What is prolactinoma
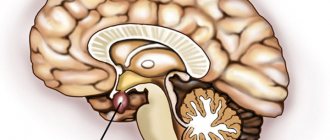
Pituitary prolactinoma (adenoma) is a benign, prolactin-dependent tumor. This neoplasm develops from glandular tissue.
This type of adenoma affects the anterior part of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of the hormone prolactin. The latter regulates milk production and the menstrual cycle in women, metabolism, which determines the nature of the clinical picture of prolactinoma.
Prolactinomas account for 40-50% of pituitary tumors.
More often, pituitary adenoma is diagnosed in women. Moreover, in this category of patients, microprolactinomas are mainly detected (59% of the total number of tumors).
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How are the lymph nodes connected to the thyroid gland?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2020
On average, the size of the tumors does not exceed 2-3 mm. However, in men, medium and large pituitary adenomas are more often diagnosed, whose size is 26-35 and 36-59 mm, respectively. Such neoplasms provoke neurological disorders.
Prolactinomas are relatively rare tumors. Pituitary adenomas of this type are diagnosed in 100-755 patients for every 1 million people. Every year, 6-10 new cases of tumor development are registered.
The risk group includes women aged 20-50 years. In men, pituitary adenoma is registered 10 times less often. But after 50 years, dependence on gender does not play a decisive role.
Prolactinomas, depending on location and size, are classified into two types:
- Intrasellar. They are small in size (no more than 10 mm) and as they grow, they do not affect the area of the sella turcica.
- Extrasellar. The size of these prolactinomas exceeds 10 mm, and therefore the tumors affect the area of the sella turcica.
The size of the tumor determines the nature of the clinical picture and treatment tactics. The risk of malignancy of such tumors is extremely low. Prolactinomas develop into cancer in 2% of patients.
Causes
The true causes of the development of prolactinomas have not been established. More often, neoplasms of this type develop separately from other pathological processes.
Genetic disorders can provoke the appearance of prolactinomas. The latter includes the hereditary disease multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. This pathology is characterized by hyperactivity of the pituitary gland, parathyroid and pancreas.
In 5% of patients, prolactinoma occurs as part of the syndrome of isolated pituitary adenomas. In this case, the tumors grow quickly and have a pronounced clinical picture.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How to avoid calcifications in the thyroid gland
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
Not only the pituitary gland is responsible for the synthesis of prolactin. This hormone is also produced by other organs.
Based on the above, it follows that the following factors can provoke the appearance of prolactinomas:
- liver and kidney pathologies;
- thyroid dysfunction ;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hypothyroidism;
- long-term use of certain medications .
The risk of developing adenomas due to hormonal imbalance caused by pregnancy and a number of other factors cannot be excluded.
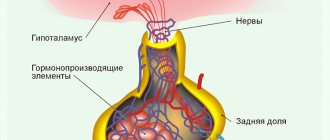
Causes of pituitary prolactinoma
Like most tumor diseases, pituitary adenoma occurs for reasons that are not fully understood. In some patients, excessive growth and activity of cells that form prolactin is observed in a genetically determined disease. It is called polyendocrine neoplasia.
Growth of pituitary adenoma
This means that the endocrine glands, due to a failure of regulation, go beyond the control of the hypothalamus and begin to intensively produce hormones. In such cases, the function of the parathyroid glands, pancreas, and pituitary gland increases. Multiple ulcerative defects are found in the digestive system. Isolated inheritance of a tendency to prolactinoma also occurs.
We recommend reading the article about pituitary insufficiency. From it you will learn about the causes and symptoms of pituitary insufficiency, types of hypopituitarism, as well as the diagnosis and treatment of pituitary insufficiency.
And here is more information about pituitary adenoma.
