The child's body is very fragile and susceptible to many diseases. Very often the reason for this is insufficient attention to hygiene along with reduced immunity.
Children love to learn everything new, exploring new territories and objects, which sometimes leads to various types of injuries: bruises, abrasions, scratches, etc. And if these places are treated incorrectly or insufficiently, various diseases associated with pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic may develop microorganisms. One of these diseases is streptoderma.
What is streptoderma?
Streptoderma is a purulent infectious disease caused by infection of the surface layers of the skin with streptococci. Develops after streptococci enter damaged areas of the skin.
If detected early and treated correctly, it lasts less than a few weeks. In cases where defense mechanisms do not work well and treatment is not thorough enough, the disease can last more than a month and cause complications.
Some factors that have a negative impact on the course of the disease:
- Weak immune response due to malnutrition, anemia, general intoxication or helminthiases;
- Lack of adequate treatment for damaged skin;
- Frequent contact of the wound with water;
- Poor personal hygiene, insufficient child care;
- Frequent hypothermia or overheating;
- Concomitant infections that provoke copious secretion of mucus that irritates the skin (otitis, rhinitis, etc.);
- Chronic skin diseases: pediculosis (lice), scabies, allergies, dermatitis and others.
Streptococci are microorganisms that are part of the normal microflora of the human body. They are considered opportunistic and do not normally cause any disease.
However, under certain conditions (reduced immunity, prolonged contact, inflammatory processes) they can cause considerable harm to human health. In such cases, they can cause many diseases such as tonsillitis, meningitis, glomerulonephritis, bronchitis, scarlet fever, myocarditis, sepsis, rheumatism and others.
DOCTORS RECOMMEND!
Dermatitis is a rash in the form of blisters, peeling, discomfort, itching, burning, etc. The reasons may be different, depending on which there are several types of dermatitis, for example, infectious, allergic, atopic, food, etc.
The cream contains exclusively natural ingredients, including beekeeping products and plant extracts. High efficiency, virtually no contraindications and minimal risks of side effects. Amazing results of treatment with this drug are evident in the first weeks of use. I recommend.
Oral antibiotics
Oral antibiotics for streptoderma are not indicated in all cases. The question of the need to prescribe antibacterial drugs is decided by the attending physician. Antibiotics are necessarily prescribed for ecthyma, extensive skin lesions, signs of beginning complications, as well as for high fever and other symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
The choice of antibacterial drug is determined by analyzing the bacterial contents of the rash. For streptococcal infections, penicillin drugs are most effective:
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Flemoxin Solutab";
- "Amoxiclav";
- "Augmentin".
However, penicillins often cause allergic reactions. Therefore, if a patient experiences undesirable effects, these medications should be replaced with antibiotics from the macrolide group, cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones:
- "Clarithromycin";
- "Azithromycin";
- "Sumamed";
- "Rovamycin";
- "Cefuroxime";
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Levofloxacin".
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed for a period of 5 to 14 days. Most often, antibiotics are used orally; intramuscular or intravenous administration is indicated only in severe cases.
How does streptoderma begin in children?
Streptoderma most often develops in children. Their fragile immunity is not always able to fight streptococcus.
There are two main factors leading to the development of this disease in children:
- Violation of the integrity of the skin: wounds, abrasions, cuts, scratches, insect bites, and sometimes microcracks and other subtle damage. If the wound is not disinfected, the pathogenic microorganism begins to multiply rapidly, which provokes the onset of the disease;
- Streptococcus is a conditionally pathogenic microorganism that lives inside the intestines, on mucous membranes and on the skin, and exhibits its pathogenicity when tissue is damaged and the body’s defenses are weak;
Due to the fact that streptococci have a long incubation period, the first signs appear no earlier than after a week.
The development of the disease proceeds according to the following scenario:
- A rash appears that can occur on different parts of the body, most often on the face;
- Initially, the rash appears as small blisters filled with liquid; over time, the liquid becomes cloudy, and the blisters enlarge and spread, sometimes merging;
- These blisters are called conflicts; after they ripen (5-7 days) or as a result of mechanical opening, a crust forms in their place, which then disappears, sometimes pigment spots may appear;
- The rash causes terrible discomfort and itches, which affects the child’s behavior and mood;
- A slight increase in temperature up to 37.5 degrees is also possible; in advanced cases, it can increase significantly.
