Causes
The causes of right ventricular myocardial hypertrophy are acquired or congenital. In the first case, restructuring of the heart muscle is usually a consequence of diseases of the respiratory system:
In addition, a primary change in chest volume is possible with various deviations. These include:
Primary damage to the pulmonary vessels, which leads to hypertrophy, can develop as a result of:
An increase in the mass of the right ventricle occurs in various diseases of the respiratory and circulatory systems.
Right ventricular hypertrophy in infants is associated with congenital heart defects:
With congenital defects, hypertrophy appears at an early age.
Complications
Without adequate treatment, thickening of the PP can cause dangerous complications. Main consequences of GPP:
- cardiac arrhythmia, conduction disturbance (type of blockade);
- heart failure;
- pulmonary embolism (complete);
- myocardial infarction;
- progressive cor pulmonale;
- sudden cardiac death.
Article on the topic: Ulcerative stomatitis in children - treatment with medications or folk remedies, diet
Symptoms
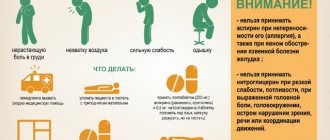
Symptoms of right ventricular hypertrophy are not specific and are directly related to the causes of the disease. At the very beginning of the pathological process, signs may be absent or not noticeable. However, as the myocardial mass increases, the manifestations become more pronounced:
Right ventricular hypertrophy in a child is often accompanied by a decrease in oxygen concentration in the peripheral blood. As a result, his skin becomes bluish in color, which is especially noticeable when crying.
Aberrant conduction (Confluent contractions)
Sometimes with arrhythmias, so-called drain contractions, or drain complexes, are observed [Chazov E. P., Bogolyubov V. M., 1972; Doshchitsin V.L., 1979; Tomov L., Tomov P., 1979]. Possible occurrence of confluent contractions of the atria or ventricles. Confluent contractions appear when two different sources of excitation exist, synchronously causing depolarization of the atria or ventricles. There is simultaneous or almost simultaneous excitation of the atria or ventricles by impulses coming from different directions - from the sinus node and from the ectopic pacemaker.
The resulting complex recorded on the ECG is the result of a merger or combination of two different forms of excitation. For example, with late ventricular extrasystoles, the ventricles can be excited in a normal way - through the atrioventricular node and in an unusual way - from an ectopic source of excitation located in one of the ventricles. The QRS complex, when two excitations merge, has an intermediate appearance between normal contractions and complexes caused by impulses emanating from ectopic areas.
The width of these complexes usually does not increase more than 0.06 s compared to normal QRS complexes. The PQ interval of drain complexes can be equal to its usual duration or slightly shorter. However, this shortening should not exceed 0.06 s, since the impulse emanating from the ventricles needs no more than 0.06 s to cause excitation of the ventricles and prevent the impulse from the sinus node from spreading to them.
In cases where the PQ interval of the confluent complexes is shorter than in normal contractions, the ventricles are excited first by an impulse from the ectopic focus. The initial part of the QRS complex is caused by ectopic excitation and differs in shape from ordinary sinus complexes. As for the final part of the QRS complex, it is always different from the shape of ordinary sinus complexes. This is due to the fact that the final part of the QRS complex is determined either by isolated excitation of the ventricles only from the ectopic focus, or by their depolarization under the influence of two impulses simultaneously.
“Guide to electrocardiography”, V.N. Orlov
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of increased size and mass of the right ventricle is usually made using standard cardiac examination methods. These include:
Right ventricular hypertrophy on the ECG, unfortunately, becomes noticeable only with pronounced and most often irreversible changes. That is why even normal examination results do not exclude the presence of pathology.
ECHO-CG has the greatest diagnostic value in determining hypertrophy.
Basic visual signs of the angle α at various positions in the electrical axis
On the ECG diagram, the method of visually finding the position of the EOS is available. In this case, the alpha angle is determined with an accuracy of ±100.
