Home » Articles from an expert » Diagnostics
What are the signs of a heart attack in a woman? A qualified cardiologist will tell you about this. Myocardial infarction is a common disease nowadays. It affects a large number of both men and women. This text material will discuss in more detail the disease itself, as well as the signs of a heart attack in women, first aid for this pathology.
What it is?
In simple words, myocardial infarction is a clinical form of coronary heart disease that occurs when there is insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle (myocardium) and occurs with the development of death of myocardial cells and the formation of an area of necrosis (death) of the myocardium. The incidence of heart attacks increases with age.
People over 50 years of age develop a heart attack 5 times more often than younger people. It is also observed more often in men than in women. Mainly left ventricular infarction occurs, because the heaviest load falls on it; infarctions of the right half of the heart are quite rare.
There are several types of myocardial infarction:
- Developed for no apparent reason (spontaneously), as a result of a primary disturbance of coronary blood flow caused by the formation of erosion, rupture, or crack of an atherosclerotic plaque.
- Developed due to a lack of oxygen flow to the heart muscle.
- Sudden death, including cardiac arrest. This type is diagnosed before blood samples can be taken or before there is an increase in the level of biochemical markers of necrosis in the blood.
- Myocardial infarction associated with a PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) procedure.
- Associated with coronary stent thrombosis.
Risk factors for myocardial infarction include: increased levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), high levels of triglycerides in the blood, arterial hypertension, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and previous myocardial infarction.
Risk factors for heart attack in women
There are known factors that contribute to the development of myocardial infarction in women. They are associated with the structural features of the body and lifestyle of girls and women. Among them:
- heart structure: a woman's heart is on average slightly smaller than a man's. The weight of a female heart is 200–300 g, a male heart is 270–380 g;
- structure of blood vessels: the lumen of arteries, including coronary ones, is much smaller in women. This contributes to increased pressure of blood flow on the walls of blood vessels and more intense cholesterol deposition;
- increased formation of atherosclerotic plaques and their localization: as a rule, in women, atherosclerosis more often affects small vessels;
- higher incidence of diseases that contribute to the occurrence of heart attack , in particular diabetes mellitus;
- higher prevalence of obesity.
The absence of cardiac pain during a heart attack is especially common in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Another group can include risk factors for heart attack, which are relevant not only for women, but also for men:
- hereditary predisposition;
- elevated blood lipid levels;
- bad habits, in particular smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- elevated homocysteine levels;
- excess weight;
- high blood pressure;
- psychosocial factors, stress tolerance.
Most often, the direct impetus for myocardial infarction is excessive nervous tension, stress, high physical activity, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, vascular (often hypertensive) crises, and less often - surgery, hypothermia. What pressure can trigger a heart attack? A dangerous blood pressure value is considered to be above 140/90 mm Hg. Art.
Classification and stages
Periods of development of myocardial infarction (phases)
- The most acute phase. Developing heart attack. The phase lasts from 0 to 360 minutes. This is the period of the most striking symptoms. At this time, progressive necrosis occurs in the affected area, which usually ends by the end of the sixth hour.
- Acute phase. Acute myocardial infarction. The period lasts from 6 hours to 7 days. All major complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and relapse are most likely at this time.
- Subacute phase. Healing (scarring) infarction. The period lasts from 7 to 28 days. The affected area of the myocardium becomes scarred. The patient's condition has stabilized and he can be discharged from the hospital.
- Chronic phase of myocardial infarction. The fourth period is a healed myocardial infarction, post-infarction cardiosclerosis. Starts from the 29th day. The scar is usually fully formed by this time. If by this time signs of heart failure and rhythm disturbances persist, they are usually stable.
Myocardial classification also depends on a number of other criteria, which are presented in the table.
| Classification | Types of heart attack |
| By area of necrotic focus |
|
| According to topographical characteristics |
|
| According to the depth of the lesion |
|
| According to the development of complications |
|
| By multiplicity of development |
|
| By location of pain |
|
Signs of a heart attack in a woman: early symptoms and treatment features
The problem in question is a severe form of coronary heart disease.
Acute infarction is the death (necrosis) of some areas of the myocardium, due to which the muscle loses the ability to contract normally and perform its functions.
It is a mistake to believe that a heart attack occurs suddenly. Most women who suffered it noted 1-2 characteristic symptoms 4 weeks before the incident.
Causes of heart attack
For the myocardium to function properly, the muscle must receive a sufficient amount of oxygen supplied by the blood. If its inflow is disrupted, the first, subtle symptoms of a heart attack appear in women, which are mostly ignored. They are associated with the progression of diseases that provoke a heart attack:
- atherosclerosis;
- blockage (embolism or obstruction) of the heart arteries;
- spasms of the coronary vessels.