What can trigger the onset of the disease
The direct cause of streptoderma is the pathogen - streptococcus. However, in order for the development of the disease to begin, additional unfavorable conditions are necessary. These include all factors that contribute to decreased immunity:
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system;
- circulatory disorders;
- suffered acute infections.
In children, symptoms of streptoderma may occur after a sore throat or scarlet fever. These diseases are caused by the same microorganism - streptococcus.
In addition, the causes of streptoderma may include a violation of the integrity of the skin. After all, the infection enters the epidermis through wounds. Even small scratches, abrasions and bites can become a gateway for bacteria to enter.
The acidity (pH) of the skin also plays a big role. Its normal values are considered to be values from 5.2 to 5.7 units. If the pH increases to 6–7 units, then the microflora of the epidermis is disrupted. The result is a favorable environment for the proliferation of microbes.
People with hormonal disorders often suffer from streptoderma. Improper functioning of the endocrine glands affects the condition of the epidermis. With hormonal imbalance, the skin becomes oily and becomes covered with acne. This epidermis is very susceptible to infection.
What does streptoderma look like in children?
At the beginning of the disease, pink spots with rounded outlines appear on the skin. And after a few days, purulent blisters develop - conflicts. They have a size of 2 - 5 mm, they are constantly increasing in size, and in some cases can reach several centimeters. After ripening, they burst, the place where the bubble was becomes covered with a dark crust, and the outbreak spreads.
If left untreated, it can reach large sizes. The affected areas consist of conflicts of different stages and areas covered with a dark crust.
Photo
Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of infection with parasites (Ascaris, Giardia, Toxocara). Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which must protect the body from various diseases. E. Malysheva shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that it’s enough... Read more »
Symptoms of streptococcal impetigo
Most often, the disease occurs in the form of streptococcal impetigo. This is the mildest form of pathology. A slight redness appears on the skin, and then blisters (phlycten). There is purulent content inside them. Phlyctens can grow up to 1–2 cm. This rash is observed mainly on the face. Then their walls rupture and pus comes out. At the site of the rash, crusts form, which subsequently fall off. As the skin heals, a spot remains, which then fades. There are no traces left in the rash areas. The disease lasts up to 2–4 weeks.
Sources of infection
The pathogenic form of the microorganism can appear on the affected skin in the following ways:
- From the child's own skin;
- May be present on objects and things touched by the infected person (blanket, plastic toys, dishes and other objects);
- From a person who is not sick, but is a carrier of pathogenic streptococcus;
- Transmitted from a sick person;
- It can be found in water, soil, on pets, etc.
Sometimes this disease can develop into a small epidemic (in orphanages, schools and other places where children gather), the source of infection is a sick child, and upon contact with others, he infects them, and they infect others.
Diagnosis of the disease
To treat and select a medicine for streptoderma, qualified diagnostics is necessary. Moreover, the initial stages of this disease have signs inherent in herpes, candidiasis, atopic dermatitis, allergies, and eczema. To make a diagnosis, the doctor does:
- conversation with the child’s parents to collect anamnesis;
- visual examination of the patient to identify primary and secondary signs of the disease;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- To find out how to treat streptoderma, inoculate the liquid and dried crusts on a nutrient medium. Thus, the type of bacteria and their sensitivity to antibiotics are determined;
- feces for coprogram and oviworm;
- examination of the gastrointestinal tract to confirm or exclude chronic streptoderma.
The listed methods contribute to the correct diagnosis. The doctor prescribes complex therapy using medications for local and general use. In some cases, auxiliary healing with folk remedies is recommended.
Tired of fighting dermatitis?
Peeling of the skin, discomfort and itching, redness, rashes in the form of blisters, cracks, weeping wounds, hyperemia, burning are signs of dermatitis.
Treatment requires an integrated approach and this cream, which has a 100% natural composition, will be a good helper.
