Viral bronchitis develops when various viruses enter the human body. This disease can become a complication of influenza, measles, parainfluenza, whooping cough and adenovirus infection. People with weakened immune systems are more likely to get sick; the risk group also includes young children and the elderly. In weakened people, antibodies do not perform their protective function well, so pathogens settle on the bronchial mucosa, leading to their irritation and inflammatory process. Viral bronchitis occurs more often in young children than in adults.
Causes and risk factors
If a person has had the flu or acute respiratory viral infection, then bronchial disease caused by viruses may appear against this background. Also, such a disease can occur independently due to bacilli that have entered the human body. The most common causes of weakness are:
- Flu;
- Damage to the mucous membrane due to adenovirus;
- Damage to the nose and nasopharynx due to rhinovirus infection;
- Enteroviruses;
- Rubella;
- Paramyxoviruses;
The main reasons that pose a danger in the development of the disease are:
- Elderly people and children;
- Painful enlargement of the tonsils of the nasopharynx or palate;
- Chronic course of the disease in which the sinuses are affected;
- Chronic inflammation of the bronchial mucosa;
- Weakened immunity;
- Allergic diseases;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Tobacco smoking;
- Environmental pollutant;
- Disease of the esophagus.
- Infection, affecting the channels of the mucous membrane of the alveoli, provokes an inflammatory process, which is caused by:
- Overflow of blood vessels;
- Swelling of the mucous membrane;
- Enlargement of the mucous gland;
- Endoscopic resection;
- Expansion of the epithelium of the intestinal mucosa.
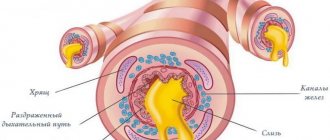
Swelling of the mucous membrane provokes a failure of blood supply to the bronchial channels, the channels become clogged with mucus, and a cough begins.
Mechanism and causes of the disease
Viruses begin their destructive activity in the nasopharynx, and then penetrate the throat, trachea and bronchi. There they invade epithelial cells and destroy them. These dead cells make up part of the sputum that is released from the respiratory tract of patients with bronchitis.
The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets, that is, transmitted through coughing and sneezing. For example, to infect 2-3 people, it is enough for the sick person to sneeze several times in a small room. The most contagious is considered to be a person who becomes ill at the height of the infection, that is, during the period of active reproduction of microorganisms. The incubation period of the disease is 2-7 days.
The main cause of bronchitis is the penetration of viruses into the body; people who have had their tonsils removed are especially susceptible to them. One of the consequences of tonsillectomy is the widening of the entry point for infection and its rapid spread down the respiratory tract.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
- cold and wet weather;
- working with harmful volatile substances in production;
- smoking and alcoholism;
- weakened immunity after long-term illnesses;
- seasonal outbreaks of acute respiratory infections;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx and bronchopulmonary system;
- autoimmune diseases or a tendency to allergic reactions.
Symptoms of viral bronchitis
Symptoms causing viral bronchitis require examination and proper treatment. During the course of the disease, no characteristic changes are noticed in blood tests. The changes indicate that a disease is developing that is not caused by viruses, but bacterial. In adults, the symptoms of viral bronchitis are expressed as follows:
- Wheezing in the chest area.
- A dry, hacking cough lasts for several days, then turns into a wet cough, during which mucus is released.
- Painful sensations in the chest, weakness, weakness, lethargy.
- Sudden rises in fever up to 39.
The bronchial illness lasts for 2 weeks, and then the patient recovers. Attacks of hysterical cough torment at night, then weakness goes away, and cough syndrome lasts for a month or more. It is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis to ensure that there is no tuberculosis or lung cancer. A disease of this form can be cured in 14 to 30 days.
Clinical symptoms
The disease develops acutely, most often against the background of acute respiratory viral infection. The main clinical manifestations of viral bronchitis include:
- cough,
- fever,
- intoxication syndrome,
- chest pain,
- catarrhal inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
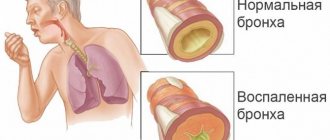
The first and main symptom is cough , which at first is dry (non-productive), but after two or three days it becomes wet (productive). The sputum discharge is transparent, viscous, and odorless. Coughing attacks may be accompanied by chest pain.
Like most viral infections, acute bronchitis occurs with a rise in body temperature, usually to febrile levels (above 38°C). With adenovirus infection, the temperature lasts more than 10 days.