By analyzing the position of the R and S waves in leads I and III, it is possible to determine the axis deviation. The “algebraic sum” of angle α in this case is replaced by the dominant wave from the QRS position. The R wave is dominant, which means it is an R-type ventricular complex.
And if the S wave dominates, then they speak of an S type ventricular complex. The position of the EOS is normally observed if the amplitude of the R wave in leads I and II exceeds the amplitude of the R wave in lead III.
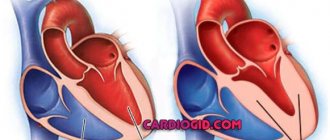
Causes of right ventricular hypertrophy
The cause of an increase in the size of the right ventricle may be a congenital defect or mitral stenosis of the heart. Most often, right ventricular hypertrophy is observed:
- In children against the background of various congenital heart defects;
- In adults, against the background of valvular heart defects and lung diseases, which are complicated by cardiac disorders.
Depending on the severity of the disease and the characteristics of its development, various configurations of the disease can be observed. Among the main causes of right ventricular hypertrophy are:
- Pulmonary hypertension, which causes increased pressure in the pulmonary artery. This causes shortness of breath, dizziness and fainting;
- Tetralogy of Fallot, which is observed in children from birth and can continue throughout the first year of the child’s life. This congenital heart defect, causing blue baby syndrome, is characterized by obstruction of blood flow from the right ventricle;
- Pulmonary valve stenosis, in which there is a disturbance in the flow of blood from the right ventricle to the artery;
- A defect in the interventricular septum, which causes mixing of blood from two parts. This causes a lack of oxygen, which leads to increased work of all parts of the heart, including the right ventricle.
Among the lung diseases that can lead to the development of this pathology are:
- Pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema;
- Chronic bronchitis and pneumonia;
- Pneumosclerosis;
- Bronchial asthma.
Limits of deviation of the electrical axis of the heart
To determine the heart axis in the frontal plane, an analysis of 2 or more limb leads is required, for which vector analysis is performed. In this case, ventricular depolarization is represented as an average depolarization vector with an arrow pointing in a certain direction.
The length of the vector represents the magnitude of the potential created by the difference in charges between the activated (or depolarized) cardiac cells and the resting cardiac cells, while the direction of the arrow represents the average direction of the depolarization vectors.
Ventricular depolarization spreads from the negatively charged area to the positively charged area.
Signs of right ventricular hypertrophy
Right ventricular hypertrophy is a fairly rare heart pathology. In addition, signs of right ventricular hypertrophy are extremely difficult to detect on an electrocardiogram, since the mass of the right ventricle is approximately three times less than the mass of the left, whose electrical activity predominates.
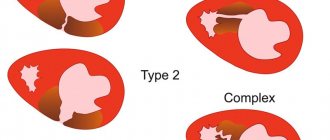
Signs of an increase in the size of the right ventricle can only be detected with a significant increase in its mass. Based on this, the following types of right ventricular hypertrophy are distinguished:
- Severe hypertrophy, in which the right ventricle significantly exceeds the mass of the left;
- Moderate hypertrophy, in which, against the background of an increase in the size of the right ventricle, a slower progression of excitation processes is recorded in it in comparison with the left ventricle;
- Moderate hypertrophy, in which there is a slight increase in the size of the right ventricle.
The initial stages of the development of right ventricular hypertrophy have vague symptoms, and in some cases there are practically no symptoms. However, as the pathology develops, accompanied by a stable increase in the size of the right ventricle, the following symptoms appear:
- Difficulty breathing, which is combined with heaviness in the chest and pain;
- Sudden attacks of dizziness, which may be accompanied by loss of consciousness;
- Abnormal heart rhythm, which can be described as “heart fluttering in the chest” or a feeling that several beats are missed;
- Severe swelling of the legs.
Definition of EOS
The electrical axis is the average direction of action potentials passing through the ventricles during their activation (depolarization). The ventricular complex, QRS, representing their depolarization, is used to determine the electrical axis.
