In many cases, the earlier cancer is diagnosed, the more successfully it is treated and the better a person's chances of making a full recovery. Early cancer can be detected during regular medical examinations, during home self-exams, and during specially scheduled screenings.
Most health departments have information about cancer screening and early detection programs.
Moreover, some types of cancer can be detected in the early stages using special medical exams, which are divided into two subtypes:
- General diagnostic examination for men and women.
- Separate analysis of a person’s health status depending on gender characteristics.
Early cancer: signs, manifestations, symptoms
Every person should be very careful about the health of their body. First of all, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Study skin and wound surfaces that do not heal for a long time, changes in size or in the form of any moles and skin indurations.
- Starting at the age of 50, check your stool regularly (once a year) for the presence of blood hidden in the stool. This is done because cancer can cause bleeding. Thus, a flexible sigmoidoscopy should be performed every five years, or a colonoscopy should be performed every ten years.
- When visiting the dentist, have your mouth examined to detect possible early cancer. Also, you need to independently pay attention to changes in the color of the lips, gums, tongue, cheeks, and the appearance of any crusts, seals or spots on the body.
Watch your ears and eyes
Pay special attention to areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, burn easily, and heal poorly, such as the tips of the ears and the areas around the eyes. Basal cell carcinoma, the most common and least destructive type, often occurs near the eyes and on the bridge of the nose. Squamous cell carcinoma can occur on the tips of the ears and lips, often starting as a rough patch that does not heal. Melanomas can occur anywhere on the body, either in an existing mole or as a new raised nodule or spot that looks like a mole.
Diagnostic tests for men
In order to detect and prevent early cancer in time, a man needs to follow the recommendations below:
- Men over 40 years of age should have an annual digital examination to check for possible hard areas or lumps.
- Testicular testing is necessary for males between the ages of 15 and 34, as testicular cancer is most often diagnosed during this period. Symptoms of early testicular cancer include tenderness, swelling, unusual changes in the top layer of skin, and a feeling of heaviness.
What and how to check?
Get into the habit of checking your skin monthly. Suspicious spots do not always appear in areas exposed to sunlight or in visible areas. Therefore, you need to check your entire body, front and back, preferably while standing in front of a full-length mirror.
| 1. Examine your face, including your nose, lips, mouth, ears, and areas behind the ears. |
| 2. Examine the scalp by separating the hair with a comb. Men who have no hair should carefully check their entire scalp. |
| 3. Examine your hands from the palms of your hands, the back of your hands, and between your fingers. |
| 4. Then move on to the neck, chest and upper torso. Women should also check the areas between and under their breasts. |
| 5. Bend your elbow and examine your shoulder and armpit. |
| 6. Using a small mirror, examine the back of your neck and back. |
|
| 8. At the end of the inspection, check the soles and areas between all toes. |
Diagnostic tests for women
Many atypical processes at an early stage can be identified using the following procedures:
- Medical examination of the mammary glands. Determining cancer at an early stage gives a good prognosis. A woman should also regularly conduct self-examination and at least once a year have an X-ray of the mammary glands (stable after 40 years).
- Regular pelvic exams, including Pap smears from the upper part of the external genitalia and cervix. The procedure involves collecting a sample of cells using a small brush or wooden stick. The removed cells are placed in a glass plate and examined under a microscope for abnormal tissue. The test is carried out every year after the age of 18 or when a woman becomes sexually active.
During your visit to your gynecologist, your doctor will also check your ovaries, fallopian tubes, and bladder.
Who is at risk?
Skin cancer most often occurs in people over 50 or in those with prolonged or intense exposure to sunlight. However, it can also occur in younger people.
Who is at risk:
• people with fair skin or prone to sunburn; • people who were sunburned as children; • people who spend or have in the past spent a lot of time in the sun (for example, because of their work or hobbies); • people periodically exposed to sunlight (for example, on vacation); • people who visit a solarium (or have visited it in the past); • people who have more than 50 moles; • people who have a family history of skin cancer; • people over 50 years old; • people who have undergone organ transplantation.
Please note: Skin cancer can also develop in people who are not at high risk.
It's always better to be safe than sorry. If in doubt, consult your dermatologist.
