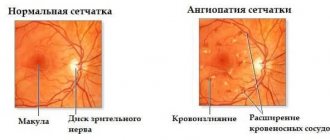
Retinal detachment is a severe disease of the organ of vision in which the retina is detached from the choroid (choroid). In a healthy eye, the retina is adjacent to the choroid, from which it receives nutrition (see structure of the eye). Retinal detachment in our time remains the most difficult pathological condition in terms of surgery and the most severe outcome. Over the past decades, there has been an increase in this nosological form, and on average, retinal detachment occurs annually in one out of every 10,000 people. Currently, retinal detachment occupies one of the main places among the causes of disability and blindness, and 70% of those suffering from this pathology are people of working age. Most often it occurs with injuries and myopia, as well as with diabetic retinopathy, intraocular tumors, and retinal dystrophies.
Causes of retinal detachment
To understand the reasons, let's consider the mechanism of the disease. The development of the disease can be provoked by physical overstrain, sudden pressure on the surface of the retina, resulting in the appearance of small defects, with the appearance of which fluid from the vitreous body moves into the space under the retina. The resulting fluid begins to separate the retina. The more fluid leaks out, the larger the detachment area will be.
Basically, this disease is observed only in one of the eyes, but at the same time, it negatively affects the other eye. Therefore, both eyes are examined with equal care.
- The disease can occur through eye injury (penetrating injury). In addition to the retina, other membranes of the eye can be injured.
- Another reason for the appearance of the disease is diseases of the visual organs (uveitis, tumors of the vascular membranes, retinitis, age-related macular degradation, diabetic retinoptia and other diseases).
- The occurrence of peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophies, which cause visual impairment and can occur even in healthy people. In such cases, the disease can be detected using a three-mirror Goldmann lens.
Risk factors that provoke the disease:
- eye injury;
- retinal detachment in the fellow eye;
- the presence of this disease in close relatives;
- peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy of the retina;
- activities associated with constant physical stress and heavy lifting;
- the presence of various retinal pathologies.
Who is at risk?
- people diagnosed with diabetes mellitus;
- people suffering from high myopia, astigmatism (as these conditions provoke thinning of the retina);
- athletes involved in hazardous sports (weightlifting, boxing, wrestling).
At-risk groups:
- persons with moderate and high myopia
- elderly people with concomitant diabetes mellitus
- persons with hereditary dystrophic diseases of the retina (vitreoretinal degenerations)
- persons with inflammatory diseases of the posterior segment of the eyeball (retinitis, chorioretinitis)
- pregnant women
The connection between blunt trauma (contusion of the eyeball) and penetrating wounds of the eye with retinal detachment is beyond doubt. The causes of retinal detachment are the development of dense fibrous strands in the vitreous body, membranes on the surface of the retina and under it, their contraction and tension of the retina. As a result of hemorrhages in the retina and vitreous body, compaction of the retina develops, adhesions with the vitreous body are formed, which lead to the appearance of valve and perforated ruptures. Blunt trauma provokes retinal detachment within two years after injury in 80% of cases.
Symptoms
- The appearance of “flashes”, “sparks”, floating dots, “lightning”, floating dots resembling “soot flakes”.
- The appearance of “curtains” or “veils” before the eyes. Washing with tea or other special preparations does not give results. At this moment, it is important to remember how the disease began to manifest itself, from which side it began (where the “curtain” appeared).
- Local loss of visual fields, narrowing.
- The objects you are looking at begin to become distorted, their size and shape change, and subsequently object vision decreases.
- With the rapid development of the disease, a veil may appear before the eyes.
When a retinal vessel ruptures, black dots and spots appear before a person’s eyes, and pain and discomfort may also manifest themselves.
When cobwebs and floating spots appear before the eyes, this may indicate that retinal detachment has occurred, which has caused hemorrhage in the middle of the vitreous.
In some cases, patients notice that after a night's rest their vision has returned to normal. This is due to the fact that the fluid that accumulated under the retina overnight has resolved and the retina has returned to its original place. But after a few hours, the disease will manifest itself again.
