Paronychia (paronychia) is an inflammation of the periungual fold, which most often occurs on the hands, but sometimes develops on the feet (especially the big toes). Paronychia begins with infection in the soft tissue of the finger when the periungual fold is cut, a manicure or pedicure is performed with poorly disinfected instruments, or incorrect removal of hangnails. Inflammation of the nail folds on the hands can be caused by exposure to household chemicals or active substances in the workplace. The soft tissues of the nail phalanx of the big toe are injured by constantly wearing tight shoes, which can provoke the development of paronychia.
After infection enters the subcutaneous tissue of the periungual fold, redness and slight swelling appear at the base of the nail, which causes pain when pressed. If treatment for paronychia is not started in time, the inflammatory process in the cushion continues to develop and pus accumulates at the site of inflammation, which gradually leaks into the nail bed area and grayish or greenish-yellow spots are clearly visible through the transparent plate. Purulent inflammation of the tissues of the nail phalanx of the finger can cause damage to the growth zone (matrix) of the nail and the abscess will provoke the growth of a deformed nail plate.
Paronychia of the finger at the initial stage can be easily cured at home using external means. If a strong abscess with suppuration appears near the nail, be sure to consult a doctor so that a specialist can take a smear of purulent discharge for microbiological examination and identify the pathogen that caused inflammation of the periungual fold. After identifying the causative agent of the purulent process (most often it is staphylococcus), the doctor prescribes a course of treatment for paronychia using antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
♦ VARIETIES OF PATHOLOGY
❶ Simple. As a rule, the cause of the disease is minor injuries to the nail phalanx of the finger. The soft tissues around the nail plate become inflamed, moderate swelling is accompanied by redness and mild discomfort when pressed. In rare cases, peeling appears around the nail, but there is no suppuration and the abscess does not spread to the nail bed;
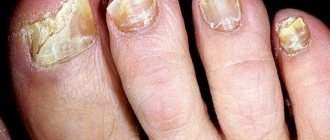
❷ Tourniol. Candidiasis is a type of paronychia that affects both the fingers and toes. Damage to the periungual fold is accompanied by infection of the soft tissues with a fungal infection of the genus Candida. The inflammation is moderate without significant swelling, but suppuration gradually appears and the thin layer of skin at the base of the nail plate (eponychium) disappears. If treatment is not started in time, the fungus affects the nail plate, which begins to turn yellow and become deformed;
❸ Pyococcal. A pyogenic infection (streptococci, staphylococci) penetrates into the damaged roller and the soft tissue around the nail rapidly swells, and after a while a purulent yellowish abscess forms around the plate, when pressed on it a throbbing pain appears. The surgeon opens the abscess, frees the inflamed nail phalanx from pus and applies a bandage. Further treatment of purulent paronychia continues at home;
❹ Ulcerative. The development of erosive (ulcerative) paronychia can be caused by both active chemicals and pathogenic bacteria. The inflamed cushion near the nail becomes covered with small ulcers, which cause pain and itching. A secondary infection can join the disease and provoke the development of purulent inflammation;
❺ Psoriatic paronychia. Inflammation of the periungual fold can cause psoriasis, the development of which affects the functioning of the matrix. Vesicular rashes appear around the nails, which are destroyed and dried crusts form on the inflamed skin. Serous-purulent fluid oozes from a scaly abscess next to the nail;
❻ Horny paronychia. Excessive thickening of the stratum corneum around the nail is accompanied by papular rashes. The nail fold swells moderately, cracks appear on the keratinized skin and the cuticle becomes inflamed.
♦ TREATMENT OF PARONYCHIA
• Opening of the abscess. Surgery is required to remove pus from an inflamed abscess near the nail plate. Using a scalpel, the surgeon opens the abscess (using an anesthetic injection), cleans the inflamed cushion from pus and applies a bandage with a tampon soaked in an antibacterial agent. After a day, the bandage can be removed and treatment of paronychia can be continued at home using medications prescribed by a doctor; • Products for external use. You can relieve inflammation and get rid of pain using compresses with tampons soaked in chlorhexidine solution. It is also useful to treat inflamed areas near the nails with ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol, tetracycline ointment (after opening the abscess).