Early cancer: symptoms that occur most often
Common conditions associated with cancer include changes in bowel or bladder function, wounds that take a long time to heal, unusual bleeding, lumps or lumps in different parts of the body, skin lumps, upset stomach, and difficulty breathing, swallowing, coughing, or hoarseness. In no case should you wait for pain to occur, because early cancer in some cases may not have early symptoms at all.
However, it should be remembered that the highlighted conditions are not always a sign of cancer, but indicate serious health problems. Only an oncologist can make a reliable diagnosis based on tests.
Which sunscreen is best?
You need a broad spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 plus if the UV index is above 3. You need two tablespoons (about as much as you can fit in the palm of your hand) of sunscreen for your entire body , including ears, neck, face, arms and legs.
Apply it while indoors because it takes about 15 minutes for it to absorb into the skin before it starts doing its job. Reapply the cream every two hours or immediately after swimming or heavy sweating. Use SPF 15-plus balm to protect your lips. Find important facts about breast cancer in our material at the link.
Early cancer: what should be the treatment?
The choice of therapy depends on the location, stage of diagnosis, age of the patient and general health.
Typically, treatment for early cancer includes the following methods:
- Surgery:
Local removal of the tumor, as well as, if necessary, the tissue around it and nearby lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy:
This treatment of early cancer is carried out by targeting mutated tissues. The high-energy beam of light damages or removes cancer cells. Radiation can come from the machine - external exposure. An implant (a small container of radioactive material) placed near the tumor is also sometimes used. This is a type of internal radiation. Some patients may receive two types of radiation therapy at the same time.
- Chemotherapy:
The method involves the use of pharmacological drugs that interfere with the normal functioning of the tumor. It is carried out cyclically: after the treatment period there is a recovery period, etc.
- Hormonal therapy:
Some cancers, especially breast and prostate cancer, are hormone dependent. For this reason, your doctor may recommend medications that prevent the growth of cancer cells in the early stages of the disease.
- Biological therapy (immunotherapy):
This is a form of treatment for early cancer that uses the body's natural powers to fight cancer and prevent further development of the disease. Forms of biological therapy include: monoclonal antibodies, interferon, interleukin-2 (IL-2) and some types of colony-stimulating factors (CSF, GM-CSF).
What are the first symptoms?
A person may already be worried about something, but he does not associate it with the development of cancer. For example, if a smoker's cough changes, he should see a doctor. It is important that one examination can be used for both screening and early diagnosis. For example, a woman came with complaints about some kind of formation in the mammary gland.
She was not sent for three months to collect tests and consult with a cardiologist, but immediately had a mammogram on the same day. In this case, it is early diagnosis. But if a 50-year-old woman does not have any symptoms, but she receives an invitation to have a mammogram, then this is already screening. Because the examination is done when there are no symptoms.
Prognosis of early cancer
Survival statistics when early cancer represent a very high chance of a person making a full recovery. However, it should be remembered that the prognosis depends on factors such as the rate of spread, the type of tumor, the age of the patient and the general conditions of the disease. Therefore, it is very difficult to tell the patient exactly how long he will live after diagnosis.
To establish the most accurate five-year survival rate for early cancer, the following should be considered:
- the percentage of people with a specific cancer type and stage, which is established for a specific age group of the population;
- time of remission, possibly until complete recovery;
- the treatment methods used, their effect on the body;
- recovery after therapy, especially radiation and chemotherapy;
- the body's response to treatment.
"Gene Jolie"
Angelina Jolie is not just a Hollywood star, but also a real fighter! The actress’s mother and aunt died at a relatively young age from the so-called hereditary tumor syndrome. And Angelina, with her characteristic determination, preventively (that is, in advance) removed her mammary glands and ovaries (target organs for hereditary cancer, the high risk of which was discovered by her genetic analysis).
She was the first public figure to openly admit that she had the operation to save herself from a still non-existent, but without emergency measures, an almost inevitable threat. Jolie's personal risk, according to doctors, was 87%. Thus, she created an important precedent that will certainly help save the lives of many women around the world!
What can a person do on his own to prevent early cancer?
To minimize the possibility of developing cancer and prevent early cancer , a person must:
- Be concerned about your health and be physically active, spend a lot of time outdoors.
- Know and follow the main rules on how not to die from cancer.
