatine tonsils, small purulent formations may appear;
- general weakness of the body;
- frequent headaches that can last for a long period of time;
- frequent persistent, dry cough;
- body temperature can rise to within 37.5 degrees;
- muscle pain.
If chronic pharyngitis is an addition to existing diseases, then its symptoms are added to the symptoms of the main disease.
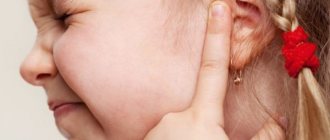
Often with pharyngitis, an increase in the submandibular and occipital lymph nodes is observed. If you press on them at this moment, this leads to severe pain. The fact that the infection has spread to the middle ear may be indicated by the occurrence of congestion and pain in the ears.
Quite often, acute pharyngitis that develops in a child is confused with other diseases, such as measles or scarlet fever. Also, its primary symptoms are in many ways similar to another throat disease, sore throat. However, in the case of a sore throat, all the signs are more pronounced: a high temperature of up to 39 degrees, as well as severe pain in the throat. Many experts indicate that the symptoms of pharyngitis are similar to those of diphtheria. The difference in this case is the absence of the painful gray-white film that forms on the mucous membrane of the throat during diphtheria.
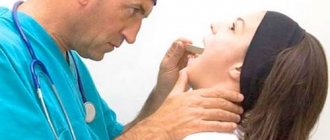
Important signs of the disease include neurological disorders, which, however, may indicate another pathology. Therefore, to establish an accurate diagnosis, the patient should consult an ENT doctor.
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), experienced doctors will be able to provide the patient with the necessary consultations, examinations, and also offer him effective treatment. The clinic is equipped with the latest technology, which allows doctors to quickly make a diagnosis and begin therapy. The clinic is located in the Central Administrative District at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10.
Signs
In fact, inflammation of the pharynx is the most common form of acute respiratory viral infection. With viral pharyngitis, the symptoms resemble a common cold:
- sore throat of varying intensity with dry throat;
- soreness in the back of the throat;
- fever in children is accompanied by increased sweating and weakness;
- cough is caused by an accumulation of clear fluid flowing down the back of the throat;
- cervical lymph nodes do not always enlarge;
- temperature rise 37.2-38.0 °C;
- when the infection spreads to the tubopharyngeal ridges, the pain is transmitted to the ear area.
Pharyngitis affects the general condition of the sick person. There is a loss of strength, a headache, and the voice becomes rough.
On a note! When examining the pharynx, unilateral severe tissue swelling is sometimes noted. If this area becomes cloudy or, conversely, shines, a consultation with an ENT doctor is necessary. This sign indicates a complication and may threaten laryngeal edema.
If the causative agent of pharyngitis is the herpes virus, the disease in adults and children occurs in the form of ulcerative lesions of the walls of the pharynx.
In this case, inflammation of the respiratory tract is accompanied by a serious condition, signs of intoxication, and high fever. Therefore, treatment requires the use of antiviral drugs (Acyclovir).
With chronic pharyngitis, the picture of the disease depends on the duration and stage of the disease. The leading symptom of an advanced form of the disease is a cough caused by the accumulation of mucus in the throat. Over time, it becomes the cause of a nervous state.
Causes of the appearance and development of pharyngitis
Medical practice shows that the main cause of the development of acute, and subsequently chronic pharyngitis, most often is the inhalation of too cold or polluted air by a person, and the onset of the disease can also be accompanied by exposure to various types of irritants on the mucous membrane. Therefore, experts divide this disease according to etiological types:
- infectious pharyngitis. Its development is caused by viruses and bacteria;
- traumatic can develop from injuries to the mucous membrane, during operations or when foreign objects enter the pharynx;
- allergic.
A variety of reasons can lead to the development of acute pharyngitis, including smoking and drinking alcohol, inhaling chemical fumes, dust, hot steam, and exposure to radiation.
Also, pharyngitis can develop as a side disease against the background of other pathologies. For example, it often forms during caries, sinusitis, and sinusitis.
Chronic pharyngitis is often a continuation of the acute form of the disease and is extremely rarely diagnosed as an independent pathology. In addition, the patient may experience diseases such as gastrointestinal disorders, gastritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis. Bad habits or surgery (tonsil removal) can also lead to chronic pharyngitis. In addition, chronic pharyngitis can develop due to the ingestion of elements of the stomach contents into the pharynx; a similar effect can occur if a person has diseases such as a hiatal hernia. Among the main reasons for the development of pharyngitis it is worth highlighting:
- breathing problems and nasopharyngeal diseases (sinusitis) caused by injuries;
- human use of medical vasoconstrictor drugs.
During the development of chronic pharyngitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs, which covers the larynx, which in turn leads to frequent colds. All kinds of infectious pathologies, inflammation of the pharynx, tonsils (angina) also contribute to the development of the disease.
Forms of pharyngitis
There are acute and chronic pharyngitis.
For acute pharyngitis
The following symptoms are typical:
- dryness and sore throat;
- pain when swallowing, especially when swallowing saliva (the so-called “empty swallow”);
- Sometimes a rise in temperature to 37.5-38°C and general weakness are observed.
Chronic pharyngitis
usually occurs at normal temperatures. Quite often a dry cough is observed, and there is a constant desire to cough and “clear” the throat. The patient has to swallow mucus all the time, which causes pain. As a result, irritability increases, attention and performance decreases, and sleep is disturbed.
Ways of infection with pharyngitis
Infection with pharyngitis can occur against the background of a viral infection that affects a person’s throat. This may include the following diseases:
- different types of colds, flu;
- sore throat, diphtheria;
- fungal infections.