In such cases, our readers recommend using this product - ZDOROV cream-wax with bee venom.
It has the following properties:
- Relieves itching after the first use
- Eliminates rashes and peeling skin in 3-5 days
- Reduces excessive skin cell activity
- After 19-21 days, completely eliminates plaques and traces of them
- Prevents the appearance of new plaques and an increase in their area
Streptococcal throat infection: sore throats and pharyngitis
Sore throat is an acute infectious disease of the body that occurs with symptoms of acute inflammation of the structures of the pharyngeal lymphoid ring. There are several types of the disease, among which purulent tonsillitis is considered especially dangerous. Anginas are divided into catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, fibrinous, ulcerative-necrotic tonsillitis and phlegmonous. Their symptoms vary from each other. Sore throat is one of the most common diseases after influenza and acute respiratory infections.
Children get sick more often. Most adults become ill before the age of 40. The seasonal nature of the disease is noted. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets and through household items. The cause of sore throats can be an infection that is localized in the maxillary sinuses, in areas of dental caries, and gums. In chronic tonsillitis, autoinfection often occurs (self-infection from local foci of infection). The state of the human immune system is of primary importance in the development of the disease.
Rice. 1. The photo shows acute catarrhal tonsillitis. “Red throat” - hyperemia of the area of the lateral ridges and larynx. Swelling, pain, redness and enlarged lymph nodes are the main symptoms of streptococcal sore throat.
Rice. 2. The photo shows a purulent sore throat. Streptococcal infection is the main cause of the disease.
Rice. 3. The photo shows chronic tonsillitis. The tonsil on the left is significantly increased in size. Pus and purulent plugs in the lacunae are visible.
Up to 70% of tonsillitis cases are caused by viruses. Among them, the most common are coronavirus and rhinoviruses. The remaining 30% comes from bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms. Up to 80% of cases of sore throats caused by bacteria are caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes, GABHS).
To timely prescribe an antibiotic for angina, it is necessary to identify antigens to GABHS using the Streptatest system.
Streptotest is a universal tool that allows you to determine the cause of a sore throat in 5 minutes. It will quickly establish the presence of group A β-hemolytic streptococcus in the oral cavity, which means it will help to promptly prescribe adequate antimicrobial therapy. In the absence of a pathogen, streptotest will allow you to avoid unnecessary treatment of sore throat with antibiotics. Streptotest has high (about 90%) specificity and high (about 95%) sensitivity.
Rice. 4. Streptatest has high (about 90%) specificity and high (about 95%) sensitivity. Allows you to determine the cause of a sore throat in 5 minutes.
Streptococcal tonsillitis is complicated by purulent otitis media, sinusitis, peritonsillar abscess, mastoiditis, meningitis, and pneumonia.
Streptococcal infection can cause an autoimmune response, which leads to serious complications of internal organs:
- rheumatic damage to the heart muscle;
- joint damage (arthritis);
- kidney damage (glomerulo- and pyelonephritis).
When microbes enter the bloodstream and massively multiply, sepsis and meningitis can occur.
Treatment of sore throat is carried out with antibiotics of the following groups:
- Penicillin group drugs (Phenoxymethylpenicillin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin).
- Macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin).
- Cephalosporins (Cefatoxime, Cefuroxime).
Routes of transmission
The route of infection is the mechanism by which an infectious pathogen moves from an infected organism.
There are three main ways of transmitting streptoderma:
- Contact – the patient’s skin touches the child’s wounded skin (dynamic games or any other touch);
- Contact and household - the use of common objects and any other objects touched by the patient;
- Airborne - when the pathogen ends up on wounded tissues through coughing or sneezing. It is quite rare.
What pathologies can streptoderma be confused with?
Sometimes this disease is similar to others:
- Atopic dermatitis. The hallmark is chronic itchy lesions and abnormally dry skin.
- Candidiasis. This pathology is characterized by papules or red, moist plaques, usually affecting the mucous membranes.
- Simple herpes. This pathology is characterized by blisters that become crusty.
- Dermatophytosis. In this case, the lesion is usually scaly and red blisters may appear on the legs.