Fever is often accompanied by intoxication syndrome of varying severity. Intoxication is characterized by: lethargy, decreased performance, dizziness, headaches, nausea. Any ARVI is characterized by pronounced catarrhal manifestations: runny nose, lacrimation. The patient indicates pain in the throat and eyeballs.
The patient’s breathing becomes more frequent and shallow; during auscultation, dry (at the beginning of the disease) and then wet (at the height) wheezing of medium and large caliber can be heard.
An organism with a healthy immune system is able to overcome the infection within three to five days and the disease ends in complete recovery.
Important! If the symptoms of the disease do not subside and the patient’s condition does not improve, then this indicates the addition of bacterial flora and requires antibiotic therapy.
Diagnostics
Before prescribing therapy, the doctor must carry out a number of diagnostic measures:
- Interview the patient about complaints about the disease.
- Carry out visual inspection.
- Tapping areas of the body and analyzing sound phenomena.
- Listening to sounds during the functioning of organs.
- An x-ray of the lungs and bronchial tract is prescribed.
- Taking tests.
After receiving the x-ray, the doctor will determine the type of disease, as well as the area damaged by the infection. After receiving the result of a blood test, the doctor determines the type of bronchitis: a virus or bacteria - provoked the disease. When the patient completes the examination, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes health therapy.
How to treat viral bronchitis? This form of the disease, aggravated by a bacterial infection, requires the use of antibiotics. If there is no microbial infection, then antibacterial agents are not used, since they do not act on the infectious virus. Antipyretic drugs are prescribed at high temperatures. Therapy includes expectorant medications and airway dilators.
Nutrition for bronchitis
For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to adhere to the following nutritional principles:
- Eating in small portions four to five times a day.
- Predominance of proteins in the diet (along with sputum, a large amount of protein comes out when coughing; it is necessary to compensate for its losses to prevent protein starvation).
- Consumption of foods high in vitamins A, C, E, which help the body cope with infection.
- Drink plenty of warm drinks. Teas with linden, raspberry, lemon, vegetable and fruit juices, alkaline mineral water, boiled milk with honey are very useful. The fluid entering the body thins the mucus and makes it easier to remove. In addition, diuresis increases, which contributes to effective cleansing.
- Eating fresh onions. It not only has antimicrobial and antiviral effects, but also effectively thins sputum.
How to treat bronchitis of viral origin
Treatment of viral bronchitis in adults is carried out on an outpatient basis. The hospital treats infants and elderly people, as well as patients with severe pathology, pneumonia and bronchial obstruction syndrome. At the initial stage of the disease, the patient has attacks of hysterical coughing and a high fever. The patient needs:
- Complete rest;
- Compliance with diet;
- Drink plenty of warm liquid;
- Smoking is prohibited;
- Ventilate the room several times a day;
- Regular wet cleaning of the house.
- How to treat viral bronchitis? Doctors include medications in the therapeutic course:
- Antipyretic, antiviral, antitussive, expectorant effects;
- Medicine of the mucolytic group;
- Relieving spasms;
- Drugs that enhance immunity;
- Complex of vitamins.
In addition to medications, doctors always recommend to patients in their wellness cycle:
- Inhalations;
- Physiotherapy;
- Massage;
- Breathing exercises;
- Warming up at home.
Viral bronchitis caused by an infectious pathogen is contagious. To protect yourself from infection, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment, in case of a mass epidemic, wear masks, lubricate your nose with oxolinic ointment.
Treatment
Treatment tactics for acute viral bronchitis include:
- Bed rest , especially during the acute period of illness. It is necessary to ventilate the room in which the sick person is located more often and carry out wet cleaning.
- With viral bronchitis, the patient needs to drink a large amount of liquid (preferably warm). Food should be more gentle (small pieces, soft, more liquid food). It should be taken in small portions, but more often.
As for drug therapy, most often it is symptomatic treatment. Antiviral drugs are prescribed only in severe and unclear cases.
How to treat acute viral bronchitis? The main groups of drugs used in its therapy include:
- antitussives - include cough suppressants and mucolytics,
- anti-inflammatory,
- antihistamines,
- vitamin complexes,
- immunocorrectors,
- antiviral.
Attention! Antibacterial therapy for viral bronchitis is not indicated. Antibiotics are prescribed only by a doctor if there are signs of a bacterial infection.
Another fairly effective method of treatment and rehabilitation is physiotherapy. Physiotherapeutic procedures can be started only after the acute period of the disease has subsided.