The term "cardiac electrical axis" usually refers to the electrical axis in the frontal plane as measured by the limb leads. The QRS axis is the main vector of ventricular activation, which is the overall direction of electrical activity.
Treatment of right ventricular hypertrophy
Against the background of right ventricular hypertrophy, therapy should be directed primarily to the cause that causes it, namely:
- To eliminate pulmonary valve stenosis;
- To normalize lung function;
- For the treatment of heart defects.
In addition, treatment of right ventricular hypertrophy should include symptomatic therapy aimed at normalizing blood pressure and pulse, maintaining the functioning of the heart muscle and its additional nutrition.
As a rule, surgical treatment is indicated in cases where enlargement of the right ventricle causes heart disease. Such operations are usually performed in the first year of a child’s life after diagnosis.
www.neboleem.net
Symptoms of RPG
In its acquired form, this syndrome is characterized by the absence of specific symptoms by which right gastric hypertrophy can be determined.
Signs of right ventricular hypertrophy are similar to the manifestations of many other ailments and at the initial stage of development of the pathology they practically do not manifest themselves, beginning to really bother the patient only with a significant increase in the size and mass of the right ventricular myocardium.
These signs include:
- prolonged pain in the right sternum of a sharp, stabbing nature;
- dyspnea;
- dizziness, accompanied by loss of orientation in space and fainting (in some cases);
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- swelling of the lower extremities, which becomes more pronounced towards the end of the day.
The main clinical signs of RPH include an increase in heart rate (tachycardia) and a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
Diagnostic methods
With RPG, pathological changes are recorded not only in the myocardium. Over time, they are characterized by spreading to the pulmonary arteries and blood vessels, which causes the development of other ailments:
- aortic sclerosis;
- hypertension of the pulmonary circulation;
- Eisenmenger syndrome (excess of pressure in the pulmonary artery over the aortic).
Timely diagnosis of prostate cancer allows not only to prevent the development of these pathologies, but also to significantly facilitate the fight against the syndrome as a whole. The presence of right gastric hypertrophy can be confirmed or refuted only thanks to cardiac examination devices:
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the structure of the heart muscle).
An electrocardiogram as a method for diagnosing RPG is less indicative. Hypertrophy of the right ventricle on the ECG is expressed only in changes in the waves of the cardiogram, which can only indicate the fact of a change in the size of the ventricle; the severity of the pathology cannot be determined in this way.
RVH syndrome is “displayed” on electrocardiography only in moderate and acute forms of the course.
An echocardiogram has much greater diagnostic value.
This research method allows you to determine not only the presence of an enlargement of the right gastric region, but also its exact size, as well as diagnose defects in the structure of heart tissue.
Echocardiography as a method for diagnosing RVH is often combined with Doppler ultrasound, which allows further examination of the direction and speed of blood flow.
This method of research makes it possible to determine right gastric hypertrophy even in a moderate form of the course, thanks to which it is possible to prevent the progression of the growth of cardiomycytes in the heart muscle.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
The goal of treating right ventricular hypertrophy is to stabilize the size of the affected section and prevent the growth of cardiomycytes in the future. The main methods of treating pathology are surgery and drug therapy.
Drug treatment of prostate cancer involves eliminating the symptoms of the pathology by taking medications from various pharmacological groups:
- anticoagulants;
- diuretics;
- cardiac glycosides;
- blood pressure normalizers;
- beta-adrenergic blockers.
To maintain the positive effect, some of the prescribed drugs should be taken throughout life. Complex therapy for right gastric hypertrophy also includes complete cessation of bad habits, correction of daily routine and nutrition.
Prevention of prostate cancer primarily involves regular and timely diagnosis of the condition of the heart muscle. This is especially true for patients at risk, which includes people with congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system and those who have recently suffered from various bronchopulmonary diseases, as well as athletes who are keen on cardio training.
prososud.ru