The generalized term “fluorosis” in medicine is used for diseases associated with excessive intake of the microelement fluorine and its compounds into the body (long-term intoxication when the norm exceeds 1.4-1.6 mg/day). Intoxication can lead to damage to various human organs, but most likely and primarily to dental tissue ( dental fluorosis ) and, much less frequently, other bone tissue.
The disease is usually divided into forms
Endemic dental fluorosis (a disease peculiar to a particular area or a particular group of people). It occurs in areas where drinking water (namely, with it the main amounts of fluorine enter the body) contains excess fluorine, according to Russian standards - more than 1.5 mg/l.
Sporadic (irregular) form . It occurs even with normal levels of this microelement in drinking water. The reasons are not yet known.
Professional (industrial) uniform. In people employed in a number of industries and constantly in contact with fluorine compounds (for example, aluminum, cryolite production).
Iatrogenic (caused by improper actions) form. For example, long-term and excessive use of fluoride-containing drugs.
General symptoms of dental fluorosis and some of its features
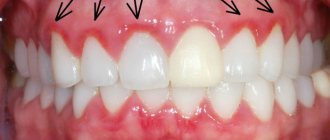
At the initial stage, the disease manifests itself as local staining, from white to light brown and brown, of the tooth enamel. Enamel staining can be subtle, in the form of stripes, spots or other defects, but subsequently can acquire a clear and even threatening form with the destruction of hard dental tissues.
Endemic dental fluorosis develops even before the period of teething, and, as a rule, permanent teeth are affected. It is believed that the maternal placenta represents a barrier to the entry of excess fluoride into the fetus’s body, and the mineralization of the tissues of baby teeth generally ends before birth. But this barrier disappears after the birth of the child. Therefore, if a child stays for more than 5-6 years during the development of the rudiments of permanent teeth in an area with a high content of fluoride components in drinking water, there is an increased risk for the development of the disease.
Cases of damage to already erupted healthy teeth with already formed enamel are extremely rare. That is, dental fluorosis usually does not affect people who come to an area with a high concentration of fluoride (a hotbed of endemic dental fluorosis ), but who have already formed dental tissues. However, cases of such damage have been described in adults with long-term consumption of water with a fluorine content of more than 6-7 mg/l.
Endemic dental fluorosis can occur in fairly large populations. According to statistics, when the fluorine concentration in water is from 1.0 to 1.5 mg/l, the susceptibility rate reaches 20-30%, and when the content is above 2.5 mg/l it already exceeds 50%.
Experts believe that the risks of this disease and the degree of dental damage for a particular person are associated with the ability of his body to resist fluoride intoxication and the degree of sensitivity to incoming fluoride compounds. Therefore, symptoms of dental fluorosis in some cases are also observed in children who live for a long time in areas with a relatively low (less than 1 mg/l) content of fluorine compounds in drinking water. On the other hand, physical work in a hot or warm climate contributes to increased water consumption and a constantly increased dose of fluoride entering the body, which can cause fluorosis (endemic) even with a low concentration of this microelement in water.
Prevention
To avoid the development of the disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Use filtered or bottled water for drinking. This is especially true for people who live in regions with high amounts of fluoride in the water supply.
- Monitor your diet carefully. Diversify your diet with plant foods, as well as foods rich in vitamins C and D. Eliminate or reduce the consumption of fish and seafood.
- Choose your toothpaste carefully - it is better to use one without fluoride.
- When preparing formula for formula-fed infants, use only clean water.
- When introducing complementary foods, give children juice and milk more often instead of water.
- If necessary, take calcium supplements and vitamins (strictly as prescribed by your doctor).
- Visit the dentist regularly - at least once a year.
Dental fluorosis can cause damage not only to a person’s appearance, but also to their health. Fortunately, modern medicine can eliminate any consequences of this disease. It is worth remembering that a timely visit to the dentist will prevent the development of the pathological process and return the snow-white radiance to your smile.