Indirect causes of heart attack in women and risk factors:
- excess body weight;
- age over 50 years;
- lack of physical activity;
- smoking;
- high cholesterol in the blood;
- alcohol abuse;
- diabetes;
- intense hormonal imbalance, including menopause;
- previous heart attack;
- chronic cardiac pathologies;
- arterial hypertension;
- exposure to stress and fatigue.
Consequences of a heart attack
All complications diagnosed due to a heart attack are classified into 3 categories:
A heart attack, even during hospitalization, can cause the following consequences in the early period:
An acute complication of a heart attack in women is scarring of the damaged area of the myocardium, which leads to the development of chronic heart failure. Late consequences are also called Dressler syndrome. It includes inflammatory pathologies:
- pleurisy;
- pericarditis;
- pneumonitis
Age of heart attack in women
The described diagnosis among representatives of the fairer sex is more common after 55-60 years. This is due to a sharp decrease in the concentration of estrogen in the body due to menopause. Due to a deficiency of hormones, cholesterol plaques accumulate on the walls of blood vessels, and atherosclerosis begins, which in most cases provokes acute myocardial infarction.
Modern medical statistics show that heart attacks have become significantly younger over the past 10 years. Symptoms of an impending heart attack are found in women much younger than this age. This problem is associated with the following factors:
- stress;
- overwork;
- unbalanced diet;
- addiction to alcohol;
- smoking;
- lack of physical activity.
Myocardial infarction - symptoms in women
The clinical picture of the acute condition in question is nonspecific, so it is difficult to recognize the approach of a heart attack.
Many symptoms, including sleep, activity and blood pressure, are masked by other problems during a heart attack. Because of this, the symptoms of the pathology are attributed to fatigue, emotional stress or lack of sleep.
It is important to remember several features accompanying myocardial ischemia in the early stages of its development.
Precursors of heart attack in women
Necrosis of individual areas of the heart muscle begins with oxygen starvation of the tissues. A heart attack in women is the result of prolonged myocardial hypoxia. There are signs that indicate a violation of blood circulation and oxygen supply even before the onset of irreversible changes. If detected early, an attack can be prevented.
The earliest symptoms of a heart attack in women:
- fatigue even with low loads (climbing stairs);
- dizziness;
- frequent changes in blood pressure;
- attacks of shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- sometimes – pain in the sternum;
- anxiety;
- bleeding gums;
- digestive problems;
- swelling of the legs and feet;
- frequent urge to urinate at night;
- snoring or apnea.
Heart attack - symptoms, first signs in women
The above phenomena are rarely associated with a heart attack. Similar sensations can be caused by simple overwork or stress, so the first signs of a heart attack are almost always ignored. Gradually they become more frequent and intensified, before the attack the following symptoms occur:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- severe shortness of breath;
- chest pain, which can radiate to the arm, shoulder, shoulder blade, neck and lower jaw;
- sweating;
- nausea, rarely – vomiting;
- a sharp jump in blood pressure;
- dizziness with loss of consciousness;
- fast or unstable heartbeat;
- anxiety, panic.
Symptoms of heart attack in women at a young age
The younger a person is, the more difficult it is to suspect an impending heart attack. The signs of a heart attack in a 30-year-old woman are blurred, most are so mild that they are not noticed.
In the intense pace of life, modern girls are accustomed to not attaching importance to periodic dizziness, fatigue or pressure changes, and these symptoms may indicate myocardial hypoxia.
It is important to closely monitor your well-being, and if you suspect problems with blood circulation, visit a cardiologist and get an ECG.
Symptoms of heart attack in older women
In old age, the body reacts sensitively to the slightest changes, and therefore the clinical picture of oxygen starvation of the heart muscle is more pronounced. Signs of a heart attack in women over 60 include the conditions listed previously and several additional symptoms. The pain in the chest is severe, burning, radiating throughout the entire arm, starting from the shoulder, to the left half of the lower jaw.
Symptoms of heart attack in older women:
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- numbness of the upper limb;
- dry cough;
- speech disorders;
- darkening of the eyes;
- pale face, slightly bluish skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- frequent pulse.