- Insect bites. Papules are visible at the site of the bite and can be painful.
- Scabies. The damage consists of abscesses, small blisters, and itching at night.
- Chickenpox. In this case, blisters appear throughout the body, and the oral mucosa may be affected.
In our material we will tell you how you can effectively treat stomatitis in children.
Here you will learn about the most effective methods of treating infant heat rash.
Why does a child grind his teeth in his sleep? Here we will look at the main reasons that can lead to such a problem.
Forms and symptoms of streptoderma in children
Let's look at the symptoms that may occur as a result of these diseases:
- Deterioration in health;
- General intoxication of the body;
- Painful sensations in the head area;
- A slight rise in body temperature (up to 37.5), in severe or advanced cases - higher;
- Drawing or aching pain in joints and muscles;
- Nausea, vomiting, dizziness;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Blood tests may get worse.
How long streptoderma will last depends on the form of the disease, the degree of damage and the effectiveness of treatment. Typically, treatment time lasts from several days to several weeks. The classification of the disease as one or another type depends on the location of the lesion, the depth of penetration and the degree of damage to the skin. There are several main forms of this infection.
Streptococcal impetigo
This form of streptoderma is the most common and one of the most common among children. In this case, characteristic inflammatory rashes are formed, which look like small blisters and affect small areas on the skin. Impetigo can spread quickly due to its high contagiousness (infectiousness).
Streptococcal impetigo is characterized by the fact that the disease does not penetrate into the deep layers of the skin. Since the protective mechanisms of the skin are able to restrain further penetration of the infectious agent.
Manifestation:
- Areas of redness appear on the skin, indicating the onset of the inflammatory process;
- At the site of redness, elements are formed - conflicts, which are similar in appearance to acne. Filled with liquid, mostly clear, less often cloudy or dark. An individual bubble is several mm in size;
- After a few days, the bubble becomes cloudy and bursts. The place where it was is covered with a thick crust;
- The crust peels off, the skin underneath has altered pigmentation, which returns to normal over time;
- Flyktenes ripen in no more than a week;
- Significant changes in body temperature and tests are usually not observed.
If treatment is started before the first phlyctena matures, the disease will not progress further. But since everyone is accustomed to not seeking medical help until the last minute, it usually lasts longer than it should.
The inflamed area itches, the child scratches it, and streptococcus gets under the nails and on the fingertips. Then he touches a towel, pillow, other objects, his face or any other part of the body with his hands, which contributes to the further spread and progression of the disease.
With proper hygiene and quality treatment, impetigo goes away within one to two weeks, with mild impetigo – less than a month. If left untreated and personal hygiene is violated, the disease can drag on and lead to negative consequences.
Bullous impetigo
The symptoms of this form are more severe and unpleasant; it is advisable to conduct a medical examination and begin treatment.
Has the following distinctive features:
- Localization: trunk and limbs;
- Large bubbles - bullae (up to several cm), single-chambered, located at a short distance from each other, can merge;
- The inflammation is severe, the temperature may rise and your health may worsen;
- The bullae are filled with serous fluid with pus, grow and then open, and an open wound may form in their place.
Slit impetigo
Common impetigo, which is localized at the edges of the mouth. Sometimes in the corners near the eyes or near the nose. It also has the traditional name “zaeda”.
Characterized by:
- The appearance of one, or less often several, conflicts;
- Usually does not spread even with minor treatment;
- Does not cause complications, responds well to treatment;
- Very rarely it becomes chronic, usually with a general weakening of the body.
Erythematosquamous streptoderma
It is also called dry streptoderma . It is easy and usually does not require the use of antibiotics.
Has the following manifestations:
- Usually localized on the skin of the face, sometimes on other parts of the body;
- Looks like red or dark pink spots;
- Over time, the redness disappears, and the skin at the site of the spots peels off in the form of white scales.
Although much milder than other forms of streptoderma, it is still highly contagious and requires isolation from other children and effective treatment.
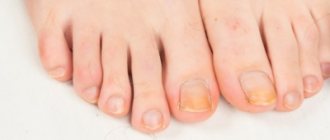
Superficial panaritium
It affects the phalanges of the fingers in the area near the nail plate. Occurs when the skin of the fingers is damaged or when intensively scratching an existing impetigo and introducing streptococcus under the nails.
