What is bronchial asthma? This disease is classified as a chronic progressive disease. The very first symptoms of asthma can begin with attacks of shortness of breath, which are always accompanied by coughing, and in advanced cases lead to attacks of suffocation. Asthma attacks occur due to the fact that irritants and allergens affect the respiratory tract, as a result of which the bronchi begin to secrete mucus and narrow, which disrupts the flow of air during breathing. With bronchial asthma, shortness of breath is the main reason why you should immediately consult a specialist.
[smartcontrol_youtube_shortcode key=”shortness of breath with asthma” cnt=”1" col=”1" shls=”false”]
The essence of the problem and differences
There are many reasons that cause shortness of breath associated with difficulty inhaling or exhaling. The feeling of lack of oxygen or dyspnea is familiar to many: jogging, climbing a mountain, climbing stairs, excessive excitement. Shortness of breath can develop suddenly even in a state of complete rest. It is usually divided into in- and expiratory. It accompanies a large number of pathologies and requires medical attention.
Differences
The main difference is that a person begins to experience a lack of oxygen when inhaling - the inspiratory form or when exhaling - the expiratory form. The symptoms of this phenomenon are also different.
Difficulty in inhaling is inherent in:
- laryngotracheal edema of various origins;
- spasm of ligaments;
- foreign object in the airways.
Lack of air on exhalation accompanies:
- inability to exhale;
- percussion examination of the lungs;
- pressure changes inside the chest;
- overfilling of the respiratory organs with air.
Both conditions require professional counseling. The clinical symptoms of inspiratory dyspnea are expressed in heavy noisy inhalation and exhalation. Expiratory pathology is manifested by incomplete exhalation with a simultaneous need for constant increased breathing and prolonged exhalation of oxygen.
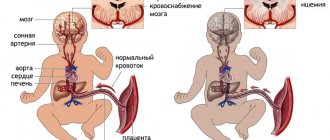
It is not uncommon for hypoxia to be accompanied by chest pain, high pressure in the venous bed, pale skin, acrocyanosis, and profuse sweat.
A mixed type of pathology is also observed: shortness of breath on both inhalation and exhalation (bronchial asthma). Dyspnea can be permanent (emphysema) or temporary (pneumonia). Often a lack of oxygen becomes a companion to quitting cigarettes. In this case, it resolves itself within a month.
How does asthma begin?
It must be remembered that the symptoms of an allergic cough are very similar to asthma attacks, the main thing is not to confuse them. It is worth remembering that the sooner you recognize the signs of asthma, the easier it will be to get rid of the disease.
Today, doctors cannot exactly explain the causes of asthma, but they suggest that it may be hereditary. Attempts have been made to cure asthma using genetic medicine, although they were not successful, for the reason that not one gene, but several, is responsible for the disease.
The disease bronchial asthma can develop after long-term illnesses of the respiratory organs, as well as if allergic diseases that cause serious complications on the respiratory system are started and not treated.
Risk factors and triggers
The causes of the pathology are closely related to the timing of the onset of respiratory problems. This alone determines the severity of shortness of breath. Pulmonologists divide dyspnea into acute and gradual forms.
The first is characterized by the appearance against the background:
- Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system. The essence is heavy breathing as a result of organic tissue damage.
- Severe sensitization with laryngeal edema.
- AMI.
The gradual development of shortness of breath is caused by:
- Chronication of pulmonary pathologies, including pulmonary edema.
- Long-term heart failure.
- Extra pounds.
- Carrying a baby (by the third trimester).
Treatment
In order to get rid of shortness of breath with this disease, doctors prescribe hormonal medications, as well as drugs that will help expand the bronchi.
Important! If previously prescribed inhalers do not help cope with shortness of breath, you should immediately call a doctor; you should not wait for the condition to worsen.
- It is necessary to eliminate irritating factors.
- Place the patient facing the back of the chair.
- Provide access to fresh air.
If the patient has an attack against the background of bronchospasm, then it is necessary to use short- or long-acting agents in treatment. Most often, doctors prescribe the drug Salbutamol in the form of an inhaler or powder for inhalation. During an attack, the dosage of the drug is 2-4 mg, taken 3 times a day.
