Acute and obstructive bronchitis. General symptoms
Common symptoms of bronchitis include cough, fever, weakness and malaise. In the acute stage of the disease, a dry cough turns into a wet one, with copious sputum production and a decrease in temperature on the 3-4th day.
Acute and chronic types of disease occur differently. Therefore, if symptoms similar to bronchitis occur, treatment should be based on a correct diagnosis. The acute form of this disease usually begins with a sharp sore throat, weakness and other signs of a cold. Soon a dry cough and fever develop, which subsides after a few days. At the same time, the cough becomes wet due to copious sputum production. In severe cases, there may be a high fever. With proper treatment, the patient recovers in ten days, or a maximum of two weeks.
An acute disease may be accompanied by obstruction of the lungs - this is obstructive bronchitis. The cough is paroxysmal and with spasms, whistling, shortness of breath are often heard, there is a state of weakness and a slight increase in temperature. This type of bronchitis is caused by the fact that the bronchi are spasmed and do not produce mucus well. Very often, this type of disease occurs in allergy sufferers and asthmatics.
I wonder if bronchitis is contagious or not?
If someone in the family gets sick with bronchitis, a logical question immediately arises: is bronchitis contagious to others or not? Bronchitis can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection, and can also occur as a type of allergy.
The latter case is not contagious, provided that other family members are not allergic to the same irritant from which the sick person suffered. Viral and bacterial infections may be involved in the development of the disease separately or together. The time from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease is called the incubation period.
During the entire incubation period, a person is a source of viruses and bacteria for others. That is, he is already sick and can already spread the infection, but there are no manifestations of the disease yet. Depending on the state of the immune system and the type of bronchitis pathogen, the incubation period can range from one to five days.
Protection against bronchitis
Often the first cause of bronchitis is the parainfluenza virus or adenovirus.
The victim may have a high fever for two to ten days, during which time the immune system actively fights pathogenic microorganisms. During this period, you can become infected from a person through airborne droplets, by using shared utensils, by kissing and inhaling the same air. Bronchitis is contagious and is accompanied first by a dry and then a wet cough, during which the victim actively releases viruses or bacteria into the environment. In order for the treatment of bronchitis to proceed quickly and without complications, you need to contact a specialist.
Acute bronchitis is contagious and occurs with many unpleasant and performance-reducing symptoms, so an adult must take a sick leave for a period of ten to fourteen days for health reasons, and children must refuse to attend kindergarten and school during this time. Is it possible to get bronchitis after a person's high fever subsides? It is possible, it all depends on who comes into contact. Which categories of people are most vulnerable to infection:
- people after surgery, after a serious illness;
- pregnant women;
- children under three years of age, especially newborns up to one month;
- aged people;
- persons with weakened immune systems, HIV-infected people suffering from chronic diseases, oncology, weakened after injury.
To protect those people for whom bronchitis is clearly contagious, they need to limit contact and communication with a sick person. If this is not possible, you need to use a respirator to protect your nose and throat.
The simplest version of a respirator is a mask, which is sold in any pharmacy. Bronchitis is transmitted by airborne droplets, so you need to use only individual dishes, do not drink from the same mug, and do not eat with the same fork. Some families do not understand the importance of individual hygiene, to the point of giving the baby food that has already been chewed by an adult. Such things should not be allowed under any circumstances.
Each person has a set of symbiont bacteria, that is, a set of beneficial or conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. In close contact, for example, among a married couple or between a mother and an infant, this set becomes common. Communication with secondary relatives should not imply such a dense exchange of microorganisms. Each family member for individual use should have:
- Toothbrush;
- towel;
- clean dishes that no one has eaten from before;
- for a child - a pacifier and a bottle.
Unfortunately, often irresponsible mothers begin to lick the nipple of a bottle or pacifier before giving it to the baby (for example, if the nipple fell on the floor beforehand). This behavior can provoke, at best, indigestion, and at worst, weaken the immune system. Children and adults who do not practice good hygiene are more likely to become infected from someone with bronchitis.
Diet for bronchitis
In order to support the immune system of surrounding family members, it is useful to prepare dishes during illness that contain:
- garlic;
- onion;
- ginger;
- fresh herbs, parsley, green onions, dill.
