In a blood test for coagulation, an important indicator is the INR norm - international normalized ratio. The indicator allows you to measure the rate of sedimentation of blood cells and the formation of clots. The marker is under constant monitoring by doctors in the case of special therapy aimed at preventing blood clots.
Blood clotting is a protective reaction of the body
Indications for testing
An INR test is prescribed to assess blood clotting, when it is necessary to determine the cause of severe bleeding or, conversely, an increased level of blood clots.
The main indications for such a blood test are:
- control of treatment with direct anticoagulants (blood thinners);
- severe pathological changes in the liver - cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- therapy with indirect antithrombotic drugs;
- cardiac and vascular pathologies - the results of analysis for atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), ischemia, and stroke are of great importance;
- pregnancy;
- gestosis.
Important!
Using this method of blood testing, doctors can promptly identify abnormalities in the patient’s condition and prescribe corrective treatment. And in the case of constant use of the drug Warfarin or other anticoagulants, the required dose of the drug is selected based on the INR level.
In what cases is a clotting test indicated?
A planned analysis is carried out three times throughout the pregnancy:
- When registering with a gynecologist.
- At 22–24 weeks (II trimester).
- At 30–36 weeks (III trimester, shortly before birth).
It should be noted that a coagulogram is performed once per trimester only during normal pregnancy . In some cases, additional research is recommended. This happens when a woman is diagnosed or suspected of:
- autoimmune diseases;
- phlebeurysm;
- liver diseases;
- Rh conflict with the child’s father;
- vascular, endocrine pathologies;
- disorders of the circulatory system,
- disorders of the genitourinary system;
- predisposition to bleeding or increased clotting;
- miscarriage of a previous pregnancy;
- multiple pregnancy;
- disorders of the placenta;
- anemia or iron deficiency anemia (more details: https://krasnayakrov.ru/organizm-cheloveka/zhelezodeficitnaya-anemiya.html);
- tendency to thromboembolism, heart attack, stroke.
Where to donate blood for INR?
You can accurately determine the level of blood clotting using the Quick and INR assessment of prothrombin, so when choosing a medical institution you need to take this into account.
You can donate blood either in a private laboratory (for a fee) or in a regular clinic, if the level of qualifications of specialists and the availability of equipment allows.
Device for self-analysis of INR
It is quite possible to conduct the study at home, but for this you need to buy a special device - an express coagulometer. This option is more suitable for people who constantly take medications to reduce blood clotting. If you need a one-time test, it is better to contact the laboratory.
Method of monitoring blood clotting during warfarin treatment
Taking anticoagulants creates a situation where the patient is between two fires. Specifically, between overdose and underdose of warfarin. Both conditions do not bode well. Too much can cause bleeding, and too little can cause the formation of dangerous blood clots. When taking heparin, the patient is regularly examined for a coagulogram; when taking warfarin, the international normalized ratio is determined. This test can be done separately from the coagulogram.
In order not to cross safety boundaries and maintain the INR within the required limits, constant monitoring of the level of blood clotting is necessary. It is important to take into account that the normal INR value for various diseases will differ from the values of a healthy person, which range from 0.9 to 1.2.
When taking warfarin, the concept of “Target range” is accepted - this is the individual INR value that is optimal for a particular patient. The target range is determined not only by the disease, but also by risk factors for thrombosis. For the same disease, the target range will vary between patients. One may have 2.5 and another 4.0.
Below are very conditional boundaries that must be adhered to:
- when taking warfrin and atrial fibrillation, the conditional INR norm is 2.0 – 3.0;
- for chronic atrial fibrillation, the conditional norm is 2.2 – 3.1;
- after valve implantation, it is necessary to maintain the numbers at 2.6 - 3.5.
In general, as a doctor and as a user of anticoagulants, I can wholeheartedly feel sorry for us who need warfarin. I don’t know of a more unpleasant drug with which you constantly have to be on guard.
How often should I measure INR?