Distinctive features are:
- Phlyctens appear around the nails, the skin is inflamed and very painful;
- Sometimes, without proper treatment, the nail plate can be torn off;
- To prevent it, it is enough for every, even very small, injury to the fingers, the wound must be disinfected.
Vulgar ecthyma
A complicated form of streptoderma that occurs when skin protection fails and streptococcus penetrates into the deep layers of the skin.
Symptoms:
- It looks like a purulent ulcer, sometimes there are several of them;
- Mainly formed in the area of the lower extremities;
- Sometimes it occurs after suffering from severe viral infections or in some chronic diseases affecting human metabolic processes;
- Treatment of ulcers is carried out together with antibiotic therapy, and a number of general strengthening measures are also used.
Stories from our readers!
“I suffered from dermatitis. His hands and face were covered with small spots and cracks. No matter what I tried, the drugs only helped for a while. A colleague advised me to order this cream.
Finally, thanks to the cream, I completely got rid of the problem. After the third procedure, the burning and itching disappeared, and after 4 weeks the signs of dermatitis disappeared. I am very pleased and recommend using this cream to all people suffering from skin problems.”
Clinical picture of bullous impetigo
Bullous impetigo is more severe. This disease is more common in infants. Bubbles with this form of the disease usually appear on the arms or legs. They reach sizes of 1–2 cm. Over time, they break through. In their place, ulcers appear that take a long time to heal. Itching bothers the patient after opening the vesicles. This form of the disease is always accompanied by a significant deterioration in health: weakness, fever, enlarged lymph nodes. Skin healing can take up to 2 months.
Diagnosis of streptoderma in children
To make a correct diagnosis, you need an experienced doctor - a pediatric dermatologist or pediatrician . A specialist can accurately determine the form of the disease already at the stage of external examination of the patient.
To confirm the diagnosis, skin swabs may be taken and bacteriological culture performed. Often, the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics is determined. This procedure allows you to begin competent treatment of the patient as soon as possible.
If necessary, additional tests may be prescribed:
- Study of blood parameters;
- Checking for helminths;
- Analysis of urine;
- Testing blood for HIV;
- Carrying out the Wasserman reaction - diagnosing syphilis;
- Analysis of the ratio of thyroid hormones.
Features of the treatment of streptococcal dermatitis
Dermatological diseases affect the skin of people of different ages and genders. Problems in this category are divided into several types and each has its own characteristics.
Often the skin is affected by a disease such as streptococcal dermatitis, which brings a lot of discomfort.
To protect yourself from this type of dermatitis and know how to deal with it correctly, it’s worth taking a closer look at the problem.
Main characteristics, treatment, precautions
A disease such as dermatitis always affects a person’s skin completely suddenly. The reaction, which manifests itself in the form of redness, rashes, itching and pain, is always extremely unpleasant for every person and everyone tries to deal with it productively.
But with ordinary dermatitis, a person can cope quickly enough, but with streptococcal dermatitis, you will have to tinker a little. A skin disease that is caused by pathogenic streptococcus bacilli, with insufficient or improper treatment.
Always has adverse consequences. More detailed characteristics of this disease and productive methods of treatment are worth considering in more detail.
External signs of illness
When a streptococcus bacillus is introduced into the human body, problems with the digestive system, liver and kidneys are practically unavoidable. But as it turned out, the problem not only adversely affects internal organs, but also affects the skin. Streptococcal skin dermatitis has many unpleasant manifestations, and its appearance is manifested as follows:
- severe redness in the affected area, occurring suddenly;
- the appearance of blisters resembling calluses of medium size;
- the contents of the bubbles are yellowish-brown in color;
- in place of the burst blisters, a rough, yellow crust forms;
- skin is quite dry.
Most often, such an unpleasant skin reaction appears precisely due to the influence of beta-hemolytic group streptococci. They act on the outer layers of the epidermis quite quickly and have the ability to penetrate quite deeply in a short time.