Classification of dental fluorosis
Fluorosis manifests itself in a very diverse manner and the external (visible) symptoms of dental fluorosis are very different. Therefore, there are various classifications of dental fluorosis (international classification, Russian classifications Patrikeev, Nikolishin), which dentists use in practice. But it is precisely this circumstance that makes diagnosis difficult.
| Classifying features | Form, type, type of tissue damage in fluorosis |
| International classification (used mainly for population surveys, 5 forms) | Presumptive fluorosis (unnoticeable spotty formations). Fluorosis is diagnosed, but very weak (spots are opaque, white, no more than 25% of the surface). Weak fluorosis (up to 50% of the surface is affected). Moderate , but very pronounced (brown spots, enamel affected). Severe (damage to almost the entire surface, destruction of enamel, extensive brown staining). |
| According to the degree of damage (there are 4 degrees) | The defeat is weak (no more than a third of the total surface of the enamel, very small chalky spots are present). Weakly expressed (no more than 50% of the surface is affected by white, sometimes brown, spots). Moderate (over 50% of the surface is affected by colored, whitish, yellow, brown spots, the size of the spots is large and they sometimes merge, partial destruction of dentin tissue occurs). Severe (numerous enamel erosions are observed). |
| Clinical and morphological forms (5 forms) | Line (damage to layers under the surface of the enamel with a white streak-like shape; stripes can merge to form a visible spot). Spotted (multiple white, and later close to light brown, spots over the entire surface of the enamel). Chalky-spotted (the main symptom is a wide variety of lesions: colored spots, dots, superficial enamel deficiency with exposure of dentin). Erosive (pronounced coloration of the enamel, enamel tissue has increased abrasion with the formation of large areas of erosion). Destructive (destruction of the tissues of the coronal parts, their breakage is possible). |
The different classification systems for dental fluorosis presented in the table, in addition to their diversity, are very cumbersome and reflect difficulties in diagnosis. Essentially, for practicing dentists there are no clear recommendations for diagnosis and, as a result, for the correct choice of treatment methods for dental fluorosis .
What forms of fluorosis are there?
So, we found out how you can get fluorosis. Now we take a mirror in our hands and examine our teeth, perhaps you will find symptoms of fluorosis on them. The lesion is symmetrical in nature, most pronounced on the premolars, first and second molars, incisors and canines of both the upper and lower jaws, both on the outer and inner sides of the teeth. The classification of fluorosis is based on the degree of development of the disease. The following forms of fluorosis are distinguished: streaked, spotted, chalky-speckled, erosive, destructive.
- The initial stage
is characterized by the appearance of white streaks, weakly or strongly expressed on the tooth enamel. These chalky streaks become most noticeable when the surface of the tooth dries. - Next, the stripes merge and form white spots (see photo of fluorosis No. 1). A feature of the spotted form
of fluorosis is that the enamel in the area of the spot becomes smoother and shiny. In this form, fluorosis is often confused with caries in the spot stage. However, the differences are obvious: fluorosis appears immediately from the moment of teething and is multiple in nature, while caries forms locally, mainly in the area of contact with the gums and on the masticatory tubercles. - The chalky-mottled form
is characterized by darkening of the spots to yellow and light brown (see photo No. 2). At the site of their formation, the enamel becomes rough and uneven, and multiple dots and inclusions appear inside. The spots become clearly defined. It is necessary to distinguish fluorosis in the chalky-mottled form from enamel hypoplasia. - During the erosive
and
destructive stage
of fluorosis, loss of hard tooth tissues - enamel and dentin - occurs. Defects (erosions) become more noticeable, up to a change in the shape of the tooth crown and its breaking off in the future. - Subsequent progression of the disease is characterized by damage to the skeletal bones. A large accumulation of fluoride in the bones provokes osteosclerosis, osteoporosis, as well as the development of a cancerous tumor - osteosarcoma. This occurs if the patient continues to drink water with a fluoride concentration of more than 6 mg/l.