At the very beginning of taking warfarin, the INR will have to be measured every 2-3 days. Next, when the dose of warfarin is selected, we switch to the regimen of 1 determination per week. If the patient has undergone coagulation measurements three times and they are within the specified interval, then you can switch to measuring once every 2 weeks. However, many people ignore this rule, and as a result they experience complications: I have seen patients receiving warfarin with an INR of 20.
What if the test is less than the target value?
Is your INR less than the norm determined by your doctor? This means that blood clotting has increased and you are at risk of thrombosis. You should consult your doctor; the dose may need to be adjusted.
Preparing for analysis
The reliability of the INR test results is always accurate; the main thing is to properly prepare for the delivery of biological material.
- The last meal should be 7–8 hours before the procedure, since the biomaterial is collected on an empty stomach.
- The day before the procedure, do not overwork the body with heavy physical activity, avoid stress and emotional overstrain.
- Do not carry out medical manipulations - exclude IVs, injections - 48-72 hours before the procedure.
When taking anticoagulants on a regular basis, it is recommended to take the daily dose 10–12 hours before the test.
How to take a coagulogram correctly
The result of a coagulogram during pregnancy depends on the correctness of blood sampling and patient preparation. To prepare for the analysis, you need:
- limit the consumption of fatty foods and spices 3 days before the procedure;
- on the eve of the study, exclude physical and emotional stress;
- Take the test on an empty stomach, you can drink a glass of water in the morning.
In addition to a coagulogram, during pregnancy you need a general blood and urine test, and a biochemical analysis. Usually all studies are scheduled for one day.
How is the INR test performed?
A blood test or coagulogram to assess the state of homeostasis takes place in several stages.
- Biological material is collected from a vein in the elbow.
- The resulting blood is placed in a glass tube and diluted with a preservative - citrate.
- The settled blood cells are separated from the plasma. The function of citrate at this stage is to bind calcium ions and prevent clot formation.
- PTI is calculated. With the help of thromboplastin, the effect of the preservative is neutralized and the rate of clotting of pure plasma is observed.
- The international normalized ratio is calculated using a mathematical method.
Study time is 2–3 hours. Results can be obtained by evening or the next day.
Consequences of impaired hemostasis during pregnancy
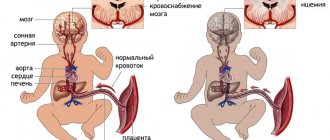
Good hemostasis during pregnancy is important for the proper development of the fetus and the uncomplicated course of labor. The fetus receives oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood. If it is thick, blood clots form, then the fetus develops hypoxia - lack of oxygen. This leads to disruption of the formation of organs and the appearance of developmental defects. The risk of premature birth increases.
High coagulability is also harmful to a woman’s health. Blood clots form in the veins of the legs, disrupting the blood flow in them. Legs quickly get tired, swell and hurt. There is a risk of a blood clot breaking off and getting into the lungs.
Low coagulability is less dangerous for the fetus. But it increases the risk of bleeding during childbirth, especially if it occurs with complications. Uterine bleeding with poor coagulation is almost impossible to stop. To save a woman, the uterus has to be removed. A coagulogram is a mandatory analysis when planning and after pregnancy. The study allows you to assess the likelihood of blood clots or bleeding. You need to get tested if you experience bruises, nosebleeds, gum bleeding, or blood clots in your urine for no reason.
INR norm and interpretation of results
Normal values in healthy people who do not take anticoagulants differ from those in patients who regularly use antithrombotic drugs. Slightly different values during pregnancy, and sometimes there are differences by age.
Table “INR norms for different categories of people”
| Normal for a healthy person | Reference values for people taking anticoagulants | |||
| In an adult | In children | During pregnancy | Direct acting drugs | Indirect acting medicine |
| From 0.8 to 1.2 | From 0.8 to 1.16 | From 0.8 to 1.3 | From 2.0 to 3.0 | From 2.5 to 3.5 |
Deviations in the INR in the coagulogram downward or upward indicate the development of negative abnormalities in the patient’s body.