The following methods have shown high effectiveness in the treatment of bronchitis:
- local UV irradiation,
- microwave and UHF therapy,
- massage,
- physical therapy and breathing exercises.
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a very good effect, but it only appears with long-term use.
When the symptoms of the disease are taken by surprise, and the medicine cabinets are empty and there is no opportunity to visit the pharmacy, you can use traditional methods that can significantly alleviate the course of the disease. The following have a therapeutic effect:
- decoctions of various medicinal herbs (chamomile, thyme, linden),
- honey,
- dried fruits compote.
Complications
Untimely treatment of viral bronchitis leads to many types of complications. Here are the types of complications:
- Severe respiratory disease caused by fibrous obstruction of bronchioles;
- Bronchogenic pneumonia, in which the walls of the bronchioles become inflamed;
- An acute pathological syndrome in which oxygen deficiency develops.
Bronchial ailments infected with a virus, which are repeated often increase the risk of developing the following ailments: bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis for viral bronchitis is favorable. Most often it goes away within a week, leaving no trace behind. However, in some cases complications may occur, the most common of which are:
- addition of a bacterial infection,
- transition to a recurrent or chronic form,
- development of an allergic reaction,
- pneumonia,
- sepsis,
- adverse reactions to the medications used.
It must be remembered that even such a harmless disease as acute viral bronchitis can cause serious complications. But you can significantly reduce the risk of their development by consulting a doctor in time and following all his recommendations.
Prevention
Treatment of bronchitis in children and adults is prescribed by a doctor; self-medication leads to deterioration of health and to complications of various types. Doctors recommend taking preventive measures:
- Strengthen immunity;
- Follow the diet;
- Complete rest during illness;
- Breathe fresh air;
- Sports activities;
- Ski trips;
- Vaccinations;
- Quit smoking.
Doctors also recommend timely treatment of bronchial asthma, inflammation of the sinuses, and peptic esophagitis.
Features of formation and manifestation
As the name suggests, the main cause of this disease is a virus. Therefore, viral bronchitis more often appears in certain seasons of the year or in a specific climate. It often occurs in those who have to be in crowded places.
Since viruses are easily transmitted through personal contact with carriers, it only takes one person for the disease to spread. Because of this, epidemics occur in school and student groups.
It should be said that symptoms of the disease do not appear in all adults who had to interact with a carrier of the virus. With a strong immune system, the body copes with this problem. But if the body is weakened by an untreated disease or frequent stress, then the occurrence of bronchitis is very likely.
Therefore, additional factors can be identified that contribute to the development of viral bronchitis:
- weakness of the immune system;
- presence of respiratory system diseases;
- untreated infectious disease;
- sensitivity to cold and dampness;
- emotional exhaustion.
If these features are present in adults and children, there is an additional risk of developing the disease. Therefore, if signs of bronchitis are detected, you should not expect that the disease will go away on its own.
It is much easier to treat viral bronchitis, like any other disease, at an early stage of its development. Therefore, it is very important to detect it as early as possible and seek help.
This means paying attention to any changes in how you feel and being aware of the symptoms of the disease. They need to be described to the doctor, which will help him make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The main symptoms:
- temperature increase;
cough;
- chest pain;
- labored breathing;
- weakness and fatigue;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- wheezing.
The cause of the disease may be a recent viral disease. It can be assumed that his treatment was not effective, and a complication arose in the form of viral bronchitis.
The listed symptoms require additional diagnostic procedures, since they may also be inherent in other ailments. Therefore, before treating the disease, you need to make sure that the patient has it.
Age characteristics
Elderly people who get sick due to viruses have a hard time of it, and during the course of the disease they develop oxygen deficiency in the respiratory system and heart failure. Viral flu is difficult for older people to tolerate.
Treatment of viral bronchitis in children is carried out after a thorough medical examination. Children under three years of age, as well as kindergarten children, are most susceptible to this disease. Older children are less susceptible.
It is recommended to treat viral bronchitis in a child at the first symptomatic signs.
Viral bronchial disease can be quickly cured with correct and timely diagnosis. Unauthorized treatment or untreated disease leads to dangerous complications.
Viral form of bronchitis
Viral bronchitis is the most common type of bronchitis. It is characterized by inflammation of the bronchi, which occurs under the influence of infections.
Most often, the infection enters the respiratory tract along with the inhaled air, and then begins to develop, causing changes in the tissue of the bronchi. As a result, the main symptoms of the disease appear.
Most often, children suffer from viral bronchitis due to the weakness of their immune system and sensitivity to weather changes, but this type of disease is also common among adults.