How to recognize gastritis
Gastritis is a gastrointestinal disease in which inflammation affects the surface inside the stomach and mucous membranes. The disease can take on several forms and stages, each with its own symptoms. Common symptoms of all forms include:
- "Hungry" pains;
- Abdominal pain soon after eating;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Bad feeling;
- Dry mouth;
- Salivation.
For a more accurate diagnosis and determination of the type and form of gastritis, the child must undergo several procedures:
- Conducting a general blood and/or urine test of the child;
- Ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Detection of the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori;
- Determination of acid level in gastric juice;
- Gastroscopy.
Gastroscopy is the fastest way to find out about the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and identify diseases in this area. The procedure lasts only a few minutes and brings minimal inconvenience.
Symptoms of childhood gastritis
As noted above, children express their complaints in different ways - much depends on age. The task of mom and dad is to recognize the “first signs” in time and take appropriate measures. The most characteristic signs are:
- Drawing, persistent pain in the stomach area.
- If the child is hungry or, conversely, has eaten too much, the pain intensifies.
- The baby often burps, he experiences heartburn or sour belching.
- There is a burning sensation in the abdomen and frequent diarrhea.
- The lively mood gives way to sadness and apathy.
- Drowsiness appears and heart rate increases.
- Even calm children become nervous and irritable.
Types and forms of gastritis
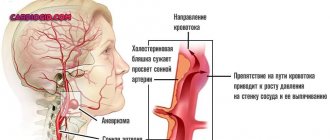
Gastritis has only two forms: acute and chronic. At the same time, gastritis can smoothly transition from the acute stage to the chronic stage (in the absence of adequate treatment).
Symptoms of the acute form appear a short time after eating low-quality food. An attack can also be triggered by taking medications, chemicals, or caused by bacteria. In the chronic form of gastritis, the walls of the stomach become thinner, normal acid production is disrupted and stomach cells lose their ability to regenerate. All this leads to digestive problems and ultimately leads to gastric atrophy. In this state, the stomach is no longer able to digest food.
We recommend watching a video about the causes of attacks of acute gastritis, which describes this type of gastritis in detail and accurately:
Types of gastritis differ in several ways:
- According to the nature of inflammation: catarrhal, fibrinous, corrosive and phlegmonous.
Catarrhal gastritis is characterized by a pinpoint location of lesions, swelling of the mucous membranes and thinning of the walls of the stomach in places of inflammation. Fibrinous gastritis is characterized by the appearance of a film on the walls of the stomach, as well as superficial and deep damage to the walls. Corrosive gastritis is characterized by the appearance of necrosis (death) on the walls of the stomach, as well as deep lesions of the mucous membranes and the appearance of ulcers. Phlegmonous gastritis is also called purulent.
- According to the number and location of lesions: focal gastritis and diffuse.
In focal gastritis, the lesions are located in single points, while in diffuse gastritis, large areas are affected over the entire surface of the stomach.
- By origin: bacterial, autoimmune, eosinophilic, reactive and idiopathic gastritis.
Bacterial gastritis is caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. Autoimmune disease manifests itself against the background of a decrease in the body’s resistance to external factors. The appearance of eosinophilic gastritis is possible in the presence of allergies. Reactive gastritis develops against the background of other diseases. Gastritis is called idiopathic when it is impossible to determine its origin.
- According to the acidity level: hypoacid, hyperacid, maintaining the same level.
Hypoacid gastritis is caused by a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid, while hyperacid gastritis is caused by an increase in the production of the same acid.
Children's gastritis. What kind of disease is this?
Any pediatrician knows that a child’s digestive system is formed before the age of seven. At this time, the acidity in the children's ventricle remains low. Gastritis is usually diagnosed at the age of 6-10 years. Like the “adult” disease, it has 2 forms. An exacerbation may occur against the background of infection, poisoning or a severe stressful situation. Any irritant can disrupt the well-functioning digestion process. With prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors, acute gastritis develops into chronic. Periods of exacerbation begin to alternate with remissions.
Doctors are sounding the alarm. In recent years, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract have become the norm for high school students. Teenagers are very worried about final exams and are more likely to buy fast food. The result of this lifestyle is stomach problems that do not go away for years.
