Inflammatory processes of the female genital area in the modern world affect many representatives of the fair sex, and in this case, inflammation of the uterine appendages (ovaries and fallopian tubes) is considered a very common disease. This illness can occur not only because the girl sat on something cold or got cold feet. Of course, hypothermia is considered the main cause of this disease, but other factors also contribute to the inflammatory process. Let's try to figure out why the appendages hurt. Symptoms and treatment of this disease will also be discussed.
For what reasons does inflammation of the appendages occur in women?
Why do the appendages hurt?
In medical terms, this disease is called salpingoophiritis. If we are talking about damage exclusively to the fallopian tubes, then this is called salpingitis. If the inflammation process affects only the ovary, then it is oophiritis. The way in which the inflammatory process develops in the body is directly influenced by pathogenic microorganisms; they can also be opportunistic. There are two types of this disease:
- Andexitis is a specific type, caused by diphtheria-type bacteria;
- Salpingoophiritis is a nonspecific type, caused by viruses, fungi, chlamydia and streptococci.
Infection can penetrate the uterine appendages in the following ways:
- ascending method (microbes end up in the uterus from the vagina, and then can end up in the ovary);
- in a descending manner (the abdominal cavity is inflamed and this pathogenic process affects other tissues);
- hematogenously (microbes enter from other organs).
If there are certain factors, then inflammation of the appendages in women is more provoked:
- the body is hypothermic and therefore can become inflamed;
- weak immunity;
- an intrauterine device is used as a contraceptive method;
- unprotected sexual contacts;
- the woman has given birth or had an abortion, which means she is at risk.
This disease affects the body in three varieties:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Latent (that is, no symptoms are observed, or the disease is sluggish).
It is noteworthy that a woman of any age can get this disease. There may be very young girls who have not yet entered into sexual activity and mature women who are experiencing menopause. And the reasons can be very different.
Complications of acute adnexitis
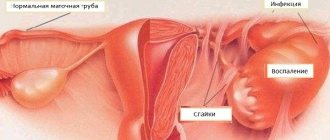
Complications of acute adnexitis include ovarian abscess, when the infection enters the ovarian tissue and forms a purulent cavity there, resulting in melting of the ovarian tissue.
Another no less dangerous complication of adnexitis is the formation of a purulent cavity in the fallopian tubes—pyosalpinx. When the process progresses further and passes into nearby tissues, going beyond the appendages and penetrating into the abdominal cavity, a tubo-ovarian abscess occurs.
If at this stage medical assistance is not provided on time, then we are already dealing with peritonitis, and this is already a formidable complication that poses a threat to life!
Symptoms of inflammation of the female appendages
If we talk about the symptoms of the disease, then in the case of a pathogenic process in the female body, much is determined by the following factors:
- how pathogenic the microorganism is, what type it is;
- how does the disease pass? Is it acute with pronounced signs, or chronic, where the signs are weak and often not noticeable at all;
- How capable is the female body of resisting harmful organisms, how is it able to resist inflammation, and what is the state of the immune system.
If the form of the disease is acute, then the signs of a pathogenic condition in the patient are of the following nature:
- there is severe tension in the abdomen (especially its lower part);
- the lower abdomen is subject to pain, and it can spread to the legs and lower back;
- body temperature is high, can reach 39 degrees;
- the menstrual cycle is subject to irregularities (that is, bleeding may begin abruptly or menstruation may be delayed);
- vaginal discharge has an abnormal appearance (greenish color, with admixtures of pus, possibly a yellowish tint, foamy type or too abundant).
If such a disease is not cured in a timely manner to the end, when it was in an acute form, then there is a possibility of it becoming chronic, and here the symptoms will directly depend on the remission or aggravated period. Half of the women who suffer from chronic adnexitis are subject to the following pathological changes:
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- sexual functions are upset;
- There are ailments of the urinary organs of a concomitant nature.
When adnexitis enters an aggravated phase, all symptoms also worsen.
What are the symptoms and forms of adnexitis? Let's figure it out
Symptoms of salpingoophoritis depend on its form. It is customary to distinguish between acute and chronic adnexitis. In the acute form, the most important symptoms are:
- general malaise;
- temperature rise to 38 °C;
- sometimes nausea and vomiting;
- copious discharge from the genital tract of a mucous or purulent nature (possibly bloody);
Complaints of severe pain in the lower abdomen, aching or pulling in nature, still come to the fore. Often the inflammatory process is bilateral in nature, sometimes a unilateral process also occurs, the localization of pain symptoms depends on this.
Adnexitis in chronic form
If the disease was not treated on time or properly, then adnexitis may develop in a chronic form, and it passes with periodic exacerbations of the chronic type. If we talk about the symptoms of this form of the disease, then we should note pain in the abdomen (at the bottom of it), which is aching and dull, it radiates in the lower back, and the vagina also suffers from it. Moderate pain is determined by pressing the fingers on the abdomen.