Causes and mechanism of development of paronychia
The direct cause of the disease is the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the skin. Bacteria enter through small cracks in the skin injured during manicure, when exposed to chemical agents or high temperature. Paronychia often occurs as an occupational pathology in agricultural workers, builders, cooks, hairdressers, factory workers and other people whose profession involves constant trauma to the skin of the hands.
The process goes through two stages: infiltrative and purulent. At the onset of the disease, redness is observed in the area of the nail fold. At the site of skin damage, a slight swelling develops, and intercellular fluid gradually accumulates, in which pathogenic bacteria are located. As the fluid accumulates, it peels off the nail fold, causing a blister to form. The contents of the vesicle quickly turn from transparent to purulent, which is due to the death of a large number of leukocytes and bacteria.
In the absence of treatment, the process develops in two directions. First: breakthrough of the abscess, cleansing of the wound from granulations and gradual healing. The second direction: progression of the process with penetration of infection into the deep layers of the skin, spread to muscles, tendons and bone tissue with the development of osteomyelitis. In addition, pus can penetrate into the tendon sheaths of the finger, and from there onto adjacent fingers and the hand.
Frequent causative agents of paronychia are pyogenic streptococci, candida, and staphylococci.
Why does paronychia appear?
The skin of the hands and feet is much stronger than the skin on other parts of the body. This is due to the fact that the arms and legs “are in contact with the outside world” and are subject to negative influences. And this can be said about the palmar and plantar surfaces of the hands and feet, but not about the skin next to the nail. It is soft and easy to injure.
Paronychia of the finger on the hand occurs for a number of reasons. The most common etiology is injury to the nail folds. For example, getting hit by a splinter. Another reason is exposure to chemicals. Not necessarily aggressive options; paronychia can be a consequence of the influence of washing powder or dishwashing detergent.
Paronychia can be caused by a fungal infection or failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. Paronychia on the legs can occur due to wearing tight and narrow shoes.
In some patients, inflammation is an occupational disease. The risk group includes:
- Surgeons (treat the skin before surgery with antiseptics, which are quite aggressive).
- Shoemakers (regular contact with glue).
- Employees of chemical laboratories.
- People who frequently hand wash in hot water.
Paronychia is an inflammation that is a consequence of improper treatment of the periungual fold during pedicure/manicure. In 99% of cases, inflammation occurs along with a secondary infection. The most common pathogens include fungi, pyogenic bacteria, streptococci and staphylococci. If an infant is sick, the pathogenesis is often based on a bacterial infection.
In its development, paronychia goes through several stages. This is infiltration (inflammation, which is characterized by an increase in tissue density), accumulation of pus, its release to the surface, cleansing of purulent masses (very rarely occurs on its own) and filling the cavity with new tissues.
Classification of paronychia
There are several types of paronychia:
- According to the phase of the process: serous-infiltrative and purulent.
- According to the location of the primary inflammatory focus: superficial and deep.
- According to the duration of the disease: acute and chronic paronychia.
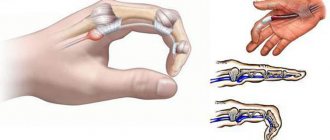
With superficial paronychia, the process is localized directly in the thickness of the periungual ridge, and a deep-lying lesion appears in the thickness of the tissue at the base of the nail. In the absence of treatment for deep paronychia, the process penetrates under the nail and it gradually peels off. Peeling of the nail plate with paronychia of the finger, or subungual panaritium, is the most common complication of this pathology.