No one is safe from infection with streptococcus bacillus. The problem occurs in adults and children so quickly that it is not even possible to eliminate it in the initial stages. Treatment of the problem requires the intervention of a doctor, because independent attempts to eliminate the problem can lead to complications.
How exactly does streptococcus infection occur?
Streptococcus rods are always present in the air and have the ability to persist on various surfaces and personal items. Streptococcus can easily become infected through shared objects, personal hygiene items, food, or you can get the problem directly from the air.
In order for streptococcus to gain a foothold on the human body and begin to have an extremely active effect on the body and skin, the person at risk must have the following problems:
- decrease in the protective function of the body as a whole and the level of the protective mechanism of human skin;
- insufficient cleansing of the skin from various contaminants;
- the presence of varicose veins and other problems with blood vessels;
- a sharp change in temperature conditions - an instant transition from too high to too low a temperature;
- the presence of microcracks and wounds on human skin that are not properly treated;
- presence of abrasions, insect bites, scratches;
- the presence of chronic diseases of various types;
- the constant presence of nervous breakdowns and stressful situations;
- intoxication of the body.
Often the problem in adults and children manifests itself due to the presence of several provoking factors at once. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms are able to act on the human body much faster.
An experienced medical specialist should accurately determine the provoking factor that contributed to the formation of the problem. If only traces of the impact of the problem are eliminated, and the provoking factor remains unattended, the result of eliminating the problem will be extremely temporary.
Treatment methods
To completely eliminate streptococcal dermatitis in adults and children, affected subjects should definitely consult a doctor. After all the necessary examinations and laboratory tests, individual treatment is prescribed for each specific person. Quite often, the following drugs and techniques are used to eliminate the problem of streptococcal dermatitis:
- regular treatment of affected skin with boric or salicylic alcohol;
- applying wet-dry dressings soaked in various pharmaceutical solutions;
- use of antihistamines and antibiotic pharmaceuticals;
- using various hormonal drugs.
Separately, remedies are prescribed to eliminate the root cause of the disease. Some patients wish to combine traditional medicine with pharmaceutical medications. In this case, the patient needs to consult a dermatologist and choose the safest herbs and techniques for himself.
If several external and oral agents are used in the treatment process, a person should maintain a certain time interval before using each.
During treatment, you should abandon standard hygiene products and replace them with more gentle options. Ointments and creams.
Which are used to treat the problem must have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties.
Oral medications should be taken with extreme caution, without violating medical recommendations. If any unpleasant moments arise or there is no result from the treatment at all, and the situation gets even worse, you should inform your doctor about this situation.
What happens if streptococcal dermatitis is not treated?
A dermatological disease caused by streptococcus bacillus must be treated without fail. This problem does not have the ability to resolve itself, and without the intervention of medications, it has an even more detrimental effect on human skin. Lack of treatment for streptococcal dermatitis or its incorrect implementation is what leads to the following consequences:
- damage to a fairly large area of skin;
- the formation of wounds, too dry and dense crusts;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor and suppuration processes;
- degeneration of streptococcal dermatitis into eczema.
If the problem is left untreated, it becomes permanent and it becomes quite difficult to get rid of it. Streptococcal bacillus has the ability to change its location and affect internal organs.
Self-medication of the problem leads to unpleasant consequences, which you will have to get rid of quite quickly. Streptococcal dermatitis, which is in the later stages, is quite difficult to treat and the victim is unable to solve his problem for quite a long time.
How to behave during treatment
Getting rid of this problem, whether it occurs in adults or children, will take quite a lot of time. During this period, a person needs to take more careful care of his skin and follow certain rules. In order to completely eliminate a dermatological problem and restore a beautiful appearance to your skin, a person in everyday life should follow these instructions:
- constantly monitor skin hygiene and treat affected areas;
- try to avoid injury to the skin, exposure to mechanical and chemical irritants;
- strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and do not change the rules of treatment on your own;
- do not comb the skin in the affected areas and do not try to remove the scabs until they fall off on their own.
More detailed instructions and rules for each individual person will be provided by the attending physician. The patient is required to be alert, diligent, and able to use medications correctly.