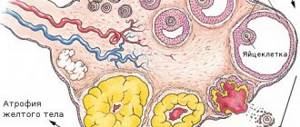
Transformations occur in the ovaries, which can be structural and also functional; if inflammation of the appendages in women is chronic, then the menstrual cycle begins to be disrupted, this is most often expressed in scanty periods, or, conversely, heavy periods. And with adnexitis, girls often feel that their sexual performance decreases or disappears altogether, and when sexual contact occurs, pain is felt.
Stages of acute adnexitis
During the development of this form of the pathological process, four stages are noted:
- Acute endometritis and salpingitis without symptoms of irritation of the pelvic peritoneum.
- Acute endometritis and salpingitis with symptoms of irritation of the pelvic peritoneum.
- Acute adnexitis, which is accompanied by the formation of an inflammatory conglomerate and an abscess.
- Abscess rupture.
The course of the disease usually goes through two phases:
- Toxic when aerobic flora and symptoms of intoxication predominate.
- Septic, when anaerobic flora joins, the symptoms of adnexitis intensify and the process of developing complications begins. In this phase of adnexitis, a purulent tubo-ovarian formation is formed with the threat of its perforation.
As already noted, the symptoms and treatment of adnexitis are closely related.
Diagnosis of the disease
It should be noted that all the symptoms listed above may indicate the presence of other ailments. So, an accurate diagnosis should be made by a gynecologist who examines the patient, collects anamnesis, conducts laboratory tests: tomography, ultrasound, laparoscopy, and it is necessary to take a general blood test.
The results of blood tests can show the presence of an inflammatory process in the appendages, since in this case the blood formula undergoes significant changes. Also, when a woman is examined by a gynecologist, she experiences severe pain in the uterus and ovary.
Consequences of the chronic stage: signs
A constantly ongoing inflammatory process, even in a weak form, has a negative effect on nearby organs. Over time, inflammation can spread from the uterine appendages to the bladder and intestines. In this case, chronic adnexitis is noted with symptoms of inflammation of the corresponding organ. If it is the bladder, the woman is bothered by frequent urination and aching pain above the pubis. If the pathology moves from the uterine appendages to the intestines, colitis develops. It is manifested by abdominal pain, especially during bowel movements, as well as nausea and chills.
About preventive measures
In order to prevent all this, it is necessary to take into account certain preventive measures:
- visits to the gynecologist should become regular, and you should not avoid examination in the chair; you should regularly take smears;
- you need to avoid overcooling, dress appropriately for the weather, change your underwear after visiting the pool, do not sit on cold objects, since the reproductive organs are located in such a way that all the negative effects can come from sitting on the cold;
- if there is a need to terminate a pregnancy, then this should be done as early as possible, and medications or a mini-abortion (curettage) should be used;
- all foci that can become infectious must be cured (here we are talking about teeth, intestines, since this is where the cause of inflammation is located);
- if there are gynecological ailments, they must be treated in a timely manner;
- It is very important to eat right;
- intimate hygiene must be strictly observed;
- douching should be avoided;
- It is very important to prevent stressful situations from arising.
So, such an illness is undoubtedly very serious, it must be treated in a timely manner, and it is very important to strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions. Inflammation of the appendages, symptoms and its treatment can only be determined and performed by a doctor, you need to remember this once and for all.
Chronic adnexitis
With incompletely treated (or not treated at all) acute inflammation of the appendages, chronic adnexitis soon develops. At the same time, the pain in the lower abdomen is less intense and long-lasting, of a “dull nature”, appearing periodically, more often after hypothermia.
Symptoms may appear before menstruation, changing its character - menstruation may be delayed and absent (amenorrhea) or begin earlier, be abundant or, on the contrary, scanty, accompanied by pain (dysmenorrhea). There is also sometimes discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), which leads to dyshormonia in relationships with a partner.
Also, nearby organs can be involved in the pathological process and inflammation of the bladder (cystitis), kidneys (pyelonephritis), and intestines (colitis) can develop in parallel with adnexitis.
But the most important point remains pathological processes at the tissue level due to inflammation, adhesions develop in the uterine appendages (obstruction of the Fallopian tubes and disruption of the hormonal function of the ovaries), which results in infertility. And when a woman goes to the doctor because of unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant, she sometimes doesn’t even know about the root cause!
How to treat such a disease
If such a disease is identified during the diagnostic process, then the treatment implies a complex nature, that is, medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, gynecological massage,
Antibiotics are widely used in the treatment process, which must be selected in such a way that their spectrum of action is wide and their half-life is maximized. It is very important that during such a period a woman leads a certain lifestyle, namely, abstains from drinking alcohol, smoking, eats right, shows abstinence from sexual life, engages in physical exercise; in case of inflammation of the appendages, this is very important.
It is very important to prevent the disease from starting, since in such cases the inflammation process becomes chronic, and this can cause infertility.
If we talk about treatment with antibiotics, then they must be consumed for a favorable outcome of the disease. If we talk about the dosage and duration of treatment, then everything should be determined by a specialist.