Symptoms of paronychia
Paronychia of a finger occurs on an arm or leg a few days after a small wound becomes infected. At the site of injury, the skin turns red and gradually swells. As the disease progresses, the skin peels off and fluid appears in the resulting blister. More often, the contents of the bladder are yellowish in color, and blood is often mixed with pus.
The damaged area hurts, at first the pain is paroxysmal in nature, but gradually its strength and duration increases. The pain intensifies at night.
Chronic paronychia differs from acute paronychia in its slow course with mild symptoms of the disease. The pathology occurs with alternating phases of exacerbation and remission. Often, chronic inflammation of the periungual fold occurs in old age and as an occupational pathology.
Treatment
What can you do
This disease should not be left to chance. At first glance, some parents think that there is nothing wrong. The skin around the nail turns red, and the child complains of pain. But if the pathology is started, the process will lead to quite dangerous complications and then the doctor will be forced to open the source of pus surgically. Therefore, at the first symptoms you should consult a specialist. An experienced doctor will give recommendations and in a few days there will be a noticeable improvement. The most important thing is to follow the doctor’s advice and prevent the acute form from becoming chronic.
What does a doctor do
Treatment depends on the stage of the disease.
If the doctor diagnoses the very beginning of the inflammatory process, he recommends various topical agents: ointments, balms, anti-inflammatory creams.
If suppuration appears, the specialist opens the lesion, cleans the wound cavity and applies a special bandage. The little patient may have to take a course of anti-inflammatory medications. This depends on the identification of a particular pathogen during diagnosis.
Surgery may be necessary if conservative therapy does not help or when the disease is advanced. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia and takes little time. Then the patient will have to go for a dressing change. During the operation, the doctor has to remove part of the nail plate. After healing, a new one gradually grows in place of the old nail.
How to treat paronychia?
Treatment of the disease consists of opening the abscess and cleaning the wound. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. In some cases, a small abscess is opened without anesthesia.
If there is a threat of spread of the process or a chronic course of the disease, antibiotic therapy using broad-spectrum drugs is prescribed. Pain syndrome is relieved by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics. Drugs are selected individually.
Treatment of candidal paronychia involves the use of ichthyol and antimycotic drugs. Ichthyol applications are carried out once a day until the inflammatory reaction disappears, then an ointment with an antimycotic (ketoconazole, isoconazole and others) is applied to the damaged area 2 times a day. If local treatment is ineffective, systemic antimycotic drugs (fluconazole, nizoral and others) are used for a course of 2-4 months.
Drug treatment of paronychia
Treatment largely depends on the etiology and form of the pathological process, the presence and absence of an infectious agent, fungal infection. In therapy, products for internal use (tablets), antiseptic solutions, anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments and creams are used.
Antibiotics
If diagnostics show that the cause is bacteria, then antibiotic therapy cannot be avoided.
The duration of the course varies from 7 to 14 days.
Antibiotic drugs with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity are usually used.
To treat paronychia, the antibiotics presented in the table are prescribed:
| Drug name | Active substance | Mode of application | Contraindications |
| Erythromycin | Erythromycin | An adult is prescribed 200-400 mg every six hours. If necessary, increase to 4000 mg per day. Children 40 mg per kg of weight. | Significant hearing loss, hypersensitivity, pregnancy, arrhythmia, lactation. Be careful with kidney pathologies. |
| Cephalexin | Cephalexin | The average dose for an adult is 250-500 mg every six hours. The tablets are taken half an hour before meals. | Intolerance, pregnancy, lack of sucrase in the body. Caution against the background of renal failure. |
| Tetracycline | Tetracycline hydrochloride | 250-500 mg 4 times a day or 500-1000 mg twice a day. Children over 8 years of age are prescribed depending on weight and the interval between applications. | Children under eight years of age, pregnancy, kidney and liver pathologies, leukopenia. |
Dosages are indicated in accordance with the instructions for the drugs; they may differ from the doctor’s recommendations.