If we are talking about using creams, then you should not apply them unless absolutely necessary, and the amount of product used should not be too large.
Oral medications should be used strictly according to the instructions, using the permitted dosage.
If any of the drugs causes a negative response from the body, then you should immediately inform your doctor about this and continue the course of treatment with another drug.
You should not use traditional medicine for treatment without consulting your doctor. Only after the doctor’s permission can a person supplement standard treatment with additional techniques.
What is the difference between streptoderma?
Many skin diseases, being at different stages of clinical development, can be similar to streptoderma; in some cases, it becomes almost impossible to distinguish them only by appearance.
In such cases, additional tests are performed, and they also monitor changes in the patient’s symptoms over time. It is advisable that a specialist deal with this; making an independent diagnosis, as well as self-medication, can not only not help, but also do harm.
It is necessary to distinguish streptoderma from the following diseases:
Pyoderma
Streptoderma is a branch of pyoderma, because any purulent skin inflammation in medical practice is usually called pyoderma. In the case of streptoderma, the phlyctenae are transparent, filled with serous fluid, sometimes with a small admixture of pus. Pyoderma is similar to impetigo vulgaris, but this is not a serious problem, because in both cases a tank is performed. sowing and selection of the necessary antibiotics. And before determining antibiotic sensitivity, nonspecific antibiotics are used that act on various microorganisms. You can read detailed information in the article on the topic of pyoderma in children.
- Allergic rash. At the initial stage, streptoderma is similar to a common allergic rash, which looks like transparent blisters. This makes it difficult to make an early diagnosis; sometimes you need to wait several days until the bubbles (with streptoderma) begin to burst. And this is not very convenient, so to clarify it is necessary to carry out a series of tests, or conduct a small test: lightly press your fingers on the rash - with an allergic rash, the skin at the point of pressure will turn white.
- Syphilitic rash. Elements of a syphilitic rash have a more inflamed appearance, but identifying them purely visually is not very practical. Therefore, if a dermatologist has any doubts, he can prescribe the Wasserman reaction.
- Chicken pox. The chickenpox rash starts from the head, so it is sometimes mistaken for streptoderma. But when it spreads throughout the body and the patient’s temperature rises sharply, the diagnosis becomes obvious - chickenpox.
- Herpes. Herpes differs from slit-like impetigo in that with herpes the blisters take longer to mature, and after they mature, cracks do not form. Another difference is that impetigo forms in areas where the skin is damaged. Here you can find out in detail what herpes is in a child.
- Candidiasis of the corners of the mouth. With candidiasis, changes appear on the mucous membrane, similar to those with thrush - small white precise rashes.
Symptoms of vulgar ecthyma
With vulgar ecthyma, damage occurs to the deep layers of the skin. This is the most severe form of streptoderma. It develops with a strong decrease in immunity: in patients with diabetes, tumors, viral infections.
Affected areas are noted on the legs and buttocks. Large blisters with thick walls, filled with pus, form. After their breakthrough, painful ulcers appear that heal very slowly. Rough scars remain on the skin. The disease is always accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication: high fever, weakness, enlarged lymph nodes, headache.
Treatment of streptoderma in such a severe form should be started immediately. Vulgar ecthyma is often complicated by sepsis. In addition, staphylococci are often associated with streptococcal infections, which leads to even more severe skin damage.
Treatment of streptoderma in children
The disease is highly contagious and can quickly spread throughout the body, causing unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, it is always necessary to treat, even if there are no serious manifestations and it seems that it will “go away on its own.”
You need to start with hygiene:
- At first, you should not bathe or otherwise wet the affected areas of the skin. Wetting promotes the spread of the disease.
- Areas of the skin that have not been affected by infection must be wiped daily with warm water or a decoction of medicinal herbs.
- Make sure that the child does not touch or scratch the infected areas of the skin; the doctor may also prescribe medications to reduce itching.
- The child must have personal household items: towels, bed linen, a change of clothes, dishes and cutlery. They need to be disinfected regularly.
- Toys need to be washed.
- If a child is injured, it is necessary to disinfect the wound.
Here you can read more about the treatment of streptoderma in adults.