Symptoms in women
The first symptoms indicating damage to the pituitary gland in women occur at the initial stage of the tumor process. The clinical picture is characterized by phenomena that develop complexly or in isolation.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Normal thyroglobulin levels
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
An increase in the concentration of prolactin in the blood disrupts the synthesis of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. This leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle, which manifests itself in the following forms:
- increasing the period between menstruation to three months;
- amenorrhea, or complete absence of menstrual flow;
- reduction in the duration of menstruation to three days or less;
- light or heavy discharge during menstruation;
- uterine bleeding not caused by the menstrual cycle.
Pituitary adenomas disrupt the ovulation process, and therefore the development of infertility is possible. The latter is also caused by ovarian dysfunction that occurs against the background of prolactinoma.
Damage to the pituitary gland in women provokes galactorrhea. This condition is characterized by frequent discharge from the mammary glands. Prolactinoma often causes bilateral galactorrhea. Discharge can be abundant or rare.
The development of the tumor process is accompanied by a decrease in estrogen levels, as a result of which the woman loses interest in the opposite sex. At the same time, the volume of lubricant secreted by the vaginal mucosa decreases.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
Why do antibodies to thyroglobulin increase?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
An increase in prolactin concentration stimulates the adrenal glands. This leads to rapid male-pattern hair growth. Overactive adrenal glands also cause acne.
If the pituitary gland is damaged in girls, the organs of the reproductive system do not develop sufficiently. Hypoplasia (reduction in size) of the uterus may occur.
High levels of prolactin cause psycho-emotional disorders. When pituitary tumors occur in women, their range of interests narrows and depression develops.
Patients with prolactinoma have problems concentrating, remembering information, and sleeping. The course of the tumor process is accompanied by nervous excitability and increased fatigue.
Clinical picture
The clinical manifestations of the disease are determined by the degree of prolactin production and the compressive effect of the tumor on nearby organs.
One of the first manifestations of prolactinoma in women is menstrual irregularity, which is expressed by:
- oligomenorrhea or opsomenorrhea (extension or shortening of the cycle from normal);
- amenorrhea – complete absence of menstruation;
- impaired production of FSH and, which leads to anovulation and impossibility of conception.
Increased prolactin causes milk to leak from the nipples - galactorrhea, not associated with pregnancy. This symptom often leads to mastopathy in a woman.
An increase in size of prolactinoma can lead to compression of the optic nerve, which manifests itself:
- narrowing of the field of view;
- double vision;
- sometimes blindness.
A neoplasm that compresses brain tissue can cause changes in the central nervous system:
- headache;
- irritability;
- apathy;
- anxiety.
Against the background of prolactinoma, minerals begin to be washed out of the bones, which leads to the development of osteoporosis. Lack of estrogen causes fluid retention in the body and leads to weight gain in women. With increased production of androgens, acne appears and hirsutism develops.
READ ALSO: What is acromegaly: causes and symptoms, photos and treatment of pathology with increased production of somatotropin by the pituitary gland
Symptoms in men
An increase in prolactin concentration has a negative effect on the synthesis of testosterone and the transformation of this hormone into dihydrotestosterone. However, the first signs of a tumor process in the pituitary gland in men appear late.
A decrease in testosterone concentration affects the performance of the genital organs. In men, against the background of prolactinoma, the volume of semen secreted decreases and sperm motility decreases. This is explained by the fact that due to a tumor of the pituitary gland, the supply of nutrients to the ovaries is disrupted.
Testosterone plays a key role in the formation of sexual desire and potency in men. The lack of this hormone provokes a decrease in libido.
Testosterone deficiency causes dysfunction of the prostate gland, which is responsible for the production of a specific secretion that ensures sperm motility.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
What consequences can a pancreatic cyst cause?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 28, 2020
An increase in prolactin concentration stimulates enlargement of the mammary glands (gynecomastia). In rare cases, against the background of a tumor process in men, fluid is released from the nipples.
Damage to the pituitary gland contributes to a decrease in dopamine, as a result of which psycho-emotional disorders develop. Men with prolactinoma become irritable and prone to mood swings. Tumor development negatively affects cognitive functions.