Signs of the onset of an acute period
More than 100 years ago, the founders of the theory of myocardial infarction, V.P. Obraztsov and N.D. Strazhesko, in addition to the classic anginal symptoms, identified a number of atypical forms in which the disease can manifest itself. Symptoms of a heart attack in women most often have the following forms of manifestation:
- Anginal status - recorded in 60–75% of cases. When this form develops in women, the pain is localized in the left upper part of the body: neck, shoulder, arm, upper chest. There is a feeling of self-limiting toothache. A characteristic feature in women is also acute pain in the back of the head. The remaining manifestations of anginal status are the same as in men: profuse sweating, cyanosis of the skin, numbness of the limbs, panic. The pain is intense and does not go away from taking nitrates.
- Status asthmaticus is registered in 10% of cases, its main characteristic is the presence of signs of bronchospasm. In this case, in the absence of physical activity, the patient experiences shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. These symptoms intensify when turning the body. This form of symptoms occurs in older women, against the background of a previous heart attack or prolonged hypertension.
- Abdominal form - manifests itself in 2–3% of cases. It develops when the posterior wall of the myocardium is damaged. Symptoms of such a heart attack lead to a false suspicion of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
Anginal status in asthmatic and abdominal forms may appear later. But the primary symptoms of atypical forms complicate diagnosis, and only an experienced emergency doctor is able to immediately make the correct diagnosis.
Source: https://AptekaTamara.ru/bolezni/priznaki-infarkta-u-zhenshchiny.html
The first signs of a heart attack
The first symptoms of myocardial infarction in adults appear suddenly; they can be identified using 4 main signs:
- Pale skin, sticky cold sweat,
- Interruptions in cardiac activity - arrhythmias and fibrillation. The patient complains of a feeling of irregular heart function, uneven heartbeat. A common symptom is a feeling of cardiac arrest, which is accompanied by intense fear,
- Acute burning retrosternal pain that radiates to the left shoulder blade, shoulder, arm, jaw, sometimes to the stomach or perineum. Once the pain occurs, it does not subside and is not relieved by conventional painkillers (in the hospital they are eliminated with narcotic analgesics). The patient holds on to his heart, may instantly weaken, fall,
- Heart failure - usually develops several hours after the onset of the attack, and sometimes faster, manifested by shortness of breath, cyanosis of the skin.
Nonspecific symptoms are also possible, for example, increased blood pressure, weakness, loss of consciousness, intermittent breathing. These same signs may be harbingers of future myocardial damage.
During myocardial infarction, the patient complains of sudden pain in the heart and behind the sternum, noticeable disturbances in the functioning of the heart. It should be borne in mind that patients with diabetes have a dangerous, painless form of the disease. In this case, the patient experiences not pain, but discomfort in the heart area.
A heart attack most often occurs in the morning, closer to dawn. This is due to the fact that at night the heart does not work as intensively as during the day, and the morning rise is associated with the release of hormones into the blood that stimulate its activity. Therefore, in the morning hours, such phenomena as increased blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, arrhythmias, and, as a result, ruptures of atherosclerotic plaques are most likely. But this does not mean that a heart attack cannot overtake a person at other times of the day.
Myocardial infarction in women: features
The danger of its appearance for women occurs approximately 10 years later than for men, since atherosclerosis develops later in the female body. This is due to the peculiarities of the influence of female sex hormones on lipid metabolism. Estrogens are a powerful factor in protecting the body, in which nature has invested reproductive function.
This pattern is directly related to atherosclerosis. During reproductive age, the risk of cardiovascular complications in women is three times less than in men. According to the Framingham study, with the onset of menopause at age 50, cholesterol levels reach comparable values in men and women, but in women there is an increase in this indicator in the future, while in men it remains unchanged.
Female myocardial infarction is rare before the age of 50, but then the incidence begins to increase. Today, it is also assumed that there is a relationship between myocardial infarction and long-term use of contraceptives.
Myocardial infarction in men: features
It is well known that morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular pathology in men is 3-5 times higher than in women. The main culprit is atherosclerosis.
In men aged 50-59 years, myocardial infarction is recorded 6 times more often than in women. According to the All-Russian Scientific Society of Cardiologists, in young and middle-aged men it more often becomes the first symptom of coronary heart disease, debuting without previous clinical manifestations, than it happens in women.
How you feel during a heart attack
It is very dangerous not to pay attention to the symptoms of a heart attack in women - first aid must be provided as soon as possible, otherwise the risk of death increases significantly. Accustomed to various discomforts and immersed in daily responsibilities, girls often miss the moment when they need to put aside all their worries and take care of their own health. Despite the fact that in the fair sex the disease is not as obvious as in men, this absolutely does not mean that it should be endured on your feet in the hope that everything will go away by itself.