Detachment in the lower parts of the eye is very dangerous, since we may not notice it for a long time.
Features of the operation
Retinal detachment is a complex disease, but it can be treated. The surgical procedure itself is not long, but requires a certain recovery period. So, the technology of the operation is as follows:
— Removal of the vitreous.
— Removing scar films from the retina and pressing it to the shell of the eye using a special liquid.
— Laser cauterization.
— Replacement of process fluid with silicone oil.
— Removal of the “substitute” from the eye (after a month and a half).
In principle, after this your organ of vision can be considered healthy.
Diagnosis of the disease. Treatment methods
If you notice even the slightest signs of the disease, be sure to contact an ophthalmologist, this way you will prevent the development of the disease and preserve your vision.
If symptoms begin to appear due to a traumatic brain injury, in addition to the ophthalmologist, consultation with a neurologist will be necessary.
Basically, the disease is localized on the periphery of the retina (here the blood supply is lowest). That is why direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy of the fundus is performed.
To better examine the pupil, it is dilated using special drops (dropped into the eyes).
With this inspection you can determine:
- localization of detachment;
- how many gaps there are, and what they are;
- is there retinal dystrophy and where is it localized;
- if the detachment has a connection with the vitreous body.
To clarify or confirm the diagnosis, it is also necessary to use additional methods:
- check visual acuity (vision in the affected eye disappears abruptly, especially in cases where the detachment is centrally localized);
- determination of intraocular pressure (usually this indicator does not change, but this does not apply to cases where an injury or blow has occurred, then the pressure becomes higher);
- ophthalmological perimeters (determination of visual fields). If a disease occurs, the fields will be narrowed;
- conducting ultrasound examinations (used if there are contraindications to other methods, or if the diagnosis needs to be more accurately established);
- laser tomography (the method is used when it is necessary to study the condition of the optic nerve).
Diagnostic features
In principle, this process is not complicated, but it requires special equipment. Therefore, at the first symptoms of illness, immediately run to the doctor. So, in addition to your immediate symptoms, the doctor should also take into account the results of computer studies. First of all, the specialist must check intraocular pressure and visual acuity.
A mandatory procedure is to determine the width of the field that the affected organ can see. It will also be necessary to conduct an electrophysiological study, which will show how complex the situation is and whether tissue and nerve cells can be preserved.
Treatment
The only treatment option is surgery. The choice of method will depend on the location of the defect, its complexity, and size.
There are several types of operations:
- sclerotherapy (the damage is sealed using diathermy (laser or current)). The tissue that is located around the retina becomes scarred and does not allow fluid to penetrate under the retina;
- pneumatic retinopexy (the defect is sclerosed using freezing or using a laser). Next, air is introduced into the eye into the vitreous cavity, which puts the retina in place;
- vitrectomy (two small holes are made in the sclera in order to have proper illumination of the surgical field, and a cutting emitter and thin tweezers are inserted inside). The removed vitreous is replaced by gas. After time, the gas dissolves and is filled with its own moisture;
- local filling (a small silicone filling is sewn onto the sclera, so that the sclera is pulled inward and together with the choroid, and comes closer to the retina);
- retinal ballooning (the essence of the method: a catheter with a balloon is temporarily sutured into the sclera in the area of detachment projection). The balloon is inflated and the same effect is obtained as when filling the sclera.
Laser therapy
Signs of retinal detachment will help not only establish an accurate diagnosis, but also determine the method of surgical intervention. Today, the safest and most common is a laser method of eliminating the disease. Its advantage is that the patient’s recovery time is significantly reduced, and he is discharged on the same or the next day. Naturally, such an operation cannot be called cheap, but it is effective.
The only nuance of this treatment method is that it is used for relatively small ruptures or as an additional tool to other types of surgical interventions. Otherwise, this method of fixing the problem is more preferable and safer. Moreover, in this case there is practically no possibility of infection of the eye with a working tool.
Possible consequences of retinal detachment
The most terrible and common consequence of this disease is blindness. That is why it is necessary to seek the help of ophthalmologists as early as possible. Only surgical intervention will stop the progression of the disease, restore vision and avoid its loss.