Recent studies have shown that the role of vitamin C in strengthening immunity is not at all as significant as it was thought over the past twenty years. However, using lemon, lime or tangerines is useful in any case. Spices, herbs and garlic should be added to food after the main heat treatment is completed, that is, immediately before consumption. This way you can retain the maximum beneficial properties.
When cooked for a long time, greens not only lose their taste, but also lose most of their vitamins. With ginger you can prepare not only tea, but also soups and main courses. To ensure a pleasant taste, you need to purchase fresh ginger root and chop it finely. Only a doctor can tell how many days bronchitis will be contagious. Without appropriate treatment, the disease can become chronic in both adults and children.
For chronic bronchitis, a temperature above 38.5 degrees is not typical; usually it either does not rise or rises to 37.5 degrees.
Chronic bronchitis has remissions, when a person is conditionally not contagious. During remission, the victim does not suffer from severe cough, fever or swelling of the airways. Then a relapse occurs, during which all the typical manifestations of bronchitis are observed:
- wet cough with a large amount of sputum;
- weakness, headache, muscle soreness;
- spasms when coughing, a suffocating lingering cough that is difficult to stop on your own.
During remission, the likelihood of becoming infected is quite small; for an adult with a strong immune system, it is completely absent. During a relapse, there are the same chances of transmitting the disease as with acute bronchitis.
How to quickly cope with bronchitis in a child?
Treatment of children should be carried out by a pediatrician on an individual basis. You cannot give a child antibiotics or other medications if his classmate or classmate from kindergarten had “something similar.”
Prescription of drugs should not occur en masse, but separately in each specific case.
Children who do not have bacterial bronchitis do not need to take antibiotics for prevention. Many mothers do not understand that medications are selected depending on the specific type of pathogen. If the medicine is not used as directed, it will not be of any benefit.
Bronchitis can cause a lot of unpleasant complications. If the patient's temperature cannot be reduced within a week, this suggests that the infection has spread down the respiratory tract. Potentially, bronchitis can cause pneumonia; in children, bronchitis is often accompanied by otitis media. The infection enters the ear through the Eustachian tube. To avoid complications and cope with the disease as quickly as possible, you need to contact a competent pediatrician. Traditional medicine methods can be used on children only in consultation with the attending physician.
If a child has a fever, no hot compresses, socks with heated salt, heating pads, mustard plasters or pepper plasters should be applied to the bronchial area. This promotes the spread of inflammation into deeper layers of tissue. Only a day after the temperature has steadily returned to normal, these methods can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Foot baths with mustard or medicinal herbs can be used a day after the temperature drops.
Prevention of bronchitis
The victim must be provided with rest and bed rest for the entire duration of the illness. Do not go to school or kindergarten, do not play with other children.
Often mothers allow their child not to attend school, but do not forbid them to play with other children and go for a walk. At this time, children become infected from each other, especially on playgrounds. During illness, it is enough to ventilate the room; you can refuse to walk. To prevent your child from contracting bronchitis from a playmate, you need to strengthen his immunity.
respiratoria.ru>
Chronical bronchitis. Symptoms
If chronic bronchitis (symptoms) has been identified, treatment should be started immediately, since over time it will become increasingly difficult to overcome. This type of disease is most often incorrectly treated acute bronchitis, which drags on for a long time. Accompanied by a wet cough, profuse sputum in the mornings and evenings. As the disease progresses, weakness, decreased performance, and severe shortness of breath appear. The cough itself can become unproductive with severe attacks.
Causes of shortness of breath in adults
Factors in the development of shortness of breath: tobacco smoke, hazardous work, poor environment
Respiratory tract diseases also occur with bronchial obstruction syndrome in adults. If a man or woman suffers from chronic bronchitis, it may be difficult to breathe constantly. Long-term smoking, occupational hazards, environmental conditions, and age over 45 years provoke a gradual increase in symptoms. Risk factors for the development of shortness of breath with chronic bronchitis are:
- Inhalation effects:
- tobacco smoke, active and passive smoking;
- harmful working conditions - dust, chemical pollutants (pollutants in the environment), vapors of acids and alkalis, sulfur compounds with oxygen, nitrogen oxides, black smoke and others;
- indoor air pollution with poor ventilation due to heating, cooking using bioorganic fuel;
- air pollution.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Diseases of childhood:
- bronchiolitis obliterans,
- bronchopulmonary dysplasia,
- ciliary dyskinesia syndrome.