If you do not want to expose your life to unjustified danger, then immediately contact a doctor if:
- pain suddenly appeared in the lower jaw, although no dental problems had previously been observed;
- suddenly the urge to vomit began;
- in parallel with chest pain, unpleasant sensations appeared in the back of the head or in the neck area;
- sweating increased, and the skin became pale, clammy and cold;
- great weakness and fatigue appeared;
- I feel dizzy from time to time.
No ordinary illness or aging of the body can cause such consequences, therefore, if you notice at least one of the signs of a heart attack in a woman, first aid should be provided immediately.
Why do women experience attacks differently?
The unusual symptoms that accompany arterial blockage and the death of myocardial cells in representatives of the weaker half of humanity are largely due to physiological characteristics:
- girls' heart sizes are much smaller;
- the number of beats per minute in the female population normally reaches 90, while the heart muscle in men contracts no more than 75 times;
- The body produces estrogen, a female hormone that provides the necessary amount of cholesterol, thereby protecting against the appearance of plaques inside the coronary arteries. Unfortunately, after menopause, this unique property disappears, so among those who are admitted to hospitals with this diagnosis, a large percentage are pensioners.
Features of heart attack treatment
It is worth noting that with regard to treatment and rehabilitation, the differences between prescriptions for men and women are practically not so significant. In particular, doctors recommend special nutrition for women after a heart attack, physical therapy, and also strongly advise completely stopping smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Atypical forms
Signs of an extensive heart attack in atypical forms of the disease also vary:
- Abdominal variant of MI. How to recognize a heart attack: intense pain in the upper abdominal segment, dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting), tension in the anterior part of the peritoneum. If an “acute abdomen” is suspected, patients must be referred for an ECG to rule out MI.
- Asthmatic variant. Most often it develops in patients over 60 years of age who have already had an MI. The pain syndrome may be mild or completely absent. The only signs of a heart attack in women and men are severe shortness of breath (even suffocation).
- Arrhythmic course. Pain may be absent or mild. The first signs of a heart attack in men and women in this case are various heart rhythm disturbances.
- Painless (asymptomatic) form of MI. A common variant of the course of a heart attack, most often found in women, patients with diabetes, as well as elderly patients suffering from cerebrovascular accidents. As such, the signs of a heart attack in men and women in this case are absent or mild.
- Cerebrovascular MI. This form of pathology is diagnosed in elderly patients and is clinically manifested by problems with blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. How does a heart attack manifest: symptoms of a heart attack in women and men such as vomiting, fainting, nausea, and dizziness come to the fore.
Myocardial infarction in men and women is indicated by the following symptoms (indicating a lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle):
- frequent shortness of breath, which occurs not only during intense physical activity, but even in a calm state,
- chest pain (has a paroxysmal character), a feeling of pressure, compression in the chest,
- lack of air,
- Painful sensations may occur in the legs while walking,
- Often there are problems in the functioning of the brain - memory impairment, inability to concentrate attention on an unknown object (a consequence of circulatory problems),
- attacks of dizziness, short-term loss of consciousness,
- decreased sexual desire, problems with potency.
Serious reasons for concern
At first glance, only a certified doctor can understand how to recognize a heart attack in women, although in reality, any average person can find out that it’s time to call an ambulance for themselves or a family member.
Of course, when the situation reaches the point where the girl loses consciousness or experiences incredible pain, then no questions arise - you need to urgently go to the hospital or wait for a team of doctors. But if you only suspect signs of a heart attack, what to do and how to distinguish this disease from others that have similar manifestations? First of all, you need to stop being nervous and try to understand whether you are really having a heart attack, because it develops specifically in the fairer sex.
Precursors of a heart attack
According to the results of scientific research, precursors of a heart attack in women often occur 25-30 days before the blood flow to the arteries is blocked and necrosis begins. These include:
- constant fatigue, which cannot be eliminated even in the absence of physical and mental stress;
- difficulty falling asleep and other sleep disorders;
Important! The two above symptoms that occur before a heart attack appear only in women and long before the attacks, so if you do not miss them and undergo a comprehensive cardiac diagnosis, you can completely avoid the death of part of the heart muscle.
- swelling in the extremities due to stagnation of blood, which accumulates in certain areas;
- anxiety and unreasonable fear;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract - we are not talking about poisoning and dysphagia, but about dysfunctions that arise unreasonably and suddenly. In the female body, the diaphragm is located slightly higher, therefore, when pain occurs on the posterior wall of the myocardium, the unpleasant sensations radiate to the stomach;
- breathing problems (shortness of breath), which had not previously bothered and began to appear in combination with other signs - such discomfort should not be ignored in any case, since it may indicate coronary insufficiency, which, in turn, without treatment will cause tissue necrosis and failure of the “internal engine”;
- nagging pain in the chest, which can spread significantly towards the shoulder, arm and neck.