If prolactinoma appears in boys before puberty, the formation of a number of organs is disrupted. Due to a tumor of the pituitary gland, sparse and soft hair appears, and the body remains youthful for a long time. At the same time, fat deposits begin to actively accumulate in the pelvic area.
How does a tumor affect the body?
Among all tumors of the pituitary tissue, prolactinomas are the leaders and account for a third of all diagnosed neoplasms. They are considered benign, and in exceptional cases they degenerate into cancer. Women get sick ten times more often than men. This is due to the greater role of prolactin in the female body:
- responsible for the formation of breast milk after childbirth;
- regulates the formation of estrogen;
- controls menstrual function and fertility.
Men normally have a small amount of this hormone in their blood. It is responsible for the synthesis of testosterone and ensures sperm activity. Prolactinomas in the male body usually reach much larger sizes than in women.
With excess prolactin production:
- the formation of estrogen in women and testosterone in men decreases;
- there is infertility and decreased libido in both sexes;
- men complain of low potency and enlarged mammary glands, and women of irregular menstrual cycles.
The symptoms of the disease also depend on the size of the prolactinoma. Small adenomas grow inside the sella turcica and are manifested only by hormonal imbalances. Upon reaching 1 cm in size, the tumor extends beyond its normal location and puts pressure on the brain tissue and optic nerves that pass nearby.
Symptoms of the extrasellar form
An extrasellar tumor affects the tissues that make up the sella turcica. With such prolactinoma, the nature of the clinical picture does not depend on the gender of the patient.
Compression of brain tissue causes severe headaches that worry constantly. Most often, unpleasant sensations are localized in the temporal zone.
In case of damage to the ternary nerve, the pain syndrome spreads to the facial part of the head. At the same time, the facial muscles retain their previous activity.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
What treatments are there for thyroid cysts?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 25, 2020
With a pituitary adenoma, visual disturbances are often observed due to the proximity of the corresponding nerves and the tumor. This type of disorder manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- narrow field of view;
- disturbance of color perception;
- double vision (diplopia);
- the presence of black spots before the eyes (scotomas);
- strabismus;
- blurred vision.
Depending on the affected area, one eye may be lost from the field of vision. In some cases, the tumor process provokes a pituitary infarction. This condition is characterized by temporary loss of consciousness, attacks of nausea, vomiting, and symptoms of meningitis.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that hormonal imbalance occurs against the background of many pathological processes, a set of diagnostic measures is prescribed to identify prolactinoma.
If a tumor process is suspected, a blood test is performed for prolactin and other hormones produced by the pituitary gland. However, this diagnostic method does not give clear results.
Changes in the concentration of pituitary hormones are caused by the menstrual cycle, pathologies of the adrenal glands, renal failure, circadian rhythm and many other factors.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
How to identify and treat adrenal adenoma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 25, 2020
Therefore, if a pituitary adenoma is suspected, a test with thyrotropin-releasing hormone is prescribed. This substance is administered intravenously. In a normal state, thyroliberin helps to increase the concentration of prolactin by more than 2 times. With adenoma, this indicator does not change or increases slightly.
To detect prolactinoma, a CT scan of the brain is necessary. The method allows you to determine the presence, size and location of the tumor. MRI and craniography are prescribed for a similar purpose.
Diagnosis of prolactinomas
Treatment of pituitary prolactinoma is possible only after a final diagnosis has been established.
The most effective method for diagnosing a benign neoplasm of the pituitary gland is considered to be computed tomography, which consists of X-ray scanning of brain tissue followed by digital processing of the research results. This examination includes the injection of a special contrast agent.
In oncological practice, the method of magnetic resonance imaging, which is based on X-ray examination of the affected area in an electromagnetic field, is widely used to diagnose microprolactinomas.