Most of these diseases are airborne, meaning a person can become infected by simply breathing the air or coming into contact with other people who are already infected. Later, against the background of a cold, flu, or sore throat, pharyngitis develops, which is initially difficult to diagnose. Only an examination by a specialist will allow you to promptly identify the disease and begin its treatment.
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis
At the initial stage, primary signs appear:
- dry throat and discomfort,
- soreness,
- burning and constant thirst,
- swallowing saliva causes unbearable pain.
- Symptoms increase rapidly, weakness appears,
- general malaise.
As the process progresses, the following may appear in the future:
- high body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- sometimes the pain radiates to the ears, patients note that they are full;
- the upper cervical lymph nodes are palpated;
- a dry cough appears.
- Upon examination, you can observe that the back wall of the pharynx turns red, hyperemia can also affect the palatine arches.
- The patient experiences all the signs of intoxication - perhaps dizziness, muscle pain, and an overwhelming gag reflex.
Attention! Do not forget that the acute form is often the first manifestation of some infectious diseases, such as scarlet fever, measles or rubella. For diagnosis, swabs are taken from the throat, which are sent for virological and bacteriological examination.
What complications can the disease cause?
As mentioned above, pharyngitis itself does not pose a serious danger to human life. However, if the disease becomes complicated, it can lead to serious health risks. For example, if the disease is not treated and becomes advanced, then a person may ultimately develop increased sensitivity to various infections and pathogens. Pharyngitis of the streptococcal type can cause the development of purulent and non-purulent complications. Let's consider each of these options.
- Non-purulent complications (rheumatism) lead to the formation of inflammatory nodules in various tissues, including the heart, and the musculoskeletal system. Experts call this complication post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
- Purulent complications (peritonsillar or retropharyngeal abscess). If this form of pharyngitis complication develops, there is a real threat to the patient’s life. If effective treatment is not carried out, the pathology can develop into sepsis (blood poisoning).
Also, initial pharyngitis can subsequently cause the following serious health problems:
- inflammation of the lymph nodes located in the neck (cervical lymphadenitis), this disease is especially difficult to resolve in adults;
- sialadenitis or inflammation of the salivary gland; treatment of such a pathology often requires surgery;
- inflammation of the auditory tubes and middle ear, which can lead to complete or partial hearing loss;
- laryngitis - inflammation inside the larynx can also lead to serious consequences;
- tracheitis - this inflammation of the mucous membrane of the trachea is a provocateur of bronchitis and pneumonia with transition to pneumonia;
- chronic bronchitis - in this case, the infection from the larynx spreads to the lungs; treatment will require taking strong antibiotics.
It is also important to remember that chronic pharyngitis is often caused by initially untreated acute pharyngitis.
Causes of the disease
Viral pharyngitis can be caused by different viruses, so the opinion that it is a consequence of only influenza or ARVI is fundamentally wrong.
Pathology can develop under the influence of:
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- influenza and parainfluenza viruses;
- coronaviruses;
- cytomegaloviruses;
- herpes simplex viruses.
Pharyngitis of a viral nature can easily become chronic, so treatment must be carried out to the end.
Causes of development in children
Viral pharyngitis in children is a fairly common phenomenon that develops against a background of decreased immunity. Sometimes a child just needs to drink a little cold water or eat ice cream - and the illness will immediately make itself felt.
In addition, in kindergartens and schools, this pathology has long become an invariable companion of flu and colds, and if one child gets sick, the rest are also at risk.
Viral pharyngitis can even develop in a newborn baby after close contact (kissing or hugging) with a carrier of the infection. In this case, the situation with diagnosing and treating the pathology becomes significantly more complicated, so taking independent measures to alleviate the child’s condition is out of the question.
When to see a doctor
Pharyngitis is a disease that is quite difficult to determine in the first stages. Therefore, if a person experiences pain when swallowing food, or he feels a constant slight malaise, the temperature rises, there is no need to waste time, it is better to immediately contact a specialist. He will be able to conduct the necessary examination and make an accurate diagnosis. If there is no pharyngitis, and the person has a simple cold or sore throat, then he will be prescribed one course of treatment. If an ENT doctor can identify the signs of pharyngitis, then the sooner he starts therapy, the better and more effective it will be for the patient.
Recommendations for the occurrence of pharyngitis in adults and children
Soreness and dryness, as the first symptoms of an acute inflammatory process, can be alleviated:
- drinking plenty of warm liquids;
- rinsing with saline solutions or antiseptics;
- using painkillers in the form of lozenges;
- active humidification of the air in the room.
Uncomplicated acute pharyngitis does not always require medical intervention. With the right approach, you can independently cope with the symptoms and achieve a full recovery. But the absolute criterion for visiting a doctor, especially when treating pharyngitis in children, is the appearance of respiratory problems.
If inflammatory symptoms do not subside within 48 hours, and after starting active therapy you notice an increase in pain, you should also contact an otolaryngologist. If intensive treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner, the risk of developing serious complications increases. Inflammation of the trachea, middle ear or bronchial tree, as well as purulent abscesses on the tonsils or in the retropharyngeal space will require surgical intervention.
How is the disease treated?
Treatment of pharyngitis largely depends on its form (acute or chronic). It includes medication assistance, when the patient is given medications of various properties, including:
- immune stimulants;
- painkillers;
- reduce fever;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
In addition, the patient will have to use all kinds of rinses. In the chronic form of the disease, in addition to drug treatment, various procedures and physiotherapy are also prescribed.
Treatment at home
It is not recommended to treat pharyngitis at home without first consulting a doctor. After the examination, the doctor may prescribe various rinses for the patient, which he can do himself at home.