Causes
The appearance of childhood gastritis can be due to a number of reasons. Among the most common:
1. Poor nutrition. Children who are transferred to “adult” food too early are especially susceptible to the occurrence of gastritis. Frequent consumption of fried foods, smoked foods, salty, canned and spicy foods negatively affects the child’s not yet stable fermentation system. Excessively frequent intake of the wrong foods leads to irritation and inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
2. Changing the correct frequency and balance of nutrition. Frequent snacking, dry food, and the absence of thermally processed foods in the diet lead to negative changes in the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
3. Poor nutrition. Often, busy mothers or fathers are not able to have time to prepare a full lunch or dinner. Therefore, preference is given to quickly preparing semi-finished products.
4. Lack of a quiet place to eat. Today, many children are accustomed to eating in front of TV or computer screens. Information flowing from the screen interferes with the normal functioning of the stomach, which is why food is poorly digested, and all the prerequisites for the appearance of gastritis appear.
5. Stress and nervous tension. Intensive work at school, quarrels with friends or parents - all these situations can cause stomach cramps or circulatory problems in the child. These conditions are the first steps to gastritis.
6. Infection with bacteria. The insidious bacterium Helicobacter pylori lies in wait for a child almost everywhere: from the school desk to the door handle to the apartment. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the child’s hygiene: so that he washes his hands after coming from outside and before each meal.
7. Genetic predisposition. The risk of a child getting gastritis is much higher if there are close relatives suffering from this disease.
Reviews
My son is 10 years old. A month ago, he came up after dinner and said that his stomach hurt. It didn’t go away until the morning, and we went to the pediatrician. The doctor ordered tests and suspected gastritis reflux. The gastroenterologist's assumptions were already confirmed. We were treated with porridges and soups, took No-Shpu for children, Metronidazole (bacteria were found) and Bifiform to restore the microflora. The boy felt much better and was healthy after 2 weeks.
Oksana, 32 years old
My daughter was very worried about the testing and was constantly worried. The result was gastritis, although I warned her not to forget to eat regularly. She had terrible pain and heartburn. Fortunately, I found a good gastroenterologist and cured her quickly. And he advised me to go to a sanatorium next spring to avoid exacerbations. Let's do so. We still follow the diet.
Lisa, 44 years old
It is difficult to understand what exactly is bothering a baby when he is only 1.5 years old! The pediatrician immediately said that the causes of insomnia and constant crying could be related to the stomach. We took tests. They reported that the gastric mucosa was indeed inflamed. We took medications that are allowed for children, and we were also advised to take sea buckthorn oil. The inflammation has subsided, my son no longer cries and sleeps peacefully. The pain went away, it helped us!
Katyusha, 27 years old
Treatment of gastritis in children
In order to save a child from an unpleasant disease, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of gastritis. After identifying the type of disease, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
In children, treatment is based on a strict diet, which relieves the stomach and allows it to recover. However, there are times when serious drug treatment is necessary.
In order to relieve the symptoms of the acute stage of gastritis, the following procedures are carried out:
- From the first days of an attack of gastritis, it is necessary to provide the child with bed rest;
- In the first few hours, the child should be given small amounts of water to drink frequently;
- If nausea or vomiting is present, the stomach should be rinsed and a remedy for discomfort should be taken (Motilium, for example);
- If the abdominal pain is severe, you can take a drug that relieves cramps - No-shpu (Drotaverine) or Papaverine;
- 12 hours after the onset of an attack, you can give your child low-fat kefir or porridge, homemade jelly, low-fat soups and pureed vegetable purees;
- To reduce the amount of gas in the stomach, you should use proven drugs such as Enterosgel or Smecta. Regular activated carbon is also good for such purposes;
- Ranitidine is prescribed to reduce acid production. Analogue of the drug: Famotidine;
- During the entire treatment period, you must follow a strict diet.