Local processing
Paronychia on the leg or arm must be treated using local remedies. Antiseptic solutions are prescribed. Frequency of application – up to three times a day. Treat the inflamed cushion with drugs - Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, brilliant green.
Between manipulations, Ichthyol ointment can be applied. Multiplicity up to 3 times a day. It is placed under a bandage. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Treatment for fungus
If there is an advanced form of the fungus, antifungal tablets are used to cure paronychia.
- Intraconazole. It contains a substance of the same name in a dosage of 100 mg. Release form: capsules. The product has an antifungal effect. The dosage depends on the type of pathogen and the clinic. Treatment lasts from several weeks to a couple of months.
- Fluconazole. The dosage is 250 mg per week. The reception lasts for several months.
Additionally, local remedies are used in the treatment course - Clotrimazole cream, Akriderm, Miconazole, Mycostop. Apply to the affected area 1-3 times a day. The course of therapy varies from 2 to 4 weeks.
Drugs to prevent secondary infection
The drug treatment regimen often includes drugs designed to prevent the development of a secondary infection. Prescribe local medications in the form of cream, solution, powder and ointments:
- Levomekol ointment is applied in a thin layer to the affected area. The treatment course is up to ten days.
- Baneocin (powder). Apply under a bandage up to 4 times a day. The maximum daily dosage of powder for an adult is no more than 1000 mg.
- Dioxidin (ointment). Apply to the nail and skin once a day. Therapy lasts 21 days.
To eliminate suppuration, use Vishnevsky ointment. Apply only under a gauze bandage. Change 2-3 times a day. Use up to 20 days is allowed.
Surgery
When conservative therapy does not produce results, the disease progresses, the abscess has to be opened to prevent complications. The most commonly used surgical procedure is called the Quenewell procedure.
The essence of the intervention is that the surgeon exposes the corner of the nail plate, removes purulent masses and pathological tissues, and installs drainage. After the operation, a wound remains. To speed up regeneration processes and prevent infection, ointments and solutions are prescribed - antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antibiotics (listed above).
The operation requires care, since damage to the nail bed leads to further deformation of the nail.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of paronychia at home is possible only at the first signs of the disease. If there is swelling of the periungual fold, wash the inflamed area in warm water using antibacterial soap. Then antibiotic ointments are applied or the area is treated with iodine solution or brilliant green (brilliant green).
Propolis is heated in warm water, kneaded between fingers, turning the lump into a flat cake. The resulting cake is applied to the sore spot several times a day for a couple of hours.
If the process progresses (formation of a vesicle with pus) or if traditional methods of treatment are ineffective, it is necessary to stop the procedures and seek help from a doctor.
Reasons for the development of the disease
- Fungal disease of the feet, hands and nails.
- Breaking a hangnail.
- Having a bad habit of biting your nails or sucking your fingers.
- A poorly done manicure.
- Getting a splinter under the nail.
- Nail injury.
- Using tight shoes.
- Frequent contact with chemicals.
- Ingrowth of the nail plate into soft tissue.
Treatment of paronychia
- Pour the white of 1 egg into a container and add 96% medical alcohol to it until the first component begins to turn into flakes. Strain the resulting mixture, wrap the separated flakes in gauze and apply to the sore spot for at least 7 hours. After the allotted time, change the bandage and apply a new one. The duration of treatment is 3-5 days until the symptoms of paronychia completely disappear.
- You can relieve pain using a simple recipe: combine 50 grams of warm water and a pinch of vitriol. Dip the damaged finger into the mixture and hold for several minutes.
- A simple kombucha compress will help get rid of paronychia.
- Add 2 tablespoons of soda to a cup of hot water and dip your finger in it. After the procedure, lubricate the sore spot with iodine. Repeat the procedure several times a day until complete relief occurs.
Disease prevention
You can prevent the development of paronychia yourself by following simple precautions:
- Keep your nails clean and tidy.
- Give up the bad habit of biting your nails and licking your fingers.