If the drug does not bring a positive effect, it is necessary to use Berotec or Fenoterol in treatment. The drugs are available in the form of a dosed aerosol. Dosage of the product: 1-2 doses 3 times a day. The drug has a strong bronchodilator and tocolytic effect, therefore, when used correctly, it quickly dilates the bronchi and increases breathing volume. If necessary, doctors prescribe the short-acting drug Terbulin to patients.
Available in powder form, intended for subcutaneous injection. Improvement in breathing occurs an hour after administration of the drug, lasting up to 4 hours.
The drug Terbulin effectively stops an attack of shortness of breath for a period of up to 4 hours
If short-acting drugs stop an attack of shortness of breath, but after a while it appears again, then drugs with a long-term effect are prescribed.
For example:
- Formoterol, a beta2-adrenergic agonist that has an adrenomimetic as well as a bronchodilator spectrum of action
- Clenbuterol helps reduce swelling and congestion in the bronchi
In order to relax the muscles of the bronchi, doctors prescribe the patient drugs from the group of m-cholinergic receptor blockers, for example: Atrovent.
Additional medications for shortness of breath:
- Prescribed NSAIDs: Pital, Tayled
- Inhaled glucocorticoids: Becotide or Beclazone
- Expectorants: ACC, Mukobene, Bromoxine
If the cause of shortness of breath is the development of cardiac asthma, then in this case it is necessary to use medicinal glycosides.
Drugs for shortness of breath in asthma:
- Digoxin
- Korglykon
- Strophanthin
The drugs described above cannot be used independently to relieve an attack; if used incorrectly, serious health complications can occur.
Triggers of shortness of breath on inspiration
The most likely symptoms for respiratory diseases are:
- Foreign body.
- Pneumothorax.
- LA embolism.
- AMI, heart failure of varying severity, angina of any form, leading to pulmonary hypoventilation.
- Paralysis of the diaphragm.
- Nervous breakdown accompanied by hypoxia.
- A state of constant anxiety, causing hyperventilation with dizziness and fainting.
- Pneumonia.
- Obstructive bronchial diseases.
Causes of shortness of breath on exhalation
Expiratory dyspnea is provoked by the following diseases:
- Gaining extra pounds.
- Anemia, including iron deficiency.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary trunk.
- Cardiac asthma.
- Dyskinesia of the respiratory tract.
- Pulmonary asthma.
In addition, practitioners group shortness of breath based on the primary pathology that caused it. From this point of view, inspiratory dyspnea is classified as a group of cardiac pathologies. Expiratory – pulmonary.
Cardiac shortness of breath occurs when:
- Hypertension.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia.
- Pulmonary vasculitis.
- Cardiosclerosis.
- Arrhythmias.
Pulmonary dyspnea occurs when:
- Lung tumors.
- Tuberculosis.
- Silicosis.
- Poliomyelitis with paralysis of the intercostal muscles.
- Actinomycosis.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Myasthenia.
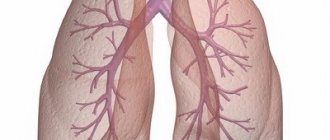
Wheezing in bronchial asthma
Wheezing is elastic waves that occur in the lungs during an attack of bronchial asthma or acute respiratory diseases. They can be heard even without special equipment. Wheezing can be either wet or dry. Dry wheezing occurs during bronchial spasm, when the mucous membrane of the lungs swells due to the presence of viscous sputum in the bronchi. Moist rales are formed due to the presence of liquid secretion in the bronchi. Wheezing can spread both in certain areas of the chest and cover the entire chest.
[sma[smartcontrol_youtube_shortcode key=”First aid for bronchial asthma” cnt=”1" col=”1" shls=”false”]
Pediatric dyspnea
Although the triggers for shortness of breath in children are basically the same pathologies as in adults, it is customary to classify childhood dyspnea as a separate group. This is due to the specific nature of diseases that lead to breathing problems in a child.
These include:
- Distress syndrome of newborns, when pulmonary edema occurs due to circulatory disorders in the pulmonary circle. The condition requires emergency medical attention.