Systemic treatment
Systemic treatment is a method of influencing the patient’s condition in which the drug is delivered to all human tissues and organs through the bloodstream. It affects the entire body and is used mainly in severe cases.
That is, in cases where local treatment is not effective enough. During systemic therapy, the doctor must monitor the patient’s condition, because systemic treatment may also have side effects.
For the systemic treatment of streptoderma, various antibiotics are used (mainly penicillin, less often cephalosporins or macrolides) and restorative drugs, vitamins and immunomodulators.
A doctor may decide not to use penicillin antibiotics for several reasons:
- The patient has recently taken antibiotics of this group;
- Intolerance to such antibiotics;
- The microorganism is resistant to them.
Antibiotics for streptoderma
The following groups of antibiotics are used:
- Penicillin antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Augmentin, Flemoxin Solutab, etc.;
- Macrolides: Fromilid, Sumamed, Azitral, Erythromycin, etc.;
- Cephalosporins: Ciprofloxacin, Cephalexim, Pancef, etc.
Local treatment
Local treatment involves treating the infected area with antiseptics, applying antibacterial ointments, and in extreme cases, ointments with hormones, and applying various lotions.
Let's look at some of them:
- Liquid antiseptics: brilliant green, boric acid, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, fucorcin and others;
- Antibacterial ointments: erythromycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, baneocin, zinc and others;
- Antibacterial ointments with hormones: Prednisolone, Canison Plus, Lorinden S, Triderm and others.
For any questions related to the choice of drugs, please contact specialists.
External means
How to smear the affected areas of the skin for streptoderma? This question often worries patients. Before applying ointments, rashes must be treated with the following antiseptic solutions:
- brilliant green;
- fucorcin;
- iodine solution;
- boric acid"
- hydrogen peroxide;
- "Miramistin";
- "Chlorhexidine";
- alcohol and aqueous solution of methylene blue;
- potassium permanganate.
Alcohol solutions with dyes (brilliant green, fucorcin, methylene blue) most effectively affect the causative agent of the disease. However, they cannot be used for rashes on the face, as well as for the treatment of streptoderma in infants and the elderly. These drugs may cause skin irritation. Antiseptics with iodine, chlorhexidine and Miramistin are not recommended for children under 3 years of age.
Rashes are treated with antiseptics 3-4 times a day. Local topical agents can be applied to the affected areas only 30 minutes after applying the solutions.
For streptoderma, ointments with antiseptics and antibiotics are prescribed:
- "Tsindol";
- zinc ointment;
- salicylic ointment;
- "Baneotsin";
- "Levomekol";
- "Sintomycin";
- "Streptocide";
- Fusiderm.
These local products penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis and prevent the growth of bacteria. They are applied to the skin or used as compresses.
It is important to note that Acyclovir ointment should not be used for streptoderma. This is an antiviral agent that does not affect streptococci.
Sometimes dermatologists recommend hormonal ointments with corticosteroids to relieve itching. Under no circumstances should such remedies be used independently. The question of their appointment can only be decided by the attending physician. They are not indicated for all patients. They are usually prescribed for streptococcal ecthyma, the chronic course of the disease, as well as for the combination of streptoderma with dermatitis. Corticosteroid ointments “Pimafukort”, “Akriderm”, “Triderm” are used.
During treatment, it is not recommended to take hygienic water procedures. Streptococcus multiplies rapidly in a humid environment, and rashes after washing can begin to spread to healthy areas of the skin.
Hygiene and prevention
Since streptoderma is an infectious bacterial disease, the best way to prevent infection is to keep your skin clean. Insect bites, cuts, and superficial wounds should not be ignored.
After damage occurs, wash the area with warm water and apply a disinfectant. Even if the child develops a pathology after this, it is necessary to keep family members safe.
The following measures will help you prevent the spread of infection:
- Wash infected areas with warm water and soap.
- Cover them with a non-stick bandage to prevent your child from scratching the wounds with his nails.
- Wash your child's clothes separately every day.
- Trim your child's nails to prevent scratching and secondary infections.
- When applying a topical antibiotic, always wear latex gloves and then wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.