- Use special rubber gloves for working in the garden and around the house, especially when in contact with chemicals.
- Carefully monitor your chronic diseases, in particular diabetes mellitus deserves special attention.
- Treat your hands with disinfectants and antiseptics.
- Disinfect manicure tools before use and be extremely careful during the procedure. Visit only experienced craftsmen who know all the intricacies of the matter and carefully monitor the disinfection of their equipment.
- Trim your nails promptly to avoid ingrown nails.
Paronychia is a disease that affects the nail plate and the skin around it. This disease causes unpleasant symptoms and discomfort. Paronychia is treated with surgical intervention, otherwise there is a high risk of complications, including amputation of the phalanx of the finger.
Source: https://24doctor.info/disease/paronikhiya/
Prevention of paronychia
Preventive measures include using protective gloves when washing dishes or in the workplace. During a manicure, it is not recommended to completely remove the cuticle, but to push it aside. In addition, the manicure and pedicure procedure is carried out with well-sharpened and clean instruments for personal use. When visiting nail salons, it is recommended to ensure that sterile instruments are used.
Suppuration in the area of the nail plate is not only painful, but also not aesthetically pleasing. The result of treatment depends on the exact diagnosis. To do this, you need to carefully approach the symptoms. Each type of paronychia has its own characteristics. Knowing this, treatment can be directed in the right direction.
Prevention
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to wash your hands more often, especially if your occupation involves contact with chemicals and the risk of minor injuries - cuts, hangnails, etc.
When doing a manicure at home or with a professional, you need to ensure that the tools are properly disinfected, since there is a risk of not only paronychia, but also nail fungus. You can’t completely cut off the cuticle, just like you can’t cut your nails short or bite them.
If there was inflammation of the periungual fold on the foot, it is advised to be more careful in choosing shoes - they should be the right size and made of high-quality materials and socks - it is better to give preference to natural fabrics.
Paronychia: definition
The process of inflammation of the folds of skin on the sides of the nail is called paronychia. It is classified as a dermatological disease and is acute. In rare cases, it becomes chronic.
Women are most often affected. But even men with children are diagnosed with periungual paronychia at least once in their lives.
- without suppuration;
- with suppuration;
- with loss of nail;
- with infection of deep muscle tissue (tendinitis);
- with melting of the phalanx of the nail cavity due to purulent exudate.
In any case, this condition causes painful discomfort. The quality of life is impaired.
Classification and symptoms of manifestation
In dermatological circles, paronychia of the periungual plate is considered a disease with a variety of types and a distinctive clinical presentation.
In 90% of the population the disease occurs in an acute form. Location: dorsum of the fingers, turning into the palm. The infection can penetrate deep into the internal tissues of the finger or affect the entire hand.
Simple
It appears as a separate disease, or as an initial symptom of other types of paronychia.
The reasons may be:
- mechanical injuries;
- negative effects of temperatures;
- infection of damaged areas (not purulent).
- inflammatory process (moderately expressed);
- swelling (mild);
- pain (moderate intensity).
Early symptoms
In its development, paronychia goes through several stages. Each has its own clinical manifestations.
- Infiltration. The inflammatory process causes tissue compaction. Redness and swelling of the nail plate occurs.
- Suppuration. Inflammation leads to tissue death. They, mixing with particles of lymph, begin to rot. Severe pain appears around the finger, and a clearly visible swelling forms. A bubble grows in its place.
- Permission. The skin over the blister becomes thinner, breaks, and pus flows out. When pressing on the affected area, the discharge of pus intensifies.
- Cleansing from purulent contents. After the pus has completely drained from the phlyctena cavity, an ulcer forms in its place. Over time, it becomes crusty. When it disappears, the abscess cavity is filled with tissue.
An experienced doctor, upon examination, can distinguish pyococcal paronychia from candidal paronychia. If the cause of infection is staphylococci and streptococci, sharp pain occurs, the boundaries of the lesion are unclear, and pus is abundant.