- False croup - swelling of the ligaments due to inflammation causes inspiratory shortness of breath and suffocation. Calling an ambulance in a timely manner can save you.
- ARI, cold.
- Heart defects: tetralogy of Fallot, patent foramen ovale, ductus batalli. Shortness of breath here compensates for congenital hypoxia.
- Anemia due to Rhesus conflict.
Clinical manifestations
With intense inhalation with stimulation of the contractility of all muscles of the bronchopulmonary system, we speak of the expiratory form of dyspnea. This happens in the case of bronchitis and asthma.
Difficult exhalation is caused by the accumulation of sputum in the bronchopulmonary system, indicating infection, inflammation, and the prevalence of exudative processes. Symptoms of inspiratory dyspnea affect the behavior of patients. They experience muscle tension, swelling of the jugular veins, gurgling in the throat, fear of turning their head, and it seems to them that the lungs are floating down. Accurate diagnosis to prescribe an adequate course of therapy requires auscultatory examination.
The symptoms of both types of dyspnea are presented in the table.
| Pathology | Diagnostics and clinic | |
| Inspiratory dyspnea | AMI | Pain behind the sternum, radiating to the neck and left arm, under the shoulder blade. Fear of death. A twelve-lead ECG, cardiac ultrasound, cardiac angiography, and troponin are performed. |
| Arrhythmias | Interruptions in the pulse towards a decrease or increase in frequency, extrasystole, dizziness, fainting. The diagnosis is made based on physical examination, auscultation, ECG, blood pressure. | |
| Heart defects | The clinical picture is determined by the affected valve: wet cough, congestion, syncope, disruption of the cardiovascular system. Auscultation and echocardiography are performed. | |
| Heart failure: IHD | Signs of pulmonary congestion, cough, large heart, pleural effusions. Diagnosis is made based on laboratory tests (BNP), CT scan. | |
| Expiratory dyspnea | Pulmonary edema | Cough, shortness of breath, acrocyanosis, wheezing, hypotension. Auscultation and radiography are performed. |
| Pulmonary embolism | Chest pain, shortness of breath, hemoptysis. The diagnosis is confirmed by MSCT and ECHO KG. | |
| Pneumothorax | Pain syndrome during manipulations. A physical examination, CT scan, and x-ray are performed. | |
| Pneumonia | Shortness of breath, fever, cough, chest pain. Diagnosis by blood test (leukocytosis), radiography. | |
| Bronchial asthma | Difficulty inhaling, often exhaling, wheezing, fear of suffocation due to persistent bronchospasm. Diagnosis is based on medical history, CBC, biochemistry, and respiratory function testing. | |
| Foreign body | Anamnesis gives the cause, the diagnosis is confirmed by bronchography, bronchoscopy. | |
| Pulmonary fibrosis | Symptoms: shallow breathing with a constant feeling of lack of air. Confirmed by x-ray. | |
| Tumor | Anamnesis, tumor markers, and chest x-ray help to establish the cause of persistent shortness of breath. | |
The first signs of bronchial asthma
- One of the most obvious signs of asthma is allergies. If you experience coughing attacks or difficulty breathing due to allergens in the form of dust or plant pollen, you should immediately consult a doctor to exclude the initial stage of asthma.
- Frequent colds regardless of the time of year. Frequent bronchitis is a harbinger of asthma. It is necessary to carry out off-season prophylaxis to boost immunity.
- Difficulty breathing when exhaling air from the lungs.
- Wheezing in the lungs, followed by coughing with shortness of breath.
- Sweating increases.
- Severe pain and burning sensation in the chest area.
- Pale face and feeling of constant anxiety, it is extremely difficult to catch your breath.
The first signs of bronchial asthma in an adult are always of a different nature. In most cases, this is the presence of shortness of breath, which creates the risk of asphyxia, pale or even blue skin, panic, and dry cough. The main thing is not to miss asthma and the first signs.