If the acute stage has progressed into the chronic phase, treatment will be much longer and more difficult:
- Provide bed rest;
- Avoid any stress, excessive physical activity and nervous situations;
- Provide sufficient time for sleep and rest;
- Limit watching TV and time spent on the computer;
- Monitor your child's diet. Strictly follow the diet prescribed by the doctor and ensure that the child chews food thoroughly;
- Avoid long breaks between meals and snacks on dry food;
- From the first days, the doctor prescribes vitamins A, B1, B2, B6 and C;
- The doctor may prescribe a solution of hydrochloric acid, pancreatin, abomin (treatment with such medications is carried out in a hospital);
- To relieve severe pain, the following medications are recommended: atropine sulfate, belladonna preparations, Papaverine, No-shpa and others;
- In case of increased excitability of the child, sedatives are prescribed: valerian or sodium bromide. In rare cases, with severe agitation, the use of tranquilizers is permissible: trioxazine or seduxen;
- If the level of acid in the stomach is high, the following are prescribed: Almagel, sodium bicarbonate, Vikalin;
- Steroid hormones are prescribed to children with concomitant anorexia, asthenia and poor nutrition (methylandrostenediol, nerabol);
- With elevated levels of hydrochloric acid, quaterone, pyrylene and benzohexonium are prescribed with caution;
- If gastritis develops against the background of another disease, the first thing the child is treated for is the disease - the cause of gastritis;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures for chronic gastritis include: electrophoresis of novocaine, platyphylline and magnesium sulfate, as well as paraffin applications;
- For children whose disease is in remission, it is useful to drink mineral water (Essentuki No. 4, No. 17), as well as undergo treatment in sanatoriums;
- To relieve inflammation, it is useful for children to give decoctions of chamomile and other medicinal herbs. However, it is worth remembering increased sensitivity and dosage.
Alternative medicine for gastritis with high acidity
When the inflammatory process in the stomach is accompanied by an increased level of acidity, the following alternative medicine recipes can come to the rescue:
- A decoction based on elecampane roots. Take 15 g of raw material, add a glass of hot water. Set on low heat for 15 minutes. After cooling, filter the solution and take ½ cup 3 times throughout the day.
- A decoction of calamus roots. Add 19 g of raw materials and a glass of boiling water to the container. Set on low heat, cook for 15 minutes. Take ¼ cup 3 times throughout the day. This remedy allows you to quickly cope with heartburn.
- Tincture of mullein flowers. Take 10 g of raw material, add a glass of hot water. Leave for half an hour. Take a dessert spoon at times throughout the day.
- Tincture of calendula flowers. Pour 10 g of raw materials into glasses of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes and take 10 ml 3 times throughout the day.
- Tincture of marshmallow root. Pour 6 g of raw material with a glass of hot water. Filter and take a dessert boat 3 times throughout the day.
- St. John's wort decoction. Pour 10 g of herb with a glass of boiling water. Set on low heat, cook for 15 minutes. After cooling, filter. The general daily dosage is a glass, consumed in 3 doses. The therapeutic course will be 2 months, with a rest period of 1-2 weeks.
- Melissa infusion. Take 10 g of raw material, pour a glass of boiling water. Wait 30 minutes, filter. Use the entire amount throughout the day.
- Mint infusion. Take 10 g of raw material, pour a glass of boiling water. Use 10 ml of purified product throughout the day.
- Infusion of flax seeds. Pour 10 g of raw material into a glass of boiling water. Take the purified infusion 20 ml 3 times throughout the day.
- Potato juice. This remedy will help you get rid of heartburn, vomiting, and nausea. But only juice from red varieties will do. On an empty stomach, consume the product in an amount of 50-100 ml.
- Sea buckthorn. Take 60 g of fruits, add 2 cups of hot water to them. Set on low heat and simmer for 10 minutes. Consume 2-3 glasses per day.
- Aloe juice. The daily intake will be 40 ml, consumed in 2 doses. The therapeutic course will be 2 months.
Diet for a child
The basis of treatment for any type of gastritis is proper balanced nutrition and a diet that is gentle on digestion. The diet is based on several principles:
1. The temperature of cooked food should be medium. Food that has cooled or “just off the heat” should not be given;
2. Cooking should be done by steaming, boiling or baking;
3. The child should eat 5-6 times a day;
4. Too long breaks are unacceptable;
5. The child’s breakfast should be complete - you can give liquid porridge, omelettes or casseroles;
6. At school or kindergarten, the child should eat yoghurt, fruits, vegetables or boiled chicken;
7. For gastritis, it is advisable to grind food into gruel or puree. Eating solid food is not advisable;
8. Do not force a sick child to forcefully eat food or insist on him eating large portions;
9. There is no need to feed your baby at night.
Since gastritis can only appear in children starting from the age of three (that is, when the child is already eating adult food), dietary recommendations will be the same for all ages. The exception is those cases when the diet and composition of the diet are determined by the doctor.
An example of a child's menu:
Breakfast: any cereal, milk, yoghurt, tea, omelettes.