- Give preference to healthy foods:
- eat fresh vegetables (especially cruciferous vegetables) of different colors, since they retain a complex of vitamins and amino acids - known antioxidants;
- eat garlic and onions, which boost human immunity;
- do not eat overcooked meat, as it produces many carcinogens;
- use as little vegetable oil as possible for cooking (do not fry);
- Avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays and frequent trips to the solarium.
- Know how to recognize cancer in time.
Causes of malignant tumors
Scientists today have already been able to prove that cancer is caused by several factors.
- Mutation. At a certain point, the cells of the body, instead of dying after fulfilling their function, begin to divide tirelessly, resulting in a new growth.
- Carcinogens. This name hides a whole group of substances that provoke the appearance of a cancerous tumor. Carcinogens can be chemical and physical. The first group of substances enters the human body through water, food and household chemicals. That is why one of the main preventive measures against cancer is proper nutrition. Physical carcinogens are radiation and ultraviolet irradiation, as well as tobacco smoke. Fortunately, ordinary citizens do not receive radiation in large doses anywhere. But under the southern sun, almost all residents of large and small cities willingly fry their skin every year, who have remembered the benefits of sun, air and water since Soviet times. Alas! Sunbathing on the seaside beach has lost its usefulness today. Such procedures cause considerable harm to the body, since ultraviolet waves have become very aggressive these days. Of course, giving up sunbathing as a measure to prevent cancer is pointless if you continue to smoke. Today, it is this addiction that leads to cancer more often than other causes.
- Free radicals. Many people have also heard about these particles. Radicals take away electrons from cells, making them defective. In order to neutralize the effects of these aggressive particles, it is necessary to enrich the diet with foods containing antioxidants.
- Tissue homeostasis, or pH imbalance. Acidification or alkalization of the body causes disruptions in metabolic processes and provokes the onset of many different diseases.
- Decreased antitumor and general immunity. A certain number of cancer cells are formed in the human body every day. However, our immune system recognizes such tumors and destroys them before they become a serious threat. Therefore, supporting immunity is one of the most important aspects in the system of cancer prevention.
- Psychological factor. Oncologists say that the process of formation of a malignant tumor is triggered by stress.
- Cancer virus. Scientists have already been able to prove that some types of oncology are caused by a special type of virus, which makes it possible to implement such a preventive measure of oncology as vaccination.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the prevention of cancer lies, first of all, in following the rules of a healthy diet and an active lifestyle. However, the site sympaty.net hastens to warn its readers that the diet for the prevention of malignant tumors has some features that lovers of healthy food know far from everything about.
This is not an accident
Sporadic (that is, random) cancer can occur in anyone. The main cause of the disease is genetic mutations in cells. Over the years, a critical amount of them accumulates in the body, so the development of tumors in old age is a natural and almost inevitable phenomenon. As oncologists like to say, every person will live to see their cancer, unless they die first from a heart attack or stroke.
But there are also hereditary forms of the disease that affect people from the same family for generations. The path to cancer for carriers of certain gene mutations is shorter than for other people. If an ordinary cell needs to accumulate 5-6 significant mutations to turn into a cancer cell, then with a hereditary gene defect 4-5 are enough.
Hereditary tumor syndromes account for only 5% of all cancers. But the risk of becoming a victim of a terrible disease for people who carry the defective gene is not just higher than for others - it is almost fatal. For example, the risk of developing breast cancer for an ordinary woman is about 8–12%, and for carriers of mutations in the BRCA1 gene it is more than 60%.
What screening tests make sense to undergo if I want to protect myself?
Screening programs that exist must be modified if it is known that, for example, a relative had a tumor with a genetic syndrome. If someone at a young age gets colorectal cancer, then most likely there is a genetic abnormality and it is necessary to do a test to identify it.
And if the mutation is confirmed, there is a high probability that relatives also have it. This means that screening for the patient’s relatives should begin not at the age of 50, but earlier, and examinations should be carried out more often, and they should be examined using other methods, more intensive, because the risk of getting sick is high. Methods for gene typing and tumor study are already available in large Russian cities.
The verdict is overturned!
They say, “much knowledge means much sorrow.” But this is not the case. Knowing about their predisposition to hereditary tumor syndrome, people can lay out straws in advance. True, there is not yet a single method to help protect against the disease. For some, regular preventive examinations will be more effective, for others, preventive operations. It all depends on the organ.