Also, for early diagnosis, a laboratory blood test aimed at determining the concentration of prolactin plays a significant role. It is recommended to collect biological material three times a day, repeating the study after some time. This is necessary to avoid errors that may be associated with stress and nervous tension.
Treatment
Prolactinoma is treated with medications. In the absence of positive results, surgical removal of the tumor or radiation therapy is prescribed.
If there are appropriate indications, 3 methods of treating prolactinoma are used.
The treatment regimen is selected taking into account the size of the tumor. For microprolactinomas, medications are used that restore metabolic processes and functions of the endocrine system. Larger tumors require medications that stop the growth of the tumor and help reduce its size.
On this topic
- Endocrine system
What are the symptoms and signs of a thyroid cyst?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- February 19, 2020
The basis of treatment for prolactinoma is the drugs bromocritine and cabergoine. The first is a derivative of ergot alkanoids.
Bromocritine drugs increase the sensitivity of hypothalamic receptors that respond to dopamine. This hormone inhibits the synthesis of prolactin and a number of other protein compounds that are synthesized by the pituitary gland.
Cabergoine preparations have a similar effect. However, drugs in this group do not stop the synthesis of other hormones, with the exception of prolactin.
Some patients develop tumor resistance (resistance) to the effects of these drugs. In this case, the dosage of medications is increased or another method of treatment is used.
In 80-85% of patients, the size of prolactinoma resistant to bromocritine decreases with regular consumption of cabergoine preparations. It is important to follow the dosage of the medication as determined by your doctor. Failure to comply with the requirements leads to damage to the heart valves.
Surgery for pituitary adenoma is performed when drug therapy does not produce positive results, the tumor continues to grow, or serious visual disturbances are diagnosed. In addition, this method of treatment is indicated if necrosis of neoplasm tissue is detected.
In 70% of patients, adenoma removal is performed through the nasal sinuses. If necessary, the tumor is first frozen (cryodestruction method) or subjected to chemical treatment.
Radiation therapy is rarely used in the treatment of prolactinoma. This method is more likely than others to cause complications. Therefore, radiation therapy is usually supplemented with other treatment methods.
Treatment of prolactinoma and prognosis
Medical tactics are determined by the activity of prolactinoma. According to indications, conservative treatment or surgical intervention is carried out.
Standard therapy involves measures to reduce prolactin levels using pharmacological drugs . Medicines are selected individually, and their dosage regimen is determined by an endocrinologist.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of prolactinomas:
- Levodopa;
- Cabergoline;
- Bromocriptine;
- Cyproheptadine.
Bromocriptine therapy has a positive effect in 85% of cases. After several weeks of course treatment, the level of “milk hormone” returns to normal levels.
Cabergoline is often preferred; this remedy has fewer side effects, and the prolonged nature of the action allows you to take it 1-2 times a week.
Pharmacotherapy can reduce the diameter of the tumor and restore vision. Microprolactinomas disappear in some cases. The drugs restore the menstrual cycle and restore fertility. In male patients, sperm count improves, and sexual function returns to normal due to the normalization of testosterone production.
Radiotherapy makes it possible to gradually stop taking pharmacological agents, but the positive effect of exposure to ionizing radiation fully develops only after several years. One of the side effects of radiation is pituitary failure, requiring hormone replacement therapy.
During conservative treatment of large prolactinomas, periodic monitoring is carried out using tomography. If a positive effect cannot be achieved, they resort to surgical intervention - adenomectomy. The tumor is removed through a small incision in the projection of the nasal sinuses.
Prolactinomas are prone to recurrence; complete clinical recovery occurs in only 25% of patients . The least favorable prognosis is for macroprolactinomas and adenomas that have undergone malignancy.
Almost half of patients experience relapses within 5 years after surgery.
Plisov Vladimir, medical observer
12, total, today
( 166 votes, average: 4.46 out of 5)
Diabetes mellitus: treatment with folk remedies
Adrenogenital syndrome: symptoms and treatment