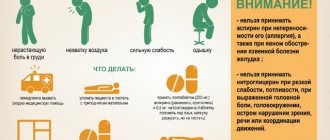
First aid for heart attack
If the disease catches you at a time when no one is around, don’t panic! You can provide first emergency aid for a myocardial infarction yourself at home! First of all, explain in detail to the ambulance dispatcher how to get into your apartment or house, since there will be no one to meet the doctors. Leave the front door open.
Algorithm of actions for providing first aid for a heart attack:
- Open the windows or turn on the air conditioner to bring in fresh air.
- Place a nitroglycerin tablet/capsule under your tongue. This way the drug will penetrate the blood faster and relieve some of the pain.
- Another medicine that can help in the first minutes of a heart attack is aspirin. It thins the blood and eases symptoms. For the drug to act quickly, the tablet should be chewed. The approximate dose is 300 mg.
- Sit or lie down, first placing a pillow or any handy object under your back and head that will allow you to keep your upper body slightly higher than your lower body. Legs need to be bent at the knees. In this position of the body, it will be easier for the heart to carry out blood supply. Then we just have to wait for the doctors.
Timely treatment of a heart attack largely influences the favorable prognosis of survival during the disease, the frequency of relapses and the occurrence of complications. Treatment must be carried out in an inpatient setting in a resuscitation or intensive care unit.
The difference between the symptoms of a heart attack and angina pectoris
It is important to learn how to accurately differentiate the symptoms of a heart attack from angina attacks.
The symptoms of these diseases are similar because they have the same causes: with angina, as with a heart attack, painful attacks appear due to insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the heart muscle - the myocardium. Lack of blood supply to the myocardium occurs mainly due to atherosclerosis - the process of cholesterol deposition in blood vessels. Over time, the lumen in the vessels becomes smaller, and one day a cholesterol plaque completely blocks the blood flow to the muscle.
The main difference between the symptoms of angina pectoris and a heart attack is the inability to relieve painful symptoms with nitroglycerin.
The thing is that without blood supply to a certain area of the myocardium, irreversible processes begin in it - necrosis (death) of muscle tissue. Therefore, tablets are ineffective in this situation. Also, painful sensations during a heart attack do not disappear after rest.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction
Such painful attacks are more common among the fairer sex aged 45 years and older, but this does not mean that this diagnosis is not typical for men. The pathological process is accompanied by increased blood pressure, and can end in myocardial ischemia. Doctors identify the following warning signs of a heart attack:
- frequent shortness of breath with minimal physical exertion;
- tight feeling behind the sternum;
- angina attacks;
- increased sweating;
- acute lack of oxygen;
- forgetfulness, loss of orientation in space;
- muscle weakness.
Among women
Modern women over 45 years of age are faced with a high probability of myocardial infarction due to reduced resistance to stress and heavy physical labor. The characteristic signs of ischemic necrosis in the female body differ from the course of the disease in men, and disruption of the blood supply to the heart muscle causes not only acute pain, but also other signs of the disease. This:
- intermittent breathing during sleep, snoring;
- impaired water balance, which precedes swelling of the face, hands, feet;
- disturbance of heart rhythm, as with arrhythmias;
- frequent urination at night;
- numbness of the limbs;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased bleeding of gums;
- more frequent migraine attacks;
- stomach pain;
- painful sensations radiating to the left shoulder.
Nature of pain
This is one of the most dangerous heart pathologies. With extensive heart attacks, there is definitely an acute pain syndrome that impairs breathing, binds to bed, paralyzes consciousness and limits movement. Sharp pain is accompanied not only by dizziness, but also by an unconscious state, especially when it comes to women. The first step is to call an ambulance, carry out a series of resuscitation measures, and begin treatment in a timely manner. Otherwise, the pathological process of necrosis in myocardial tissue can cost the patient his life.
Feel
An attack of acute ischemia begins with unexpected pain in the heart, which radiates to the left shoulder and does not disappear after taking painkillers. At the initial stage, these are irregular lumbago, which, in the absence of therapeutic measures, remind themselves again and again. A heart attack can be recognized by the nature of the pain, since in the relapse stage it does not go away in the clinical patient.
Complications of a heart attack
Often complications arise already in the first hours and days of myocardial infarction, complicating its course. In most patients, in the first three days, various types of arrhythmias are observed: extrasystole, sinus or paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete intraventricular block. The most dangerous is ventricular fibrillation, which can turn into fibrillation and lead to the death of the patient.
