Like any chemical substances, medications, when interacting with the human body, in some cases cause allergies. And such reactions are becoming more and more frequent from year to year; now every tenth person on the planet has experienced drug allergies at least once in their life.
Drug allergies can be either organ-specific or generalized .
In the first form, the symptoms affect one organ - the skin, visceral systems, respiratory organs, and in the second - the body reacts hyperacutely and a reaction develops that affects all organs and systems, for example, anaphylactic shock.
In principle, any pharmacological substance can cause an allergic reaction, but more often local anesthetics, antibiotics, nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs, and sulfonamides cause allergies . In children, antibacterial substances and vaccinations most often cause reactions.
The amount of a substance in case of an allergy does not matter; sometimes only traces of a given medicinal substance or inhaled vapors are enough for an allergic reaction.
Allergies occur upon repeated administration of the drug, usually weeks to ten days after the body's first contact with the allergen. Often this is an occupational disease - it often begins in doctors, paramedical personnel, pharmacies and pharmaceutical warehouse workers. Chronic patients who take many medications, people over 35, patients with reduced immunity, and allergies to other substances, both chemical and organic, are also at risk.
Pseudo-allergic reactions are also possible; in this case, allergy symptoms may appear even after the first use of the medicine, almost instantly.
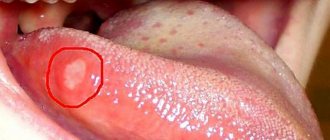
Allergic reactions can be local (at the injection site the injection site becomes red, swollen and itchy, a rash appears, tissue necrosis may develop), and general (temperature rises, symptoms of intoxication appear - headache, weakness, enlarged lymph nodes, joint pain)
Symptoms and signs of drug allergies
Taking into account the speed of development of clinical manifestations, allergic reactions are classified into three main groups.
Thus,
the first group includes those that develop immediately after the allergen enters the body or within an hour from this moment. This group includes such manifestations as:
- Anaphylactic shock
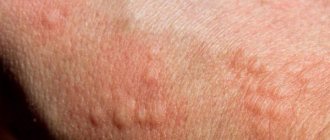
- Hives
- Spasm of the bronchial tree (bronchospasm)
- Quincke's edema
- Acute anemia associated with hemolysis.
The second group is subacute reactions that appear within 24 hours from the moment the allergen enters the body. This leads to conditions such as:
- Agranulocytosis (increased levels of granulocytic leukocytes in the blood)
- Thrombocytopenia (a drop in platelet levels below standard values)
- Fever (temperature above 37 degrees)
- Exanthema, manifested by spots and papules (pimples).
The third type of allergic reactions can appear within several days from the moment the drug enters the body. This group should include conditions such as:
- Serum sickness is organ damage associated with the formation of immune complexes in the body
- Vasculitis – immune damage to blood vessels
- Polyarthritis - joint damage
- Lymphadenopathy - damage to the lymph nodes
- Hepatitis, nephritis and other conditions associated with the development of allergic inflammation.
Drug pseudoallergy
Drug pseudo-allergy can masquerade as manifestations of true allergy. It is not associated with immune mechanisms. Thus, anaphylactic shock is an extreme degree of increased sensitivity of the immune system to certain drugs, in turn, anaphylactoid shock is similar to it in clinical manifestations, but according to the mechanism of development it is not associated with the immune system. It is not based on sensitization, but on the nonspecific release of histamine and similar substances. Therefore, the features of pseudoallergy are the following:
- Development at the first contact with a pharmacological drug
- Slow entry into the drug is a preventive measure, since the concentration in the blood does not exceed the prohibitive level
- Immune tests to identify the causative drug are negative
- The patient's allergic history is not burdened.
Substances that can cause drug allergies include:
- Papaverine
- Atropine
- Blood substitutes
- Desferam – used for hemochromatosis
- No-shpa
- X-ray contrast agents based on iodine
- Opiates – fentanyl, morphine, codeine and others
- Protamine (used to neutralize heparin compounds).