Snack at school or kindergarten: fruit, boiled veal or chicken meat, whole grain bread, vegetables, yogurt, low-fat milk, homemade jelly or weak sweet tea.
For lunch: weak broth with homemade croutons, vegetable puree soup, berry juice, compote or jelly. You can make meatballs or small steamed cutlets. Boiled or steamed fish is acceptable.
Afternoon snack: milk, fermented baked milk or yogurt, whole grain bread, berries, fruits.
Dinner: cottage cheese dishes (casseroles, steamed cheesecakes or pancakes with cottage cheese), stewed vegetables, porridge, herbal tea, rosehip infusion.
Six of the most effective treatments
The effectiveness of a particular treatment regimen for childhood gastritis is determined by a gastroenterologist. The choice of therapy depends on many factors, but should be under the strict supervision of a physician.
- If the main cause of the disease is a bacterial infection (Helicobacter pylori), antibiotic therapy is prescribed. It is eradicative in nature.
- If the production of hydrochloric acid is abnormally high, everything possible must be done to reduce its level.
- Dietary food is prescribed.
- You can achieve a positive result with the help of physiotherapeutic treatment.
- Drug therapy.
- Visit to the sanatorium area.
Now let's take a closer look at the treatment methods listed above.
Eradication therapy
Most often it is prescribed to suppress an outbreak of Helicobacter bacteria. Helps level out the bacterial background and improve the functioning of the stomach. It consists of several drugs belonging to the class of antibiotics and penicillins. For example, Omez, Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin. Taking antibiotics lasts no more than 7 days.
Diet
The composition of food plays a fundamental role in the treatment of gastritis in the youngest patients. This is especially true for cases of acute gastritis, when you need to quickly relieve inflammation and eliminate pain. Food products are ground to a puree, and all kinds of porridges are prepared.
The strict diet is maintained for 14 days. And then they follow the so-called “juice” diet for 2 months. During the dietary period, the child is gradually taught proper nutrition and healthy food. This is how you develop the habit of eating in small portions.
In case of exacerbation of gastritis, it is strictly forbidden to cook dishes with the addition of seasonings and hot spices. They are a strong irritant to the delicate mucous membrane of the children's ventricle. Parents should control their salt and sugar intake. Moderately warm food has a beneficial effect on the healing process. Whereas too hot or cold foods only increase irritation.
Valuable advice! General recommendations regarding diet are as follows. Meal frequency – at least 5 times a day, in modest portions. Ask your child to chew each bite thoroughly. Optimal cooking options: boiling, steaming, grinding in a blender. We sharply reduce the amount of fresh vegetables. Because the fiber they contain is like sandpaper for an inflamed stomach. Mushrooms in any form, fatty meats, and soda are completely removed from the diet. We'll have to endure a little without chocolate and sweet pastries.
When the acidity level is elevated, strong broths, sour juices, and fruits are temporarily excluded. They are replaced with non-acidic dairy products, all kinds of cereals, and soups. In case of insufficient secretion, on the contrary, they focus on meat broths, fermented milk products and juices.
Medicines that will definitely help
Before heading to the pharmacy, discuss treatment for childhood gastritis with your doctor. You should not give children everything, because the choice of a specific medicine is dictated by the patient’s medical history, type of gastritis and other factors.
- Low acidity: enzyme-containing drugs, pantaglucide (relieves spasms, inflammation).
- Affected mucous membrane. Suitable for its restoration: lipoic acid, pantothenate, herbal medicine.
- Increased acidity: adsorbents, drugs aimed at reducing secretory function.
- Severe pain: antispasmodics and analgesics, mineral water.
Physiotherapy
It is quite possible to cure gastritis in a child using modern methods of physiotherapy. Exacerbations accompanied by severe pain are relieved with laser therapy and ultrasound waves. In a state of remission, the greatest effectiveness is demonstrated by electrophoresis, calcium intake and preparations containing B vitamins.
Traditional methods of treatment
Sea buckthorn oil, flax seed decoction and cabbage juice are the three “pillars” of effective gastritis therapy.
- The oil obtained from sea buckthorn berries contains many vitamins B and E. It promotes the healing of wounds and erosions and eliminates inflammation. Recommended dosage – 1 tsp. twice a day before meals. Drink the oil for 30 days, take a break and repeat the intake.
- The decoction obtained from flax seeds has a thick consistency. It gently envelops the walls of the stomach. Inflammation and pain go away within a few days. To prepare a medicinal decoction, just pour 2 tsp. a glass of boiling water, leave for 12 hours. Drink 1/3 glass in the morning, then repeat at lunchtime and in the evening. The duration of therapy is 30 days.