Left ventricular heart failure is characterized by congestive wheezing, symptoms of cardiac asthma, pulmonary edema and often develops during the acute period of myocardial infarction. An extremely severe degree of left ventricular failure is cardiogenic shock, which develops with a large infarction and usually leads to death. Signs of cardiogenic shock are a drop in systolic blood pressure below 80 mmHg. Art., impaired consciousness, tachycardia, cyanosis, decreased diuresis.
Rupture of muscle fibers in the necrosis zone can cause cardiac tamponade - hemorrhage into the pericardial cavity. In 2-3% of patients, myocardial infarction is complicated by thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery system (which can cause pulmonary infarction or sudden death) or systemic circulation.
Patients with extensive transmural myocardial infarction in the first 10 days may die from ventricular rupture due to acute cessation of blood circulation. With extensive myocardial infarction, failure of scar tissue may occur, its bulging with the development of acute cardiac aneurysm. An acute aneurysm can transform into a chronic one, leading to heart failure.
The deposition of fibrin on the walls of the endocardium leads to the development of parietal thromboendocarditis, which is dangerous due to the possibility of embolism of the vessels of the lungs, brain, and kidneys from detached thrombotic masses. In a later period, post-infarction syndrome may develop, manifested by pericarditis, pleurisy, arthralgia, and eosinophilia.
Causes of heart attack
What causes a heart attack? The narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries leads to a decrease in blood flow to any part of the muscular layer of the heart (myocardium), weakening or complete cessation of blood supply to the heart muscle, and coronary heart disease develops. The acute form of coronary heart disease, which occurs with the development of necrosis of cardiac cells, is called myocardial infarction.
The main role in the development of a heart attack belongs to pathological processes in the coronary arteries of the heart: narrowing of their walls, vascular spasms, loss of elasticity, atherosclerotic changes.
In most cases, the disease develops against the background of atherosclerosis. The appearance of atherosclerotic plaques and hemorrhage causes narrowing or complete closure of the lumen of the vessel, often this process is accompanied by the formation of blood clots.
A study of the dynamics of incidence showed that the mortality rate from myocardial infarction among women was 9%, while among men it was only 4%.
At what age can you have a heart attack? According to statistics, myocardial infarction in women at a young age is much less common than in men. This is due to the fact that estrogens produced in a woman’s body have a beneficial effect on vasodilation and the functioning of the muscular layer of the heart, and have an antioxidant, cardioprotective and antiatherogenic effect. However, with the onset of menopause, estrogen production decreases significantly, the risk of developing the disease increases significantly, and the incidence rate in older women (over 60 years of age) is compared with that in men.
Diagnostics
After a heart attack, doctors do not deny the presence of a risk of relapse.
Such heart patients are at risk. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a detailed diagnosis with a number of clinical examinations, tests and laboratory studies. Otherwise, it is difficult to predict the clinical outcome and exclude mortality. Delay can cost the patient’s life, so differential diagnosis must be carried out in a timely manner.
Diagnostic measures for a heart attack are presented below:
- Ultrasound of the heart provides an objective assessment of the affected area and the degree of myocardial damage during a progressive infarction,
- Scintigraphy, as an effective method to determine the subtleties of the clinical picture, exclude the development of acute atherosclerosis,
- An electrocardiogram to determine the etiology of a pathological process, for example, reveals “clogging” of blood vessels with a thrombus,
- Laboratory studies of basic biological fluids to clarify the progressive clinical picture for a particular case.
Treatment
The main goals of priority treatment measures for myocardial infarction:
- To treat acute heart failure, cardiac glycosides (corglycone, strophanthin) and diuretics (furosemide) are used.
- Pain relief is one of the most important and urgent stages in the treatment of MI. If tableted nitroglycerin is ineffective, it is administered intravenously or a narcotic analgesic (for example, morphine) + atropine intravenously. In some cases, neuroleptanalgesia is performed - intravenous antipsychotic (droperidol) + analgesic (fentanyl).
- Antiarrhythmic therapy. To eliminate rhythm disturbances, heart failure, and restore metabolism in the heart tissue, antiarrhythmic drugs (bisoprolol, lidocaine, verapamil, atenolol), anabolics (retabolil), a polarizing mixture, etc. are used.
- Thrombolytic and anticoagulant therapy is aimed at reducing the area of necrosis. On the first day after the appearance of the first signs of a heart attack, a thrombolysis procedure can be performed to resolve the thrombus and restore blood flow, but to prevent the death of cardiomyocytes, it is more effective to do it in the first 1–3 hours. Thrombolytic drugs are prescribed - fibrinolytics (streptokinase, streptase), antiplatelet agents (thrombo-ASA), anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin).