Patients describe shortness of breath in chronic obstructive bronchitis as “difficulty, heaviness in breathing, lack of air.” It is progressive in nature, becomes daily, intensifies with exercise and respiratory infections.
If, during chronic bronchitis, it becomes difficult to breathe constantly, shortness of breath does not go away after an exacerbation of bronchitis, this indicates that complications of the disease are developing: respiratory failure, enlargement and expansion of the right side of the heart (chronic pulmonary heart).
Bronchitis in children
Unlike the organs of adults, children's lungs are not yet strong and perfect, so any virus can trigger bronchitis. And often with obstruction. Breathing with bronchitis is difficult, moist rales and whistling are heard when inhaling and exhaling due to the narrow passages of the bronchi. In addition, children do not know how to cough up accumulated mucus well, so the child coughs. Nighttime coughing attacks are typical. The general symptoms are almost the same as those of bronchitis in adults. However, they are all more pronounced, and the disease lasts much longer - up to two to three weeks. Children should be kept from contact with sick people and ARVI should be treated promptly. Avoiding obstruction will help to avoid allergens in the diet and household chemicals.
The child fell ill with asthmatic bronchitis.
With this type, the cough is predominantly paroxysmal at night and lasts from several hours to two weeks or more. A cough can occur after physical exertion, emotional stress, or dietary errors. At the beginning of the attack it is dry, and then it becomes wet. More often, attacks occur from an allergic component (dust, fluff, feather pillows, carpets, books, etc.). To avoid relapses, you need to carry out wet cleaning twice a day, remove carpets, change feather pillows to holofiber or padding polyester, and humidify the air in the room. It must be remembered that asthmatic bronchitis is a variant of bronchial asthma.
Help with asthmatic type.
- Remove the allergic component.
- Remedies for bronchitis in children are antiallergic drugs (Suprastin, Tavegil, Zodak, Zyrtec, Claritin).
- Make inhalations with Berodual and Pulmicort.
- See a doctor immediately.
- If you have a food allergy, drink Activated Carbon, Polysorb, Smecta.
The main thing is timeliness and efficiency
Treatment of bronchitis is divided into two main types of treatment:
- Targeted treatment - inhalations, expectorants, warming, etc.
- Accompanying general measures and physiotherapeutic procedures, such as drinking plenty of fluids, massage and therapeutic breathing exercises.
It is the combination of targeted treatment and general procedures that will help achieve quick results, since even the best medications do not remove congestion in the lungs. Therefore, it is very important to introduce additional measures, such as breathing exercises for bronchitis.
If in the past the word “bronchitis” evoked associations with pots of steaming potatoes and endless wraps, now medicine offers an easy-to-use and effective inhaler-nebulizer. It is filled with medications: “Lazolvan”, “Ambrobene”, “Berodual”, “Ventolin” along with saline solution. But you can use Borjomi alkaline water or another one prescribed by your doctor.
Drug treatment should be prescribed by a doctor based on the nature of cough and wheezing, as well as the general condition of the body. Given the high cost and addiction to medications, sometimes you have to turn to unconventional methods of treatment, which sometimes turn out to be much more effective than medications. Therefore, if you are concerned about bronchitis, treatment with folk remedies should not be ruled out.
Traditional methods of treating bronchitis
Remember! If a child has been diagnosed with bronchitis, treatment with folk remedies should only be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since many remedies will cause the opposite effect and obstruction of the lungs.
Perhaps the most effective remedy is radish juice. You need to wash it, cut a hollow in it and pour sugar or honey into it, after an hour juice will appear in this hollow, which will be an excellent syrup for better sputum discharge.
An infusion of young spruce cones in alcohol, which is added in the amount of one spoon to hot tea along with honey and goat fat, helps well. After drinking a cup of this drink, you need to immediately go to bed. In this case, you need to breathe only through your nose, which will require excluding conversations.