For example, when there is a threat of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer, early diagnostic measures (ultrasound, mammography, testing of tumor markers) are not very effective. It has been proven that they do not guarantee timely detection of the tumor. And ovarian cancer is often detected only in advanced stages.
Moreover, a number of neoplasms are prone to metastasize even at the first stage, so even early detection of the disease does not always save from death. This is especially true for some hereditary tumor syndromes. Thus, when breast cancer is detected at the first stage, at least 98% of women have a chance to live 5 or more years, and for carriers of mutations in the BRCA1 gene this figure is only 82%.
Therefore, observational tactics are permissible only for very young women (up to 30–35 years old). Before this age, they need to have time to give birth to children, and then have their target organs removed prophylactically. The effectiveness of such operations for patients with hereditary breast cancer and ovarian cancer is considered a firmly established fact.
Hereditary medullary thyroid cancer is a rare disease caused by pathogenic mutations in the RET oncogene. Identification of such a mutation in a still healthy person is a good reason to remove the thyroid gland in advance. It has been established that simply frequent observations will not protect a person from death, and timely surgery almost completely reduces the risk of the disease. The loss of an organ is effectively compensated by hormone replacement therapy.
When there is a threat of hereditary colon cancer, regular observations, on the contrary, are very effective. Studies have shown that if you have a colonoscopy every 1-2 years, you can significantly reduce the risk of death from this disease. Prophylactic surgery is not usually performed on a healthy colon.
How to avoid lung cancer?
Most cases of lung cancer are preventable.
You can significantly reduce your chances of developing lung cancer by preventing exposure to risk factors. Smoking is a major risk factor for lung cancer.
Causes of lung cancer
Quit smoking
Stopping smoking is the most important way to reduce your risk of lung cancer. The lungs will begin to repair themselves almost immediately.
The duration of smoking and its frequency will affect the regenerative ability of lung tissue. But even after years of smoking, quitting can significantly reduce your risk of lung cancer.
Avoid exposure to asbestos and radon
If you work directly with asbestos or other hazardous materials, be careful and try to limit your exposure to these substances. Radon levels in homes and commercial buildings can also be determined.
If you live or work in an older building and suspect radon or asbestos levels are above acceptable levels, getting a radon or asbestos test done can give you peace of mind.
Maintain a healthy diet
Nutrition is very important to maintain good health. A diet containing enough of the following foods provides your body with the nutrition it needs to function properly and heal damaged cells:
- fruits
- vegetables
- vitamins
- minerals
You can also follow these simple rules to maintain a healthy diet:
- Eat five or more servings of fruits and vegetables per day.
- Include other plant foods such as beans and grains in your daily diet.
- Stay away from foods that have high levels of fat.
- Avoid drinking alcohol or limit the amount of alcoholic beverages you drink.
Warning signs
The cause of hereditary cancer is a mutation of a single gene received from parents, due to which the tumor develops in a specific organ. Moreover, the presence of a family history in this case is not so important. For example, if we take the most common hereditary syndrome of breast cancer (BC) and ovarian cancer (OC), it can appear even in a woman in whose family no one suffered from this disease. After all, a pathogenic mutation can be inherited from the father.
Hereditary tumor syndrome has clear clinical signs:
- Cancer occurs at a relatively young age (about 20–25 years earlier than usual).
- There is often a family history of cancer (one type of tumor in several relatives or different types of cancer in one relative).
- Several tumors in an organ at once (or neoplasms in both paired organs: breast, kidneys).
- Certain histological and immunohistochemical features of the tumor.
| Type of hereditary cancer | Contribution to morbidity | Genes in which mutation increases risk |
| Mammary cancer | 5–10% | BRCA1, BRCA2, CHEK2 and others |
| Ovarian cancer | 15% | BRCA1, BRCA2 |
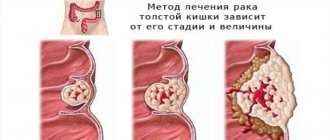
| Colon cancer | 1–3% | MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2 |
| Stomach cancer | 3% | CDH1, BRCA1, BRCA2 |
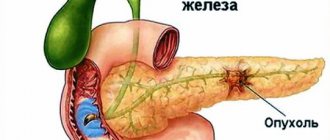
| Pancreas cancer | up to 7% | BRCA2, PALB2 |
| Prostate cancer | up to 5% | BRCA2 |
| Medullary thyroid cancer | up to 30% | PTEN |