Signs of a heart attack in a woman: symptoms and first aid at home – Chest pain
A heart attack is an acute pathology in which myocardial cells (heart muscles) necrotize.
The site of necrosis is replaced by connective tissue, which cannot contract under the influence of electrical impulses emanating from the central nervous system.
The death of myocardial cells is a consequence of prolonged ischemic disease. A scar appears on the human heart muscle, interfering with the normal functioning of the heart.
Heart attack
Note! According to statistics, women are at risk of having a heart attack, which is explained, first of all, by the hormonal background of the female body, more precisely by the production of the hormone estrogen. But in general, a heart attack in women is not much different from that in men: the weaker sex tolerates the disease a little easier, since it is more emotional and has a lower threshold of sensitivity.
Heart attack. Typical symptoms
This hormone dilates blood vessels, which has a positive effect on the functioning of the myocardium. But if there is a hormonal imbalance in the body (this can happen during pregnancy, menopause, ovulation, or in case of irregularities in the menstrual cycle), then the “production” of estrogen is noticeably reduced. Because of this, disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system may occur.
Early symptoms of myocardial infarction
Some statistics: about 250 women die every day from a heart attack, but this figure, what’s even worse, is growing rapidly.
It is for this reason that any woman must know about the main manifestations of myocardial infarction, as well as first aid during attacks. This will help avoid more serious consequences of the disease.
Every person must know the signs of a heart attack.
Early symptoms of pathology
A woman can find out about an upcoming heart attack by some indirect signs. The fact is that a heart attack “makes itself known” several hours before the onset of an exacerbation. Therefore, it is so important to know what will happen next and, accordingly, take care of first aid. And if a woman knows some of the early symptoms of pathology, she will be able to avoid the possible consequences of this pathology.
Signs of a heart attack in women. First aid
Table No. 1. Early symptoms of a heart attack
NameDescription
| General weakness, fatigue | What is considered normal in men may be a signal of an imminent heart attack in women. This signal can also be weakness in the body, severe fatigue. In this case, all the characteristic signs of ordinary fatigue are felt, but its peculiarity in the pre-infarction state is that it can occur even after a long rest. |
| High blood pressure, severe migraines | They are also considered to be early signs of a heart attack. |
| Sleep disorders | Symptoms may include difficulty falling asleep, chronic insomnia, and other disorders of a similar nature. |
| Breathing problems | Previously, shortness of breath did not bother the woman, but now the problem has begun to appear, often in tandem with other symptoms. This condition should not be ignored, because it may indicate coronary insufficiency, which, in turn, in the absence of timely treatment leads to cell necrosis and heart failure. |
| Nagging pain | They begin in the chest but can spread to the left forearm. |
| Arrhythmia | The pathology occurs due to dysfunction of the coronary artery, which is the main source of nutrition for the myocardium. |
| Swelling of the legs and feet | In most cases, this is due to a violation of the outflow of fluids, which occurs due to heart failure. |
| Digestive tract dysfunction | We are talking about sudden and unfounded violations. The diaphragm in the female body is located slightly higher, therefore, if pain occurs on the back wall of the heart muscle, it can also spread to the stomach. |
If at least one of the above symptoms is detected, a woman should immediately seek medical help.
Main symptoms of a heart attack
Main symptoms of a heart attack
It is extremely dangerous to ignore the signs of a heart attack in a woman, first aid should be provided as early as possible, otherwise the likelihood of death will increase. And in order not to expose your health to unjustified danger, you should consult a doctor after one of the symptoms of the pathology has been identified.
Signs of pathology include:
- pressing, burning or squeezing pain behind the sternum (on the left) or in the abdomen;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- burning in the heart area;
- visual impairment;
- vomiting (may or may not);
- anxiety, fear of death;
- dizziness;
- slow, slurred, or slurred speech;
- decreased blood pressure;
- nausea;
- intense sweating.
You should immediately consult a doctor at the first signs of a heart attack.
Neither general malaise nor banal aging causes such consequences, therefore, when these signs appear, first aid should be provided and the woman taken to the hospital.
Note! There are practically no gender differences in treatment and rehabilitation period. For women who have had a heart attack, doctors prescribe physiological therapy and also recommend completely giving up alcohol and smoking.
Providing first aid
First aid for myocardial infarction
If the symptoms listed above appear, you must first call an ambulance. If this can be done and the carriage arrives no later than ten minutes later, then the likelihood of avoiding severe complications of a heart attack increases significantly.
Step 1. Place the patient on some flat surface and place a small pillow under her head.