The likelihood of developing a pseudo-allergic reaction increases in the following cases:
- Administration of high doses of the drug that exceed acceptable standards for weight and age
- Diseases of hypothalamic nature
- Diabetes
- Liver diseases
- Pathology of the digestive tract
- Chronic sinusitis
- Cardiopsychoneurosis.
Diagnostics
What to do if clinical signs of allergy appear? First of all, do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor . Diagnosis of drug allergies is quite difficult, as it is caused by a number of aggravating factors:
- the symptoms are largely similar to those of other diseases;
- the time interval between taking medications and the first manifestations of the disease can be quite long, which makes it difficult to establish an exact cause-and-effect relationship;
- the same drug can cause a different clinical picture.
Causes of drug allergies
Before the development of a drug allergy, there is always a period of sensitization, that is, the first meeting of a pharmacological drug with the cells of the human immune system. Only with the second contact with the same drug is it possible to develop an allergic reaction.
According to statistics, approximately 70% of side effects of drugs are allergic in nature. However, they can lead to patient mortality in 0.005% of cases. In general, the prevalence of drug allergies reaches 12%, and has recently been increasing.
The most allergenic medications are:
- Antibiotics, which are associated with approximately 50% of allergic conditions in pharmaceuticals
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Anti-tetanus serum
- Sulfonamides.
However, any drugs can lead to the development of sensitization. Oddly enough, this may be a glucocorticosteroid drug prescribed to treat allergies, and other drugs used for this purpose.
Risk factors are also identified, the presence of which increases the likelihood of increased reactivity of the immune system. These include:
- Occupational exposure to drugs (occurs among pharmacists and healthcare workers)
- Long-term use of the same drug, therefore intermittent use with periods of breaks is recommended
- Uncontrolled use of a large number of medications in one patient
- Family history, if relatives have similar reactions to drugs
- Fungal skin lesions
- Having food allergies
- Concomitant diseases of an allergic nature - bronchial asthma, hay fever and others.
Drugs that cause allergies can be of two classes:
- Pure allergens are preparations of protein origin, which include dextrans, serums and vaccines
- Haptens are drugs that acquire allergenic properties only after combining with blood serum proteins. As a result, a complex compound consisting of an antigen and an antibody is formed.
The speed and likelihood of developing an allergic reaction depends on the route of entry of the drug into the body. It is least when taken orally (these are tableted and capsulated forms most often). In second place is the intramuscular route of administration of the drug. With intravenous administration, the risk of allergies becomes even higher. However, the greatest danger is posed by the intradermal route of administration of the drug.
Release form
An important factor in allergic manifestations is the form in which the drug enters the body. The reaction that occurs from tablets, as a rule, does not manifest itself quickly, because depends on the rate of absorption of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract, which may take half an hour or more. The body reacts much faster to taking medication intramuscularly or intravenously. In the latter case, entering the blood immediately, the antigen triggers an immediate reaction, accompanied by rather severe symptoms. If a person is not given emergency assistance at this moment, death is possible.
Treatment of drug allergies
An allergist will help cure any type of allergy. Single registration center, consultation +7 (Moscow and regions).
Treatment of patients with drug allergies is carried out in the following areas:
- Discontinuation of the drug that served as the trigger for the development of allergies. If a patient is taking several medications at the same time, they are all discontinued.
- Prescribing a hypoallergenic diet, since such patients often have concomitant food allergies. As part of the diet, foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates, as well as spicy, salty, sour, bitter and sweet foods should be excluded. For such patients, it is recommended to increase the water load on the body - regular drinking water, tea (you should not drink brightly colored drinks)
- The use of antihistamines, which are indicated for urticaria and angioedema. For more severe manifestations of allergies, they will be ineffective. It is recommended to administer antihistamines intramuscularly. This will allow you to get a therapeutic effect in the shortest possible time.