It should be noted that until the woman’s condition returns to normal, all antibiotics are taken by injection (usually this lasts 3.4 days). Then you can switch to tablets, and the dosage can be reduced.
Causes of adnexitis
The cause of adnexitis is often sexually transmitted infections, for example, chlamydia, gonococcus, trichomonas, sometimes Staphylococcus aureus, etc. The cause of adnexitis can also be a frequent change of sexual partner, unprotected sex, as well as too rapid resumption of sexual life after childbirth, abortion or gynecological operations.
The state of immunity plays an important role, since if a woman is constantly under stress, she is more susceptible to adnexitis. Adnexitis can also be caused by hypothermia due to the fact that a woman does not dress appropriately for the weather. The presence of an intrauterine device can also provoke inflammation of the appendages.
What else can be treated?
Inflammation of the appendages in women involves more than just treatment, since antibacterial drugs are not the only ways to get rid of such a dangerous disease. Pain can be relieved with non-steroidal medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect. This also reduces the process of inflammation. It would be good to take anti-allergic reaction medications and vitamins.
In order to effectively relieve the signs of an acute process, as well as to treat the chronic form, physiotherapeutic procedures are actively used. When the period of rehabilitation treatment begins, immunomodulators can be used. If adnexitis manifests itself in a chronic form, then it would be good to go for treatment to a sanatorium or resort. Treatments such as medicinal baths, the use of paraffin and mud all help greatly.
In order to relieve signs of pain, swelling and reduce body temperature, you need to use special-purpose suppositories; they are very helpful in relieving inflammation. There are also candles that help strengthen human immunity, which is very important for any illness. And such products also have a cleansing effect on the body.
It must be said that the prescription of any type of suppositories is carried out only by a doctor, however, this type of therapy is exclusively additional.
Treatment of the disease
If the appendages hurt, treatment should be started in a timely manner. Usually the patient is sent to a hospital, where she is first prescribed a diet that excludes the consumption of salt, carbohydrates and pepper. In case of severe pain, the patient should stay in bed in the first days. Pain and inflammation are well relieved by cold, so the doctor may also recommend applying a cold compress to the lower abdomen.
Drug treatment of inflammation of the appendages begins with taking antibiotics. Since the disease occurs due to the action of different groups of microorganisms, several types of such drugs are usually prescribed.
Thus, treatment is carried out with the following antibacterial agents:
- penicillins (“Amoxiclav”);
- macrolides (“Erythromycin”);
- cephalosporins (“Ceftriaxone”);
- nitromidazole derivatives (“Metronidazole”);
- antifungal drugs (Diflucan, Nystatin).
The doctor may prescribe other antibiotics, but they must have a positive effect on the flora, which usually lives in an oxygen environment. In the first three days, antibiotics are administered using injections, after which the patient begins to take pills and the drug dose is reduced. The effect of treatment occurs already in the first days after its start. But if taking antibiotics does not bring the desired result, then surgical intervention is possible.
In addition to these drugs, treatment in a hospital is carried out using intravenous infusions of saline solutions, glucose, hemodez and other medications. To relieve pain and reduce inflammation, the patient is recommended to take anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs in the form of tablets. These include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketarol and other drugs.
As soon as the acute form of inflammation subsides, procedures such as electrophoresis with lidase or iodine, pulsed high-frequency currents, and ultrasound are prescribed.
Treatment of adnexitis
When treating acute adnexitis, hospitalization is necessary, since the acute form of adnexitis can have serious consequences and complications: the formation of purulent cavities in the tubes, purulent melting of the ovaries, peritonitis, etc. The patient is prescribed bed rest, medications are used for pain relief, and broad-spectrum antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are used to eliminate the inflammatory process. In the presence of a purulent process, surgical treatment is used.
When treating chronic adnexitis, the same scheme is used, except that antibacterial drugs are selected taking into account the pathogen, and corticosteroids are used as anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition, immunostimulating and restorative therapy is carried out. Physiotherapeutic methods are also used in the treatment of adnexitis: magnetic therapy, microwave and UHF therapy, paraffin therapy, mud therapy, etc.
Treatment of adnexitis with folk remedies at home
Treatment of adnexitis with folk remedies at home is used for chronic adnexitis. You should not use folk remedies to treat acute adnexitis, since in the acute form of adnexitis there is a significant risk of developing severe complications, including life-threatening ones. As a folk remedy for treating adnexitis at home, douching, enemas or baths of infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory action are used:
- yarrow,
- pharmaceutical chamomile,
- caragana officinalis,
- St. John's wort,
- calendula,
- series,
- sage,
- calamus,
- Kalanchoe juice,
- Golden mustache,
- eucalyptus.
In addition, to stimulate the immune system, aloe juice, ginseng infusion, echinacea purpurea infusion, mumiyo, honey and other bee products are taken orally. It must be remembered that folk remedies for treating adnexitis at home should be used only after consultation with your doctor.