When is the INR norm different for women than for men?
Normal INR values in women may differ from those in men if the woman’s hormonal levels undergo changes. This happens in 2 cases:
- during pregnancy;
- when taking hormonal contraceptives.
In such situations, values may greatly exceed the reference limits. If there is a constant increase, there is a need for special therapy.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
An increase or decrease in the international normalized ratio indicates the development of pathological conditions in the body.
Table “Causes of deviations from the norm”
| Decrease in indicators | Increased amount of antithrombin |
| Negative effects on blood clotting of diuretics and contraceptive drugs | |
| Hematocrit abnormalities | |
| Increased blood viscosity | |
| Incorrectly selected dose of anticoagulants (if such drugs are taken regularly) | |
| Increasing values | Lack of vitamin K in the body |
| Liver diseases | |
| Disturbances in the normal absorption of fats in the intestine | |
| Deviations in hemostasis at the genetic level | |
| Negative reaction of the body to indirect anticoagulants |
Range of INR values depending on the dose of warfarin
Regardless of whether the indicators are higher than normal or lower, contacting a doctor is mandatory. A high INR level is dangerous due to external and internal bleeding, and a low level is dangerous due to thromboembolic complications.
Coagulogram indicators: norms during pregnancy
During the period of gestation, coagulogram norms change somewhat, which is associated with activation of the hemostatic system. This is explained by hormonal changes in the body, the emergence of a new uteroplacental circulation and the body’s preparation for blood loss during childbirth. The main indicators of the hemostatic system that are determined during pregnancy:
Fibrinogen
This protein is produced in the liver and is involved in the formation of blood clots.
The normal level of fibrinogen is 2-4 g/l, but during pregnancy its amount increases (in the second trimester to 4.8 g/l, and by the time of birth to 6 g/l).
APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time)
APTT refers to the time it takes for a blood clot to form.
Normal APTT is 23-35 seconds.
When the APTT is prolonged, there is a risk of hypotonic bleeding, and when it is shortened, there is a risk of developing DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation).
Prothrombin time
The time required for thrombin to form from prothrombin, and thrombin is involved in the formation of a blood clot, which stops bleeding.
During pregnancy, its norm is 14-18 seconds.
Thrombin time
It means the time required for the transformation of fibrinogen into fibrin, which, turning into a blood clot, completes the process of stopping bleeding.
Although fibrinogen is increased during gestation, thrombin time remains within the normal range - 11-18 seconds.
Prothrombin index (PTI)
Normally during pregnancy it is 78-140% and indicates the activity of the prothrombin complex of the woman’s plasma compared to the measured prothrombin time of the control plasma.
With an increase in PTI, premature placental abruption is possible.
Lupus anticoagulant
A healthy pregnant woman does not have it in her blood. Occurs in autoimmune diseases, preeclampsia, antiphospholipid syndrome and indicates a high risk of miscarriage.
Platelets
Blood cells involved in the formation of a hemostatic plug when the vascular wall is damaged.
The norm is 150-400 thousand/µl.
A significant decrease in platelets indicates either a decrease in their synthesis or increased destruction. There may be a decrease in platelets due to insufficient nutrition, as well as the threat of developing disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
D-dimer
Parameter of thrombus formation and fibrinolysis (fibrin resorption). During pregnancy, its level gradually increases and by the end of gestation exceeds the normal levels of non-pregnant women by 3-4 times. Complicated pregnancy (preeclampsia, diabetes mellitus, kidney disease) is characterized by significant levels of D-dimer.
The normal D-dimer level is less than 248 ng/ml (exceeding the figures indicates a tendency to thrombus formation).
Antithrombin III
The norm is 71-115%.
Antithrombin belongs to the proteins of the anticoagulation system and inhibits thrombin (inhibits blood clotting). If the indicator decreases, thrombosis may develop. Monitoring the indicator is important when taking anticoagulants (heparin).