Goat fat, honey and milk are traditionally “rescuers” from bronchitis and any kind of cough. Heat the milk to forty degrees, add honey and fat.
Rubbing with kerosene and honey is also often used. Remember that kerosene is a technical product and is carcinogenic if used frequently.
What can be done to prevent the disease?
Boost your immunity throughout the year. This means that you need to eat right, saturating the body with vitamins and microelements. Then the risk of getting sick will be significantly lower. In winter, when the choice of fruits and vegetables is less varied, you should not neglect folk remedies.
loading…
Medicines for general strengthening of the body, prepared on the basis of ginger, lemons, honey, and walnuts, have an excellent effect on boosting immunity.
Here is one of them:
- 4 lemons,
- 200 g ginger,
- 300 g honey.
Wash everything you need, clean it of dirt, remove the seeds from the lemon. Pass the ginger and lemons through a meat grinder or chop using a food processor, mix with honey - the healing mixture is ready. Transfer the resulting contents into a glass container, take a teaspoon daily, adding to tea or boiled water (not hot to preserve the properties of honey).
There are quite a lot of similar recipes, some are not only healthy, but also tasty, for example, based on dried fruits and honey. Children take healthy medicine with pleasure and ask for more. The main thing is not to be lazy, take the prepared mixtures systematically, then this will definitely reduce the risk and help you not get a cold.
Breathing exercises: purpose and effectiveness
A lot of systems have been developed, but the most famous is Strelnikova’s breathing exercises, which has shown its maximum effectiveness for bronchitis.
What is the reason for the popularity of this gymnastics specifically for such a disease:
- Elimination of stagnation of mucous secretion in the bronchial tree.
- Restoration of atrophied bronchial mucosa through internal massage.
- Increasing local bronchial immunity and, as a result, reducing the incidence of diseases.
- Relieving inflammation and sanitizing the pathogenic environment in the bronchi.
Gymnastics is effective not only for acute bronchitis, but also for chronic forms. Moreover, it will help you develop the habit of proper breathing and teach you how to breathe correctly during bronchitis.
What are the differences in symptoms?
Bronchitis and pneumonia are related diseases. One often precedes the other. The respiratory tract consists of the nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs. If the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles are affected, then a diagnosis of bronchitis is made. If the pathological process has spread to the alveoli and further to the lung tissue, then a diagnosis of pneumonia is made. To better understand how bronchitis differs from pneumonia, let’s summarize the main points in a table.
| Sign | Bronchitis | Pneumonia |
| Pathogen | VirusBacteria predominates | Bacteria predominate Viruses Fungi |
| What is affected | TracheaBronchiBronchioles | AlveoliLung tissue |
| Peculiarities | The mucous membrane is affected, it swells, turns red, thickens | An infiltrate begins to form at the site of inflammation |
| Start | Slow | Acute |
| Temperature | 37-38оС | 38-40оС |
| Cough | Dry with gradual transition to wet | Wet |
| Sputum | White and yellowish, viscous | Yellow, greenish-brown, “rusty” |
| Chest pain | Rarely, with advanced forms | Often, occurs when inhaling or coughing, radiates to the side |
| Shortness of breath | Rarely, during physical activity | Eat both at rest and during physical activity |
| Violation of general condition | Moderate | Strong |
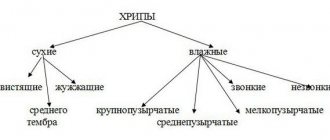
| Auscultation | Is it dry mixed wheezing? | Wet wheezing |
| Percussion | The sound is not changed | Muffled sound in the area of inflammation |
| X-ray | Strengthening the pulmonary pattern | Darkening in the area of inflammation |
| Blood analysis | Increase in leukocytes, ESR insignificant | A sharp increase in leukocytes, ESR, neutrophilia |
| Treatment | Outpatient, rarely in hospital | Only mild forms can be treated at home; inpatient treatment is recommended. |
The degree of manifestation of symptoms depends on what pathogen caused the disease and its severity. It is important to know how to distinguish bronchitis from pneumonia in an adult, but even more important in a child. The peculiarity of a child’s body is that inflammation from the bronchi very quickly (a day or several days) spreads to the lungs.