Place the patient on the floor or other hard surface
Step 2. After this, unbutton your clothes, as they can make breathing difficult.
Clothes need to be removed or unbuttoned
Step 3. Do not allow the woman to stand up, because this could cause a damaged heart to stop functioning altogether.
Step 4. First aid is to give the patient nitroglycerin and aspirin, or validol.
Nitroglycerine
Step 5 . If, half an hour after the call, the ambulance still has not arrived, give the woman more nitroglycerin under her tongue.
Step 6 . If you notice that the patient has begun to panic, immediately stop the attack with Corvalol or valerian.
Corvalol
Step 7 . Do not forget to constantly monitor the patient’s breathing. If it is weakened, and the heart beats more and more slowly, then resuscitation, consisting of indirect cardiac massage or, as an option, artificial respiration, begins only in the absence of breathing, consciousness, or pulse!
Artificial respiration using the “mouth to nose” method: a – exhalation of the victim; b – blowing air In this case, close the nose or mouth, respectively
About heart attack in pregnant women
The body of a pregnant woman intensively produces the hormone estrogen; moreover, the volume of myocardial perfusion per minute increases markedly, which is why the risk of a heart attack is minimal. Nevertheless, such cases still occurred in medical practice.
The risk of heart attack in pregnant women is small
Note! The risk group includes those pregnant women who have previously taken contraceptives (oral contraceptives) for a long time, which negatively affect the condition of the blood vessels.
What triggers the development of a heart attack?
In most cases, pathology develops in women after 50, that is, 10-15 years later than in men. But there are a number of factors that lead to the described pathology and can accelerate its development.
Heart attack and what leads to it
These factors include:
- diabetes;
- previous heart attacks;
- genetic predisposition;
- excess weight;
- lack of physical activity;
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis, high cholesterol;
- chronic kidney diseases;
- smoking.
Bad habits and excess weight can lead to a heart attack
To sum it up. Causes of female heart attack
At the end of the article, you should talk a little about the reasons for the development of pathology in representatives of the fairer sex (they differ little from the causes of male heart attacks).
- Vascular obstruction after surgical operations (such as angioplasty, arterial ligation, etc.).
- Blood clots in the coronary artery (they are observed in 95% of all cases).
Coronary artery thrombosis - Spasms of the arteries of the heart, provoked by angina pectoris.
Spasms of the arteries of the heartSpasm of heart vessels
But regardless of the reason, the main thing is to get the patient to the hospital as quickly as possible, and also, if possible, provide pre-medical first aid.
It is important to hospitalize a person with a myocardial infarction as quickly as possible
The first warning signs, symptoms and signs of myocardial infarction in women
Myocardial infarction in women is a dangerous disease that occurs mainly in postmenopause. Within two hours after the first signs of a heart attack appear, up to 30% of patients die. This is partly due to the peculiarities of the course of the disease in the female population.
The article talks about how to recognize a heart attack in women, provide first aid at home and live after a cardiovascular accident. The information provided about the causes and precursors of a heart attack in women will help prevent the development of a terrible disease and its complications.
Signs
Myocardial infarction is a focal lesion of the heart muscle due to acute disruption of blood flow. Vascular sclerosis, spasm or thrombosis prevent blood flow to myocardial cells. The resulting oxygen starvation causes damage and death of heart cells (necrosis). Pain and other symptoms appear, the detection of which helps to recognize a heart attack in women.
Prevention
It should also be remembered that myocardial infarction can recur. To prevent this, you need to change your lifestyle and monitor your health. Namely:
- give up smoking and alcohol (an exception may be dry red wine in small quantities)
- Monitor your weight and, if necessary, reduce weight to your physiological norm
- lead an active lifestyle, but avoid physical overload
- Maintain normal blood pressure with medications prescribed by your doctor
- if your cholesterol level is high, take the necessary medications (again, prescribed by your doctor)
- follow the basic principles of proper nutrition, while excluding fried and spicy foods from the menu, eating the right amount of fiber, increasing the amount of low-fat dairy products and fish in the diet, and keeping salt to a minimum.
- you can't lift heavy things
Forecast for life
Myocardial infarction is a serious disease associated with dangerous complications.
Most deaths develop in the first days after myocardial infarction. The pumping ability of the heart is related to the location and volume of the infarct area. If more than 50% of the myocardium is damaged, as a rule, the heart cannot function, which causes cardiogenic shock and death of the patient. Even with less extensive damage, the heart does not always cope with the load, resulting in heart failure.
After the acute period, the prognosis for recovery is good. Unfavorable prospects for patients with complicated myocardial infarction.