- If, against the background of all of the above, clinical regression is not observed or the symptoms, on the contrary, intensify, then corticosteroid therapy is indicated.
The choice of antihistamine is very important. The tolerability and effectiveness of treatment depends on this. Features of the choice of these funds are as follows:
- You should choose a drug with high efficiency and minimal side effects.
- High selectivity of antihistamine action
- The absence of a calming effect (sedation), which allows it to be taken by patients whose work is associated with increased concentration and activity of thought processes.
These properties are fully inherent in second generation drugs. These include Cetirizine, Loratadine and Ebastine. However, these drugs require prior metabolic conversion in the liver to be therapeutically effective. This is associated with some “lag” in their effectiveness. The newest antihistamines, such as Disloratadine and Fexofenadine, do not have these disadvantages. Therefore, they are used with the greatest effectiveness in cases of developed toxic-allergic reactions.
Important advantages of drugs in this group, which belong to the second and third generation, are:
- Only one dose required
- Possibility of increasing the dosage by 2 times, which will not entail an increase in the likelihood of developing side effects
- The risk of allergic reactions to these drugs is minimal.
First aid for drug allergies
First aid for the development of anaphylactic shock should be provided promptly and promptly. You must follow the algorithm below:
- Stop further administration of the drug if the patient’s condition worsens
- Apply ice to the injection site, which will reduce the absorption of the drug into the bloodstream.
- Inject this area with adrenaline, which also causes vasospasm and reduces the absorption of additional amounts of the drug into the systemic circulation
- For the same result, apply a tourniquet above the injection site (periodically loosen it for 2 minutes every 15 minutes)
- Take measures to prevent aspiration and asphyxia - place the patient on a hard surface, turn the head to the side, remove chewing gum and removable dentures from the mouth
- Establish venous access by installing a peripheral catheter
- Administering a sufficient amount of intravenous fluids, with 20 mg of furosemide being administered for every 2 liters (this is forced diuresis)
- If there is an intractable drop in pressure, use mesaton.
- At the same time, corticosteroids are administered, which exhibit not only antiallergic activity, but also increase blood pressure levels
- If the pressure allows, that is, systolic above 90 mm Hg, then diphenhydramine or suprastin is administered (intravenously or intramuscularly).
Prevention of drug allergies
To prevent the development of an allergic reaction to pharmacological drugs, the following circumstances must be taken into account:
- Careful clarification of the patient's allergy history. If it is burdened, then a person should not hide it from the doctor. It is necessary to immediately say how the allergy manifested itself and to what medications it developed
- The doctor should avoid polypharmacy when treating a patient, that is, one should not prescribe a large number of medications, especially those with unproven effectiveness.
- When indicating allergic reactions, it is necessary to exclude intramuscular and intravenous routes of administration.
- Use long-acting medications with caution
- If the patient has diseases of an allergic nature, it is necessary to avoid the use of drugs with pronounced allergenic properties.
- The presence of skin diseases is a contraindication for penicillin preparations, since 8% of people may immediately develop severe acute allergic manifestations
- It is advisable not to use antibiotics for prophylactic purposes
- It is better to use monocomponent drugs rather than multicomponent ones.
Childhood symptoms as a serious problem
Childhood intolerance is especially dangerous and can appear even at an early age. In children, the reaction to medications begins with the appearance of a rash on different parts of the body, then becomes more complicated and develops into a respiratory problem. Delayed treatment in children can result in death.
What do the signs of allergies to medications look like in the photo in different children and adults:
Dermatitis in babies occurs more often than in adults, because their bodies are fragile and easily react to medications. Treatment of children should be treated carefully, strictly following the pediatrician’s recommendations.
Information about the medications to which the child reacts should be clearly recorded in the patient's chart. Otherwise, instead of receiving effective treatment, the patient may develop an additional disease called allergy.