Photo No. 1. Initial form of development of dental fluorosis
Photo No. 2. Chalky-mottled form of dental fluorosis
Causes of dental fluorosis and why symptoms appear
The exact causes of this disease are not yet known. But several possibilities are being considered:
- fluoride compounds are toxic to ameloblasts (cells involved in the formation of enamel), and they lead to distorted formation of the enamel layer
- fluoride compounds, as enzyme inhibitors, suppress the activity of the phosphatase enzyme and disrupt the proper mineralization of enamel tissue
- excess incoming fluoride additionally interacts with ions of calcium, magnesium, manganese and trace elements, and this disrupts the proper mineralization of enamel tissue
- fluoride affects the activity of the thyroid gland, changing its functions during the formation of tooth enamel.
The exact mechanisms of changes in enamel tissue during fluorosis are also not fully understood. It is believed that in the initial stage, damage and partial destruction of the crystalline prisms that make up the enamel layer occurs. The spaces between the prisms widen and are filled with material of an amorphous structure (in fact, with the material of destructed prisms). In these spaces (the primary lesion zone), heterogeneous mineralization of the enamel tissue occurs, i.e. areas with increased and decreased mineralization alternate. Further development of the lesion is associated with the processes of demineralization and increased pathological permeability of the enamel layers, the appearance and increase in the size of micropores.
Treatment methods for dental fluorosis
The choice of specific methods for treating dental fluorosis and their effectiveness depend mainly on the stage or degree of damage to dental tissues.
| Stage or extent of damage | Treatment methods for dental fluorosis |
| At the slightest sign of damage (presumable fluorosis) | Limiting fluoride amountswhich enters the body. Replacing the drinking water source (at least mostly). Remineralizing therapy. Taking phosphorus-calcium drugs. |
| Superficial enamel lesions with color changes (eg, mottled form) | Carrying out teeth whitening procedures using the Air-flow method with subsequent remineralization of affected dental tissues. |
| Erosive and destructive lesion | Therapeutic tissue restoration with filling (for example, composite) materials. For large lesions, restoration is carried out with orthopedic dental crowns . If there is a risk of breaking off part of the teeth, the pin technique is additionally used. For front teeth, veneers are used. |
How to treat fluorosis
The choice of methods to combat the problem directly depends on the stage of the disease. The earlier it is detected, the greater the chances of a speedy recovery.
Recent Entries
Is it possible to give a mirror: how to protect yourself from bad omens It became known about the influence of cell phone towers on human health Is it possible to eat bananas bought in Russia?
Remineralization
In the first two stages of enamel damage, the patient is prescribed tooth remineralization. This is a procedure for supplying the affected enamel with useful microelements. It is performed using electrophoresis and consists of applying applications with calcium and phosphorus to the surface of the diseased tooth. This therapy is carried out in a course of 10 to 25 procedures.
Remineralization of the tooth surface during fluorosis is effective only in the early stages of the disease
At home, use toothpaste with a special composition for remineralization. Additionally, you can use various products with whitening properties (rinses, gels). They must be prescribed by a dentist.
Enamel whitening
In parallel with remineralization, teeth whitening is carried out, which can be chemical, laser or LED.
- Chemical bleaching. With it, the teeth are treated with a special solution, which includes hydrogen peroxide, carbamide peroxide, various acids and enzymes.
- Laser whitening. Each tooth is illuminated with a laser beam for two minutes. The affected areas are pre-treated with a special gel based on hydrogen peroxide.
- LED whitening. A special gel is also applied to the teeth, after which they are irradiated with an LED lamp. As a result, the enamel is saturated with oxygen, which reduces the level of pigmentation.
These procedures require 10–15 visits to the dentist.
There are a number of contraindications for which bleaching is not recommended:
- severe forms of periodontal disease;
- extensive caries;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- the possibility of allergic reactions to the components of the solutions.