If the cause of paronychia is a fungal infection, the eponychium, the thin layer of skin covering the nail, disappears. The back cushion begins to overhang, and when you press on it, a cheesy discharge is released.
Clinical manifestations in an advanced stage
In advanced stages, the purulent inflammatory process can spread deep into the epidermis, affecting the lower dermis and bone tissue. At this stage, symptoms of various pathological processes may appear.
If inflammation reaches the skin tissue, phlegmon develops. Damage to the tendon sheaths causes tenosynovitis. When bones become infected, osteomyelitis appears. But the most dangerous thing is sepsis, blood poisoning.
How is paronychia of the finger treated?
Although adults are most affected, children are also diagnosed with paronychia.
In children
An individual approach is used in treating a child. Treatment methods for pediatric patients are no different from those for adults. First, eliminate the root cause.
Of great importance are: age, weight, duration of the inflammatory process. This allows the attending physician to adjust the prescription: how many times a day to apply the ointment, how many grams of ointment to use.
Particular attention is paid to antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs. They must be appropriate for the children's age group.
In adults
To cope with the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, and each type of paronychia has its own. The purpose will be different:
- Simple - local treatment. Antiseptics (ichthyol ointment) are used.
- Pyococcal or purulent - surgical opening, drainage for washing with antiseptics. Mandatory therapy with antibiotics from the penicillin group.
- Candidomycotic - treatment with antifungal ointments Clotrimazole.
- Ulcerative - first, anti-inflammatory ointments, then avoid contact with the irritant, wear protective gloves.
- Horny and paronychia caused by psoriasis - treatment is based on eliminating the underlying cause. Additionally, corticosteroids are used locally. Physiotherapy includes irradiation of lesions with ultraviolet light.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out in the hospital:
- Aniline dyes.
- Baths with the addition of potassium permanganate.
- Chlorhexidine compresses.
- Wet dressings soaked in furatsilin.
Treatment should begin at the first symptoms of inflammation. For example, soak your hands in a warm solution: water and antibacterial soap. Duration: 15 minutes.
Treat with any antiseptic.
Reasons for appearance
More pathogenic microorganisms accumulate on human hands than on other parts of the body. Any crack, abrasion, or wound located next to the nail can cause pathogenic bacteria to penetrate deep into the epidermis. If infection with fungi, staphylococci and streptococci becomes possible, a purulent-inflammatory reaction develops, causing severe pain.
Provoking factors
Damage to the integrity of the skin of the hands is not the only provoking factor. Constant contact with water, high temperatures and chemical reagents is dangerous. You can get an infection under the nail fold by biting off a hangnail with your teeth, getting a manicure or pedicure in a beauty salon.
A common cause of paronychia is ingrown toenails. Sometimes paronychia becomes a complication of diseases such as dermatitis, eczema, diabetes. The disease is often diagnosed in people with a history of HIV infection or syphilis. In this case, the main emphasis during treatment should be on eliminating the primary provoking factor. Otherwise, local therapy will not be able to give a positive result.
Paronychia can also act as an occupational disease. The risk group includes:
- surgeons who constantly treat their hands with antiseptics;
- shoemakers working with shoe glue;
- chemical laboratory technicians;
- cleaners who often use household chemicals and hot water.
Pathology always occurs with the involvement of an infectious agent. In children, the main cause of inflammation of the skin around the nail fold is the habit of thumb sucking.
Complication
The main symptoms of complications are:
- transition of the inflammatory process into an abscess of the subungual notch;
- delamination and subsequent complete destruction of the nail;
- development of tendinitis - infection of deep tissues;
- transition from acute to chronic stage.
Timely measures to eliminate the disease will eliminate complications.
Paronychia multiforme of the fingers is common, but treatment is simple and does not cost a lot of money. Even at home, given the clear symptoms, you can understand what type of disease it is. The main thing is to get treatment at home in time or seek help in a hospital.