[smartco[smartcontrol_youtube_shortcode key=”Bronchial asthma. What to do to breathe" cnt=»1" col=»1" shls=»false»]>BezOkov recommends: therapy and prevention
Dyspnea is one of the “self-help” pathologies. When you are short of air, the first thing you need to do is calm down and call a doctor immediately. Then open the window or window - in the cold season. You should not take a “lying” position: you need to sit comfortably in a chair.
Unbutton the shirt collar that is squeezing your neck, loosen the tie, remove the scarf from your shoulders.
The chest should be in a state of freedom. If desired, make a cup of tea and drink it. It is not recommended to use any medications before the ambulance arrives.
If inspiratory and expiratory shortness of breath has become part of the patient’s life, occurs with the slightest effort, and complicates active life, consultation with an experienced specialist, primarily a therapeutic specialist, is necessary. A complete clinical and laboratory examination, which will be prescribed by a doctor, will become the basis for correct diagnosis and identification of the cause of dyspnea.
Usually these are CBC and OAM, ECG, plain X-ray of the lungs, FLG, blood sugar test, other biochemical indicators, pulmonary function test, pink flowmetry, spirogram and bronchogram, CT, MSCT, diagnostic bronchoscopy, microscopy of sputum and its culture on bacmedia. Once the cause is established, a course of adequate complex therapy is carried out.
You can also take care of your health yourself:
- Give up bad habits, part with nicotine. Stop communicating with people who smoke, preventing passive smoking.
- Bring your weight back to normal. Do physical exercise, come to the gym.
- Walk in the fresh air for at least a couple of hours a day. In this case, walking or gardening is preferable - physical activity.
- Take control of your emotions, stop being nervous about nonsense.
- Get tested for tuberculosis, since it is often the cause of sudden shortness of breath.
Necessary therapeutic measures for bronchial asthma
It must be remembered that drug treatment can only be prescribed by a highly qualified specialist. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate; it can lead to serious consequences, even death.
- Correct use of the inhaler. Doctors do not recommend using more than two injections in a row. It is necessary to wait an interval of 20-30 minutes. Frequent use of aerosols is not recommended, it can become addictive, and in the future it will only worsen the situation, the heart rate may increase, blood pressure may change.
- If shortness of breath changes, it is necessary to take immediate action and do not wait for the situation to worsen.
- Frequent use of the inhaler is not recommended. This may lead to addiction to the drug.
It is worth remembering that after a severe attack of bronchial asthma you should immediately consult a doctor. Indeed, during an attack, the vesicles of the lungs may rupture, and blood may accumulate in the pleura, thereby causing severe shortness of breath and a new attack.
The most important thing is to recognize all the signs of the disease in time and begin treatment on time. To do this, you need to turn to a specialist for help in time, and not self-medicate, which can be life-threatening. Only comprehensive treatment and timely medical examinations can help cope with such a serious disease. Every person should know how asthma begins and its first symptoms.
Next Post
Previous Post
Prevention
The essence of preventive measures is to ensure normal ventilation of the lungs. Many techniques have been developed for this.
The main ones:
- A set of therapeutic breathing exercises that stimulate blood flow and saturate the blood with oxygen. The simplest example would be inflating 5-10 balloons every day.
- Non-exhausting physical activity that trains the heart, blood vessels and lungs. This could be light jogging, Nordic walking with ski poles along a proven route, swimming, or morning exercises.
- Have a medical examination every year.
Traditional recipes to help
To get rid of shortness of breath and facilitate the discharge of sputum, you can also use the following folk recipes:
- 10 g of licorice root and tricolor violet mixed with 40 g of thyme are infused in boiling water for 5-10 minutes, after which the resulting infusion is taken orally, you need to drink a glass a day in 4 servings;
- 10 g of anise fruit, nine-sil root, coltsfoot leaves, thyme and violet are also poured with boiling water and infused for 5-10 minutes, after which it is drunk according to the above principle;
- if it is not possible to make herbal decoctions to relieve an attack of shortness of breath, then you can drink one or two cups of strong coffee or tea;
Traditional recipes should be treated with caution, since the patient may also have an allergic reaction to some ingredients, which will not relieve shortness of breath, but will aggravate the attack.