- Fresh cabbage juice perfectly restores the mucous membrane and contains many nutrients. Traditional healers prescribe it for ulcerative gastritis. The treatment regimen is as follows. For the first week, drink 1/2 juice per day mixed with the same amount of water. Divide the glass 4 times. The next week they drink a glass, but in a ratio of 1:2. For the third week, children drink cabbage juice with water 2 times a day in a 1:1 ratio.
Possible complications
Gastritis itself is not a serious disease. However, it is important to remember that when the disease starts, it threatens with very unpleasant consequences, namely, thinning of the walls of the stomach can lead to the formation of ulcers and the occurrence of peritonitis (the contents of the stomach will be released into the abdominal cavity).
In particular, corrosive gastritis can threaten a child with problems with the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and liver. In addition, asphyxia, gastric bleeding, shock and, as a result, death may develop.
Gastritis in children is much more treatable than in adults. Most often it is done without medications. Changing your diet and following a diet can bring your gastrointestinal tract back to normal without resorting to medications. That is why it is so important to notice the first signs of illness in time. It is better to avoid unhealthy foods and eliminate the possibility of bacterial infection to prevent gastritis in children.
Preventive measures
To prevent the treatment of gastritis from taking many months, the disease is much easier to prevent. It’s not that difficult to do this – just follow preventive measures:
- Do not allow your child fast food in any form. Many children love going to McDonald's because they can enjoy crispy fries, sweet drinks and hamburgers. However, such food has a detrimental effect on the digestive system, especially of the younger generation.
- Make sure your child eats regularly. Portions should be small, and the atmosphere should be comfortable and conducive to leisurely eating.
- No cold or fresh-from-the-oven foods! Food should be warm.
- It is not recommended to change the milk formula too often.
- At least once a year, have your child examined by a pediatric gastroenterologist.
Symptoms
The symptoms of most diseases are divided into general and specific. Common symptoms of gastritis include weakness, apathy, pale skin, weight loss, increased body temperature, increased irritability, white coating on the tongue, nausea and bowel movements.
Specific symptoms are considered to be:
- pain in the upper abdomen 2 - 4 hours after eating;
- heartburn;
- heaviness and discomfort in the projection of the stomach;
- frequent belching and bad breath;
- unconscious refusal to eat;
- nausea is accompanied by vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- quick satiety during meals;
- burning sensation throughout the abdomen.
If three general and one local symptoms from the proposed list appear, you must contact the clinic for a full examination.
List of approved products
The indicated diets do not always take into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body, which is more prone to the same allergic reactions. Parents need to constantly note the slightest changes in the child’s behavior in order to adjust the diet in time.
The following foods and dishes are allowed:
- Boiled meat with low fat content, veins and small bones. Veal, poultry, and beef tongue are best suited. You can prepare various dishes for children by grinding it into minced meat or pate. It is also baked with vegetables in foil or cooked in a double boiler;
- First courses with “second” meat broth or vegetable soups;
- Side dishes are in the form of ground porridges such as oatmeal or rice, which contain a lot of starch. It is boiled to a semi-liquid state - this provides a soft envelopment of the inflamed mucous membrane;
- Fillet of low-fat fish (hake, pollock, flounder) can be used to prepare soufflés or steamed cutlets;
- It is best to use chicken or quail eggs. At the same time, they are made in the form of light omelettes or boiled soft-boiled;
- Vegetables must be peeled from thick skins. Best served boiled or as a puree;
- Non-acidic fruits. They can also be baked or made into purees, jams or jelly;
- Low-fat fermented milk products in any form;
- Honey in small quantities if tolerated;
- Herbal teas and decoctions, if there are no contraindications;
- Fresh fruit and vegetable juices;
- Homemade milk sausages.
Breakfast should be nutritious but light. For this meal, it is best to avoid the following items:
- Bananas and citrus fruits. They contain a large amount of acids and nutrients that the stomach will simply not be ready for immediately after waking up, when the mucous membrane is most vulnerable;
- Raw vegetables;
- Sweets, including homemade ones;
- Meat.
It must be followed by an afternoon snack. At this time, you can give your child any fermented milk drink, cookies or baked apple with honey. There is a first course for lunch every day, and meat with a side dish for dinner.