Intoxication increases, the condition worsens sharply. At the initial stage, it is difficult to both distinguish bronchitis from pneumonia and begin proper treatment. Even a doctor, when listening to breathing, cannot determine what exactly the patient’s diagnosis is.
Then only x-rays can provide complete information. If you have any suspicion, you should immediately go to the hospital.
Effective exercises
You need at least two weeks of training in the morning and evening. Exercises called “pump”, “hug your shoulders” and “large pendulum”, which perfectly ventilate the lungs, are very helpful. They need to be repeated, alternating 16 breaths through the nose and 16 breaths through the mouth without stopping. There are three complexes in total. “Head turns” are also good along with this. These exercises can be performed both sitting and standing.
Breathing exercises for bronchitis prevent complications of bronchitis and cope with both chronic and acute conditions. An important fact is that gymnastics prevents obstructive conditions from developing into asthma.
The main rule is that you must perform the exercise consciously and correctly, otherwise the effect will be greatly reduced. The fact of constancy is also important. Reducing symptoms is not a reason to quit the exercise routine.
Bronchitis as a result of foreign bodies entering the bronchi.
Such cases also occur quite often with a sudden deep breath, bronchitis can develop quickly within a few days, while there is a persistent cough with an obstructive sign, pneumonia quickly joins this process. This should alert such a rapid disease process, the diagnosis can be confirmed if a chest X-ray is taken, but a foreign body cannot always be seen in the image; it depends on the professionalism of the staff; you need to carefully question the child to see if he has pushed anything into his nose. And you can’t do without bronchoscopy. Treatment is the same as for ordinary bronchitis, but there is no question of antibiotics, they will need to be taken.
How to breathe with bronchitis
When there is a feeling of accumulation of phlegm in the bronchi, therapeutic breathing exercises such as repeating hundreds of breaths and movements, nose and mouth in turn, help very well. Also use the figure eight exercise for holding your breath. When you hold your breath, the diaphragm creates excess pressure, and the mucus easily moves away from the walls of the bronchi.
Bronchitis is characterized by stagnation of mucus in the lungs, so breathing exercises for bronchitis are aimed at removing excess secretions, along with which pathogens and pathological components are removed. When you have a coughing attack, you need to lower your head down, looking at the floor. The main thing is not to strain the cervical spine. Place your hands on your stomach, leaving the umbilical socket between your palms. When coughing, increase the pressure of your palms from top to bottom, cough into the floor. This technique does not injure the vocal cords and effectively removes mucus. This is safer for others because the air flow is directed downwards.
Treatment of bronchitis with medications and folk remedies, breathing exercises for bronchitis and the right approach guarantee success.
Routes of transmission of bronchitis
Frequent stress, reduced immunity, vitamin deficiency, hypothermia, nicotine addiction are the main reasons that increase the likelihood of developing acute respiratory infections and the flu. Viruses and bacteria that enter the human bronchi and cause their inflammation also suppress their protective functions, resulting in an inflammatory process of the mucous membranes of the bronchi and the formation of a large amount of secretion on it, called sputum. But how is bronchitis transmitted?
With the help of reflexes such as coughing and sneezing, the body tries to clear the airways of excess mucus, thereby carrying out the protective function of the body. This is a natural process of fighting the disease, but it causes negative consequences for people around. When you sneeze and cough, pathogenic microorganisms enter the air and onto household objects, which causes the infection to spread outward. They linger in the respiratory tract of other people, and also cause them to develop bronchitis and related symptoms.
The immune system can immediately suppress the proliferation of microbes in the body only if the human body is not weakened and has sufficient capabilities to deal with such environmental influences. This is the answer to the question of whether bronchitis is transmitted by airborne droplets.
Many people think that bronchitis is a non-contagious disease. It is impossible to become infected from a patient only if the disease is caused by allergies, polluted air or chemicals. If the inflammation is caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi, the patient becomes infectious to others during the acute period of the disease or until antibiotics are included in the treatment regimen.
You can become infected in shops and transport. Children attending preschool institutions often suffer from bronchitis in large numbers.