Treatment of moderate fluorosis
The chalky-mottled form of the disease requires more thorough treatment. To eliminate it and restore partially damaged teeth, special structures (veneers, lumineers) are used. Veneers are very thin plates that are used to give teeth a perfect shape. Products are therapeutic and orthopedic.
Veneers and lumineers are ultra-thin dental plates that differ in the thickness of the product and are used for dental restoration.
Therapeutic veneers
Therapeutic plates are made of composite materials similar in composition to dental fillings. Such veneers are applied to the enamel in layers and processed (polished). They are installed quickly, in one visit to the doctor.
Is it possible to treat caries at home?
Installation of orthopedic plates
The process of making orthopedic veneers is quite long - about 2 weeks. Therefore, the patient is given temporary plates, subsequently replacing them with permanent ones. The material for the manufacture of orthopedic veneers is ceramics with the addition of porcelain.
The procedure for installing orthopedic veneers is as follows: the affected tooth is processed (polished and sharpened). Next, a plaster cast of the tooth is made and sent to the laboratory. There, specialists use a computer program to make a three-dimensional model of the future plate. Based on this model, a veneer is created. The final stage is installing the veneer on the tooth surface.
There are a number of contraindications for orthopedic treatment:
- extensive caries;
- malocclusion;
- poor oral hygiene;
- the presence of bad habits (biting nails and hard objects, cracking nuts with teeth, opening bottles with them, and so on).
Lumineers
Lumineers differ from veneers only in thickness - the latter are thicker and denser. The maximum thickness of the lumineer is 0.3 mm. They are made from porcelain with crystalline impurities. Contraindications for installing lumineers are the same as for veneers.
The procedure for installing the plates is absolutely painless. It is very difficult to remove such structures, they fit so tightly to the teeth. Therefore, it is worth remembering that the plates are installed for a fairly long period: veneers - up to 10 years, lumineers - up to 20. Afterwards, they need to be replaced and, if necessary, treatment of the teeth that were under the plates (sometimes caries can develop on them).
Teeth with veneers installed are practically no different from healthy ones.
Dentistry for advanced disease
Severe stages - erosive and destructive - cannot be treated. Here, as a rule, a complete replacement of the tooth(s) is necessary. The patient is fitted with ceramic or metal-ceramic crowns. Their main difference from veneers and lumineers is that the crown completely covers the affected tooth, and the plates only cover its front part. Crowns are made from a mixture of metal and ceramic, which makes them especially strong and reliable in fastening.
If the tooth is severely damaged, the doctor removes the nerve and fills the canal. After this, a pin is screwed into the canal, on the basis of which the crown is installed.
Metal-ceramic crowns (prostheses) will help restore teeth in advanced stages of fluorosis
In case of fluorosis, the affected areas of the tooth are not removed or filled. Fillings often fall out and tooth decay continues.
Regardless of the degree of dental damage, you should pay close attention to your diet during the treatment period. Vegetables and fruits, dairy products (except butter), a complex of vitamins will greatly facilitate the fight against the disease. Fish and seafood consumption should be limited during this period.
Homeopathy: effective remedies
Homeopathic treatment is relevant only in the early stages of the disease. In moderate and severe forms, this approach will be ineffective.
The following remedies will help defeat the emerging disease:
- Sulfur;
- Staphysagria;
- Lachesis;
- Lycopodium;
- Thuja;
- Rus;
- Phosphorus;
- Aurum metallicum;
- Mercurius solubilis;
- Nux vomica;
- Calcarea fluorica.
These medications will strengthen enamel and dentin and improve the overall condition of teeth. They should also be used for preventive purposes. The composition of these drugs has a beneficial effect on the condition of the body as a whole and helps prevent tooth decay and damage.
Attention! Homeopathic remedies should only be prescribed by a doctor. Only a specialist will choose the optimal drug. Self-medication is unacceptable.