The disease also threatens to cause a certain area to fall out of sight, and a veil may appear before the eye.
In addition, retinal detachment is dangerous because it can cause loss of visual acuity and distortion of images of objects. A dangerous decrease in vision occurs as the disease progresses (a macula appears).
What is the disease?
So, this problem can affect almost any person, regardless of age, social status or living conditions. It is characterized by a lack of nutrition to the eyeball due to the divergence of the nervous and vascular tissues located inside it.
It should be noted that retinal detachment, the symptoms of which can be confused with signs of other pathologies, must be treated only by a doctor. Self-medication in this case will not give anything except additional problems and loss of vision. The fact is that you can get rid of the disease only through surgery.
Preventive actions
People who have diabetes, have suffered eye or head injuries, have retinal dystrophy, myopia, must undergo examinations by ophthalmologists in order to detect the problem in a timely manner. A separate risk group includes pregnant women (in some cases, retinal detachment may occur after childbirth).
In addition, people who are at risk should maintain proper sleep and wakefulness, not lift anything heavy, and avoid heavy physical activity.
How should you behave after the intervention?
It should be noted that retinal detachment is eliminated quite quickly. However, after the operation, the patient must undergo a certain recovery period. After the intervention, you should be as careful as possible with your eyes. That is, try not to overstrain your eyesight. Get plenty of rest and don't touch your eyes with your hands.
You may be prescribed medication after surgery. For example, the doctor may prescribe certain medications that prevent infection in the organ of vision and also speed up the healing of scars. If after treatment you feel discomfort in your eyes or any problems appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Please note that your vision may be blurred immediately after surgery. This situation will last for several days. Gradually, visual acuity will improve and return to normal. In any case, the prognosis for treating such a disease is positive. That is, if you follow certain preventive measures, you do not have to worry about retinal detachment.
Reviews about retinal dissection
Feedback from patients generally boils down to the effectiveness of laser treatment; there is much less discomfort with this procedure than with other types of interventions, and the recovery period is much shorter. People talk about almost complete painlessness (although some claim that there is discomfort) and the success of the treatment. Among the disadvantages, patients note the high cost of the intervention, headache after and burning in the eyes. However, most consider this a small thing compared to possible blindness.
In principle, everyone definitely recommends surgery, since the detachment will not resolve on its own.
Postoperative recovery
The duration of the rehabilitation period after surgery depends on the degree of retinal detachment, concomitant diseases, the patient’s age and the chosen surgical method.
- On the first day after surgery, a special bandage is applied to the eye. After a day, the bandage is replaced with sterile gauze, folded several times and attached to the skin around the eye with an adhesive plaster. This prevents the entry of bacteria and dust.
- The skin around the eye is treated with solutions of furatsilin, chloramphenicol using sterile cotton wool.
- You may feel some pain for a few days after surgery. It is recommended to take analgesics.
- On the first day, bed rest is prescribed, then semi-bed rest for up to 1 month.
- Physical and mental stress is prohibited. The operated person is allowed to lift no more than 5 kg.
- Avoid contact with eyes of any detergents and cosmetics.
- You will need to wear glasses or contact lenses for several months. Self-purchase may worsen the condition. Consultation with a specialist is required.
- Eye drops with a disinfecting effect (floxal) and anti-inflammatory effect (tobradex).
- It is also not recommended to drive a car, strain your eyes by reading or watching TV, or rub your healing eye.
- To monitor the restoration process of the visual organ, you need to regularly visit an ophthalmologist.
The prognosis for timely treatment of retinal detachment is favorable; in advanced cases, blindness is possible.
Edited 04/14/2019 · Comments: · Reading time: 6 min · Views: 135
Prevention
In general, there is no way to prevent peeling. However, a person can take steps to avoid this pathology:
- To avoid injury, you should wear safety glasses when playing sports or when using various sharp tools.
- If a person has diabetes, you need to regularly monitor your blood sugar levels and see an endocrinologist.
- You should have annual eye exams with an ophthalmologist, especially if there is a risk of detachment.
It is important to know the symptoms of retinal detachment, as this will help you consult a doctor in time and thus save your vision.